
Nov 26, 2020 | Advocacy, News
Pakistani authorities should urgently and impartially investigate a surge in violent attacks on members of the Ahmadiyya religious community, Human Rights Watch, Amnesty International, and the ICJ said today.
The authorities should take appropriate legal action against those responsible for threats and violence against Ahmadis.
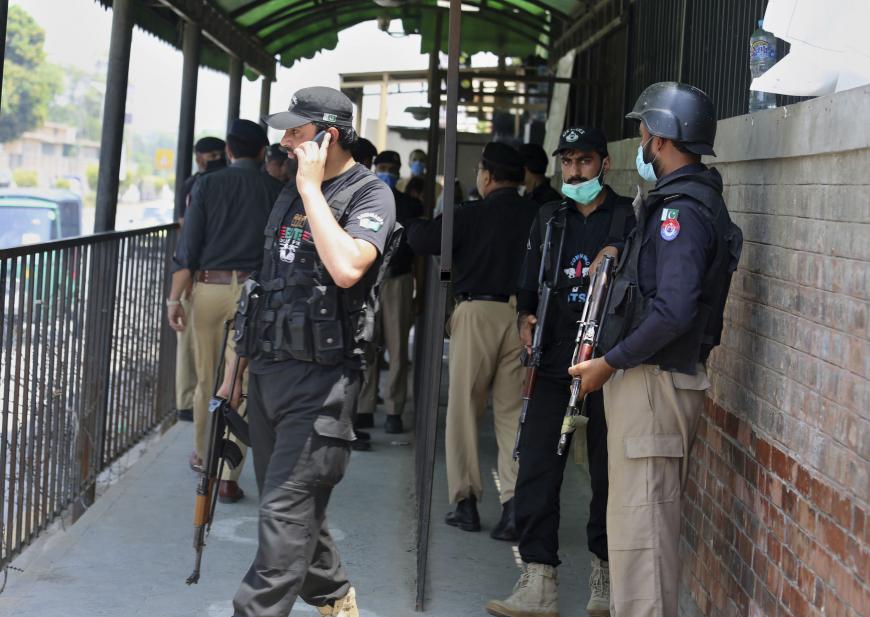
Since July 2020, there have been at least five apparently targeted killings of members of the Ahmadiyya community. In only two of the cases have the police taken a suspect into custody. Pakistani authorities have long downplayed, and at times even encouraged, violence against Ahmadis, whose rights to freedom of religion and belief are not respected under Pakistani law.
“There are few communities in Pakistan who have suffered as much as the Ahmadis,” said Omar Waraich, head of South Asia at Amnesty International. “The recent wave of killings tragically underscores not just the seriousness of the threats they face, but also the callous indifference of the authorities, who have failed to protect the community or punish the perpetrators.”
On November 20, a teenage assailant is alleged to have fatally shot Dr. Tahir Mahmood, 31, as he answered the door of his house in Nankana Sahib district, Punjab. Mahmood’s father and two uncles were injured in the attack. The police reported that the suspect “confessed to having attacked the family over religious differences.”
Several recent attacks have occurred in the city of Peshawar, in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province. On November 9, Mahmoob Khan, 82, was fatally shot while waiting at a bus station. On October 6, two men on a motorcycle stopped the car of Dr. Naeemuddin Khattak, 57, a professor at the Government Superior Science College, and fired five shots, killing him. His family said he had a “heated argument over a religious issue” with a colleague a day before. Jamaat-i-Ahmadiyya, a community organization, issued a statement saying Khattak had previously received threats and was targeted because of his faith.
On August 12, Meraj Ahmed, 61, was fatally shot as he was closing his shop in Peshawar. On July 29, an alleged 19-year-old assailant killed Tahir Ahmad Naseem, 57, inside a high-security courtroom. Naseem was facing trial for blasphemy accusations. In a video that circulated on social media, the suspect states that Naseem was a “blasphemer.”
