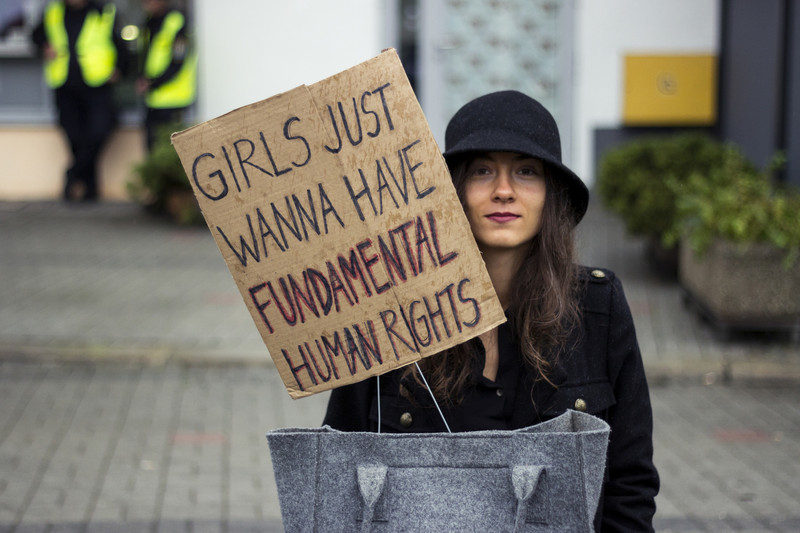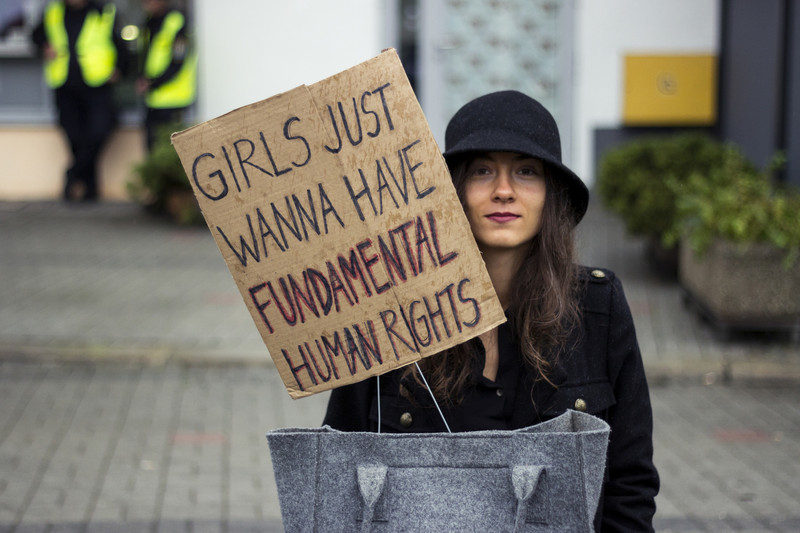
Apr 9, 2020 | Advocacy, News
A joint statement signed by the ICJ and 102 other organizations.
The COVID-19 pandemic and public health crisis is presenting grave challenges for health care systems across Europe.
As European countries work to address the pandemic, protect their populations, and meet the increased demand on health care workers and health care facilities it is vital that they adopt measures to safeguard the health, human dignity, physical and mental integrity, and reproductive autonomy of women and girls in the region.
In many countries the lack of government measures to guarantee individuals’ safe and timely access to essential sexual and reproductive health services, goods, and information during the pandemic is of particular concern.
Women and girls – this statement refers to women and girls, as the majority of individuals who are needing abortion care identify as such but it equally applies to all individuals who may become pregnant and need abortion care or other sexual and reproductive health care – are facing significant restrictions in safely accessing essential sexual and reproductive health services, particularly timely abortion care, post abortion care, and emergency contraception.
Such restrictions disproportionately impact individuals belonging to marginalized groups, including women living in poverty, women with disabilities, Roma women, undocumented migrant women, adolescents, and women at risk or who are survivors of domestic and sexual violence.
These restrictions also create unnecessary risks of exposure to COVID-19 for women and girls and their families as well as for health care providers.
Particularly grave barriers are arising for women and girls living in European countries where abortion care is illegal or severely restricted, and where as a result they must travel to other countries to access legal care or must obtain abortion medication from outside their own jurisdiction.
These issues can also arise in those European countries where individuals are forced to go through burdensome or harmful administrative processes to access abortion care or where they may have difficulty finding doctors in their country willing to provide care.
