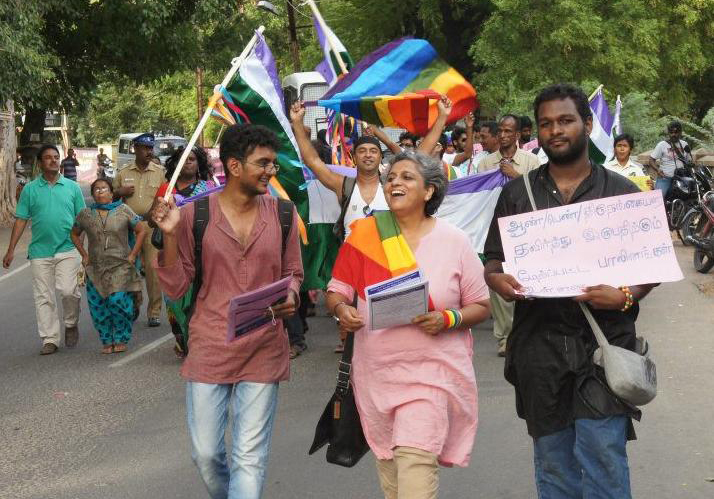Aug 6, 2019 | News
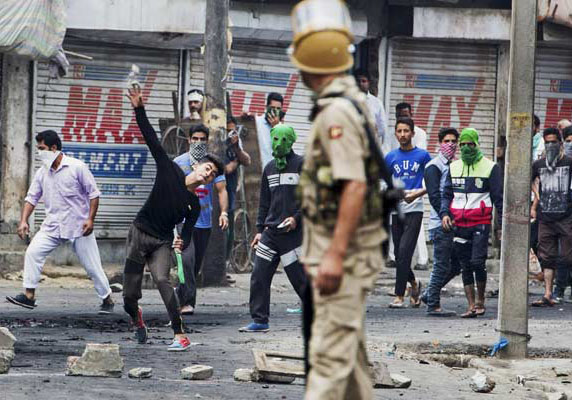
The Indian Government’s revocation of the autonomy and special status of Jammu and Kashmir violates the rights of representation and participation guaranteed to the people of Jammu and Kashmir under the Indian Constitution and in international law and is a blow to the rule of law and human rights in the state and in India, the International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) said.
The Indian Government today pushed through a legislative package effectively eliminating the special status accorded to Jammu and Kashmir under Article 370 of the Indian Constitution, which granted autonomy to Jammu and Kashmir and limited the Indian Government’s legislative powers in the state. The move was preceded by a communication blackout, arbitrary detention of political leaders, banned movement and meetings of people, and increased military presence, purportedly to quell protests.
“The Indian Government has pushed through these changes in contravention of domestic and international standards with respect to the rights of people in Jammu and Kashmir to participate and be adequately represented, accompanied by draconian new restrictions on freedoms of expression, assembly, and travel, and with an influx of thousands of unaccountable security personnel,” said Sam Zarifi, ICJ’s Secretary General.
“The legality of the Indian Government’s measures to eviscerate Article 370 will certainly be tested before the Indian judiciary, which should look closely at the serious violations of proper legislative and Constitutional processes,” Zarifi said. “All eyes are now on the Indian Supreme Court to fulfill its functions in defense of the rights of people of Jammu and Kashmir and the Indian Constitution,” Zarifi said.
The procedure adopted to revoke the special status and autonomy of Jammu and Kashmir appears to be incompatible with judgments and observations of high courts and the Indian Supreme Court, who have clarified that the President of India would need the agreement of the government of Jammu and Kashmir to change its status. The amendments effectively render Article 370 inoperative in its entirety, without meeting the Constitutional requirements in spirit.
The revocation of special status of Jammu and Kashmir without agreement from the state government is contrary to the spirit of Article 370, which envisioned that the will of the people would be taken into account in decisions relating to state’s special status and autonomy.
“The Indian Government rushed through the amendments at a time when Jammu and Kashmir was under the direct rule of the Central Government, and the state legislature was dissolved. As the government of Jammu and Kashmir is not empowered to discharge its functions, it has not been consulted, let alone agreed to the revocation,” Zarifi said.
