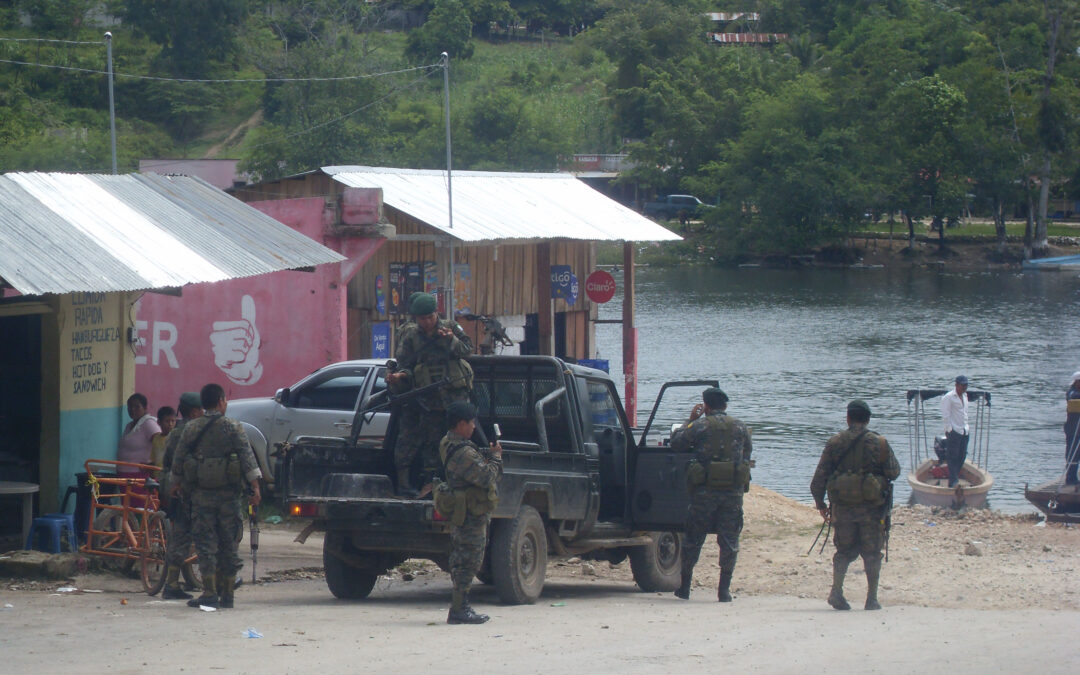

Jan 29, 2016 | News
La CIJ expresa su preocupación frente a una nueva denuncia abusiva de la Fundación contra el Terrorismo, esta vez contra el Director de la CIJ para Centroamérica y un consultor que contribuye con el Bufete de Derechos Humanos, y contra el Director de Centro de Acción Legal, Ambiental y Social.
Esta denuncia se suma a otras en contra de abogados y abogadas de Guatemala. A través de querellas y acusaciones falsas, esta Fundación pretende afectar la función que estos profesionales cumplen como defensores de los derechos humanos.
Estas denuncias falsas son parte de una campaña iniciada hace más de un año y que ha querido afectar a más de cien personas, a quienes la Fundación contra el Terrorismo ha calificado como terroristas y guerrilleros (as), sin aportar pruebas.
Efectivamente se han presentado denuncias contra funcionarios y ex funcionarios del Ministerio Público, como la ex Fiscal General Claudia Paz y Paz y la actual Fiscal General Thelma Aldana, el Fiscal de Derechos Humanos o en contra de jueces y juezas del Organismo Judicial que ejercen su función en forma independiente, promoviendo un discurso de odio en contra de estas personas que actúan como defensores y defensoras de derechos humanos.
