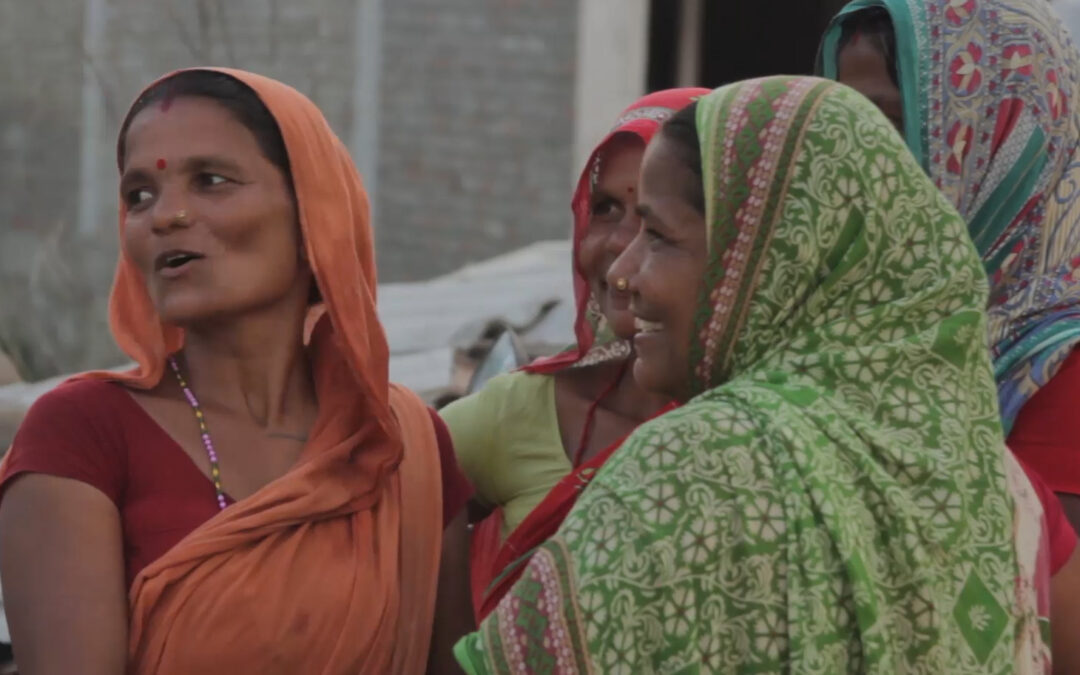Apr 17, 2018 | Advocacy, Cases, Legal submissions, News
The ICJ and other NGOs jointly intervened before the Grand Chamber of the European Court of Human Rights in a case against Spain on the denial of entry of asylum seekers in the enclave of Melilla.
The ICJ, the European Council on Refugees and Exiles, the AIRE Centre, Amnesty International and the Dutch Refugee Council argued that the European Convention on Human Rights prohibits refusal of entry, and/or return of a person to face serious violations of human rights, including of the right to life, the prohibition of torture or inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment, or flagrant denial of justice and of the right to liberty.
They submitted that these refusals of entry are also contrary to the rights set out in the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights (CFR) and the prohibition on non-refoulement found in the 1951 Geneva Convention on the Status of Refugees (Refugee Convention).
The joint interventions presents the argument that, for these prohibitions to be practical and effective and not theoretical and illusory, Contracting Parties must have in place effective systems for identifying people within their jurisdiction who are entitled to benefit from the prohibition on refusing entry.
Spain-ICJ&others-AmicusBrief-ND&NT-ECtHR-GC-legalsubmission-2018 (download the thirty party intervention)

Apr 17, 2018 | News
From April 16 to 20, the ICJ is conducting a research mission to Uzbekistan to identify the priority ESC rights issues which will be the focus of its project on access to the economic, social and cultural (ESC) rights (ACCESS project).
During the mission, ICJ experts will meet with key stakeholders, including relevant State bodies, CSOs, legal experts, international organizations in Uzbekistan and other actors to discuss legal and practical aspects of ensuring access to justice for ESC rights.