“The lack of consultation with the people of Kashmir is all the more troubling because the changes pushed by the Indian Government will materially affect Kashmir’s status as India’s only Muslim-majority state, including special rights for citizens of the state to own and hold land and seek education and employment,” Zarifi said.
The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) in successive reports in 2018 and 2019 has noted that the region of Jammu and Kashmir, under dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947, has been the theatre of grave human rights violations, including unlawful killings, enforced disappearances and torture, committed with impunity by Indian security forces.
The UN High Commissioner for Human Rights in both reports recommended to the Indian Government to “fully respect the right of self-determination of the people of Kashmir as protected under international law”.
The ICJ condemns the legislative steps taken with respect to Jammu and Kashmir, and calls on the Indian Government to implement in full the UN High Commissioner’s recommendations, including respecting the right to self-determination of people of Jammu and Kashmir, and to respect, protect and fulfill the human rights of people in Jammu and Kashmir.
Contact
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Secretary General,e: sam.zarifi(a)icj.org, t: 41 (0)22 979 38 00
India-Jammu Kashmir and Autonomy-News-press release-2019-ENG (full story with additional information, in PDF)

Aug 5, 2019 | News
The ICJ today raised concerns that the proposed Zambian Constitutional Amendment Bill 2019 may negatively impact the independence of the judiciary in Zambia.
The proposed amendments to provisions regarding disciplinary measures and processes against judges and the composition of the Supreme Court and Constitutional Court are particularly concerning, according to a statement by a group of organisations including the ICJ.
“The ICJ implores the President of Zambia and the Zambian legislature to ensure the alignment of all constitutional amendments with international human rights standards on the independence of the judiciary, the rule of law and the separation of powers,” said Arnold Tsunga, the ICJ’s Africa Director.
The joint statement calls upon the President of Zambia and the Zambian legislature to ensure that the proposed constitutional changes are in line with international human rights standards.
According to such standards, individual judges ‘may be dismissed only on serious grounds of misconduct or incompetence, in accordance with fair procedures ensuring objectivity and impartiality set out in the constitution or the law’. Examples include ‘incapacity or behaviour that renders them unfit to discharge their duties’ and ‘physical or mental incapacity that prevents them from undertaking their judicial duties.’
Moreover, disciplinary proceedings regarding judicial officers must be held by an institution independent of the executive and the legislature to secure the independence of the judiciary.
Article 143 (a) of the Zambia Constitution currently provides that ‘a judge shall be removed from office on the following grounds: (a) a mental or physical disability that makes the judge incapable of performing judicial functions; (b) incompetence; (c) gross misconduct; or (d) bankruptcy.’
However, the Amendment Bill worryingly replaces subsection (a) and allows for removal when a judicial officer is ‘legally disqualified from performing judicial functions.’
Furthermore, the proposed amendment does not set out the circumstances or infractions that could lead to the ‘legal disqualification’ leaving the provision open to abuse and in violation of the principle of legal certainty and the rule of law.
“The amendment introduces unnecessary obscurity and vagueness to the Constitution, which, in turn, increases the risk of judges being removed on politically motivated grounds and threatens the rule of law,” Tsunga added.
Another worrying aspect of the proposed amendment is the suggested changes to Article 144 of the Constitution transferring the authority to determine whether judicial officers are removed from the Judicial Complaints Commission to a Tribunal Appointed by the President.
The amendment allows for the possibility of a Tribunal staffed by members of the executive and the legislature, further heightening concerns about threats to judicial independence.
“It is vital that the processes and procedures for the removal of judicial officers in Zambia are constrained in terms of tightly defined constitutional provisions, overseen by independent decision makers without improper influence by the executive and the legislature,” said Tsunga.
The full statement is available here.