Ante esto hechos, la CIJ demanda:
- Que el Estado de Guatemala, por medio de las autoridades correspondientes, inicie una investigación exhaustiva e imparcial acerca de las actividades que realiza la Fundación contra el Terrorismo sobre todo, que investigue el origen de aquellas actividades que dirige en contra de defensores y defensoras de Derechos Humanos;
- Que el Estado de Guatemala, por medio de las autoridades correspondientes, brinde la protección debida a defensores y defensoras de derechos humanos;
- Que una vez finalizada la investigación el Estado de Guatemala, a través de las autoridades y mecanismos correspondientes, adopte las medidas necesarias de acuerdo a derecho con respecto a la Fundación contra el Terrorismo y su Director, por llevar a cabo campañas de odio en contra de defensores y defensoras de derechos humanos.

Jan 20, 2016 | News
The Indonesian government’s efforts to counter and punish attacks such as the deadly assault in central Jakarta last week can only succeed if they strengthen respect for rights and rule of law, said the ICJ today.
Indonesia’s National Counterterrorism Agency (BNPT) and the State Intelligence Agency (BIN) claimed that they lacked sufficient authority under the country’s existing Anti-Terrorism Law to stop the attacks.
Eight people were killed in an attack by armed men in central Jakarta on 14 January.
“Plans discussed by Indonesian authorities to amend the 2003 Anti-Terrorism Law to make it ‘more effective’ in addressing terrorist threats mostly focus on weakening hard-won protections for suspects and the rule of law,” said Emerlynne Gil, ICJ’s Senior Legal Adviser for Southeast Asia.
“In order to help the Indonesian government meet its obligation to protect its people from acts of terrorism, experience from around the world and Indonesia’s Suharto era shows that security can only be achieved through justice,” she added.
The head of the National Police, Gen. Badrodin Haiti, said that the Anti-Terrorism Law prevents police from prosecuting Indonesians returning home after allegedly serving as combatants in Syria.
One of the proposals is to give intelligence officers the authority to make arrests under the Anti-Terrorism Law.
“Giving intelligence officers the authority to make arrests will likely lead to an increase in violations of human rights,” said Gil.
“The roles of intelligence and of law enforcement are fundamentally different and need to remain separate,” she added.
The ICJ pointed out that there were not enough safeguards under Indonesia’s laws, specifically the State Intelligence Law, to ensure the accountability of the intelligence agency or its officers.
Another proposal is that authorities be given the power to arrest anyone they see as having a “strong indication” to be planning acts of terrorism.
The ICJ, however, observes that this proposal appears to allow Indonesian authorities to avoid judicial oversight so that it would be easier for them to arrest any person, irrespective of whether there is sufficient evidence of criminal activity or an intent to prosecute.
This proposal also appears to allow authorities to detain and interrogate persons suspected of involvement in terrorist acts with a view to gaining intelligence information without necessarily contemplating the filing of criminal charges.
As ICJ’s Eminent Jurists Panel on Terrorism, Counter-terrorism, and Human Rights has underscored, the practice of arrest and detention for the sole purpose of intelligence gathering may mean the arrest and detention of those “who are not necessarily criminal suspects, but who are also believed to have information that will ‘substantially’ assist the collection of intelligence relating to terrorism.” Detaining people for the sole purpose of intelligence gathering in the absence of evidence of criminal activities is a form of arbitrary detention.
Such a practice can also lead to secret or unacknowledged detention, which under international law constitutes enforced disappearance and is absolutely prohibited, the Geneva-based organization adds.
“The obligation to protect human rights and keep people safe from acts of terrorism are not at opposing poles,” said Gil. “They are complimentary and mutually reinforcing duties of protection incumbent on the State.”
“In fact, protecting human rights can be an effective shield in defending societies from acts of terrorism,” she added.
All measures to counter terrorism must strictly comply with obligations Indonesia has under international law.
Contact:
Emerlynne Gil, Senior International Legal Adviser of ICJ for Southeast Asia, t: +66 840923575 ; e: emerlynne.gil@icj.org
Background:
Indonesia’s Anti-Terrorism Law requires judicial approval to arrest a suspect in a terrorism case. Under the law, authorities may arrest any person “strongly suspected of committing a crime of terrorism on the basis of sufficient initial evidence.”
