
Apr 15, 2021 | News
The ICJ today condemned the promulgation by President Gotabaya Rajapaksa of new vague and overbroad anti-terrorism regulations, which make the already deeply flawed Prevention of Terrorism Act (PTA) open to further abuse.
The Prevention of Terrorism (Proscription of Extremist Organisations) Regulations No. 2 of 2021, published by way of Gazette notification on the 13 April 2021, outlaw 11 organisations identified as ‘extremist’ and provides criminal penalties for those accused of various kinds of associations with these and other organizations that may be similarly disfavoured.
A person who acts in contravention of the regulations is liable to a term of imprisonment up to twenty years, while any person who “conspires to commit or attempts, abets or engages in conduct in preparation to commit an offence” may be sentenced to a term of imprisonment of up to ten years.
“These ill-defined offences follow a similar pattern of the Sri Lankan executive unilaterally promulgating abusive regulations in the name of fighting terrorism over the years” said Ian Seiderman. “These latest ones come just a month after the decreeing of the ‘de-radicalisation’ regulations which allow for the Government to arbitrary detain people for up to two years without trial.”
Moreover, the listed acts shall amount to an offence not only in relation to the eleven
identified organizations, but also to any other organisation “representing or acting on behalf of such organisation or is connected with or concerned in such organisation or which is reasonably suspected of being connected with or concerned in any of the activities”. This is in violation of the principle of legality as the State may ex post facto identify any organisation as having associated with the eleven banned organisations.
The ICJ said that the Regulations were in contravention of the guarantees under article 13 of the Sri Lankan Constitution and its international legal obligations under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights.
A key precondition to a fair trial recognized internationally is that criminal offences must be prescribed by law and conform to the principle of legality. Vague laws undermine the rule of law because they leave the door open to selective and arbitrary interpretation and prosecution. The vague wording of a law also has an adverse impact on framing of the charge against the accused.
Following the promulgation of the ‘de-radicalisation’ regulations a number of persons belonging to minority communities were reportedly arrested under the PTA, including for ‘spreading Wahhabism via social media’ and ‘promoting terrorism related activities’.
“While the Sri Lankan Government has an obligation to protect its inhabitants from the threat of terrorism, that protection is a part of, and must not be seen in conflict with, its overall duty to protect human rights; ‘threats to national security’ can never be used as a justification for contravening basic standards in relation to freedom from arbitrary arrest”, said Ian Seiderman.
The ICJ has consistently called for the repeal of the Prevention of Terrorism Act, which has been used to arbitrarily detain suspects for months and often years without charge or trial, facilitating torture and other abuse. The ICJ reiterates its call for the repeal and replacement of this vague and overbroad anti-terror law and all regulations brought under it, in line with Sri Lanka’s international obligations.
The UN High Commissioner for Human Rights in her most recent report on Sri Lanka has reiterated the call for a moratorium on the use of the Prevention of Terrorism Act for new arrests until it is replaced by legislation that adheres to international best practices.
Contact
Osama Motiwala, ICJ Asia-Pacific Communications Officer, e: osama.motiwala(a)icj.org

Apr 13, 2021 | News
Today, the ICJ called on the Belarus Ministry of Justice and other relevant authorities to end the recent practice of using legal proceedings against lawyers in retaliation for discharging their professional duties and to reinstate those already disbarred.
In recent months, in the context of widespread violations of the human rights of those protesting against the outcome of the disputed 2020 presidential election, there has been an unprecedented increase of cases of disbarment of lawyers especially those who comment on violations of the human rights of their clients. Among the most recently disbarred lawyers are Konstantin Mikhel, Maxim Konon, Mikhail Kirilyuk and Yulia Ivanchuk.
“This recent wave of criminal and disciplinary proceedings against lawyers is highly worrying and it constitutes an attack on the independence of the legal profession. These proceedings, be they of criminal, administrative or disciplinary nature, should be discontinued or reconsidered as being contrary to the international human rights law concerning the independence of the legal profession,” said Temur Shakirov, Senior Legal Adviser of the ICJ Europe and Central Asia Programme.
There is a clear pattern of the misuse of disciplinary proceedings against lawyers who represent political opponents of the government or those who openly criticize the government on issues of public significance.
