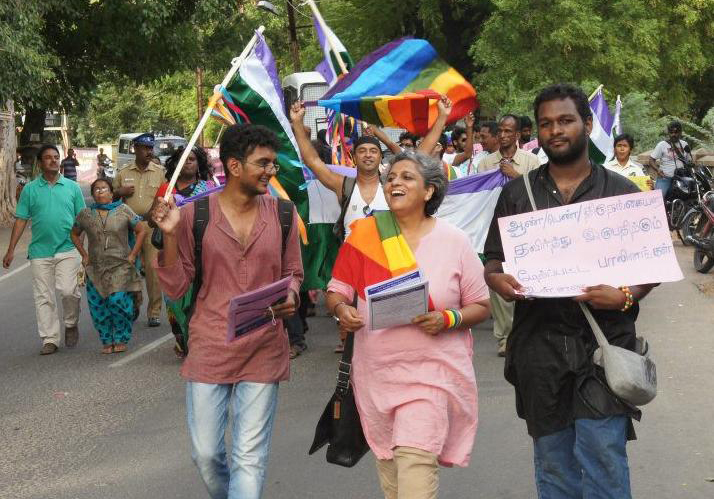
Nov 20, 2018 | News
On the Transgender Day of Remembrance, the ICJ calls on all South Asian States to fulfill their international obligations to respect, protect and ensure the right to life of all transgender persons, including by investigating alleged violations of their right to life promptly, thoroughly and effectively.
While there has been some progress in protecting the human rights of transgender individuals through legislation and judicial decisions, in South Asia rampant violence from both state and non-state actors continues to place their lives at risk.
Most governments do not collect data on violence against transgender persons.
Trans Murder Monitoring, which records cases of murder of transgender persons based on accounts from individuals and civil society organizations, reports 2609 unnatural deaths of trans and gender-diverse persons across 71 countries between January 2008 and September 2018.
In South Asia, between 2008 and 2016, 58 transgender persons were reported murdered in India, 37 in Pakistan, 2 in Nepal, and 2 in Bangladesh.
“It is laudable that Pakistan, India and Nepal have taken measures to end discrimination against transgender persons, and have recognized their right to self-identify,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia-Pacific Director.
“However, violence, harassment, extortion, rape and murder of transgender persons continue to be committed. Police frequently refuse to file complaints, and are often themselves complicit in violence against transgender persons,” he added.
The judiciary has played an important role in protecting transgender rights in India, Nepal and Pakistan.
The Supreme Courts in all three countries have issued decisions recognizing transgender persons’ rights, including the right to self-identity one’s gender.
These decisions have acknowledged that transgender persons are particularly targeted with violence by state and non-state actors, and that police have largely failed to protect them from violence.
In some cases, the courts have ordered that new remedies be created under the law, and sought the enforcement of existing laws protecting transgender rights.
However, many of these decisions remain unimplemented, and violence against transgender people remains rampant in South Asia.
“The ICJ calls on all governments in the region to ensure that laws, policies and practices affecting transgender persons comply with international human rights law and standards,” Rawski said.
“All human rights abuses against transgender persons must be investigated, and the perpetrators brought to justice, including law enforcement officials who harass or abuse persons based on their gender identity,” he added.
Contact
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia Pacific Director, t: +66 644781121 ; e: Frederick.rawski(a)icj.org
Background
In India, in 2014, the Supreme Court in NALSA v. UOI recognized the right of transgender persons to self-identify their gender.
The Court has further acknowledged the existence of human rights violations against transgender persons at the hands of the police and private individuals and recommended that state and central government take steps to create public awareness about transgender persons’ rights.
Per a 2015 survey by the Kerala Government, “52% of the TGs [transgender people] are facing harassment from the police and “96% do not raise complaints against violence because of their gender identity”.
In Nepal, in 2007, the Supreme Court in Sunil Babu Pant v. Government of Nepal recognized the right of individuals to identify as male, female or “third gender”.
However, transgender persons continue to face arbitrary harassment and detention by security forces under laws like Public Offences Act, 1970, which allow for arrests without due process for up to 25 days.
This resulted in the Supreme Court of Nepal ordering law enforcement officials to desist from arresting persons based on their “personal interest or appearance,” though the decision remains largely unimplemented.
In Pakistan, in 2009, the Supreme Court directed the Government to recognize the human rights of transgender persons and subsequently, in 2018, the Parliament passed a law prohibiting discrimination against transgender persons.
The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2018 of Pakistan prohibits harassment of transgender persons, including sexual, physical, mental and psychological harassment, and creates new remedies for complainants in addition to those available under the criminal justice system.
The effectiveness of the law remains to be seen, as police are often complicit in violence against transgender persons, particularly in extorting money from transgender women sex workers.