The Chairperson or Deputy Chairperson of a District Court determines whether sufficient initial evidence exists or has been obtained by authorities.
Under article 42 of Indonesia’s State Intelligence Law, the accountability of intelligence operations of the State Intelligence Agency is in principle ensured through a written report on these operations submitted to the President of Indonesia.
This provision has been criticized for failing to provide sufficient accountability, as the presidency is firmly within the Executive branch and lacks capacity to investigate and prosecute in the ordinary criminal justice system.
Furthermore, article 24 of the State Intelligence Law provides that the State has the obligation to give “protection” to all intelligence personnel when carrying out their intelligence duties and functions. Such protection is extended to their family members.
The law does not define “protection” and hence may be construed as the State being obliged to grant immunity to intelligence personnel and their family members from criminal prosecution or civil liability.
Jan 14, 2016 | News
As today marks the fifth anniversary of the toppling of Ben Ali’s regime, the ICJ calls on Tunisian authorities to adopt key legal and policy reforms to combat impunity and to deliver justice to victims of past human rights violations.
Under Ben Ali’s regime, thousands of human rights violations, including torture and other ill-treatment, unlawful killings, enforced disappearances, and arbitrary arrests and detentions, were committed by law enforcement and other security officers.
Numerous similar violations were also committed during the December 2010 to January 2011 uprising and some of them continue today.
“The political and institutional reforms introduced in Tunisia over the past 5 years should not be the sole yardstick to measure the success of the transition,” said Said Benarbia, Director of the ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme.
“Victims of human rights violations, in particular under Ben Ali’s rule, and during the uprising still await justice,” he added.
Despite several cases being brought before Tunisian courts, in particular military courts, these proceedings have yet to establish the truth about violations, ensure that all those who are responsible are held to account, and fulfill the rights of victims to effective remedies and reparation.
“Until their rights to effective remedies and reparation are realized, including by holding the perpetrators to account, the transition will remain incomplete,” Benarbia said.
Indeed, despite numerous legal and policy reforms, including the adoption of the “Transitional Justice Law”, and the establishment of the Truth and Dignity Commission (Instance Vérité et Dignité), the ICJ is concerned that justice for victims remains mostly elusive.
Obstacles that impede victims’ access to justice and effective remedies include current weaknesses in the Tunisian criminal procedures, such as the broad discretion of the public prosecutor to dismiss cases without providing specific reasons (and the lack of ability of victims effectively to challenge such decisions), the lack of effective measures for the protection of victims and witness, inadequate laws on the definition of crimes and superior responsibility, and the use of military courts to address human rights violations.
“Key reforms both in law and practice are needed for Tunisia to properly address past abuses in Tunisia, end pervasive impunity and provide victims with justice,” Benarbia said.
Contact:
Theo Boutruche, Legal Adviser of the ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, tel: +96 170 888 961, e-mail: theo.boutruche(a)icj.org
Tunisia-Anniversary-News Press Release-2016-ARA (Arabic version, in PDF)

Dec 22, 2015 | News
The ICJ today called on Egypt’s newly elected House of Representatives to amend or annul the web of repressive presidential decrees promulgated since the ouster of President Morsi.
“Egypt’s House of Representatives must dismantle the catalogue of repressive presidential decrees that have been used by the authorities to stifle dissent, curtail fundamental rights and freedoms and shield state officials from accountability in cases of human rights violations,” said Said Benarbia, Director of the ICJ’s Middle East and North Africa (MENA) Programme.
Article 156 of the Egyptian Constitution provides that decrees issued by the President while the House of Representatives is not in session must be discussed and approved by the new House of Representatives within 15 days of it convening.
Failure to do so results in the laws being automatically nullified with retroactive effect.