The statement is signed by:
Commonwealth Lawyers Association (CLA)
Commonwealth Magistrates’ and Judges’ Association (CMJA)
International Bar Association’s Human Rights Institute (IBAHRI)
International Commission of Jurists (ICJ)
Judges for Judges (J4J)
Lawyers’ Rights Watch Canada (LRWC)
Southern Africa Litigation Centre (SALC)

Jul 31, 2019 | News, Publications, Reports, Thematic reports
In a report released today on Libya’s criminal justice system, the ICJ said the United Nations, international actors and States must prioritize accountability for crimes under international law in their engagement with Libya.
This includes the establishment of a Commission of Inquiry or similar mechanism to document and report on gross human rights violations and to collect and preserve evidence of crimes for future criminal proceedings.
“The Libyan criminal justice system needs comprehensive reform to dismantle the structural impunity that prevails in the country,” said Said Benarbia, the ICJ’s MENA Programme Director.
“Rather than assuming the system is capable of ensuring justice for the egregious human rights violations and abuses still being perpetrated in Libya, international actors should establish a mechanism to monitor, report on and address these violations and prioritize human rights in any agreement with Libyan authorities,” he added.
The report Accountability for Serious Crimes under International Law in Libya: an Assessment of the Criminal Justice System finds that investigations and prosecutions of crimes under international law have been limited to a handful of cases and that future cases are unlikely meet international standards necessary to ensure fair and effective justice, in particular the rights to liberty and a fair trial and the prohibition on torture and ill-treatment.
Fragmentation in Libyan executive and legislative bodies, with the internationally recognized government unable to control significant parts of the territory, has weakened political structures and led to a precarious security situation that impedes the effective functioning of the judiciary, which has remained largely unified.
“Accountability efforts in Libya are hindered by cycles of violence, weak and ineffective law enforcement agencies, the arbitrary exercise of policing and detention powers by armed groups, and a web of amnesties, immunities and defences that shield perpetrators from justice,” said Kate Vigneswaran, the ICJ’s MENA Programme Senior Legal Adviser.
“Victims should not have to wait any longer for these obstacles to be removed and justice delivered. Peace and justice in Libya can only be achieved if the rule of law is fully established,” she added.
Since 2011, crimes under international law and other gross human rights violations, including torture and ill-treatment, enforced disappearance, enslavement and rape, have been committed by State and non-State actors on a widespread scale, including against thousands of migrants, refugees and asylum seekers arbitrarily detained.
“The recent upsurge in conflict and related commission of direct and indiscriminate attacks against civilians and mass displacement of the population makes tackling the climate of impunity vital for combating the commission of crimes,” said Benarbia.
To this end, States should fully support International Criminal Court efforts to conduct Libya-related investigations and prosecutions, including with a view to enforcing arrest warrants and bringing alleged perpetrators before the court for trial.
In her address to the Human Rights Council on 24 June, High Commissioner for Human Rights Michelle Bachelet stated that “Libya is not a port of safe return” and that “[t]he international community must come together to support pathways to sustainable peace in the country.”
Key recommendations for international actors, including UN bodies and States, include:
- The United Nations Human Rights Council should establish a Commission of Inquiry or similar mechanism, with a mandate to monitor, document, establish the facts and report on gross human rights violations in Libya, including with a view to collecting and preserving evidence of crimes under international law for future criminal proceedings before national or international courts;
- States should exercise universal jurisdiction to investigate and prosecute crimes under international law committed in Libya, including when the perpetrator is within their territory or otherwise under their jurisdiction;
- States should fully cooperate with and adequately resource the ICC to enhance its capacity to conduct its investigations and prosecutions, enforce related arrest warrants, and bring alleged perpetrators to account; and
- States and UN actors should refrain from entering into or implementing agreements with Libyan authorities, including in relation to the detention of migrants, refugees and asylum seekers and the provision of arms, where it is reasonably foreseeable that violations of rights under international law might occur.