Successive Pakistani governments have failed to protect the human rights and security of the Ahmadiyya community. The penal code explicitly discriminates against religious minorities and targets Ahmadis by prohibiting them from “indirectly or directly posing as a Muslim.” Ahmadis are banned from declaring or propagating their faith publicly, building mosques, or making the Muslim call for prayer.
The authorities arbitrarily arrest, detain, and charge Ahmadis for blasphemy and other offenses because of their religious beliefs. The police have often been complicit in harassment and bringing fabricated charges against Ahmadis or have not intervened to stop anti-Ahmadi violence. The government’s failure to address religious persecution of Ahmadis has facilitated violence against them in the name of religion.
“Pakistan was part of the consensus at the UN General Assembly that required that states take active measures to ensure that persons belonging to religious minorities may exercise fully and effectively all their human rights and fundamental freedoms without any discrimination and in full equality before the law,” said Ian Seiderman, legal and policy director at the International Commission of Jurists. “The Pakistani government has completely failed to do so in the case of the Ahmadis.”
The Pakistani government also promotes discriminatory practices against Ahmadis. For example, all Pakistani Muslim citizens applying for passports are obliged to sign a statement explicitly stating that they consider the founder of the Ahmadi community an “imposter,” and consider Ahmadis to be non-Muslims.
Pakistani laws against the Ahmadiyya community violate Pakistan’s international legal obligations under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), which Pakistan ratified in 2010, including the rights to freedom of conscience, religion, expression, and association, and to profess and practice one’s own religion.
Independent experts of the United Nations Human Rights Council, including the special rapporteurs on the freedom of religion or belief and the UN special rapporteur on minority issues, and the special rapporteur on extrajudicial, summary or arbitrary executions, have previously expressed concern at the persecution of the Ahmadiyya community in Pakistan.
“Pakistan’s federal and provincial governments should take immediate legal and policy measures to eliminate widespread and rampant discrimination and social exclusion faced by the Ahmadiyya community in Pakistan,” said Patricia Gossman, associate Asia director at Human Rights Watch. “The government should repeal the blasphemy law and all anti-Ahmadiyya provisions.”
Contact
In Brussels, for Human Rights Watch, Patricia Gossman: +32-472-982-925; or +1-347-322-8638 (WhatsApp); or gossmap@hrw.org. Twitter: @pagossman:
In Geneva, for the International Commission of Jurists, Ian Seiderman: e: ian.seiderman(a)icj.org
In Colombo, for Amnesty International, Omar Waraich: +44 7378 980870 (mobile); or omar.waraich@amnesty.org.

Nov 26, 2020 | Advocacy, News
Today, the ICJ joined other NGOs in condemning the Thai police’s use of force against peaceful protesters marching to the national parliament in Bangkok on November 17, 2020.
The statement reads:
We, the undersigned organizations, condemn the Thai police’s unnecessary and excessive use of force against peaceful protesters marching to the national parliament in Bangkok on November 17, 2020. We are concerned that authorities could employ similar measures when facing protesters who have declared they will march to the Siam Commercial Bank headquarters on November 25.
On November 17, police set out barriers and barbed wire to prevent a peaceful march organized by pro-democracy movements from reaching the parliament. Protesters planned to protest outside the parliament as members of parliament and senators debated seven different proposals for constitutional amendments, including an amendment proposed by the lawyers’ non-governmental organization iLAW (Internet Law Reform Dialogue), which was supported by the People’s Movement and its allies. Police refused to let protesters through the barriers, and when the demonstrators acted to breach those barriers, police crowd control units used water cannons laced with purple dye and an apparent teargas chemical, as well as teargas grenades and pepper spray grenades, to forcibly disperse thousands of demonstrators, including students, some of whom are children. Water cannons were first used at approximately 2:25 pm and police continued their efforts to disperse protesters, with constant use of water cannons, teargas and pepper spray into the evening.