The ICJ and others have detailed how many of these presidential decrees, including the Demonstration Law (No.107 of 2013), the Counter-Terrorism Law (No.94 of 2015), the Terrorist Entity Law (No.8 of 2015), the Law on Military Courts (No.136 of 2014) and laws amending the Criminal Code (No.128 of 2014) and the Prison Law (No.106 of 2015), violate Egypt’s obligations under international law.
Key concerns relate to the right to life, the right to liberty and the right not to be subjected to arbitrary detention, fair trial rights, and the rights to freedom of expression, association and assembly.
These fundamental rights are protected by for instance the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, which Egypt ratified in 1982 and which today counts 168 states as parties.
Over the last two years, thousands of individuals have been prosecuted and convicted pursuant to such decrees, including the Demonstration Law, through proceedings that fell short of international fair trial standards.
Further, many of these decrees, in particular the Counter-Terrorism Law and the Demonstration Law, institutionalise the immunity of state officials from legal proceedings against any use of force committed in the course of their duties, including the use of lethal force when it is not strictly necessary to protect lives.
The decrees also fail to provide for any reparations mechanism for victims.
“Egypt’s parliament should, as a matter of urgency, ensure that those who have suffered human rights violations on the basis of these laws obtain effective remedy and reparations, remove all obstacles to justice and accountability, and address the impunity of state officials underpinned by these decrees”, Benarbia added.
Contact:
Alice Goodenough, Legal Adviser of the ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, t: +44 7815 570 834; e: alice.goodenough(a)icj.org
Nader Diab, Associate Legal Adviser of the ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, t: +41 229 793 804; e: nader.diab(a)icj.org
Egypt-New House of Representatives-News-Press releases-2015-ARA (full text in Arabic, PDF)

Dec 17, 2015 | News, Publications, Reports
With the signing of the political agreement on a national unity government today, the next step in Libya’s transition will be to ensure that its new Constitution fully conforms to international rule of law and human rights standards, the ICJ said today.
The statement came as the ICJ released its new report The Draft Libyan Constitution: Procedural Deficiencies, Substantive Flaws.
In the report, the ICJ calls on the Libyan Constitution Drafting Assembly (CDA) to substantially revise the Draft Constitution published in October with a view to ensuring its full compliance with Libya’s obligations under international human rights law and international standards.
Libyan authorities, including the CDA, should also put in place effective mechanisms to ensure that the drafting process is inclusive, participatory, and fully reflects the views of a broad range of stakeholders, including civil society and minority groups.
The report concludes that the Draft Constitution, in many key respects, does not conform to Libya’s obligations under international human rights law or to international rule of law standards.
“The new Constitution provides a crucial opportunity to depart from decades of authoritarianism under Moammar Ghadafi’s regime. It must therefore provide for a strong foundation upon which the rule of law, including the separation of powers, the independence of the judiciary and civilian oversight over military and armed groups, can be established and upheld,” said Said Benarbia, Director of the ICJ MENA programme.
The Draft Constitution should also be amended to provide for a comprehensive set of human rights and protections that fully accord with international human rights law, including provisions relating to non-discrimination, the right to life, the right to liberty and security, the prohibition on torture and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment, protections for minorities, the right to freedom of thought, conscience and religion, fair trial rights, and a range of economic, social and cultural rights.
“The Libyan Constitution must at a minimum conform to the definition and scope of the rights contained within the human rights treaties to which Libya is a state party. Any scope for limitation of rights must conform to the criteria for such limitations under international law and, in particular, only as are provided for by law, are proportionate, and are demonstrably necessary in a free and democratic society,” Benarbia added.
Contact:
Doireann Ansbro, Associate Legal Advisor of the ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, tel: +216 71 841 701, email: doireann.ansbro(a)icj.org
Libya-Draft Constitution Flaws Deficiencies-Publications-Reports-2015-ENG (full report in PDF, English)
Libya-Constitution Flaws Report-News-Press releases-2015-ARA (full press release in Arabic, PDF)
Libya-Draft Constitution Flaws Deficiencies-Publications-Reports-2015-ARA (full report in PDF, Arabic)