Contact:
Said Benarbia, Director, ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, t: +41-22-979-3817; e: said.benarbia(a)icj.org
Kate Vigneswaran, Senior Legal Adviser, ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, t: +31-62-489-4664; e: kate.vigneswaran(a)icj.org
Libya-Accountability report launch-News-Press releases-2019-ENG (full story, in English, PDF)
Libya-Accountability serious crimes-Publications-Reports-Thematic reports-2019-ENG (full report in English, PDF)
Libya-Accountability report launch-News-Press releases-2019-ARA (full story in Arabic, in PDF)
Libya-Accountability serious crimes-Publications-Reports-Thematic reports-2019-ARA (full report in Arabic, PDF)

Jul 29, 2019 | News
The Government of Nepal has failed to fulfill its commitment to provide justice for the victims of the country’s decade-long armed conflict, the ICJ, Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch, and TRIAL International said today.
The organizations echoed statements by victims and human rights groups about the Nepal government’s inaction on addressing conflict-era human rights violations, and a lack of transparency in the appointment of commissioners to the Truth and Reconciliation Commission and to the Commission on the Investigation of Enforced Disappearances.
“The lack of progress in holding perpetrators accountable for the suffering inflicted upon victims, their families and Nepali society as a whole, is appalling,” said ICJ Asia-Pacific Director Frederick Rawski.
“Nearly 13 years after the signing of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement, political leaders inside and outside of government are still playing games by politicizing the process. It is about time that they showed some courage, and took action to ensure access to justice, instead of continually looking after their own short-term self-interests,” he added.
“We have seen no evidence so far that the authorities of Nepal are serious about fulfilling their obligation to investigate conflict-era violations and bring all those suspected of criminal responsibility to justice in fair trials before ordinary civilian courts,” said Raju Chapagai, South Asia researcher at Amnesty International. “If the commitment to human rights obligations was as unflinching as claimed by Prime Minister KP Sharma Oli, the government would have acted diligently to deliver on its transitional justice responsibilities.”
After being elected in 2018, Prime Minister Khadga Prasad Oli renewed promises that the legal framework governing the transitional justice process would be brought into conformity with Nepal’s international human rights law obligations, as the Supreme Court had repeatedly directed. However, the government never amended the law, and instead pushed forward – without adequate consultation – with the establishment of a committee to recommend appointments to the transitional justice bodies.
“The failure of the government to deliver on its commitment to ensure truth, justice and reparations for the victims of conflict-era abuses shows a dismaying disregard for the protection of human rights,” said Meenakshi Ganguly, South Asia Director at Human Rights Watch.
The organizations called on the government to: 1) suspend the current process, and initiate a consultative and transparent process for the nomination and appointment of commissioners; 2) follow through on commitments to amend the 2014 transitional justice law to ensure that the legal framework is consistent with international human rights standards and Supreme Court rulings; and 3) adopt and publicize a plan for taking the transitional justice process forward.
“The legitimacy of Nepal’s transitional justice process lies both on a transparent and consultative appointment process for commissioners, and a strong legal foundation to allow the commissions to fulfil their mandate,” said Helena Rodríguez-Bronchú, Head of TRIAL International’s Nepal program. “Societal consensus is crucial for both factors.”
Amnesty International, ICJ and TRIAL International had previously submitted their analysis of the draft transitional justice legislation circulated in 2018 and had made recommendations on ensuring compliance with international human rights law. Human Rights Watch had also alerted for reform of the transitional justice law before appointing the commissioners. In April 2019, United Nations experts also wrote a joint letter to the foreign minister reminding the government of its commitment to amend the law and calling for a transparent process for appointing new commissioners after the terms of the previous commissioners expired.
Contact
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia-Pacific Director, t: +66 644781121 ; e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org,
Nepal-trans just-News-Press releases-2019-NEP (story in Nepali, PDF)
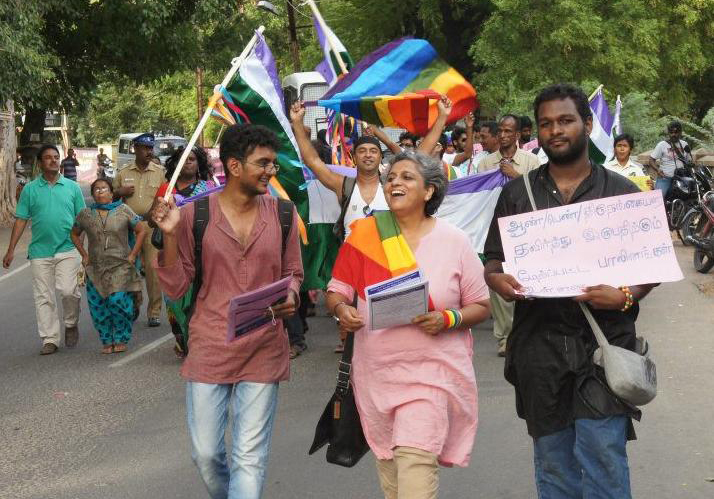
Jul 23, 2019 | News
The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2019, does not adequately protect the rights of transgender people and should be revised to address the concerns of the transgender community and to conform with India’s international human rights obligations, the ICJ said today.