Police also failed to prevent violence between pro-democracy protesters and royalist “yellow shirts” near the Kiak Kai intersection, near the parliament. Initially, riot police separated the two groups. However, video posted on social media later showed police officers informing the royalist protesters that they would withdraw and seconds later they vacated their position between the two groups. During the ensuing skirmishes, both sides were filmed throwing rocks and wielding clubs. Live broadcasts included sounds that appeared to be gunfire.
The Erawan Medical Centre reported that there were at least 55 protesters injured, mostly from inhaling teargas. It also reported that there were six protesters who suffered gunshot wounds. The injured included children: a kindergartener and elementary school students.
Although some pro-democracy protesters engaged in violent conduct in responding to royalist protesters, we emphasize that the overwhelming number of protesters were entirely peaceful. Furthermore, we wish to emphasize that while specific participants of an assembly who engage in violence are subject to a response that is lawful, strictly necessary and proportionate, they also retain all other human rights including the right to life, to security of person and to freedom from torture and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment.
International human rights law, as expressed in the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), which Thailand acceded to in 1996, protects the rights to freedom of expression (article 19) and peaceful assembly (article 21). But Thai authorities have routinely enforced censorship and stifled public assemblies, meetings, and discussions about human rights, political reforms, and the monarchy’s role in society.
In General Comment 37, which sets out the content Thailand’s legal obligations in guaranteeing the right of peaceful assembly, the United Nations Human Rights Committee—the body responsible for interpreting and applying the ICCPR—made clear that there is a presumption in favor of considering assemblies to be peaceful. Isolated acts of violence by individuals should not be attributed to others, to the organizers, or to the assembly as such. While the right of peaceful assembly may in certain cases be limited, the onus is for the State to justify any restrictions, which must pass the tests of legality, legitimacy, and necessity and proportionality.
Read the full statement in English and Thai.
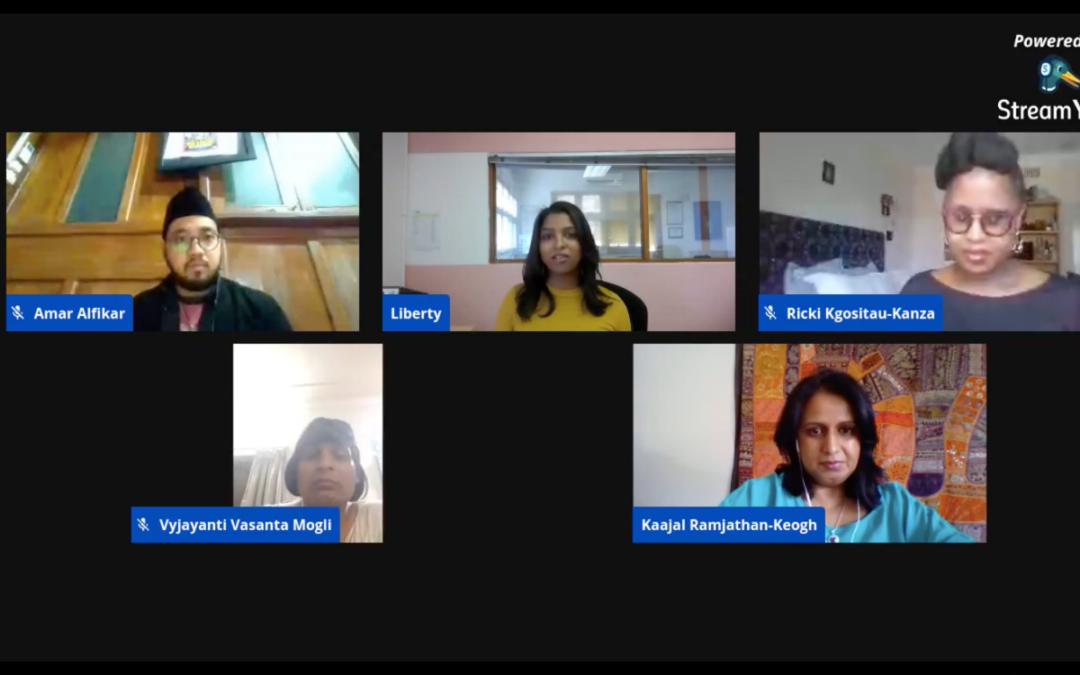
Nov 19, 2020 | News
On 18 November 2020, the ICJ hosted a Facebook Live with four transgender human rights activists from Asia and Africa. It highlighted the stark reality between progressive laws and violent lived realities of transgender people.