Disciplinary proceedings in Belarus are not independent of the executive, since they are conducted by the Qualification Commission which operates under the Ministry of Justice.
Notably, disciplinary proceedings are pending against lawyer Dmitry Layevski, allegedly following his public comments on a pending Draft Law on advocates’ activities.
Dmitry Layevski is a lawyer representing Victor Babaryko, an opposition leader in Belarus currently in detention, and Maxim Znak, former legal representative of Maria Kolesnikova, another detained opposition leader.
Earlier, a number of lawyers, including Aleksandr Pylchenko, former legal representative of Viktor Babaryko and Maria Kolesnikova, and Lyudmila Kazak, former legal representative of Maria Kolesnikova, faced disciplinary sanctions, and Lyudmila Kazak incurred an administrative fine, as a result of discharging their professional functions.
Several lawyers involved in human rights cases have been called by the Qualification Commission to undergo an examination to re-certify their qualification to practice law and have failed the exam. This procedure appears to target lawyers working to defend human rights, as a means of harassment or reprisal.
For example, following comments in mass media, Sergey Zikraskiy, a lawyer who often represented Belarusian journalists, was called to pass extraordinary re-examination which he failed. The certification is carried out by the Qualification Commission.
Criminal cases are still pending against lawyers Ilya Saley and Maxim Znak, who appear to have suffered consequences as a result of their representation of opposition leaders Maria Kolesnikova and Victor Babaryko.
“These disbarments have a significant chilling effect on work of the legal profession and undermine the ability of lawyers to defend human rights of their clients in accordance with international standards on the role of lawyers,” Shakirov said.
Background
International law and standards
According to the UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers, the State authorities must guarantee that lawyers are able carry out their professional functions without hindrance, intimidation, harassment or fear of retaliation (Principle 16). The UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers affirm that lawyers “shall not suffer, or be threatened with, prosecution or administrative, economic or other sanctions for any action taken in accordance with recognized professional duties, standards and ethics.” (Principle 16.c) They further stipulate that lawyers must not be identified with their clients or their clients’ causes as a result of discharging their functions (Principle 18).
International standards also require the institutional independence of the legal profession. The executive body of the professional associations of lawyers must be elected by its members and must exercise its functions without external interference (Principle 24, The UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers).
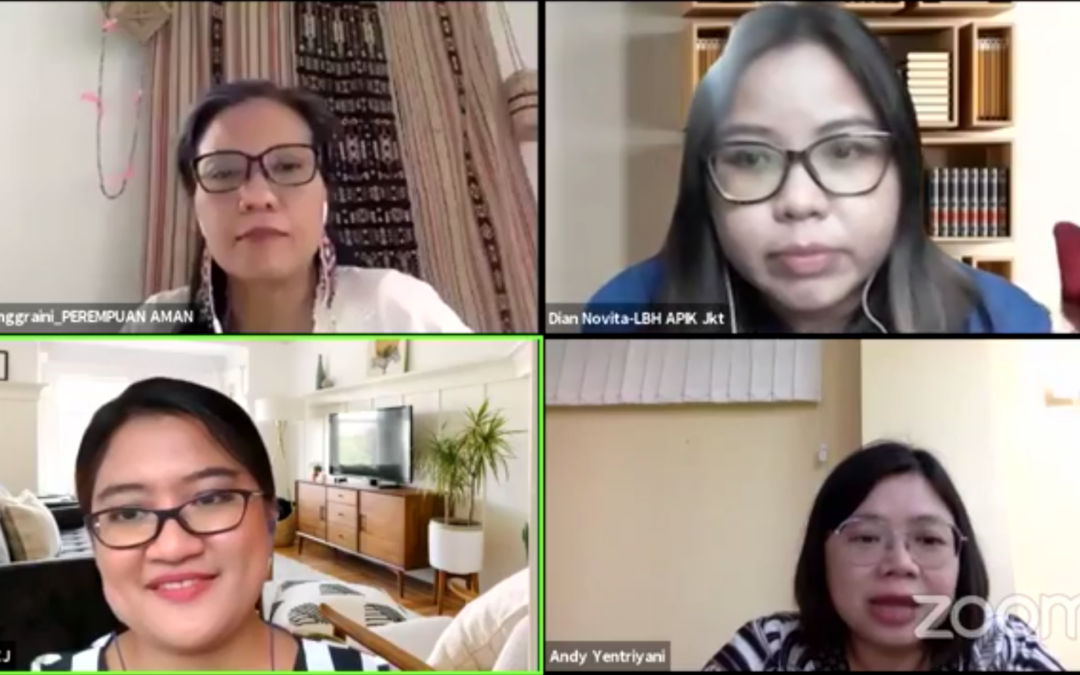
Apr 9, 2021 | Advocacy, News
The ICJ, together with the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) and the National Commission on Violence Against Women (Komnas Perempuan) in Indonesia, held a webinar on 6 April to consider ways to combat discrimination and violence faced by Indonesian women.
