
Jul 15, 2018 | News
On 14 July 2018, the ICJ co-organized a discussion on extrajudicial killings in Thailand, focusing on the cases of Chaiyaphum Pasae and Abe Saemu.
The discussion was held at the Student Christian Centre in Bangkok.
Chaiyaphum Pasae, a Lahu youth activist, was killed by a military officer in the Chiang Dao district of Thailand’s northern Chiang Mai province in March 2017. The killing took place during an attempt to arrest him as an alleged drug suspect. Officials claimed Chaiyaphum Pasae had resisted arrest and was subsequently shot in “an act of self-defence”.
Abe Saemu, from the Lisu hill tribe, was killed by a military officer in February 2017 in the Chiang Dao district of Chiang Mai province in an attempt to arrest him on allegations of drug coffences. Officials claimed Abe Saemu had resisted arrest and was killed in “self-defence”.
During the discussion, ICJ’s National Legal Adviser Sanhawan Srisod addressed the audience to set out the international law and standards that apply to investigating potentially unlawful deaths, including the rights of victims and family members, referring to the standards set out in the revised Minnesota Protocol on the Investigation of Potentially Unlawful Death (2016), which was launched in Thailand on 25 May 2017.
Participants in the event included members of the families of Chaiyaphum Pasae and Abe Saemu, the lawyers in both of their cases, interested members of the public, media representatives, students and academics.
The discussion opened with an art exhibition and Lahu dance show by the Save Lahu group. Human Rights Commissioner Angkhana Neelapaijit then made a presentation on challenges in seeking accountability for extrajudicial killings in Thailand.
A panel discussion on the latest updates in the cases of Chaiyaphum Pasae and Abe Saemu followed, moderated by Pranom Somwong from Protection International.
The panel included relatives of Chaiyaphum Pasae and Abe Saemu; Ratsada Manuratsada, a lawyer representing the families in both cases and Krissada Ngamsiljamras, a representative from the National Human Rights Commission of Thailand.
A second panel considered challenges on the administration of criminal justice in the context of unlawful deaths.
Moderated by Pratubjit Neelapaijit of UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, the panel included Malee Sittikreangkrai (Chiang Mai University); Sumitchai Hattasan (Human Rights Lawyers’ Association); Namtae Meeboonsalang (Provincial Chief Public Prosecutor, Office of the Attorney-General); Kritin Meewutsom (Forensic doctor, Ranong Hospital); and Sanhawan Srisod (ICJ).
The event was conducted in collaboration with Cross Cultural Foundation (CrCF); Protection International (PI); UN OHCHR; Human Rights Lawyers’ Association (HRLA); Thai Volunteer Services (TVS); Dinsorsee Creative Group; Center for Ethnic Studies and Development, Chiang Mai University (CESD); Legal Research and Development Center, Chiang Mai University (LRDC) and Network of Indigenous Peoples in Thailand (NIPT).
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, Senior Legal Adviser, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Office, kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org
Jun 28, 2018 | News
On 24-25 June, ICJ Commissioners from the Latin America region came together in Bogotá, Colombia, to consider and enhance ICJ strategies to combat past and resurging trends in extrajudicial executions and enforced disappearances in the region.
The meeting was the first of its kind to bring together ICJ Commissioners on a regional basis: Carlos Ayala (Venezuela); Miguel Carbonell (Mexico); Gustavo Gallón (Colombia); Roberto Garretón (Chile); Juan Mendez (Argentina); Victor Rodriguez Rescia (Costa Rica); Alejandro Salinas Rivera (Chile); Mónica Pinto (Argentina); Belisário dos Santos Júnior (Brazil); and Wilder Tayler (Uruguay).
The meeting was followed by a preparatory mission (involving two Commissioners and the ICJ’s legal representative in Colombia) on the transitional justice mechanisms envisaged under the Havana Agreement, with a particular emphasis on the jurisdiction and operation of the ‘Special Jurisdiction for Peace’. A full high-level mission will follow in September, at which time the ICJ intends to identify minimum benchmarks for the effective operation and sustainable impact of those mechanisms.
In all regions of the world, recourse to enforced disappearances and extrajudicial killings continues; victims and their families (the overwhelming majority of whom are women, children and indigenous peoples from rural areas dominated by poverty and social and political exclusion, as well as trade unionists and human rights defenders) struggle to obtain prompt and effective remedies and reparation; and perpetrators enjoy impunity through inadequate or improper laws, ineffective institutional frameworks, selective recourse to accountability mechanisms and/or political interference in the functioning of those mechanisms.