We applaud those governments that have moved swiftly to safeguard access to essential time- sensitive sexual and reproductive health care during this time, in particular through ensuring access to telehealth and early medical abortion from home.
We call on all other European governments to follow suit and to follow the guidance of medical and public health experts.
We call on the six European countries (Andorra, Liechtenstein, Malta, Monaco, Poland and San Marino) where abortion is illegal or severely restricted to urgently reform these laws, which place women’s health and lives at risk.
Limitations on travel and transport now compound the impact of these highly restrictive laws. Individuals in these countries may no longer be able to travel abroad or to obtain medication for abortion sent by post from medical providers in other countries. As a result, they face heightened risks to their health and wellbeing.
We call on those countries where abortion is legal but where clinical services are unavailable or difficult to access due to a range of barriers, including medically unnecessary requirements that oblige individuals to take multiple or unneeded trips to health care facilities or undergo mandatory hospitalization, to urgently eradicate those barriers and ensure access to services.
Urgent steps should also be taken to ensure that refusals of care because of private beliefs by doctors do not jeopardize timely access to legal abortion care.
In accordance with human rights obligations3 and the recommendations of medical experts4 the following measures should be adopted, and at a minimum remain in place for the duration of the COVID-19 pandemic:
- Ensure that abortion is treated as essential and time-sensitive health care and guarantee access to care in a timely manner.
- Authorize and make available in a timely manner telehealth consultations for anyone who is seeking abortion care or information. Specific measures should be adopted to ensure that telehealth consultations are free or low cost and easily accessible for marginalized groups.
- Guarantee timely access to early medical abortion throughout each jurisdiction and allow doctors to prescribe the necessary medication via telehealth consultation.
- Allow individuals to take all abortion medication at home. Requirements in some European countries that one pill must be taken in the physical presence of a doctor or in a health care facility should be removed.
- Remove mandatory waiting periods prior to abortion as well as mandatory counselling requirements or ensure counselling can be conducted through telehealth consultation.
- Authorize primary care doctors and midwives to provide early medical abortion.
- Adopt health system safeguards to guarantee access to care in cases where early medical abortion is not possible or is contraindicated, for individuals who need abortion care later in pregnancy or post-abortion care, or who may need to visit a health care facility for other reasons. Travel in such cases should be deemed essential and permitted even where governments have otherwise restricted free movement.
- Where a doctor’s authorization is required, this should be limited to one doctor. Requirements for multiple doctors’ approval of an abortion should be removed.
- Guarantee timely access to prenatal testing and psychosocial support where requested.
- Guarantee an adequate number of providers willing and able to provide abortion care throughout the country and widely publicize information on how women can identify health care professionals willing and available to provide abortion care. Urgently ensure that refusals of care by doctors do not jeopardize access to abortion care in a time of crisis.
- Widely disseminate information on those changes to SRHR policies and health care services that are being made in the context of COVID-19 responses.
- Ensure access to contraception including emergency contraception, including through authorizing telehealth consultations and provision of emergency contraception over the counter in pharmacies without a prescription.
Finally, we call on all policy makers across the European region to reject proposals that purport to restrict access to safe abortion care during the COVID-19 pandemic. These disingenuous proposals simply serve to exacerbate the current public health crisis and have negative effects on the health, lives, and wellbeing of women and girls.
Download the full statement with additional information and the list of signatories

Apr 9, 2020 | Events, News
Various States in the Latin American region have adopted exceptional measures to address the pandemic and manage the health crisis. These measures impact peoples’ human rights and freedoms. A series of webinars will cover this topic. The third one takes place today.
Access to justice and the right to an effective remedy are particularly at risk. In that regard, it is worth analyzing: How are justice systems reacting to the pandemic? What is required to continue guaranteeing access to justice, especially for those people and groups most vulnerable? How does this pandemic affect the provision of services in the justice sector? How can justice systems innovate to respond to this situation?
In order to address these questions, the ICJ together with DPLF, Fundación Construir, Fundación Tribuna Constitucional, Observatorio de Derechos y Justicia, and Fundación para la Justicia y el Estado Democrático del Derecho, supports an initiative of webinars led by a group of women human rights defenders in Latin America.
The webinars will be held in Spanish and through the Zoom platform. Registrations for each webinar can be made by sending an email to info@dplf.org Registered persons will receive the zoom link where the activity can be followed.