The 20th November 2020 marks the Transgender Day of Remembrance (TDOR), the day when transgender and gender diverse people who have lost their lives to hate crime, transphobia and targeted violence are remembered, commemorated and memorialized.
The discussions focused on their individual experiences of Transgender Day of Remembrance in their local contexts, the impact of COVID-19 on transgender communities and whether laws are enough to protect and enforce the human rights of transgender and gender diverse people.
The renowned panelists were from four different countries, Amar Alfikar from Indonesia, Liberty Matthyse from South Africa, Tshepo Ricki Kgositau-Kanza from Botswana and Vyjayanti Vasanta Mogli from India. The panel was moderated by the ICJ Africa Regional Director, Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh.
The panel aimed to provide quick glimpses into different regional contexts and a platform for transgender human rights activists’ voices on the meaning of Transgender Day of Remembrance and the varied and devastating impacts of COVID-19 on transgender people.
The speakers discussed the meaning that they individually ascribe to Transgender Day of Remembrance. A common theme running across the conversations was that it is not enough to highlight issues and concerns of the transgender community only on this day. Instead, these discussions should be part of daily conversations about the human rights of transgender people at the local and international level.
Liberty Matthyse discussed the importance of remembering the transgender persons who have lost their lives over the past years, and added:
“South Africa generally is known as a country which has become quite friendly to LGBTI people more broadly and this, of course, stands in stark contradiction to the lived realities of people on the ground as we navigate a society that is excessively violent towards transgender persons and gay people more broadly.”
Amar Alfikar describes his work as “Queering Faiths in Indonesia”. This informs his understanding of what Transgender Day of Remembrance means in his country and he believes that:
“Religion should be a source of humanity and justice. It should be a space where people are safe, not the opposite. When the community and society do not accept queer people, religion should start giving the message, shifting the way of thinking and the way of narrating, to be more accepting, to be more embracing.”
It was clear from the discussions that a lot of the issues that have become prominent during the COVID-19 pandemic, have not arisen due to the pandemic. In fact, the COVID-19 pandemic has had the effect of a magnifying glass, amplifying existing challenges in the way that transgender communities are treated and driven to margins of society. Speaking about the intersectionality of transgender human rights, Vyjayanti Vasanta Mogli said:
“I don’t think LGBT rights or transgender rights exist in isolation, they are part of a larger gamut of climate change, racial equality, gender equality, the elimination of plastics, and all of that.”
The panelists had different opinions on whether it is enough to rely on the law for the recognition and protection of the human rights of transgender individuals.
The common denominator, however, was that the laws as they stand have a long way to go before fully giving effect to the right of equality before the law and equal protection of the law without discrimination of transgender people.
Tshepo Ricki Kgositau-Kanza, who was a litigant in a landmark case in Botswana in which the judiciary upheld the right of transgender persons to have their gender marker changed on national identity documents, explained the challenges with policies which, on their face, seem uniform:
“Uniform policies… are very violent experiences for transgender persons in a Botswana context where the uniform application of laws and policies is binary and arbitrarily assigned based on one’s sex marker on one’s identity document which reflects them either as male or female. Anybody in between or outside of that kind of dichotomy is often rendered invisible and vulnerable to a system that can easily abuse them.”
This conversation can be viewed here.