In particular, participants identified advocacy strategies towards strengthening Indonesia’s compliance with its international legal obligations under the UN Convention on the Elimination of all forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW).
The webinar was broadcast live on Facebook and showcased the Bahasa Indonesia version of CEDAW video and attended by more than 50 women human rights defenders. The participants discussed the adequacy of measures taken by the Indonesian government to implement recommendations issued by the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW Committee) after it had reviewed Indonesia’s report in 2012. These recommendations included a call to repeal discriminatory by-laws adopted at the provincial level that restrict women’s rights in Aceh province and elsewhere; the adoption of measures taken to ensure that the draft or proposed amendments to the Criminal Code Bill and other bills do not contain provisions that discriminate against women; the need to address gender based violence and sexual violence against women including indigenous women; and the protection of women human rights defenders.
Devi Anggraini, Chairperson of Association of Indigenous Women of the Archipelago (Perempuan Aman) said although Indonesia had ratified CEDAW through Law No. 7 year 1984 to protect the individual rights of Indonesian women, policies had yet to effectively protect the collective rights of indigenous women. She shared her concerns regarding discrimination against Indigenous women in the context of large-scale development projects, exploitation of natural resources, deforestation, and expansion of agriculture, as well as their access to land and resources.
“The Indonesian government does not seek ‘free, prior, and informed consent’ by the affected indigenous people, especially indigenous women and this has caused 87.8% of indigenous women to lose control of their traditional lands,” said Devi.
Dian Novita, Coordinator of Policy Advocacy Division from Legal aid for Women and Children (LBH APIK Jakarta) raised concern about discriminatory draft laws and provincial laws.
“LBH APIK assists many cases of women who are victims of gender-based violence in which their videos containing private sexual conducts were distributed online. However, they were criminalized under the pornography law and Electronic Information’s and Transactions (EIT) Law. We are currently trying to pursue judicial review of the ETI Law from women’s perspective”, said Dian.
Andy Yentriyani, Head of Komnas Perempuan said that despite existing challenges and new obstacles, there had been some progress in responding to the Recommendations of the CEDAW Committee from the previous cycle, such as the enactment of Supreme Court Regulation no.3 year 2017 on guidance for judges in adjudicating cases involving women and similar gender sensitive regulation released by the Attorney General’s Office and the Police. “It is now our duty to monitor that these policies and training are effectively implemented. For example, we gained extraordinary support from the civil society during the campaign urging the Government to adopt the Sexual Violence Bill and this expanded participatory space for constructive dialogue for public to understand more about State responsibilities to protect and promote the fundamental rights of women.”
Watch
Contact
Ruth Panjaitan, Legal Adviser for Indonesia, e: ruthstephani.panjaitan(a)icj.org

Apr 7, 2021 | News
Victims of gross human rights violations must be provided with effective reparations and guarantees of non-recurrence by Tunisia’s Specialized Criminal Chambers (SCC), judges and prosecutors asserted during a workshop held by the ICJ and the Association of Tunisian Magistrates (AMT) on 3 and 4 April.
The workshop highlighted the need for the SCC to adopt restitution, compensation, rehabilitation and satisfaction measures to achieve to the fullest extent possible reparation for material and moral damage suffered by victims of gross human rights violations in Tunisia.
Participants further emphasized that SCC decisions should include recommendations on guarantees of non-recurrence, including on legal and institutional reforms.
The workshop was attended by more than 25 Tunisian judges and prosecutors attached to the 13 Specialized Criminal Chambers. Discussions involved also international experts and ICJ representatives.
