Oct 23, 2020 | News
On 21 and 22 October, the ICJ and Cordaid held a webinar series aimed at tackling the challenges of protecting and promoting women’s human rights and access to justice for women in the context of religious and customary laws in operation around the world.
At its global 2019 Congress in Tunis, the ICJ identified the problem, concluding that: “Worldwide, increasing attacks on the rule of law have intensified longstanding inequalities and compounded intersecting forms of discrimination against women and girls and persons from marginalized groups. This has limited their enjoyment of human rights and their effective access to justice. Moreover, in many countries, culture, tradition, or religion are being used to justify laws, policies and practices that discriminate against women and girls.”
In light of the obstacles for women, the ICJ together with Cordaid created this webinar platform for an exchange of views and strategies among human rights defenders, justice sector actors and those from the religious community. Participants came from Asia, the Middle East and Africa. Webinar 1 addressed the ways in which custom and religion shape the ability of women to access justice. The meeting also grappled with the perceived clashes between women’s human rights and pathways to justice based on custom and religion.
“Custom and religious preferences are not superior to women’s rights, they operate simultaneously,” said Nazila Ghanea, Associate Professor in International Human Rights Law at the University of Oxford.
Speakers included Professor Nazila Ghanea, Clara Rita Padilla, a lawyer from the Philippines with experience on women’s sexual and reproductive rights, Josephine Chandiru, Executive Director of Stewardwomen from South Sudan, and Claudine Tsongo, Director of Dynamique des Femmes Juristes. They focused on practical subjects, including the persistence of certain religious and cultural practices which have the potential to negatively affect women’s ability to defend their human rights. The session was moderated by ICJ Africa’s director, Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh.
Webinar 2, moderated by ICJ Commissioner and CEDAW Committee Member, Nahla Haidar, discussed obligations under international human rights law and best practice to ensure access to justice in cultural and religious contexts.
UN Special Rapporteur on Freedom of Religion or belief, Professor Ahmed Shaheed explained that “custom and religious law are, in some countries, used as cover to discriminate against women or to stop them from getting justice. These are not issues which are only present in the global south, they are rampant globally.”
Participants discussed practical measures which could be adopted by States, international organizations and civil society, to eliminate practices which exacerbate women’s inequality. In this regard, Shareena Sheriff from Sisters in Islam based in Malaysia, shared her experience on how they successfully embarked on advocacy to eliminate the harmful practice of Female Genital Mutilation in her country. She explained how Sisters in Islam worked closely with various stakeholders including community members, religious and justice actors to raise awareness on this issue.
Many speakers endorsed the importance of creating platforms such as the webinar to allow different voices from around the world to contribute their experience so as to learn from one another.
Contact
Nokukhanya (Khanyo) Farisè, Legal Adviser (Africa Regional Programme), e: nokukhanya.farise(a)icj.org
Tanveer Jeewa, Communications Officer (Africa Regional Programme), e: tanveer.jeewa(a)icj.org
Watch
The first webinar is available here.
The second webinar is available here.
Read
The report on the Tunis Declaration is available here.
Cordaid, Diverse Pathways to Justice for all: Supporting everyday justice providers to achieve SDG16.3, September 2019, available here.
Download
Universal-ICJ The Tunis Declaration-Advocacy-2019-ENG (the Tunis Declaration, in PDF)
Universal-ICJ Congresses-Publications-Reports-2019-ENG (the ICJ Congresses booklet, in PDF)

Oct 13, 2020 | News
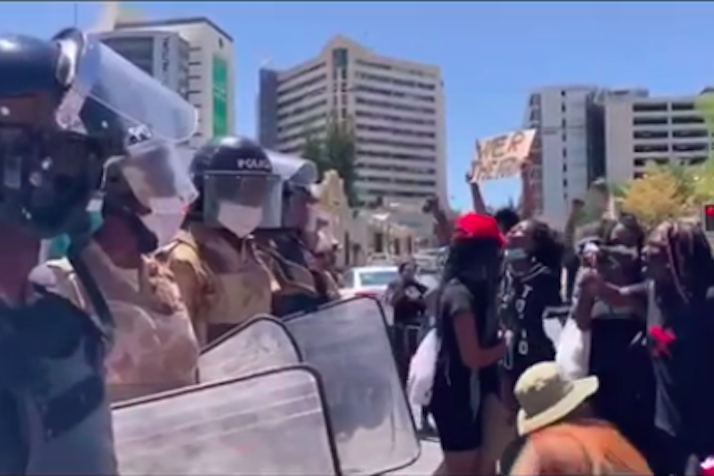
Today the ICJ condemned the apparent widespread ill-treatment and arbitrary arrest of peaceful demonstrators protesting gender based violence on Saturday 10 October in Windhoek.