Contact
Tanveer Jeewa, Communications Officer, African Regional Programme, e: tanveer.jeewa(a)icj.org

Nov 14, 2020 | Advocacy, News
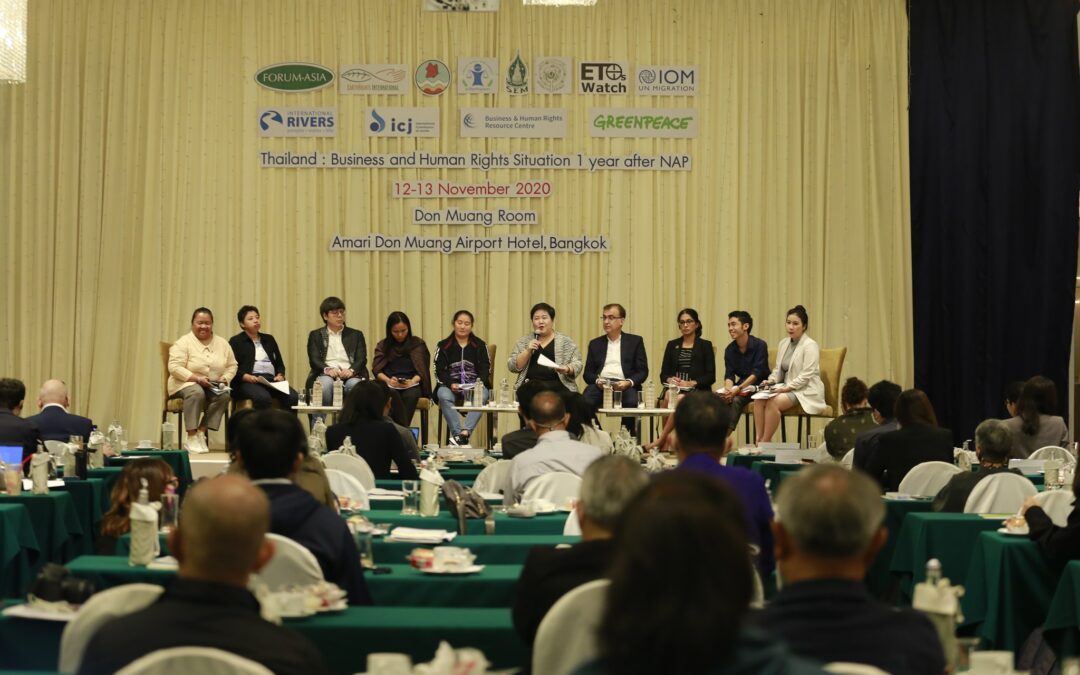
On 12-13 November 2020, the ICJ co-hosted a discussion on “Thailand’s National Action Plan on Business and Human Rights: 1-Year Progress Review” in Bangkok. The forum was co-organized with other 11 organizations.
Participants on the first day included some 95 individuals representing populations affected by business operations from all regions of Thailand and members of civil society organizations. The considered reviewed the progress that has been made by Thailand over the past year towards fulfilling its commitments in the four priority issues in its First National Action Plan on Business and Human Rights (NAP): (1) Labor; (2) Land, environment and natural resources; (3) Human rights defenders; and (4) Cross border investment and multi-national enterprises.
Several participants noted a lack of any evident and tangible progress in the NAP implementation and questioned the effectiveness of the NAP because it does not have the status of a law but is merely a resolution from the Council of Ministers. They further expressed concern at the lack of a comprehensive monitoring system in place to monitor NAP and its achievement according to the key recommendations aligned with the UN Guiding Principle on Business and Human Rights, and on legal harassment and intimidation faced by human rights defenders.
In the session regarding cross border investment and multi-national enterprises, the ICJ participants led the discussion regarding challenges to hold Thai companies accountable for human rights abuses which took place abroad. The participants looked into several obstacles to accessing to justice for victims of business-related human rights abuses in the context of cross-border investment. The discussion was based on the ICJ’s work and analysis in the draft report on the human rights legal framework of Thai companies operating in Southeast Asia, which is expected to be launched in December 2020.