The first three conversations are as follows:
- Essential justice services in times of emergency: Thursday 02 of April
At: 14.00 México-Central America/ 15 hours Colombia-Perú-Ecuador/ 16.00 Washington-Bolivia/ 17.00 Chile -Argentina/ 22.00 Geneva
- Working from home and being a judge: challenges for women that are judges: Tuesday 07 of April
At 14.00 México-Central America/ 15.00 Colombia-Perú-Ecuador / 16.00 Washington-Bolivia / 17.00 Chile -Argentina/ 22.00 Geneva
- Innovating in the justice system during times of emergency: Thursday 09 of April
At 14.00 México-Central America/15.00 Colombia-Perú-Ecuador/ 16.00 Washington-Bolivia/ 17.00 Chile -Argentina/ 22.00 Geneva

Apr 8, 2020 | Feature articles, News
A Feature Article by Rocio Quintero, Legal Adviser, ICJ Latin American Programme, based in Bogota.
Throughout several decades, a large number of Colombians have been victims of serious crimes related to the ongoing armed conflict. In particular, human rights defenders have been targets of serious human rights violations and abuses, such as killings, death threats, and harassments.
Just this year, the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) has received information of 56 possible cases of killings of human rights defenders. Unfortunately, the COVID-19 outbreak has not stopped the violence against human rights defenders.
In that regard, since the first confirmed case of COVID-19 in the country on 6 March 2020, the Organization of American States (OAS) and International Amnesty has reported six killings. The perpetrators of those crimes have not been identified yet.
Human rights violations and abuses against local communities have not stopped either. Quite the opposite seems to be true.
In that regard, it is said that armed groups, including paramilitary groups and new groups made up of dissident FARC-EP members, are taking advantage of the outbreak to commit illegal actions with fewer constraints, mainly, in rural areas of the country.
Among these actions, it should be highlighted the enforced displacement of 250 people and the forced confinement of 770 families due to combats between a paramilitary group and a guerrilla group. Both actions took place in the pacific region of the country, an area where the conflict has intensified after the peace agreement. In addition, at least three ex-members of the FARC-EP have been murdered in March 2020.
Despite the seriousness of the situation described above, the Colombian government response to the COVID-19 crisis has focused on the creation and implementation of non-conflict-related measures.
In that regard, the Government has decreed various and vital regulations to mitigate the social and economic impact created by the virus. Among others, the president declared a state of emergency and a mandatory 19-day national quarantine that started on 25 March 2020.
The Government also established a program of economic and social aid for those who will be affected most by the quarantine.
None of the measures were designed bearing in mind the particular situation of human rights defenders. Consequently, their protection is not a central element of the Colombian pandemic policies.
Since the implementation of the peace agreement and victims’ rights are not top priorities of the current Government, the approach adopted is not entirely unexpected.
Although, to be fair, it should be recognized that the State programmes for the implementation of the peace agreement have continued operating during the pandemic.
It might be argued that the pandemic has the potential to affect predominantly human rights that have not been directly linked with the internal conflict.
Therefore, following this point of view, the prioritization of non-conflict-related measures is justified and required.
Although this position is based on a valid premise, which is that the COVID-19 pandemic creates several challenges that go beyond conflict-related human rights problems, it ignores a central element of Colombian reality: the existence of an ongoing armed conflict.
Currently, the conflict affects a considerable part of the Colombian population directly, including the majority of human rights defenders. In that regard, last year, it was reported illegal actions related to the internal armed conflict in at least 10 out of 32 departments of Colombia.
In this context, ignoring the importance of the conflict might lead to the implementation of ineffective pandemic measures. This is because, in conflict zones, the protection of human rights requires addressing the specific challenges that the pandemic has created in those territories.
For instance, the presence of illegal groups can prevent local communities from getting tested for COVID-19 and access to health services. Likewise, due to the quarantine, illegal groups might identify easier the location of human rights defenders and retaliate against them.
In relation to human rights defenders, it should also be highlighted the problems related to access to adequate protection measures. In that regard, Amnesty International has denounced that the protection measures for some human rights defenders have been reduced due to the pandemic.
In a similar way, a local NGO expressed concerns for the decision of the National Protection Unit to suspend indefinitely the sessions of the commission where protection measures are defined.
In light of the above, beyond political considerations and the general Government’s priorities, it is imperative that the Government adopts a more comprehensive approach to tackle the pandemic.
It should address the differential impact the pandemic might have on people who lead social and legal transformations in the conflict zones of the country.