During the meetings, among others, the following issues will be addressed:
- current legislation ensuring ESC rights in Uzbekistan;
- ongoing and planned reforms in ensuring ESC rights;
- legal protection of ESC rights and barriers to their enjoyment;
- discussion of possible legal, practical aspects related to access to justice in the field of ESC rights.
The ICJ will rely on international standards in the area of ESC rights, in particular, the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR), to which Uzbekistan is a party.
The results of the mission will form a baseline report which will inform the construction and implementation of the ACCESS project.
The ICJ appreciates the facilitation of the Government and of the European Union, which supports the project, in arranging meetings with relevant State institutions.
Contact:
Temur Shakirov, temur.shakirov@icj.org

Apr 16, 2018 | Advocacy, News, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ and ECRE have presented today to the United Nations Special Rapporteur on the human rights of migrants a submission on access to justice for migrants in Europe.
The submission is an input for the forthcoming report of the UN Special Rapporteur on access to justice for migrants to the UN General Assembly.
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) and the European Council on Refugees and Exiles (ECRE) have provided a brief overview of aspects of access to justice for migrants, with a particular focus on asylum seekers and migrant children, in European countries.
The issues dealt with include:
- obstructions to access to justice in relation to access to the territory;
- the undue use of national security exceptions to weaken access to justice in immigration procedures;
- concerns with access to justice in expulsion and detention procedures;
- specific obstacles to access to justice for asylum seekers, including when appealing the rejection of their claims by first instance asylum authorities before a judicial or administrative appeal body;
- specific obstacles to access to justice for undocumented minors.
ICJECRE-NonLegalSubmission-SRMigrants-Access2JusticeEurope4Migrants-2018-ENG (download the submission)

Apr 16, 2018 | News
On the fourth anniversary of the apparent enforced disappearance of Karen activist, “Billy,” the ICJ repeats its calls for the Department of Special Investigations (DSI) to assume responsibility for effectively investigating the case.
To date no progress has been made to establish the fate of Billy and the DSI has declined to take up the matter.
Pholachi “Billy” Rakchongcharoen was last seen on 17 April 2014 in the custody of Kaeng Krachan National Park officials.
At the time of his apparent enforced disappearance, Billy had been working with ethnic Karen villagers and activists on legal proceedings the villagers had filed against the National Park, the Wildlife and Plant Conservation Department, the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment, and the former Chief of Kaeng Krachan National Park concerning the alleged burning of villagers’ homes and property in the National Park in 2010 and 2011.
“The very reason the DSI was created was to investigate complex cases of this kind, including where Government officials may be implicated in gross human rights violations that amount to crimes under international law,” said Kingsley Abbott, Senior International Legal Adviser with the ICJ.
“If the DSI continues to refuse to open a special investigation after four years of little apparent progress by the police, the DSI will risk being perceived as contributing to the pervasive culture of impunity that exists within Thailand,” he added.
This week, Billy’s wife, Phinnapha Phrueksaphan, advised the ICJ that the last time the DSI had discussed Billy’s investigation with her and her family was over a year ago.
The ICJ was further informed that on 9 April 2018, Phinnapha submitted a letter to the Director-General of the DSI seeking updates on the progress of Billy’s case and clarification as to why the DSI had not accepted Billy’s case for a special investigation.
“Thailand has a clear legal duty to continue to investigate the case until Billy’s fate or whereabouts are established and to ensure that the investigative process and any outcomes are transparent – which is especially important to victims’ families who play a crucial role in investigations,” added Abbott.
On 23 May 2017, Thailand established a Committee consisting of 18 officials, including from the DSI, to formulate policies for the prevention of acts of torture and enforced disappearance, and to investigate and provide remedies in accordance with the Convention against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment (CAT), to which Thailand is a party, and the International Convention for the Protection of All Persons from Enforced Disappearance (ICPPED), which Thailand has signed but not yet ratified.
On 26 June 2017, the Committee reportedly stated that it would consider past, pending and new cases of enforced disappearance, including the case of Billy.
However, the Committee has yet to demonstrate effectiveness in efforts to implement Thailand’s international human rights obligations.