The demonstrators were allegedly met with tear gas, and a number of them were subject to serious beatings by police forces.
Some 25 persons, including journalists, were arrested during the demonstrations. They were initially charged with breaching a law forbidding the public gathering of more than 50 people, though the charges were dropped on Monday.
The ICJ is calling for a prompt, thorough, impartial and effective investigation into the alleged police abuse, in line with Namibian law and the countries international legal obligations.
Officials responsible should be held accountable.
“Instead of taking seriously the demands made by the protestors and to take steps to ensure that gender based violence is addressed in a meaningful and constructive way, the police themselves appeared to have engaged in violent action against those exercising their rights to peacefully assembly and express their view,” said Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh, ICJ Africa Regional Programme Director.
The ICJ also called on the authorities to protect the right of individuals in the country to peacefully and protest, rights which are protected under Namibia’s Constitution and international law.
The ICJ said that the Public Gatherings Proclamation Act, requiring prior permission for assemblies of more than 50 people in public spaces, should be repealed or revised, as incompatible with its international legal obligations.
The ICJ has also called on Namibia to address the underlying concerns raised by the protests, notably that during the COVID-19 pandemic, gender-based violence has been exacerbated during lockdown restrictions.
In Namibia, reports of femicide and gender based violence steadily increasing and on average “three rape cases were reported to the Namibian police every day for 18 months.”
Background
The recent #ShutItAllDown and #ShutitAllDownNamibia movements, spontaneously started on social media after the killing of a young woman, Shannon Wasserfall, have led to a series of protests against government’s failure to adequately address the scourge of gender based violence in Namibia.
The protestors, predominantly young women, last week handed over a petition to government which includes a list of 24 demands. raising concerns about the poor State response to gender-based violence in Namibia.
The protestors allege that Namibian police are “negligent and nonchalant” with investigating violent crime committed against women. They are demanding that government do more to protect women against such violence, including by ensuring that survivors of gender-based violence have access to justice.
The rights to freedom of assembly and expression, freedom from ill-treatment, and prohibitions on arbitrary arrest are guaranteed under the international human rights treaties to which Namibia is a party, including the African Charter on Human and Peoples Rights and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, and the Convention against Torture, as well as the Namibian Constitution.
Contact
Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh, Director of ICJ’s Africa Regional Programme, c: +27845148039, e: kaajal.keogh(a)icj.org
Nokukhanya Farisè, Legal Adviser, nokukhanya.farise(a)icj.org

Oct 8, 2020 | News
Proposed legislation to regulate the operations and functions of the legal profession in Eswatini does not comply with international and regional standards and would severely undermine the right to an independent lawyer, the ICJ said today.
A Bill that the Government of Eswatini is reportedly seeking to introduce in Parliament would establish a Legal Services Regulatory Authority which would be responsible for issuing practising certificates to lawyers, disciplining lawyers in case of unethical conduct, developing and enforcing performance standards for legal practitioners in Eswatini, the ICJ said.
The proposed Legal Services Regulatory Authority would constitute up to 10 members of which only one would be appointed by the legal bar association (Law Society of Eswatini).
If enacted into law, the bill would severely undermine the independence of lawyers in Eswatini and may set a dangerous precedent for other countries in the SADC region, especially at this time when lawyers in other parts of the region are being persecuted by their governments, the ICJ added.
When discharging their functions, legal practitioners must be independent of control and undue influence in order for them to be able to represent their clients more effectively.
“The Legal Services Regulatory Authority proposed under the Eswatini Bill does not qualify as a self-governing professional body or an independent statutory authority because all but one of its members will be appointed by government,” said ICJ Africa Director Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh.
“The establishment of this regulatory authority is likely to have a chilling effect on the freedom of lawyers to discharge their functions without being afraid of potential retribution through disciplinary proceedings based on frivolous charges,” she added.