In particular, it should implement or adapt protection measures to be effective during the COVID-19 crisis. Similarly, the right to an effective remedy and reparation should also be not only guaranteed, but realized, in compliance with international standards.
Additionally, it is also important that the national Government reinforce its efforts to obtain a humanitarian ceasefire by all illegal groups during the COVID-19 crisis.
A total ceasefire would contribute to (i) protecting the civilian population for violent actions, (ii) implementing the pandemic measures in conflict zones, and (iii) avoiding a proliferation of the virus in vulnerable communities.
This is a crucial measure that has already been requested by national civil organisations, the Head of the UN Verification Mission in Colombia, the OAS, and some parliamentarians.
As yet, only one illegal group has accepted a ceasefire: the National Liberation Army (Ejército de Liberación Nacional, ELN), the largest active guerrilla in Colombia, who declared a unilateral ceasefire during April.
To conclude, acknowledging the importance of the conflict is essential to tackle the human rights implications of the COVID-19 crisis.
This is not only necessary to have comprehensive pandemic policies, but also to make sure that the problems and needs in the conflict zones are not neglected and aggravated during the pandemic.
On this point, as recently stated by UN Secretary-General, people who are most vulnerable during a conflict are also “most at risk of suffering “devastating losses” from the disease.”

Apr 8, 2020 | News
The ICJ today warned that Cambodia’s draft Law on National Administration in the State of Emergency (“State of Emergency bill”) violates basic rule of law principles and human rights, and called on the Cambodian government to urgently withdraw or amend the bill in accordance with international human rights law and standards.
Last Friday, government spokesperson Phay Siphan explained that the government needed to bring a State of Emergency law in force to combat the COVID-19 outbreak as “Cambodia is a rule of law country”. The bill is now before the National Assembly and, if passed by the Assembly, will likely be considered in an extraordinary session convened by the Senate. The law will come into force once it has been signed by the King – or in his absence, the acting Head of State, Senate President Say Chhum.
“The Cambodian government has long abused the term “rule of law” to justify bringing into force laws or regulations that are then used to suppress free expression and target critics. This bill is no different,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ’s Director for Asia and the Pacific.
“Any effective response to the COVID-19 outbreak must not only protect the rights to health and life, but be implemented in accordance with Cambodia’s human rights obligations and basic principles of the rule of law.”
Several serious shortcomings are evident in the State of Emergency bill, including:
- No delineation of a timeline for the imposition of a state of emergency, or criterial process for its termination. The bill provides vaguely that such declaration “may or may not be assigned a time limit. In the event that a state of emergency is declared without a clear time limit, such a state of emergency shall be terminated when the situation allows it” (article 3);
- Expansion of government powers to “ban or restrict” individuals’ “freedom of movement, association or of meetings of people” without any qualification to respect the rights to association and assembly in enforcing such measures (article 5);
- Expansion of government powers to “ban or restrict distribution of information that could scare the public, (cause) unrest, or that can negatively impact national security” and impose “measures to monitor, observe and gather information from all telecommunication mediums, using any means necessary” without any qualification to respect the rights to privacy, freedom of expression and information in enforcing such measures (article 5);
- Overbroad powers for the government to “put in place other measures that are deemed appropriate and necessary in response to the state of emergency” which can allow for significant State overreach (article 5);
- Severe penalties amounting to up to 10 years’ imprisonment of individuals and fines of up to 1 billion Riel (approx. USD 250,000) on legal entities for the vaguely defined offence of “obstructing (State) measures related to the state of emergency” where such obstruction “causes civil unrest or affects national security” (articles 7 to 9);
- No specific indication of which governmental authorities are empowered to take measures under the bill, raising concerns that measures could be taken by authorities or officials in an ad-hoc or arbitrary manner in violation of the principle of legality;
- No indication of sufficient judicial or administrative oversight of measures taken by State officials under the bill – The bill states that the government “must inform on a regular basis the National Assembly and the Senate on the measures it has taken during the state of emergency” and that the National Assembly and the Senate “can request for more necessary information” from the government (article 6) but does not clarify clear oversight procedures for accountability.
“The State of Emergency bill is a cynical ploy to further expand the nearly unconstrained powers of the Hun Sen government, and will no doubt be used to target critical comment on the government’s measures to tackle COVID-19,” said Rawski.
“If passed in its current form, this bill will reinforce the prevailing lack of accountability which defines the government in Cambodia. The government’s time would be better spent developing genuine public health policy responses to the crisis.”
Contact
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Director, e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org
To download the statement with detailed background information, click here.