Read also
ICJ Practitioners’ Guide No. 4: Sexual Orientation, Gender Identity and International Human Rights Law, which provides legal practitioners, activists and policy-makers with detailed and practical references on international standards on sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, and sexual characteristics.
ICJ Comparative Law Casebook: Sexual Orientation, Gender Identity, and Justice, which provides legal practitioners, activists and policy-makers with a compilation of legal cases on sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics.
ICJ India 2017 Report: “Unnatural Offences” Obstacles to Justice in India Based on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity, which provides a legal analysis of the discrimination and abuse faced by the LGBTI community in India based on over 100 interviews with LGBTI persons.

Nov 15, 2018 | News
The ICJ and the Alternative Law Groups (ALG) today called on the Government of the Philippines to take immediate and effective action to addressing the apparently unlawful killing of Benjamin ‘Ben’ Ramos, a prominent lawyer and a founder of the National Union of People’s Lawyers (NUPL).
Benjamin Ramos was shot by two unidentified men in the public plaza of Barangay 5, Kabankalan City on 6 November 2018.
The ICJ and ALG call on the Government of the Philippines to conduct a thorough, prompt, impartial, and independent investigation into the killing of Benjamin Ramos.
Benjamin Ramos, in his work with the NUPL, had previously provided legal assistance to the families of the victims of the ‘Sagay 9 massacre’, which involved the killing of nine sugarcane farmers from the National Federation of Sugar Workers by unidentified armed men on 20 October 2018 in Negros Occidental, a province in the central part of the Philippines.
Given the sensitive nature of the work of Benjamin Ramos, which involved confronting powerful interests, it is important that any investigation consider the suspected links between that work and his killing.
“It is essential for the proper and effective functioning of the administration of justice that lawyers are kept safe as they fulfill their duties to protect the rights of their clients and promote the cause of justice,” said Emerlynne Gil, ICJ’s Senior International Legal Adviser.
As affirmed by the UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers, governments must ensure that lawyers are able to perform all their professional functions without “intimidation, hindrance, harassment or improper interference.” In addition,“[w]here the security of lawyers is threatened as a result of discharging their functions, they shall be adequately safeguarded by the authorities”.
The organizations note that there have been at least thirty-four (34) lawyers killed since 2016, under the administration of President Rodrigo Duterte.
“The rising number of killings of lawyers is very concerning and alarming; it is an attack not only on individual lawyers but on the justice system as whole. The Philippine government must take immediate and proactive measures to ensure the safety of lawyers as they conduct their professional duties,” said Maria Generosa Mislang, National Coordinator of ALG.
Contact:
Emerlynne Gil, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, t: +662 619 8477 (ext. 206) ; e: emerlynne.gil(a)icj.org

Nov 5, 2018 | News
The ICJ convened a two-day workshop from 3rd to 4th November 2018 in Yangon, to enhance understanding of legal protections of the right to freedom of thought, conscience, religion or belief in Myanmar.
Freedom of thought, conscience and belief, often referred to as the right to freedom of religion of belief (FoRB) is considered by many to be one of the foundations of a democratic society.
The workshop was aimed at discussing State regulation of religion or belief in Myanmar and included some 40 human rights defenders, lawyers and members of religious groups, from across the country.
ICJ legal adviser Sean Bain introduced the right to FoRB under international law and standards – particularly Article 18 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, and Article 18 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights. Mr Bain also discussed the complementarity of these articles with other rights, such as the right to freedom of expression, and highlighted the limitation clauses in the international treaties which provide a framework for resolving some of the tensions that can arise in specific cases.
Michelle Yesudas, a Malaysian human rights lawyer, shared good practices and lesson learned from application of strategic litigation in FoRB related cases in Malaysian context and spoke about potential approaches and strategies that could be adapted in Myanmar context to push the legislative reform and enforcement of the law.
The ICJ’s legal researcher Dr. Ja Seng Ing and national legal Adviser Advocate Daw Hnin Win Aung jointly facilitated two panel discussions on challenges in free practice of religion or belief specifically focusing on the worship places and Freedom of Expression.
Based on their own independent research, senior legal scholars and human rights defenders from Myanmar also provided their perspectives on national challenges, particularly the absence of the State fulfilling its responsibilities to protect FoRB in Myanmar. Advocate Daw Zar Li Aye discussed available legal remedies and encouraged legal advocacy strategies to ensure protections under the law in Myanmar.
The participants raised a number of notable issues on addressing identified obstacles to the free practice of religion or belief included the need for annulling discriminatory notifications restricting the rights to practice religion freely, the need for safe space to continue the dialogue between FoRB activists, other human rights defenders and lawyers on strategic litigation.
Participants at the conference also recognized the opportunity presented before them in advancing freedom of religion or belief in Myanmar and committed to working collectively to enhance this right.