The meeting confirmed that these challenges are particularly evident in Latin America, where there has been a resurgence in recourse to enforced disappearances and extrajudicial killings in countries throughout the region and where violations of the past have in very many cases been inadequately addressed. By way of example:
- In Brazil, official statistics from 2016 attest to the occurrence of 62,000 violent deaths and potentially up to 22,000 enforced disappearances each year.
- 45 years after the coup d’état in Chile, about 800 people have been convicted and sentenced to imprisonment, but those figures belie the extensive occurrence and levels of responsibility for gross violations of human rights that occurred.
- In Colombia, more than 70,000 cases of enforced disappearance were documented by the Attorney General for the period 1970-2015 and there is general consensus that the number of missing persons likely exceeds 100,000. The wide and persistent extent of extrajudicial killings has been noted by UN and Inter-American experts and bodies as well as the Office of the Prosecutor of the International Criminal Court.
- In Guatemala, only 34 convictions for conduct involving conflict-era violations have been secured, despite the fact that the internal armed conflict of 1960-1996 involved massive and systematic human rights violations. Impunity has undermined redress and accountability and severely weakened the prevention of violations, with the National Civil Police having recorded more than 25,000 people ‘disappeared’ in 2003-2014, more than half of which were women.
- Peru’s internal armed conflict of 1980-2000 resulted in more than 69,000 people killed and ‘disappeared’, but less than 100 convictions have been secured under the judicial subsystem established in 2004 that specializes in accountability for gross human rights violations.
- In Venezuela, civil society reports at least 12,000 real or perceived political opponents having been arbitrarily detained between January 2014 and April 2018; and almost 6,000 alleged extrajudicial killings between 2012 and 2016.
In all the countries from which the Commissioners originate, several common factors were identified:
- The intrinsic risks to continuation of and lack of redress and accountability for gross human rights violations posed by executive action that undermines the rule of law;
- Also inherent to the rule of law, the critical need for independent and impartial judicial mechanisms and individual judges and lawyers to allow for transitional justice, in particular for victims and their families to access effective remedies and reparation and for the holding to account of perpetrators;
- A high level of correspondence between impunity for gross human rights violations and the corruption of public officials;
- The increased, and in some cases extensive, recourse to arbitrary and detention, which in many cases precede and allow for the occurrence of extrajudicial executions and enforced disappearances;
- A similar inter-relationship between enforced disappearances and the occurrence of torture and other forms of ill-treatment;
- The detrimental impact to ensuring accountability for violations of the past when omitting non-State and paramilitary actors from transitional justice processes; and
- The increase in highly conservative (political and popular) sentiments and movements within the region and the corresponding need to tailor responses depending on the democratic versus autocratic nature of government and its institutions.
Noting that the ICJ has long sought to combat extrajudicial executions and enforced disappearances, including through the development of UN and regional instruments and standards and through its action in Latin America and the globe, the ICJ’s Commissioners urged the ICJ to continue and expand its engagement. Noting also the increasing call by local civil society actors for support and intervention by the ICJ, the meeting considered the organization’s role in seeking redress and accountability for, and prevention of, gross violations of human rights.
Commissioners reinforced, and commented on the effective parameters of, the ICJ’s strategic and victim-centred approach to address and prevent gross human rights violations, including extrajudicial executions and enforced disappearances. Having regard to the ICJ’s mandate and worldwide network of judges and lawyers, Commissioners emphasized the unique role that the organization has by grounding its work on the transformative role of the law, justice institutions and justice actors.
The particular means by which this role can be achieved by the ICJ were discussed against the background of recent and planned activities in the region and beyond. Commissioners overwhelmingly supported these plans and the Secretariat is now poised to continue implementation of its strategies in its current programmes of work and in the development of future projects.

Jun 21, 2018 | Events, News
The ICJ will participate today in the side event “State of emergency and attacks on the legal profession in Turkey” organized by IBAHRI, the Law Society, and the Bar Human Rights Committee of England and Wales.
This side event at the Human Rights Council takes place on Thursday, 21 June, 15:00-16:00, room XXV of the Palais des Nations.
It is co-sponsored by Lawyers for Lawyers, Union Internationale des Avocats, Lawyers’ Rights Watch Canada.
In this side event, panelists will share their analysis on the impact of the state of emergency on the rule of law and the ongoing obstacles faced by the legal profession in Turkey since the failed coup in 2016.