See also
ICJ report, ‘Dictating the Internet: Curtailing Free Expression, Opinion and Information Online in Southeast Asia’, December 2019
ICJ report, ‘Achieving Justice for Gross Human Rights Violations in Cambodia: Baseline Study’, October 2017
ICJ, ‘Cambodia: continued misuse of laws to unduly restrict human rights (UN statement)’, 26 September 2018
ICJ, ‘Misuse of law will do long-term damage to Cambodia’, 26 July 2018
ICJ, ‘Cambodia: deteriorating situation for human rights and rule of law (UN statement)’, 27 June 2018
ICJ, ‘Cambodia human rights crisis: the ICJ sends letter to UN Secretary General’, 23 October 2017

Apr 7, 2020 | News
As South Africa enters into its second week of a 21-day lockdown, the ICJ calls on national, provincial and local government authorities to urgently implement measures to prevent sexual and gender-based violence (SGBV) and protect women and children from it.
The country has been under lockdown since 26 March, with the population remaining at home, physically isolated in an attempt to ‘flatten the curve’ of transmission of the Covid-19 virus.
However, the lockdown means that some are trapped in their homes with their oppressors.
“A lockdown impacts women differently. For some women, being forced into lockdown with an already abusive partner heightens the risk of abuse and violence. It also means less support and fewer chances to seek help,” ICJ Senior Legal Adviser Emerlynne Gil said.
On 3 April, Police Minister Bheki Cele said that the South African Police Services had received 87,000 SGBV complaints violence during the first week of the national Covid lockdown.
Among the complainants was the wife of a police officer who reported that her husband had raped her. The officer has since been arrested.
The South African authorities have taken some steps to enhance women’s access to protection from SGBV during this lockdown, including by ensuring that women have access to courts for urgent civil matters, such as protection orders, as well as ensuring that there is an SMS line through which they can seek help.
Social services and shelters have also been made available. However, the authorities can and should go further in ensuring that these services are widely publicized, and that women have effective access them during the lockdown.
“Under international human rights law, States are legally obliged to take measures to prevent, address and eliminate SGBV,” ICJ Legal Associate Khanyo Farisè said.
“The South African authorities should do more, in particular, by raising awareness about GBV and providing comprehensive multi-sectoral responses to victims.”
Under international human rights law binding on South Africa, such as the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women, States are obligated to take all appropriate measures to eliminate violence against women of any kind occurring within the family, at the work place or in any other area of social life.
In a previous statement, the ICJ also called on States to ensure that measures to tackle Covid-19 are gender responsive.
The ICJ calls on South African authorities to:
- Widely publicize health and legal services, safe houses and social services and police services available to victims of SGBV, including the hotline 0800-428-428 or *120*786#
- Effectively respond to reported cases of SGBV and provide protection to victims through a multi-sectoral approach involving all relevant stakeholders.
- Investigate the causes of SGBV, including the surge of this scourge in the South African context during the COVID19 pandemic, and identify further measures to protect women against SGBV that are specifically required during pandemics.
- Implement “pop-up” counseling centres in mobile clinics or in pharmacies to support women who experience SGBV.
- Include the work of domestic violence professionals as an essential service and provide emergency resources for anti-domestic abuse organizations to help them respond to increased demand for services.
Contact
Khanyo Farisè, ICJ Legal Associate, e: nokukhanya.Farise(a)icj.org
Shaazia Ebrahim, ICJ Media Officer, e: shaazia.ebrahim(a)icj.org

Apr 6, 2020 | Feature articles, News
A Feature Article by the Access to Justice for Women Team of the ICJ.
As the COVID-19 pandemic spreads across the globe, many governments are introducing a spectrum of measures to curb the spread of the novel coronavirus, including travel bans, lockdowns, curfews, and school, workplace and border closures.
While it is important that States act decisively in discharge of their obligations to protect the rights to life and health of all people during this pandemic, it is equal that they do so in a human rights compliant manner, so as not to compound the harms brought directly by the virus.
This entails, among other things, acting in a manner that provides equal protection and is non-discriminatory. Complying with these principles requires taking into account gender impacts and providing for gender-specific responses.
However, a number of measures presently being taken by governments around the world to attempt to curb the spread of the virus can be expected to exacerbate pre-existing gender inequalities and therefore disproportionately affect women’s enjoyment of social and economic rights.
Many women who are disabled, refugees, migrants, detainees, living in poverty and or belonging to ethnic, racial, religious or sexual minority groups are experiencing or are likely to experience intersecting forms of discrimination during this time of crisis.