“It is important that the SCC, consistent with international standards, adopt a comprehensive notion of victims and persons entitled to reparation,” said Philippe Texier, ICJ Commissioner.
“In this respect, reparative measures should focus not only on direct victims, but also indirect victims, including the immediate family or dependants of the direct victim and persons who have suffered harm in intervening to assist victims,” he added.
Federico Andreu-Guzmán, international expert, noted the non-derogable nature of the right to reparation under international law and that SCC should seek to ensure that all their decisions comply with this right.
“SCC decisions should include wide-reaching recommendations in order to guarantee that the violations will not be repeated,” said Said Benarbia, Director of ICJ’s Middle East and North Africa Programme.
The workshop also offered the opportunity to participants to discuss a set of recommendations targeting the High Judicial Council and its role in supporting the SCC.
The recommendations, which were developed by a group of SCC judges and prosecutors following the ICJ’s roundtable of 13-14 March, aim to find joint approaches to address ongoing procedural obstacles before the SCC and will be subject of future meetings and roundtable discussions organized by the ICJ and the AMT.
Contact
Valentina Cadelo, Legal Adviser, ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, e: valentina.cadelo(a)icj.org
Asser Khattab, Research and Communications’ Officer, ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, e: asser.khattab(a)icj.org

Apr 2, 2021 | News

The Thai authorities’ adoption of a draft law to regulate non-profit groups would strike a severe blow to human rights in Thailand, several international organizations said today. The bill is the latest effort by the Thai government to pass repressive legislation to muzzle civil society groups and non-governmental organizations (NGOs).
The “Draft Act on the Operations of Not-for-Profit Organizations” contains provisions that would have a deeply damaging impact on those joining together to advocate for human rights in the country, in violation of their right to freedom of association and other rights. The Thai government provided a perfunctory and inadequate consultation process for the bill. Because of fundamental problems in the draft law, the authorities should withdraw the draft entirely and ensure that any future law regulating NGOs strictly adheres to international human rights law and standards, the organizations said.
“This draft law poses an existential threat to both established human rights organizations and grassroots community groups alike. If enacted, this law would strike a severe blow to human rights by giving the government the arbitrary power to ban groups and criminalize individuals it doesn’t like,” said Maria Chin Abdullah, member of ASEAN Parliamentarians for Human Rights (APHR) and a Malaysian Member of Parliament (MP).
“This draft blatantly breaches Thailand’s own constitution and its human rights obligations. A thriving, independent and free civil society is an essential component of a rights-respecting, open society. The authorities should withdraw this deeply flawed draft and go back to the drawing board,” said Brad Adams, Director of Human Rights Watch’s Asia Division.
Arbitrary and vaguely-defined powers
According to the Draft Act (in Section 3), the government would have wide discretion as to which organizations will be exempted from the application of the law.
The Draft Act (in Section 4) also uses an overbroad definition of not-for-profit organizations (NPO), which has left it open to abusive and arbitrary application by the authorities.
The broad terms of the Draft Act would allow unequal treatment of certain disfavoured groups and carry dire consequences for associations critical of the government, with little scope to legally challenge government decisions. Groups as varied as academic institutions, community groups, sports associations, art galleries and ad hoc disaster relief collectives could be deemed to be NPOs and therefore be subject to the law’s mandatory registration requirement and potential criminal prosecution. The vague and overbroad definition of ‘not-for-profit organizations’ amounts to a violation of the “legality” principle, which requires any restriction to freedom of association and other fundamental freedoms be clearly “prescribed by law”.
Registered and unregistered groups alike must be allowed to function freely and be able to enjoy the right to freedom of association on equal terms. In order to enable individuals to exercise their right to freedom of association, States need to provide a simple, accessible, non-burdensome and non-discriminatory notification process for organizations to obtain their registration and must not require the authorities’ prior authorization.
“The draft law’s broad terms could be applied against virtually any group, no matter how small or informal,” said David Diaz-Jogeix, Senior Director of Programmes at ARTICLE 19. “If passed in its current form, the draft law will likely cause entire sectors of Thai civil society to collapse or take their activities underground.”