This event is part of the ICJ’s ongoing effort to convene civil society actors including lawyers to discuss critical human rights issues in Myanmar with a view to advancing the protection of human rights in the country.
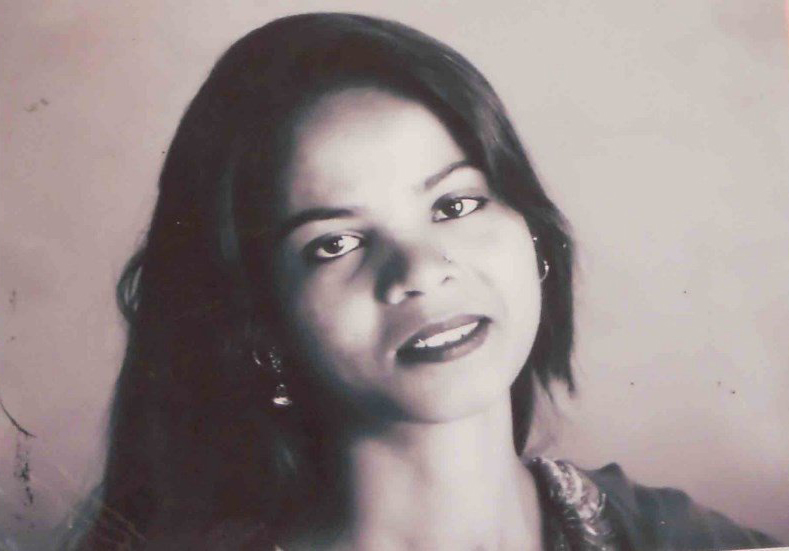

Oct 31, 2018 | News
The ICJ today welcomed the Pakistani Supreme Court’s decision to acquit Asia Noreen (Asia Bibi) of blasphemy charges under section 295-C of the Pakistan Penal Code.
Asia bibi had been on death row since 2010, when a trial court convicted her of “defaming the Prophet Muhammad” and sentenced her to death. The Lahore High Court had upheld her conviction and confirmed her death sentence in 2014.
“All eyes were on the Supreme Court to respond to Asia bibi’s final plea for justice and undo the blatant wrongs done to her and her family for eight long years,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ’s Asia Director.
“It is heartening to see that despite threats and external pressures, the SC fulfilled its role to protect human rights in this case.”
Certain Islamist groups have frequently held demonstrations calling for Asia bibi and other blasphemy accused to be hanged. After the Supreme Court announced its decision to acquit Asia bibi, the Tehreek-e-Labbaik Pakistan took to the streets condemning the decision.
“The Government should take notice of this pattern of threats and reprisals in blasphemy cases and ensure that judges and lawyers are given adequate security to perform their duties independently, impartially and without any external influence,” said Rawski.
Reasons for Asia bibi’s acquittal include an unexplained delay in the registration of the criminal complaint; material inconsistencies in the testimonies of prosecution witnesses; wrongful reliance on Asia bibi’s extra-judicial “confession”; and failure to take into account the circumstances of the blasphemy allegations, including a “quarrel”, possibly about Asia bibi’s faith.
The Supreme Court also noted that the context indicates the charges could have arisen from a “false allegation” of blasphemy, echoing concerns also raised by the ICJ that the blasphemy laws in Pakistan have typcially become an instrument of personal vendettas and malicious motivations.
Asia bibi’s appeal was the first blasphemy case being heard by the Supreme Court since 2002. The Court has so far not upheld any convictions for blasphemy under section 295-C of the Penal Code (defamation of the Prophet Muhammad), though dozens of people have been convicted by trial courts and a number of appeals are pending before various appellate forums.
The ICJ has documented in detail systematic and widespread fair trial violations in proceedings related to blasphemy offences in Pakistan.
Courts in Pakistan have noted on multiple occasions that people accused of blasphemy suffer ‘beyond proportion or repair’ in the absence of adequate safeguards against misapplication or misuse of such blasphemy laws.
The ICJ underscores that laws that criminalize the exercise of freedom of expression are non-compliant with international law, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, to which Pakistan is a party. This includes the criminalization of expression in relation to religion.
The ICJ opposed the death penalty in all circumstances and considers that it constitutes a violation of the right to life and the right not to be subjected to cruel, inhuman or degrading punishment.
Contact:
Frederick Rawski (Bangkok), ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Director, e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org
Reema Omer, ICJ International Legal Advisor (South Asia) t: +447889565691; e: reema.omer(a)icj.org
Additional information
In November 2015, the ICJ published a report documenting in detail systematic and widespread violations of the right to a fair trial in proceedings related to blasphemy offences in Pakistan, particularly in trial courts. The report confirmed concerns raised by the Supreme Court of Pakistan that individuals accused of blasphemy ‘suffer beyond proportion or repair’ in the absence of adequate safeguards.