The ICJ calls upon the Government of Eswatini to honour its domestic and international legal obligations to respect the independence of lawyers.
In this case, the ICJ urges the government to withdraw this bill and respect the independence of the lawyers to regulate themselves.
Background:
Eswatini has an obligation, in terms of its domestic constitution as well as regional and international law and standards, to respect and protect the independence of lawyers. Section 21 of the Constitution of Eswatini and regional and international human rights treaties and standards guarantee for every person the right to a fair hearing and the right to legal representation. These rights cannot be enjoyed effectively, unless lawyers are guaranteed the freedom to represent their clients and perform all their other duties without harassment, intimidation and undue interference.
The right of everyone to access to a lawyer as an essential element of a fair trial is recognized in, among other sources, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), to which Eswatini has been a party since 2004. International and regional standards on ensuring the independence of lawyers are set out in the UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers (UN Basic Principles) and the Principles and Guidelines on the Right to a Fair Trial and Legal Assistance in Africa.
Principle 16 of the United Nations Basic Principles, for instance, enjoins all governments to “ensure that lawyers are able to perform all of their professional functions without intimidation, hindrance, harassment or improper interference”.
Principle 24 affirms that, “Lawyers shall be entitled to form and join self-governing professional associations to represent their interests, promote their continuing education and training and protect their professional integrity. The executive body of the professional associations shall be elected by its members and shall exercise its functions without external interference.”
Principle 28 states that “Disciplinary proceedings against lawyers shall be brought before an impartial disciplinary committee established by the legal profession, before an independent statutory authority, or before a court, and shall be subject to an independent judicial review.”
In a recent unanimous resolution, the UN Human Rights Council recognized that “an independent legal profession” is among the “prerequisites for the protection of human rights and the application of the rule of law and for ensuring fair trials and the administration of justice without any discrimination”.
The Human Rights Council specifically expressed its concern “about situations where the entry into or continued practice within the legal profession is controlled or arbitrarily interfered with by the executive branch, with particular regard to abuse of systems for the licensing of lawyers.” It recommended that any domestic legislation should “provide for independent and self-governing professional associations of lawyers” and should “recognize the vital role played by lawyers in upholding the rule of law and promoting and protecting human rights”.
Contact:
Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh, Director of ICJ’s Africa Regional Programme, c: +27845148039, e: Kaajal kaajal.keogh(a)icj.org

Oct 8, 2020 | News
The ICJ today called for reinstatement of Tanzania lawyer Fatma Karume, characterizing a permanent prohibition from her practicing law as a violation of her rights and the independence of the legal profession.
In September 2019, the High Court of Tanzania issued an order suspending senior lawyer Fatma Karume from practising law in mainland Tanzania.
The High Court directed the Advocates’ Disciplinary Committee of Tanzania to conduct a disciplinary hearing and make a final determination on whether Fatma Karume, a former president of Tanganyika Law Society, which is the Bar association of mainland Tanzania, should be allowed to practice law.
Allegations of misconduct against Fatma Karume arose from her written submissions in a constitutional challenge to President Magufuli’s appointment of Professor Adelardus Kilangi as the Attorney General of Tanzania.
The State’s counsel complained that the language used by Fatma Karume in her submissions was unprofessional and disrespectful of the Attorney General, who was the subject of the constitutional challenge.
A year later, on 23 September 2020, the Advocates’ Disciplinary Committee found Fatma Karume guilty of the alleged misconduct and directed that she be permanently disbarred from practising law in Tanzania.
“The ICJ views the decision to permanently disbar Fatma Karume from legal practice, as a grave violation of Tanzania’s domestic, regional and international legal obligations relating to Fatma Karume’s right to be heard, her right to work and a violation of the independence of lawyers,” said ICJ Africa Director, Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh.
“Fatma Karume’s right to be heard was violated in many ways. First, the complaint of misconduct was made in the State’s rejoinder submissions and Ms Karume was not afforded an opportunity to respond on record, before the High Court made the decision to temporarily suspend her from practice. Secondly, her right to a speedy hearing was violated because it took the Advocate’s Disciplinary Committee of Tanzania a year to make a final determination in her case,” she added.
The ICJ also considers that the substance of the charges of misconduct against Fatma Karume was inconsistent with international and regional standards, in so far as they were based on written submissions made in good faith as part of the due discharge of her professional functions.