“While any steps Thailand takes towards accountability for allegations of torture, ill-treatment and enforced disappearance is welcome, the Committee should not be seen as a meaningful substitute for establishing these as crimes under domestic law,” Abbott said.
Thailand-Billy disappearance 4th year-News-web story-2018-ENG (Full story in PDF)
Thailand-Billy fourth-News-webstory-2018-THA (Thai version, in PDF)
Further Reading
Billy’s case
ICJ, ‘Launch special investigation into enforced disappearance of “Billy”’, 6 August 2015
ICJ, ‘Strengthen efforts to solve the apparent enforced disappearance of “Billy”, 16 April 2015
ICJ, ‘“Disappearance” of Billy demands special investigation’, 17 July 2014
ICJ, ‘Thai authorities must urgently investigate Billy’s ‘disappearance’’, 28 April 2014
Draft Act criminalizing torture and enforced disappearance
ICJ and Amnesty International, Open letter to Thailand’s Minister of Justice on the amendments to the Draft Prevention and Suppression of Torture and Enforced Disappearances Act, 12 March 2018
English
Thai
ICJ and Amnesty International, Recommendations to Thailand’s Ministry of Justice on the Draft Prevention and Suppression of Torture and Enforced Disappearances Act, 23 November 2017
Human Rights Committee review of Thailand
ICJ and Thai Lawyers for Human Rights and Cross-Cultural Foundation, Joint follow-up submission to the UN Human Rights Committee, 27 March 2018
UN Committee against Torture review of Thailand
ICJ and Thai Lawyers for Human Rights, Joint submission to the UN Committee against Torture, 29 January 2018
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, email: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org
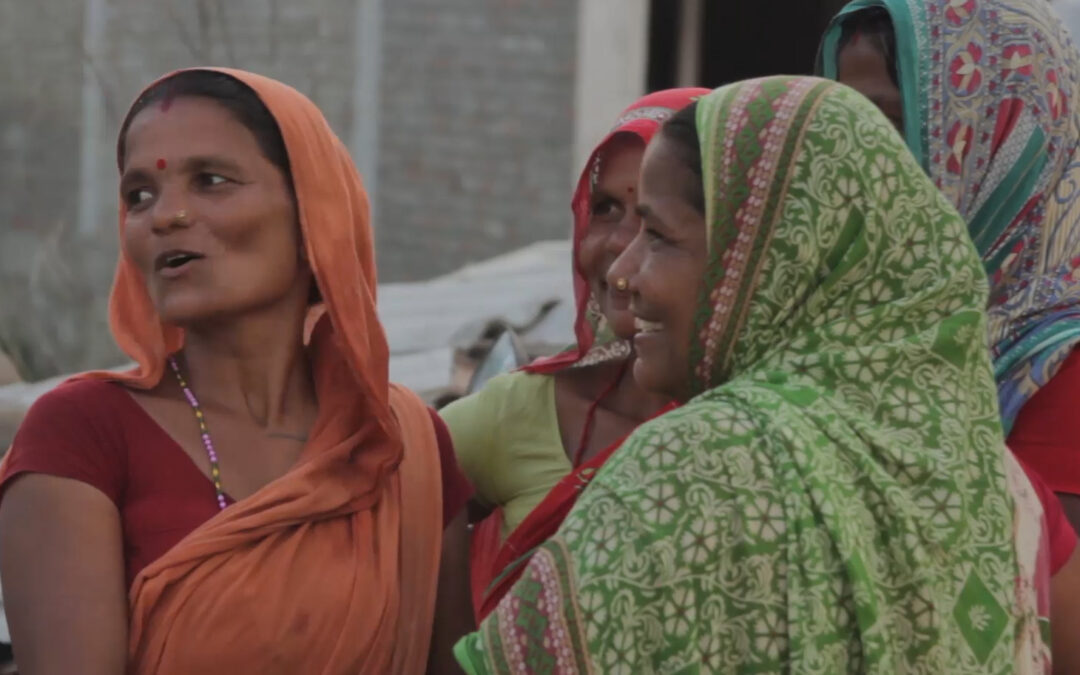
Apr 13, 2018 | Multimedia items, News, Video clips
In 2017, Nepal held its first local-level elections for almost 20 years and the first ever conducted under the new federal state structure established under the 2015 Constitution. They were significant because of the unprecedented number of women who stood as candidates and won.