“The Transgender Bill as currently drafted still fails to fully protect the rights of transgender people including to self-identify, a right that has been upheld by the Indian Supreme Court,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ’s Asia Pacific Director.
“If Parliament passes the Bill in its current form, it will miss an important opportunity to introduce a law that respects, protects and fulfills the human rights of transgender people as required by the Supreme Court’s decision in NALSA and India’s international obligations,” he added.
The Government introduced the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2019, before the Parliament on 19 July 2019.
The current draft, fails to address key concerns that have been repeatedly raised by the transgender community and human rights organizations.
Critically, the Bill continues to mandate sex reassignment surgery for transgender people who seek to identify as male or female.
This requirement clearly contravenes the Supreme Court’s judgment in NALSA v. UOI, which guarantees the right to self-identification, without any need for medical intervention. Nor does the Bill make provision for reservations in employment or education despite a mandate by the Supreme Court in NALSA.
Among the problematic provisions are those which set out lighter sentences for criminal offences when committed against transgender people (including “sexual abuse”, “physical abuse”, “verbal and emotional abuse”, “economic abuse” and denial of “passage to a public place”); inadequate or missing definitions of offences; the retention of provisions that could be used to target transgender people for criminal prosecution; and the absence of mechanisms to enforce prohibitions on discrimination in the law.
The ICJ acknowledges that the draft of the Bill contains improvements over the version passed by the Lok Sabha in 2018.
The new draft removes the requirement for a screening committee to review applications for the issuance of a gender identity certificate. It also no longer criminalizes “compel[ing] or entice[ing] a transgender person” to engage in begging
The ICJ and other human rights organizations have recommended the deletion of these provisions in light of the well-documented historical abuse that such laws enabled by making it possible to target transgender persons, and the resulting effect of creating a specter of criminality around transgender identities.
“The Bill does include some important improvements over its 2018 version, such as the elimination of screening committees for the issuance of identity documents, and problematic criminal provisions relating to begging. However, it still falls significantly short from a constitutional and an international human rights perspective,” said Rawski.
“We urge the Parliament to address the deficiencies that remain – such as provisions on mandatory sex reassignment surgery, which contravene human rights law – before passing it into law,” he added.
The current session of Parliament will close on July 26, 2019 and may be extended by two-three days. If passed by the Lok Sabha, this Bill will be introduced in the Rajya Sabha (Upper House of the Parliament) for consideration.
The ICJ urges the Lok Sabha to reconsider the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill in accordance with the constitutional and international law obligations of the Indian state, and to ensure meaningful consultation with the transgender community in its lawmaking.
Contact
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia Pacific Region Director, e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org, t: +66 644781121
Maitreyi Gupta (Delhi), ICJ International Legal Adviser for India, e: maitreyi.gupta(a)icj.org, t: +91 7756028369
Read also
ICJ Briefing Paper on India: Legal and Jurisprudential Developments on Transgender Rights, SAATHII Vistaara Coalition. The paper analyses in detail the domestic judicial developments on transgender rights as well as the legislative process undertaken until the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2018 was passed on 17 December 2018.
ICJ Briefing Paper on The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2016, analyzes the 2016 Bill, its shortcomings, and India’s international obligations, as it is the basis of the 2018 Bill.
ICJ Briefing Paper on Implementation of NALSA Judgment discusses the 2014 April NALSA decision that affirmed that transgender people have the right to decide their self-identified gender. The paper analyses the responsibilities placed on Indian authorities, gaps in implementation, and India’s relevant international law obligations.