Comments and recommendations raised by participants on the first day were presented to representatives from the Ministry of Justice, Thailand National Human Rights Commission, Global Compact Network Thailand and UN agencies, in the public seminar on the second day. The outcomes of the discussion and recommendations will also be submitted to the NAP Monitoring/Steering Committees, chaired by Director-General of Rights and Liberties Protection Department, Ministry of Justice.
Background
On 29 October 2019, the Cabinet approved and adopted the First National Action Plan on Business and Human Rights (2019-2022), making Thailand the first country in Asia to adopt the stand-alone NAP.
The NAP emphasizes the duties of State agencies to review and amend certain laws, regulations and orders that are not in compliance with human rights laws and standards and ensure their full implementation; ensure accessibility of mechanisms for redress and accountability for damage done to affected communities and individuals; overcome the barriers to meaningful participation of communities and key affected populations; and strengthen the role of businesses to “respect” human rights on a variety of key priority issues.
The event was co-hosted with:
- International Organization for Migration (IOM)
- Community Resource Centre Foundation (CRC)
- Asian Forum for Human Rights and Development (FORUM-ASIA)
- EarthRights International (ERI)
- The Mekong Butterfly (TMB)
- International River (IR)
- Spirit in Education Movement (SEM)
- Thai Extra-Territorial Obligations Working Group (Thai ETOs Watch)
- Green Peace Thailand
- Green South Foundation
- Business and Human Rights Resource Center (BHRRC)
Further reading
Thailand’s Legal Frameworks on Corporate Accountability for Outbound Investments
Thailand: ICJ co-hosts discussion on National Action Plan on Business and Human Rights

Nov 11, 2020 | Advocacy, News
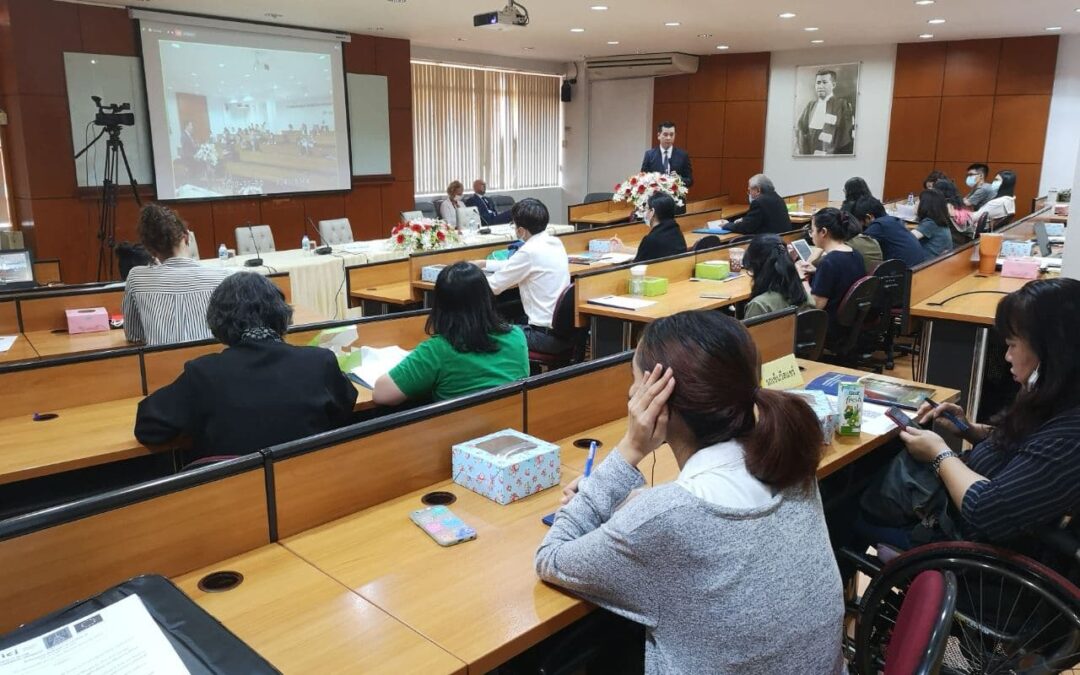
The ICJ, human rights advocates and other experts emphasized the State obligation to protect that right to health of all persons without discrimination at a public seminar held on 10 November 2020.