Excessive punishments
“Those found in breach of this law’s many faulty provisions risk lengthy prison sentences. Targetted NGOs could have their very existence extinguished at the whim of governmental authorities – enabling the silencing of critical and independent voices in Thailand,” said Ian Seiderman, Legal and Policy Director at the International Commission of Jurists (ICJ).
By making the registration of an NPO mandatory (in Section 5) and rendering any unregistered group illegal, the Draft Act would violate the right to freedom of association and severely impede the work of groups that defend and promote human rights.
Notably, under the proposed law (in Section 10), anyone found to belong to an unregistered association that operates within Thailand could be jailed for up to five years, fined up to 100,000 THB (approx. 3,200 USD), or both. This would effectively criminalize people solely for their peaceful exercise of the right to freedom of association.
“Paranoia” of foreign funding
“Around the world, bogus claims regarding foreign funding for NGOs are constantly used by repressive governments to distract from their own human rights record and to stigmatize and fuel paranoia regarding those who speak truth to power – often simply because they are critical of the government,” said Shamini Darshni Kaliemuthu, FORUM-ASIA’s Executive Director. “Now Thailand seems to want to follow suit, adding itself to an unwelcome list of rights-abusing governments trying to control or severely limit NGO funding.”
The Draft Act (in Section 6) places discriminatory restrictions on organizations that receive foreign funding. Authorities have the sole discretion to determine which activities may be carried out using funds from foreign or international sources, leaving ample room for abuse.
Moreover, the Draft Act states as a rationale for enacting the law: “several [NPOs] accepted money [from foreign sources], and used them to fund activities that may affect the relationship between the Kingdom of Thailand and its neighboring countries, or public order within the Kingdom.” This justification stigmatizes organizations that use foreign funding by equating their objectives to those of “foreign agents”. The government has failed to recognize the legitimate work carried out by organizations and their contribution to the rule of law and development of the country, merely because they are funded by foreign sources.
Privacy invaded and censorship on expression
“In addition to the ongoing criminalization of online expression in Thailand, the Draft Act gives sweeping, unchecked and discretionary administrative powers to the authorities to further obstruct the work of human rights organizations,” said Emerlynne Gil, Amnesty International’s Deputy Regional Director for Research.
The Draft Act not only confers the power to the authorities to closely scrutinize organizations, it also contains provisions to subject NPOs’ offices and members to invasive surveillance and searches without judicial oversight. The Draft Act (in Section 6) allows the authorities to enter civil society organizations’ offices and make copies of their electronic communications traffic data without prior notice or a court warrant. This is a serious threat to the right to privacy and to freely express the ideas and opinions of its members.
Without prior notice or a valid warrant, this arbitrary power clearly violates domestic and international standards on due process of law.
“In going down this route, Thailand stands to poison the space for civil society. The passage of this law would severely undercut Thailand’s claims to be a rights-respecting country with a flourishing civil society,” said David Kode, Advocacy and Campaigns Lead at CIVICUS.
Contact
Ian Seiderman, ICJ Legal and Policy Director, ian.seiderman(a)icj.org, +41 229793800
Download
The statement with additional background information and list of organizations in English and Thai.
Submissions
Amnesty International
Article 19
Human Rights Watch
International Commission of Jurists – English and Thai

Apr 2, 2021 | News
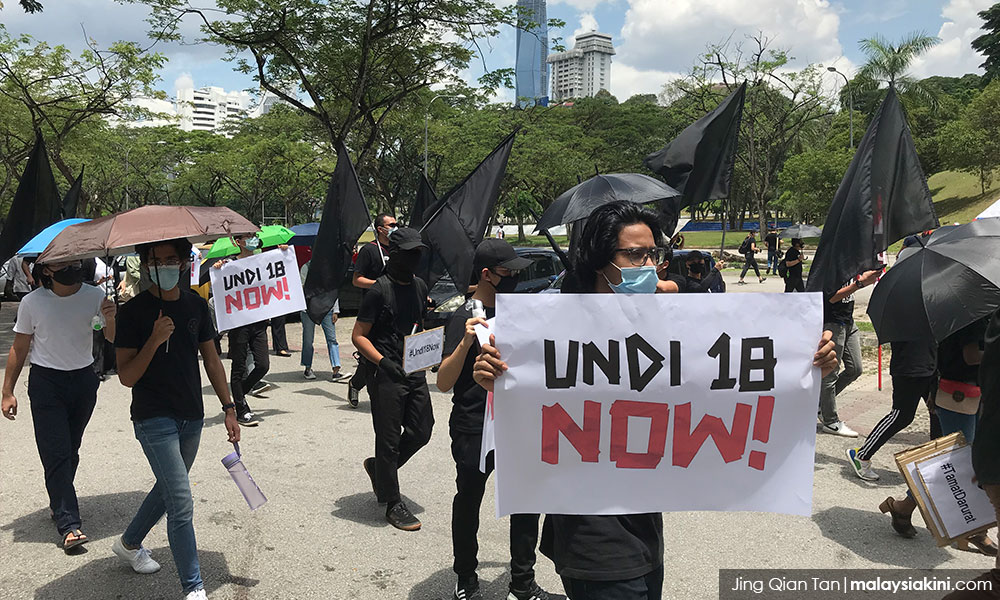
The ICJ today called on the Malaysian authorities to drop their criminal investigations of at least 11 participants in the peaceful Undi18 protests.