What Does #StayHome Mean to Women?
Lockdowns, quarantines, and school closures to control the pandemic in many countries have a differential effect on women.
Women and girls are most expected to perform caregiving role within families, which means less economic and work opportunities for them and thus denying their basic rights to development.
This condition is worsened if they are being quarantined with an abusive partner as they are exposed to greater risks of intimate partner violence during the outbreak.
Unfortunately, in many places there is a significant lack of guidelines or information on how to contact police, access medical treatment, psychological support, or access to shelters when domestic violence occurs during the pandemic.
In the UK, for example, while 25 organizations helping domestic violence victims have reported an increase in their cases since the surge of the COVID-19 epidemic, one quarter said they could not effectively support victims because of technical issues, inability to meet victims, and staff sickness.
Additionally, with resources already stretched in fighting the spread of the virus, many State authorities may not see as a priority access to comprehensive sexual and reproductive health services for women, which are already restricted by prohibitive laws and customs in many contexts.
This results in significant limitations on women’s rights to menstrual health, maternal health, and safe abortion.
Women at Work
According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), women are over-represented in more affected sectors (such as services) or in occupations that are at the frontline of dealing with the pandemic.
The ILO estimates that 58.6 percent of employed women work in the services sector around the world. Women also have less access to social protection and will bear a disproportionate burden in the care economy, in the case of closure of schools or care systems.
Women migrant workers are also vulnerable to the impact of the COVID-19 crisis, as extensive travel restrictions constrain both their ability to access their places of work in destination countries and return to their families.
Women at the Border: Refugees & Asylum seekers
There is a severe lack of secure, safe and accessible infrastructure and services in most refugee camps and temporary settlements.
Asylum seekers face right now a long wait if the courts are closed due to the pandemic, or worse, being returned to their home country without having a chance to pursue their claims, sometimes in violation of the principle of non refoulement.
As the virus hits overcrowded displacement sites, the consequences can expected be catastrophic. Moreover, in this setting, studies found that women and girls are often exposed to sexual violence and exploitation when they are forced to openly defecate or walk to shared sanitation facilities.
All State Measures to COVID-19 Must Be Gender Responsive
Under the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR), States have duty to achieve the full realization of the right to everyone to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health.
The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW) also provides of the obligation of States to take all appropriate measure to eliminate discrimination against women in the field of health care in order to ensure, on a basis of equality of men and women, access to health care services, including those related to family planning.
Furthermore, failure to recognize the gender dynamics of outbreaks limits the effectiveness of response efforts and consequently impedes women’s rights.
In order for the response to disease outbreaks such as COVID-19 to be effective and not reproduce or perpetuate gender and health inequities, it is important that gender norms and roles are identified and incorporated in all socio- economic measures established to counter the pandemic.
Further, the emergency preparedness and response plan must address gender roles, responsibilities, social norms and specific needs of women.
States should also provide new strategies for women victims of domestic violence to be protected during the lockdown.
Governments should include the work of domestic violence professionals an essential service and provide emergency resources for anti-domestic abuse organizations to help them respond to increased demand for services.
They should also consider, alternative means, such as through “pop-up” counseling centers, reporting in pharmacies, to encourage women to report domestic violence.
Governments must ensure all measures to combat the outbreak are gender responsive while being in strict accordance with human rights standards.
While states may limit or derogate from certain rights to meet a public health crisis, such restrictions are always subject to the principles of legality, necessity proportionality and nondiscrimination.
Given that women are often to be found in the more vulnerable categories of informal work, for instance, as domestic workers or self-employed home-based workers, authorities should enhance universal access to collectively-financed health services for all, including uninsured workers and their families.
States must also expand access to collectively-financed paid sick leave, sickness benefits, and parental or care leave to ensure income security for those who are sick, quarantined or caring for children, elderly or other family members.
Moreover, governments should ensure that women asylum seekers, internally displaced persons, and refugees are included in national COVID-19 surveillance, preparedness, and response plans, and ensure that menstrual hygiene, reproductive, and other primary health care commodities are well-stocked and available.
Lastly, perspectives, experiences, and voices of diverse women, including LBTI persons (as enshrined in the Yogyakarta Principles), should be included in decision-making process around the COVID-19 outbreak measures because effective global responses, to public health emergencies must be in line with the rights and needs of affected women.
***
Download the Op-Ed in other languages:
Nepali (PDF)
Tamil (PDF)
Sinhala (PDF)
Indonesian (PDF)