The ICJ sponsored the event on “Human Rights, Right to Health, and the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic” in collaboration with the Delegation of the European Union to Thailand, Thammasat University’s Faculty of Law, and the Ministry of Justice’s Department of Rights and Liberties Protection Department.
Participants in the event included interested members of the public, students, human rights academics, and members of civil society organizations.
Welcome remarks were delivered by Giuseppe Busini, Deputy Head of the European Union Delegation to Thailand and Professor Jaturon Tirawat, Director of Thammasat University’s Public International Law Centre.
Dr. Seree Nonthasoot, Member of the UN Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights in an opening address recalled the obligations of Thailand under International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights to protect the right of everyone to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health. This includes ensuring the right of access to health facilities, goods and services on a non-discriminatory basis. Among these elements are access to housing and sanitation, potable water and essential drugs. He also highlighted the need to implement a national public health strategy and plan of action to make COVID-19 vaccine a global common good.
ICJ Legal Adviser Timothy Fish Hodgson provided a briefing about human rights effects wrought by the COVID-19 pandemic, as exposed in the ICJ report – Living Like People Who Die Slowly: The Need for Right to Health Compliant COVID-19 Responses. He emphasized the particularly acute and discriminatory impact of the pandemic on already marginalized people around the world, particularly on non-citizens, older persons, women and girls, LGBT persons, persons deprived of their liberty, persons with disabilities, sex workers and healthcare workers.
A panel discussion regarding the economic social and cultural rights during and post COVID-19 pandemic, moderated by Chonlathan Supphaiboonlerd, Associate National Legal Advisor of the ICJ, addressed the measures taken by the Thai government to control the spread of COVID-19 and to mitigate social and economic impacts of the pandemic, especially their human rights effects on persons with disabilities, refugees, asylum seekers, persons deprived of their liberty, indigenous peoples and migrant workers in Thailand.
The panel included Nareeluc Paichaiyapoom, Director of International Human Rights Law Division, Department of Rights and Liberties Protection, Ministry of Justice; Dr. Lalin Kovudhikulrungsri, Faculty of Law, Thammasart University; Naiyana Thanawattho, Executive Director, Asylum Access Thailand; Dr. Siwanoot Soitong, Bangkok Legal Clinic, Faculty of Law, Thammasat University; Nattaya Petcharat, Stella Maris Seafarer’ Center Songkhla; and Suebsakun Kidnukorn, Researcher, Area Based-Social Innovation Research Center (Ab-SIRC), Mae Fah Luang University.
Watch the recording of the seminar here.
Further reading
Thailand: The ICJ and other human rights groups make supplementary submission to the UN Human Rights Committee

Nov 3, 2020 | News
The government of Nepal should act without delay to carry out the National Human Rights Commission’s recommendations, particularly those concerning Nepal’s obligation to investigate and, where justified by the evidence, prosecute those accused of serious abuses, Human Rights Watch and the ICJ said today.
On October 15, 2020, the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) published 20 years of data, naming 286 people, mostly police officials, military personnel, and former Maoist insurgents, as suspects in serious crimes. In particular, the information relates to cases where its investigators concluded there is evidence warranting investigation and prosecution for abuses including torture, enforced disappearance, and extrajudicial killing.