The ICJ also made a number of recommendations to the Pakistani executive, legislative and judicial branches to address violations caused by application of the blasphemy laws, whether due to the legislative provisions themselves or at the investigative, prosecutorial, procedural, administrative and judicial levels highlighted in the report, including to ensure that those accused of blasphemy have a fair chance at defending themselves.
In a briefing paper published in October 2016, the ICJ assessed the fair trial violations in Asia bibi’s trial and appellate hearing. The ICJ found glaring omissions both in the appraisal of evidence as well as the application of laws that brought her conviction into question.
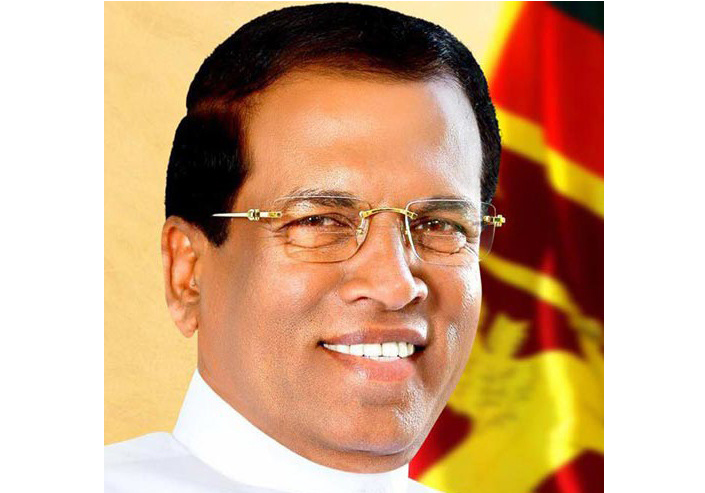

Oct 30, 2018 | News
The ICJ today called upon the Government of Sri Lanka to abide by the Constitution and its international obligations in peacefully resolving the current political crisis, and for all political leaders to commit to respect for human rights and the rule of law.
To this end, President Maithripala Sirisena (photo) should reconvene Parliament to end the constitutional crisis in line with the rule of law and democratic norms.
The ICJ urged the Government to deliver on its commitment to the transitional justice process, including by holding those responsible for human rights violations and abuses accountable, and complying with the obligations set out in United Nations Human Rights Council Resolutions 30/1 and 34/1.
It is with grave concern that the ICJ has observed the unfolding of events in Sri Lanka since the evening of October 26, 2018.
Following the withdrawal of the United People’s Freedom Alliance from the National Unity Government, President Maithripala Sirisena, in an unexpected move, appointed Former President and Member of Parliament Mahinda Rajapaksa as the Prime Minister of Sri Lanka.
These actions have transpired in disregard of safeguards set out in the 19th Amendment to the Constitution, which limit the power of the President to remove the Prime Minister at will.
The Amendment spells out specific instances during which the Prime Minister of Sri Lanka ceases to hold office under the law.
The ICJ is concerned at the President’s move to prorogue Parliament until 16 November in what appears to be an effort to avoid parliamentary scrutiny of his actions. The move has exacerbated political tensions.
“The ICJ is alarmed that Mahinda Rajapaksa, who has yet to be held accountable for the well-documented human rights violations committed during his previous tenure, has been appointed Prime Minister – in apparent violation of the Constitution,” said Frederick Rawski, Asia Pacific Director for the ICJ.
Incidents of violence and the takeover of government-controlled media by supporters of Mahinda Rajapaksa raise fears of an imminent return to the human rights violations and abusive practices which were widespread during his term.
ICJ also noted with concern ongoing crackdowns on the media and other attacks on human rights and fundamental freedoms.
The ICJ stressed that the removal of the Prime Minister in violation of the law or constitutional provisions would constitute a violation of Sri Lanka’s commitments to the international community, set out in UN Human Rights Council resolutions in 2015 and 2017, to strengthen good governance and protect democratic institutions.
The ICJ also expressed concern that political instability, or the return of an unrepentant and unaccountable Mahinda Rajakpaksa to political power, would endanger progress made on fulfilling Sri Lanka’s commitments to press forward with transitional justice processes, and its legal obligations to ensure accountability for past human rights violations and abuses, as set out in both resolutions.
“The failure to address past abuses, and to fully implement UN Human Rights Council Resolutions 30/1 and 34/1, has helped set the stage for the current political turmoil, and the possible return of an authoritarian figure who has proven his disrespect for human rights and the rule of law over and over,” said Frederick Rawski.
“The Human Rights Council will be watching closely to assess whether Sri Lanka is in breach of its commitments. Any serious threat to progress on human rights accountability will compel the establishment of an independent accountability mechanism,” he added.
Contact
Frederick Rawski, ICJ’s Asia Pacific Regional Director, t: +66 2 619 84 77 ; e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org