Jul 21, 2019 | News
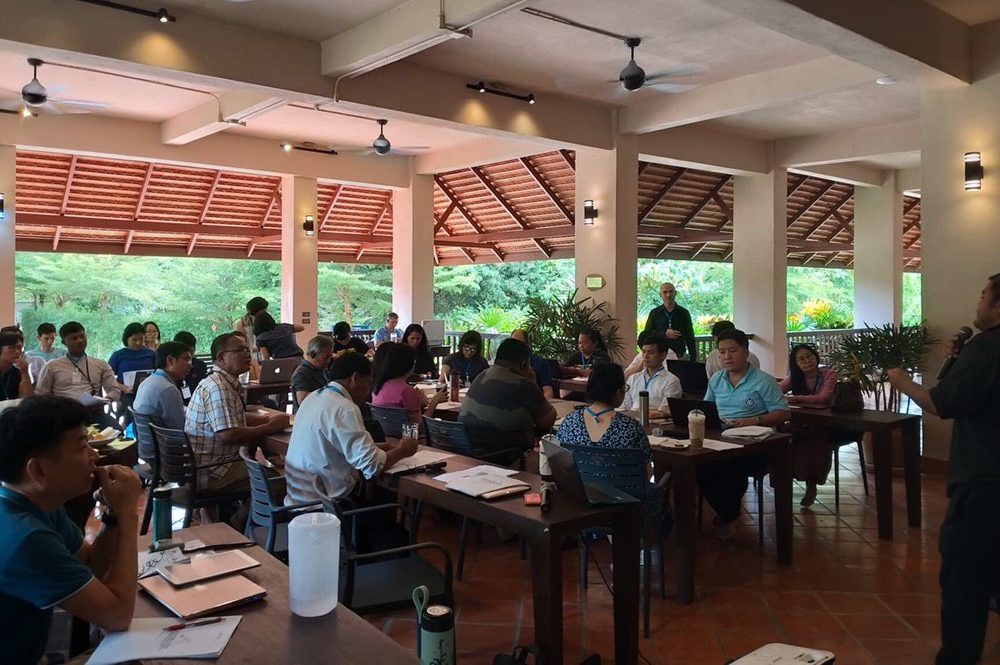
Today, the ICJ hosted a discussion on Thailand’s legal frameworks on corporate accountability for outbound investments in Chiang Mai, Thailand. The forum was co-organized with Earth Rights International.
Lawyers, members of civil society organizations and academics from Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, and Thailand attended the discussion.
Participants discussed:
- corporate civil, criminal and administrative liability and in particular, the applicable laws governing the prosecution and adjudication of human rights abuses committed by Thai corporations and gaps in Thailand’s legal frameworks. The meeting also looked into recommendations to strengthen Thailand’s domestic laws to increase access to justice for victims of human rights abuses committed by Thai corporations in the context of their business activities abroad, particularly on issues such as: limited liability of shareholders and the “corporate veil” in relation to the responsibilities of Thai corporations, the complexity of laws governing joint ventures, and challenges in bringing state-owned enterprises to justice;
- jurisdiction of Thai courts in civil, criminal and administrative cases where de facto and de jure foreign subsidiaries of a Thai corporation were involved in wrongful acts or omissions abroad, and problems posed by statutes of limitation;
- tools for preventing human rights abuses by corporations such as Human Rights Due Diligence (HRDD), Transboundary environmental impact assessments (EIA), Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) measures, and the Duty of Care principle under tort law; and
- the role of other related actors to prevent and mitigate human rights risks, including the National Human Rights Commission of Thailand (NHRCT), National Contact Points (NCPs), financial institutions and securities institutions, and provided recommendations to strengthen mandates of such organizations which would allow them to provide better protection for individuals and communities who may be affected by outbound investments.
This discussion will provide the foundation for further work and analysis by the ICJ regarding Thailand’s legal frameworks on corporate accountability for outbound investments. It will also provide the basis for ICJ strategic advocacy at the national level.