Women in Nepal have experienced systemic discrimination for decades, especially those in rural areas, among ethnic minorities and marginalized groups.
These elections presented the women of Nepal with the opportunity to break through barriers that have prevented them for decades from participating in political and public life.
The Local Level Governance Act lays out the mandate and functions of newly formed local bodies.
If the recently elected women are allowed to meaningfully participate in local governance, the new law could empower them further so that they can take the lead in addressing key human rights issues, especially the human rights of women.
This video documents the campaign of Rikam BK, a Nepalese politician, belonging to the Communist party of Nepal-Maoist (CPN-M).
In the Nepal Legislative Election held on 26 November 2017, she was elected as a Sub-Mayor (NCP Maoist) of Lahan Municipal Council winning 5000 votes.
She is the chairperson of the Dalit Preservation Abhiyan Forum, in Siraha. She has been advocating the issue of land certificates in the names of both husband and wife.
She continues to call for those deprived of land rights to have equal access to land. She is also the member of National Alliance for Women Human Rights Defenders (NAWHRD).
Many of the women featured in this video are women human rights defenders who have been working to promote and protect human rights in Nepal for decades.
Many of them participated in the Regional Conference on Women Human Rights Defenders as Political Actors, which was organized by the ICJ, with the cooperation of NAWHRD.
The conference was held from 28 to 29 August 2017 in Kathmandu.
The ICJ recently released a briefing paper laying out the key points of the conference and offering a set of future actions aimed at supporting WHRDs in their role as political actors pursuing a human rights agenda.
Watch the video

Apr 10, 2018 | News
The ICJ and its partner the Democracy Governance and Rights Unit (DGRU) of the University of Cape Town are holding a panel discussion on selection and appointment of judges within the auspices of the Launch of the Global Judicial Integrity Network.
This new Network is being launched by the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) in Vienna, Austria on today.
The panel is aimed at discussing the implementation and monitoring of guidelines on the best practice for the appointment of judges (“guidelines”).
The Southern Africa Chief Justices’ Forum (SACJF) mandated the development of these guidelines through its Concluding Communiqué during the 2015 Annual Conference of East and Southern Africa Chief Justices, held at Victoria Falls in Zimbabwe.
The ICJ and the DGRU have been working on developing the guidelines, together with a subcommittee of the SACJF, with the aim of seeing them adopted at the SACJF’s annual general meeting to be held this year between August and September in Malawi.
“The UNODC Judicial Integrity Network launch in Vienna, Austria 9-10 April 2018 gives us an excellent opportunity to start thinking a bit further down the line, and identify, anticipate and develop responses to problems that may be experienced in implementing the guidelines at a national level,” said Arnold Tsunga, Africa Director of the ICJ.
While many very good standards have been developed and adopted in Africa in the field of human rights, rule of law, and good governance, a major challenge has been to see the standards implemented in practice.
“In addition to highlighting relevant global standards, the ICJ will also present its experiences from around the world in monitoring and overcoming obstacles to implementation of such guidelines,” said Matt Pollard the Director of the Centre for Independence of Judges and Lawyers at the ICJ.
“This should contribute to planning for effective implementation of the Southern African guidelines, and be of interest to the broader audience at the launch of the UNODC global network on judicial integrity.”
The panel to be moderated by Arnold Tsunga includes Hon. Sanji Monageng, ICJ Commissioner and Justice, International Criminal Court; Mr. Jan van Zyl Smit, Associate Senior Research Fellow, Bingham Centre for the Rule of Law; Mr. Christopher Oxtoby, Senior Researcher, Democratic Governance and Rights Unit, University of Cape Town; Mr Matt Pollard, Senior Legal Adviser and Director, CIJL, ICJ.
Fore more information contact Arnold Tsunga on arnold.tsunga@icj.org (+27716405926) or Matt Pollard on <matt.pollard@icj.org> (+41 79 246 54 75)
Universal – Vienna Panel on Selection – News – Webstory – ENG – 2018 (Further information in PDF)