
Jul 1, 2015 | Advocacy
Joint statement by the ICJ and Amnesty International after a group of States, led by Egypt, proposed a resolution on “protection of the family” at the ongoing 29th regular session of the UN Human Rights Council.
Bangladesh, Belarus, China, Cote d’Ivoire, Egypt, El Salvador, Mauritania, Morocco, Qatar, the Russian Federation, Saudi Arabia and Tunisia have submitted a seemingly innocuous draft resolution (A/HRC/29/L.25) that, in fact, underhandedly seeks to divert the Council from its institutional mandate focused on the effective promotion and protection of the human rights of the individuals towards protecting the purported rights of a social institution, namely, “the family”.
The full statement can be downloaded here: Universal-ICJ+AI statement on protection of the family-Advocacy-2015-ENG (in PDF)

Jun 30, 2015 | News
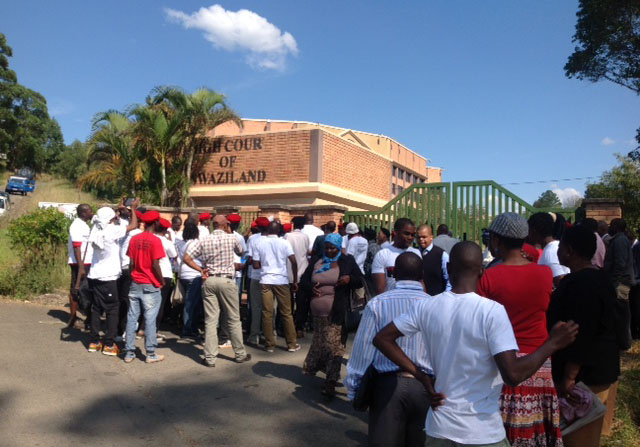
The ICJ welcomes the decision of the Supreme Court of Swaziland to uphold the appeal of imprisoned human rights defenders Thulani Maseko and Bheki Makhubu and ordering their immediate release.
“The decision marks a victory for the rule of law in Swaziland,” said ICJ Secretary-General Wilder Tayler. “We hope that this is but the first of many steps to come in restoring the integrity of the courts and reinforcing the respect for the rule of law that has undergone so much erosion in recent years.”
The ICJ considers that while the release of the two men is a necessary step for justice for the two men, alone it is not enough.
The government of Swaziland should ensure adequate reparation for their wrongful imprisonment.
More broadly, it must engage in legal and structural reforms necessary to ensure the fair and effective administration of justice, the independence of the judiciary and respect for human rights in the country.
Thulani Maseko and Bheki Makhubu were arrested on 17 March 2014 under contempt of court charges for having written articles criticizing the manner in which the then Chief Justice (CJ), Michael Ramodibedi, had handled the case of another defendant, Bhantshana Gwebu.
Mr. Gwebu had been arraigned before the CJ without legal representation, charge sheet or being informed of his rights to apply for bail.
The trial of Thulani Maseko and Bheki Makhubu was riddled with violations of basic due and fair trial principles, as affirmed by the UN Working Group on Arbitrary Detention (WGAD), which ruled on a complaint in Thulani Maseko’s case.
Background
The trial of Thulani Maseko and Bheki Makhubu resulted in their conviction and a two-year prison sentence It was improperly conducted before a presiding judge, Mpendulo Simelane, who was a potential witness and had a direct interest in the case.
They had been in custody since their arrest, save for a three-day release in June 2014, and were due for final release on the 17 July 2015.
The ICJ has previously issued a number of statements after conviction by the High Court, underscoring that the prosecution and trial Court’s judgment had constituted a breach of Swaziland’s obligations to respect the rights to freedom of expression and fair trial.
The UN WGAD opinion issued on 22 April 2015 held that the deprivation of liberty of the accused was arbitrary and in contravention of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and Swaziland’s obligations under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR).
The WGAD also emphasized that Swaziland should release the accused and facilitate the enforceable right to compensation in accordance with article 9 of the ICCPR.
In the appeal hearing yesterday, the Crown conceded most of the legal arguments by defence counsel and in particular that Judge Simelane ought to have recused himself from presiding over the case.
The Supreme Court’s written judgment is expected to be issued at the end of the session of its sitting.