In addition to domestic use, the data should provide important guidance to the United Nations in vetting Nepali security forces for peacekeeping missions, and to other countries for efforts to ensure international justice, including in their obligations to prosecute or extradite individuals suspected of responsibility for crimes under international law. They will also be of use to the United States in carrying out vetting requirements under the “Leahy laws” that prohibit military assistance to military and security forces implicated in serious human rights abuses.
“The National Human Rights Commission has taken an important step in publishing this information, which will be an essential tool for the UN and foreign governments in their engagement with Nepali security forces,” said Meenakshi Ganguly, South Asia director at Human Rights Watch. “The report highlights just how little progress there has been to establish meaningful human rights protections to address conflict era violations and ongoing abuses.”
The culture of impunity in Nepal is contributing to ongoing serious human rights abuses, the groups said. There have been numerous credible allegations of extrajudicial executions, torture, and ill-treatment, sometimes resulting in custodial deaths, and deaths resulting from the unlawful and excessive use of force in policing demonstrations in recent years. In many such cases, the authorities have refused even to register complaints, much less carry out effective investigations or prosecutions.
International and foreign authorities, including prosecutors and judicial authorities, should be aware of the commission’s data when considering targeted sanctions for people accused of serious violations, or preparing criminal cases under the principal of universal jurisdiction against those allegedly responsible for crimes such as torture and enforced disappearances, Human Rights Watch and the International Commission of Jurists said.
Particularly serious violations and abuses were committed between 1996 and 2006 during an armed conflict between government security forces and Maoist rebel forces. The former Maoist party in now part of the government. Since the conflict ended, the former enemies have effectively joined ranks to successfully shield their supporters from accountability, fostering a culture of impunity that continues to protect those responsible for ongoing extrajudicial killings and deaths in custody allegedly resulting from torture.
The NHRC said in its report that the government had mostly failed to act against suspects, despite being informed of the commission’s findings. Human Rights Watch and the International Commission of Jurists have not independently investigated all the cases documented, but the Nepal government is under an obligation to thoroughly and impartially investigate the allegations in the report with a view to bringing those responsible for these crimes to justice. Altogether the NHRC has recommended action against 98 police officers, 85 soldiers, and 65 members of the former Communist Party of Nepal (Maoist).
The NHRC presented and analyzed its findings and recommendations spanning two decades, since its establishment in 2000. It has registered 12,825 complaints and reached conclusions in 6,617 cases, making 1,195 recommendations to the government. The recommendations have been carried out fully in only 13 percent of cases, partially carried out in 37 percent, and not carried out at all in the remaining 50 percent. The government has often carried out recommendations to make payments to victims or their families but has very rarely investigated or prosecuted abuses.
In a March 6, 2013 ruling, the Supreme Court decided that the NHRC has the authority to refer these cases to the attorney general and prosecutors for investigation and prosecution, yet the NHRC has been unwilling to use that authority. The NHRC has also chosen not to use its prerogative to name those allegedly responsible for the abuses until now, waiting until the last days of the outgoing commissioners’ terms to publish the report.
“While releasing this report is an important step toward addressing entrenched impunity in Nepal, it has exposed the fact that the commission has struggled with a lack of investigative capacity, failing in many cases to summon alleged perpetrators or demand documentation,” said Mandira Sharma, senior international legal advisor at the International Commission of Jurists. “Had the NHRC used its authority to request prosecution from the attorney general where it has gathered sufficient evidence, it would have made a real contribution in tackling impunity and in addressing police failures in investigating ongoing cases of rights violations.”
The NHRC has long been dogged by political interference in the appointment of commissioners, and a widely perceived reluctance to confront the government or other powerful institutions, such as the army and political parties, that oppose accountability for rights abuses. In 2019 the government proposed amendments to the 2012 National Human Rights Commission Act that would further undermine its independence.
To download the full statement with additional information, click here. (PDF)
Contact
For International Commission of Jurists, in Nepal, Mandira Sharma (Nepali, English): +977-9851048475 (mobile); or mandira.sharma@icj.org.