The ICJ urges the authorities in Tanzania to rescind the decision to disbar Fatma Karume from legal practice and restore her right to work and in particular, her right to practice law.
In the meantime, ICJ welcomes the decision of the Tanganyika Law Society to support Fatma Karume to appeal against her disbarment.
Background
Articles 21 and 13 (6) (a) of the Constitution of Tanzania guarantee every person with the right to work and the right to a fair hearing respectively. In terms of regional law, Article 7(1) of the African Charter on Human and People’s Rights obliges governments to respect and protect the right of every individual to be presumed innocent until proven guilty by a competent court or tribunal; the right to present a defense; and, the right to be tried within a reasonable time by an impartial court or tribunal. Similar rights are recognised in Article 14 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR). In addition, Principle 27 of the United Nations Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers (UN Basic Principles) states that “Charges or complaints made against lawyers in their professional capacity shall be processed expeditiously and fairly under appropriate procedures. Lawyers shall have the right to a fair hearing, including the right to be assisted by a lawyer of their choice.”
Principle 20 of the UN Basic Principles provides that “Lawyers shall enjoy civil and penal immunity for relevant statements made in good faith in written or oral pleadings or in their professional appearances before a court, tribunal or other legal or administrative authority.” Similar provisions are included in Part I of the African Principles and Guidelines.
Contact
Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh, Director of ICJ’s Africa Regional Programme, c: +27845148039, e: Kaajal kaajal.keogh@icj.org

Sep 25, 2020 | News
On 24 September 2020, the ICJ held a webinar in collaboration with the Lesotho National Federation of Organisations of the Disabled on the right to education for children with disabilities.
Presenters and participants included representatives from civil society organizations, teachers’ unions, teachers and the Lesotho Department of Education.
“Children with disabilities have a right to access to education on an equal basis with all other children. The COVID-19 pandemic must not hamper the Lesotho governments efforts to ensure access to inclusive education for all children,” said Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh, ICJ’s Africa Director.
Participants highlighted accessibility-related problems faced by learners with disabilities in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Some examples include:
- Ordinary masks necessary to combat the spread of COVID-19 inhibit communication for learners with hearing disabilities who often communication in part by lip-reading. These require access to face visors and/or transparent masks. Some deaf students also had difficulty in understanding the COVID-19 pandemic and virus, despite efforts to explain it to them.
- Blind learners need more access to hand sanitizer as they need to touch their surroundings for mobility. This also makes social distancing more difficult for them.
- Teachers have trouble understanding how to comply with social distancing measures while assisting learners experiencing epileptic seizures.
- Many learners with disabilities have stayed at home during the pandemic, not understanding why they were not at school.
- Many children with disabilities are rendered more vulnerable to sexual violence and exploitation as they observe stay at home rules.
A representative of the Department of Education explained various measures which government had put in place to ensure that these obstacles could be overcome so that learners with disabilities could enjoy their right to education in the context of COVID-19. Learners’ health and safety would also remain a priority.
The Department noted the delays in the implementation of its inclusive education policy as a result of a lack of funding as government resources are diverted to COVID-19 responses.
The need for compliance with Lesotho’s global and regional international human rights obligations was also highlighted with participants agreeing about the importance of ensuring that there is “strength in numbers” in advocacy efforts toward the realization of children with disabilities’ right to education.
“Ensuring the right to education of persons with disabilities does not imply sacrificing and compromising their right to health. All human rights are interdependent and Lesotho should be guided by all of its human rights obligations as it continues to implement its domestic inclusive education policy during the COVID-19 pandemic,” Ramjathan-Keogh added.
Background
Article 24 of the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) and the Protocol to the African Charter on Human and Peoples’ Rights on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities in Africa require States parties to ensure that their education systems are inclusive and fully realize the right to education of all children with disabilities. The normative content of Article 24 of the CRPD and corresponding obligations of member States are expanded on in the General Comment No 4 of the Committee on the Rights of Persons With Disabilities.
For more information on the impact of COVID-19 on access to education, find the UN Special Rapporteur on the right to education’s report here.
Contact
Nokukhanya (Khanyo) Farisè, Legal Adviser (Africa Regional Programme), e: nokukhanya.farise(a)icj.org
Tanveer Jeewa, Communications Officer (Africa Regional Programme), e: tanveer.jeewa(a)icj.org