Read also:
Swaziland: ICJ condemns the harsh prison term imposed on Thulani Maseko and Bheki Makhubu
Swaziland: ICJ condemns the conviction of celebrated human rights lawyer and prominent journalist on charges of contempt of court
Swaziland: ICJ concerned at detention of human rights lawyer and journalist
American Bar Association’s statement
Contact:
Arnold Tsunga, Director, ICJ Africa Regional Programme, t +27 716 405 926 or +41 76 239 90 32 e: arnold.tsunga(a)icj.org
Matt Pollard, Senior Legal Adviser, ICJ’s Centre for the Independence of Judges and Lawyers, t: +41 22 979 38 12, e: matt.pollard(a)icj.org
Jun 29, 2015 | News
The ICJ calls on the UN Human Rights Council and the Security Council to respond to the findings of the Independent Commission of Inquiry on the 2014 Gaza Conflict, and fully implement all its recommendations.
This should be done with a view to ensuring accountability, including effective remedy and reparation, for all violations of international humanitarian law and human rights abuses committed by the Israeli Defence Forces (IDF) and by Palestinian armed groups, the ICJ says.
The ICJ further calls on the Human Rights Council to establish an independent mechanism to monitor the implementation of the Commission’s recommendations by both parties.
“Israeli and Palestinian authorities must break the chronic cycle of impunity in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. All credible evidence of war crimes, such as the Commission of Inquiry has highlighted, must be properly investigated,” said Said Benarbia, Director of the ICJ MENA Programme.
“No one who is responsible, whether military or civilian and regardless how high their office, can be allowed to escape justice,” he added.
The Report published last week, and discussed today at the Human Rights Council, documents serious violations of international law and human rights abuses committed during the conflict, such as indiscriminate attacks, including disproportionate attacks, and direct attacks against civilians and against civilian objects that are not justified under the International Humanitarian Law.
The Commission found that artillery and other explosive weapons had been used in densely populated areas, that entire neighborhoods in Gaza had been destroyed, and that unguided rockets had been used.
As indicated by the Commission, some of those acts may constitute war crimes.
To date, both Israeli and Palestinian authorities have failed to meet their obligations under international law to effectively investigate the violations and to prosecute anyone criminally responsible.
Investigations and criminal proceedings initiated by the IDF’s Military Advocate General (MAG), which is also involved in the planning and execution of the IDF’s military operations, fall short of international standards including in relation to independence and impartiality.
No criminal investigations into violations and abuses committed by Palestinian armed groups appear to have been initiated by the Gaza authorities.
The ICJ calls on both authorities to provide for effective, independent and impartial investigation mechanisms in line with international standards.
Absent such reforms, international justice mechanisms can and should fill accountability and remediation gaps where domestic authorities are unwilling or unable to effectively administer justice.
“Israeli and Palestinian authorities must reform the framework for their current investigations and prosecutions. They must also fully cooperate with international accountability mechanisms, including the preliminary examination initiated by the International Criminal Court,” Benarbia said. “The aim throughout must be to make known the truth about the violations, to identify and hold those responsible to account, to ensure victims’ rights, and to prevent any recurrence.”
Contact:
Theo Boutruche, Legal Adviser of the ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, tel: +33 670735747, e-mail: theo.boutruche(a)icj.org
POT-UN Report Gaza -News-Press release-2015-ARA

Jun 26, 2015 | Advocacy, Cases, Legal submissions, News
The ICJ submitted today a third party intervention before the European Court of Human Rights in the case of Richmond Yaw and others v. Italy regarding the detention of four migrants in Italian Centres for Identification and Expulsion.
The case raises issues related to the lawfulness of their detention in immigration centres, and the compliance of the mechanisms of judicial review and compensation for unlawful detention with the European Convention on Human Rights.
Taky Berko Richmond Yaw, Yaw Ansu Matthew, Darke Isaac Kwadwo, and Dominic Twumasi, nationals of Guinea, had been detained in the Centre for Identification and Expulsion of Ponte Galeria (Rome).
In these submissions, the ICJ presented the Court with a summary of its findings regarding the law and practice of detention of migrants and the related judicial guarantees in Italy, in its 2014 report, “Undocumented” Justice for Migrants in Italy.
Furthermore, the ICJ presented an analysis of the principles that apply in regard to arbitrary detention of persons detained for the purposes of immigration control under article 5.1.f. ECHR, in particular:
- The principle of legality, including the fact that the basis, procedures and conditions for detention must be provided by law, and the principle that detention must be carried out in good faith; and the due process guarantees related to these principles;
- The requirement that detention be undertaken only pursuant to the permitted purposes of article 5.1.f ECHR, and the need for strict construction of this requirement, and ongoing scrutiny of compliance with it, in particular in the context of long periods of detention;
- The requirements of access to an effective judicial mechanism to secure the right to habeas corpus and review of the legality, necessity and proportionality of the detention of migrants, under article 5.4. ECHR;
- The requirements of an effective remedy and reparation mechanism for unlawful deprivation of liberty under article 5.5 ECHR.