The Dang Wangi district police opened investigations against Dato’ Ambiga Sreenevasan, an ICJ Commissioner, and at least ten other individuals including Simpang Renggam MP Maszlee Malik, Petaling Jaya MP Maria Chin Abdullah, and Segambut MP Hannah Yeoh in relation to the wholly peaceful and socially distanced Undi18 protest rally held on 27 March 2021.
They are being investigated for alleged violations of section 9(5) of the Peaceful Assembly Act 2012 (‘PAA’) and Regulation 11 of the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases (Measures Within Infected Local Areas) (Conditional MCO) (No. 4) Regulations 2021 (‘MCO No. 4 Regulations’).
The ICJ said that the application of these laws against the protestors would not be consistent with international law and standards on freedom of expression and peaceful assembly.
The ICJ said that the investigations seem intended to harass and intimidate those who would exercise their rights to free expression and peaceful assembly.
If charged and convicted, violations of the PAA could result in a fine of up to RM$10,000 (approx. USD 2,410). Violations of the MCO No. 4 Regulations may result in a prison term of up to six months and/or a fine of RM$10,000 (approx. USD 2,410).
The ICJ reiterated its previous call for Malaysian legislators to reform the PAA, which imposes unjustifiably burdensome restrictions carrying excessive penalties on the exercise of freedom of expression and assembly.
Contact
Boram Jang, International Legal Adviser, Asia & the Pacific Programme, e: boram.jang(a)icj.org
Background
In July 2019, the Malaysian Parliament unanimously voted to lower the voting age from 21 to 18 years old.
On 25 March 2021, the Election Commission announced that it would postpone the implementation of this new rule from July 2021 to September 2022 at the latest. The Commission cited the COVID-19 lockdowns as a reason for the delay. This would affect the ability of 1.2 million people to vote, if elections are called later this year.
On 27 March 2021, hundreds of individuals gathered peacefully in front of Malaysia’ Parliament building to protest this delay. It was reported that the protestors were wearing face masks and trying to observe physical distancing, with some protestors donning full personal protective equipment.
On 29 March 2021, 11 individuals were summoned for questioning for alleged violations under section 9(5) of the PAA and Regulation 11 of the MCO No. 4 Regulations.
On 30 March 2021, eight of them gave their statements at the Dang Wangi police station in Kuala Lumpur. Four others, including Dato’ Ambiga Sreenevasan, will give their statements on 2 April 2021.
Section 9(5) of the PAA imposes a requirement for a five-day notice of an assembly to the Officer in Charge of the Police District. Failure to do so may result in a fine not exceeding RM$10,000 (approx. USD$2,410). Section 21A also allows the police to issue compounds of up to RM$5,000 instead of a charge being proffered subject to the written consent of the Public Prosecutor.
Regulation 11 of the MCO No. 4 permits the gathering or involvement in a gathering subject to any directions issued by the Director General. Regulation 17 states that failure to comply may result in a fine not exceeding RM$1,000 (approx. USD$241), imprisonment for a term not exceeding six months, or both. Additional emergency laws have raised the potential fine that may be imposed to up to RM$10,000 (approx. USD$2,410).