They will also discuss Turkey’s derogations from its international and regional human rights obligations, as well as the response of regional and international human rights mechanisms to this situation.
Panelists:
- Özlem Zingil, Turkish lawyer;
- Massimo Frigo, International Commission of Jurists;
- Tony Fisher, Chair of the Human Rights Committee of the Law Society of England and Wales;
- Stephen Cragg QC, Secretary of the Bar Human Rights Committee of England and Wales;
- Natacha Bracq, Programme Lawyer, International Bar Association’s Human Rights Institute.
Geneva-SideEvent-StateofEmergencyLawyersTurkey-IBAHRI&others-June2018-ENG (download the flyer)

Jun 12, 2018 | Advocacy, Cases, Legal submissions
The ICJ and others intervened before the European Court of Human Rights in a case of thirteen undocumented children held in a hotspot in Italy.
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ), the European Council on Refugees and Exiles (ECRE), the Dutch Council for Refugees and the AIRE Centre jointly intervened in the case of Trawalli and others v. Italy.
In this case, the European Court of Human Rights is called to rule, among other issues, on whether their detention and reception conditions were lawful and/or constituted an inhuman or degrading treatment under the European Convention on Human Rights.
In their third party intervention, the three human rights organizations submitted the following arguments:
a) Taking into consideration migrant children’s status as persons in situations of vulnerability and the principle of the best interests of the child, article 5 ECHR should be read in light of the rising consensus in international law towards a prohibition of detention of children on immigration grounds, in particular based on the consolidated and clear position of the UN Committee on the Rights of the Child. This applies to all instances of deprivation of liberty irrespective of their classification under domestic law.
b) In addition to the above, detention under article 5.1 ECHR will in any event be unlawful and arbitrary where it lacks a clear and accessible legal basis, outlining the permissible grounds of detention as well as the relevant procedural guarantees and remedies available to detainees, including judicial review and access to legal advice and assistance. In light of the obligations of EU Member States under EU law, the interveners submit that detention of asylum seeking children falling within the scope of the recast Reception Conditions Directive will result in a breach of the Convention standards also where it is not used as a measure of last resort, but rather is imposed without consideration of less onerous alternative measures and where the child’s best interests assessment has not been carried out and reflected in this decision.
c) Due to children’s extreme vulnerability, their detention for immigration purposes risks leading to a violation of Article 3 ECHR because of inadequate living conditions and/or to a violation of Article 8 ECHR because of a disproportionate and unnecessary interference with their development and personal autonomy, as protected under Article 8. In this sense, Article 8 must be regarded as affording protection from conditions of detention which would not reach the level of severity required to engage Article 3.
d) When the authorities deprive or seek to deprive a child of her or his liberty, they must ensure that he/she effectively benefits from an enhanced set of guarantees in addition to undertaking the diligent assessment of her/his best interest noted above. The guarantees include: prompt identification and appointment of a competent guardian; a child-sensitive due process framework, including the child’s rights to receive information in a child-friendly language, the right to be heard and have her/his views taken into due consideration depending on his/her age and maturity, to have access to justice and to challenge the detention conditions and lawfulness before a judge; free legal assistance and representation, interpretation and translation. The Contracting Parties must also immediately provide the child access to an effective remedy.
e) In order to fully comply with their obligations under the Convention, Contracting Parties must guarantee that asylum seeking children are accommodated in reception facilities which are adapted to their specific needs and provide adequate material conditions adapted to their age, condition of dependency and enhanced vulnerability. To do otherwise results in a failure by States to comply with their obligations under Article 3 ECHR and their specific obligations under EU law.