ECtHR-AmicusBrief-Yaw&others v Italy-Advocacy-Legal Submission-2015-ENG (download the third party intervention)

Jun 26, 2015 | News
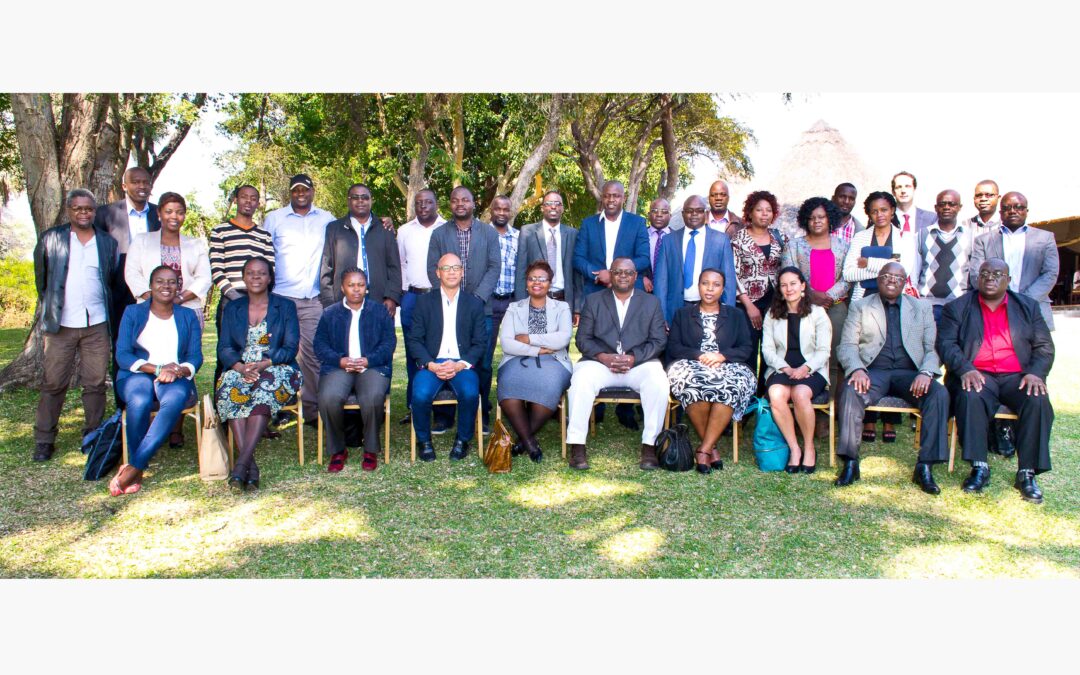
On 24 and 25 June 2015, the ICJ and the Law Society of Zimbabwe (LSZ) organized a 2 day workshop at the A’Zambezi River Lodge in Victoria Falls, on Economic Social and Cultural (ESC) Rights.
It brought together legal practitioners and NGO representatives involved in the protection of economic, social and cultural rights.
The main objective of the workshop was to share knowledge on international and national standards for the guarantee and protection of ESC Rights.
The meeting also sort to consult practitioners on and validate the new ICJ guide on ESC Rights litigation in Zimbabwe.
The Guide on ESC rights seeks to give greater effect to the rights enshrined in the Constitution.
The 2013 Constitution contains a comprehensive bill of rights including ESC rights.
The Constitution includes important provisions and arrangements for the guarantee of accessible and effective remedies including judicial remedies for rights-holders whose rights are violated.
In adopting this new Constitution, Zimbabwe has joined the increasing group of States that have equipped themselves with a domestic law that guarantees and protects all human rights.
This integrates and converges with international human rights law, in respect of which there has been remarkable progress in recognizing the need for specific protection of various categories of rights-holders such as women, children or persons with disabilities.
Judges in domestic courts have a vital role to play in enforcing and interpreting national laws in compliance with the international human rights standards and obligations to which the State has committed.
Judges and lawyers will need enhanced knowledge of this framework and will benefit from comparative experiences in using it.
The guide seeks to respond to this context and these needs. It is this imperative that has also led to ICJ organizing this workshop.