Italy-icj&others-Trawalli&others-Advocacy-legal submission-2018-ENG (download the intervention)

Jun 6, 2018 | News
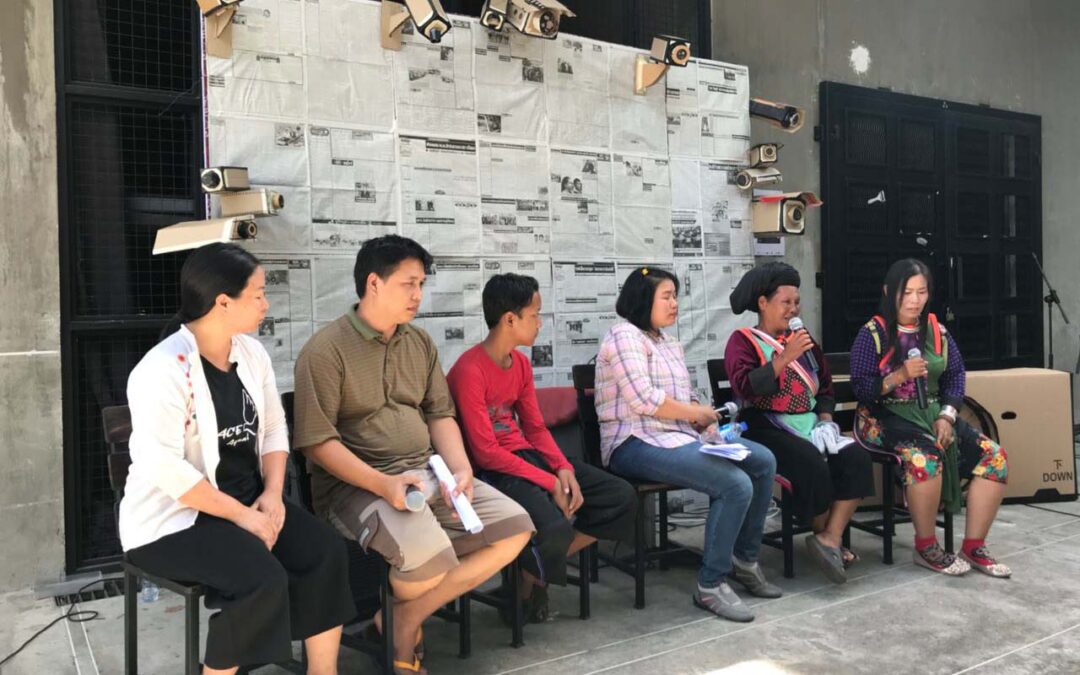
On 5 June 2018, the ICJ co-organized an academic seminar addressing the right to life under international law and the State’s duty to effectively investigate alleged violations.
The event happened on the eve of the post mortem decision to be delivered by Chiang Mai Provincial Court in the case of Chaiyaphum Pasae.
The Lahu youth activist was killed by a military official who was attempting to arrest him as an alleged drug suspect in Chiang Dao district of Thailand’s northern Chiang Mai province in March 2017.
Officials claimed Chaiyaphum had resisted arrest and was subsequently shot in “an act of self-defence”.
On 6 June 2018, Chiang Mai Provincial Court ruled that the bullets shot by the military official had caused the death of Chaiyaphum Pasae.
In its decision, the court made no finding of fault and no finding as to whether Chaiyaphum Pasae had resisted arrest before his death.
The decision by Chiang Mai Provincial Court will now be sent on to the Public Prosecutor and inquiry officers, who will in parallel continue criminal investigations into the case.
The Public Prosecutor is expected thereafter to make a decision regarding any indictment of the military official who shot at Chaiyaphum Pasae.
Participants in the seminar, which was held at Chiang Mai University’s Art Center, included Chaiyaphum Pasae’s family members, interested members of the public, media representatives, students and academics.
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior Legal Adviser, addressed the seminar on the right to life and the international law and standards that apply to investigating potentially unlawful deaths, including the rights of victims and family members, referring to the standards set out in the revised Minnesota Protocol on the Investigation of Potentially Unlawful Death (2016), which was launched in Thailand on 25 May 2017.
The event follows the ICJ’s first regional workshop on the investigation of potentially unlawful deaths and enforced disappearance in Asia, held last week in Bangkok for authorities from Thailand, Cambodia, Myanmar and Nepal.
Other speakers at the Workshop included Ratsada Manuratsada and Sumitchai Hattasarn, lawyers from Human Rights Lawyers Association (HRLA) who represented the family of Chaiyaphum Pasae, and Songkran Pongbunchan, a lecturer from Chiang Mai University’s Faculty of Law.
The Discussion was conducted in collaboration with Legal Research and Development Center Chiang Mai University (LRDC); Center for Protection and Revival of Local Community Rights (CPCR); Center for Ethnic Studies and Development Chiang Mai University (CESD); Human Rights Lawyers Association (HRLA); Protection International (PI); Holding Hands Group; Inter Mountain Peoples’ Education and Culture in Thailand Association (IMPECT); Cross Cultural Foundation (CrCF); Maayimstudio; Save Lahu Group; Lanyim Creative Group; Dinsorsee Creative Group; Northern Activist Community (CAN); and Tonkal Network.
This seminar is part of an ongoing engagement between the ICJ and Chiang Mai University’s Faculty of Law.
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, Senior Legal Adviser, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Office, t: +66 94 470 1345, e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org









