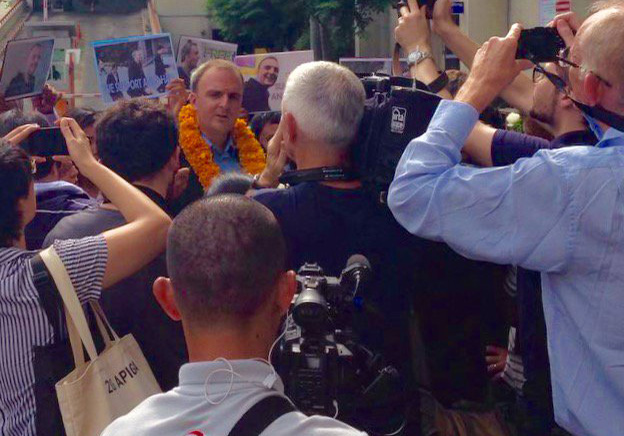Feb 13, 2017 | News
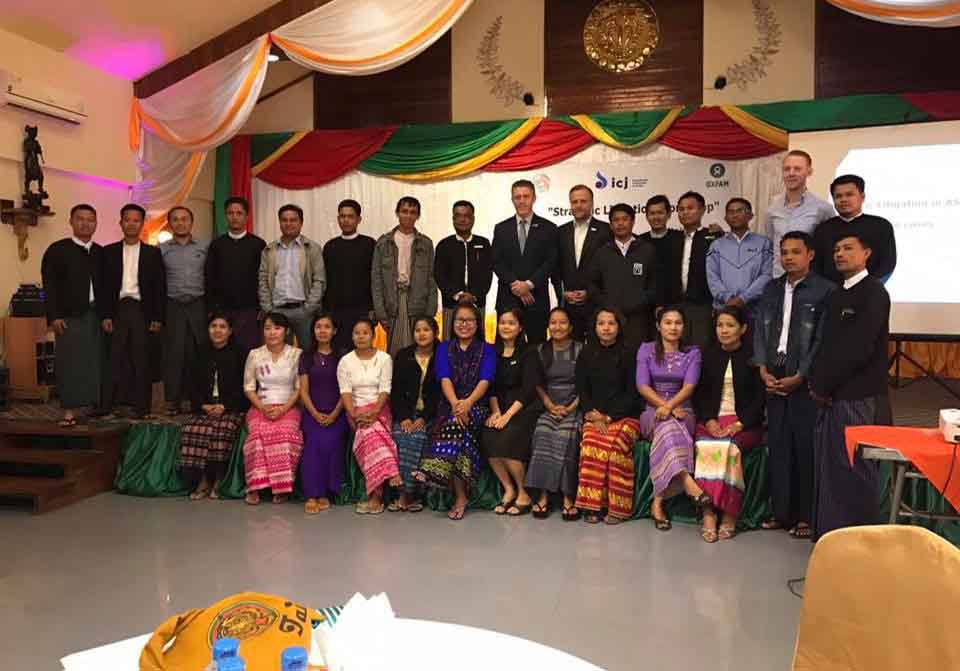
The workshop, held from 11-12 February in Sittwe, brought lawyers and civil society together to discuss of experiences of strategic litigation elsewhere in Myanmar and the region, and consider potential public purpose litigation cases in Rakhine State.
Dr Daniel Aguirre, the ICJ’s International Legal Adviser in Myanmar, provided an introduction to strategic litigation as a method for promoting accountability in a time of transition in governance.
He noted the critical role of independent lawyers in protecting human rights, by representing clients from all communities in Rakhine State.
And he emphasized the importance of strategic litigation as a means to prevent violations and abuses of human rights, or to seek reparations where violations and abuses have occurred.
Kingsley Abbot and Jintana Sakulborirak, from the ICJ’s Asia Regional Office in Thailand, discussed strategic litigation cases from the region, including in northern Thailand where community members have launched an action to appeal the legality of land acquisition for a planned SEZ in Tak Province.
The cases highlighted how media engagement is a critical part of strategic litigation, to raise public attention on human rights issues and demands for accountability in the implementation of investment projects.
Daw Aye Mon Thu, advocate from Dawei Pro Bono Lawyers Network presented the experiences of Heinda Mine cases from Dawei Region, Southern Myanmar, emphasizing the importance of trust-building and cooperation with local community as stake-holder. Such a strategic litigation cases are extremely rare in Myanmar.
Discussions followed about potential cases for strategic litigation from Kyauk Phyu and Sittwe, including issues related to land acquisition for railways construction and an SEZ appear to have been carried out unlawfully in violation of human rights.
Participants discussed the principle of undertaking litigation for broader advocacy objectives rather than solely focusing on actually winning the case in the court.
They also reflected on the challenges and limitations for Myanmar lawyers to undertake strategic litigation.
Highlighting the vital role of lawyers, speakers encouraged participants to consider strategic litigation as a means to challenge unlawful acts that violate or abuse human rights, particularly accompanying business enterprises.
Rakhine State is among Myanmar’s poorest and most isolated provinces, where lawyers and CSOs have had limited exposure to concepts of human rights and international laws.
This workshop, the first of its kind to be held in Rakhine State, is part of efforts to address this gap by building legal literacy on international human rights law and lawyers to consider litigation as a strategy to protect human rights.

Dec 6, 2016 | News
Hosted on 3-4 December, the event was attended by a total of 40 participants which includes representatives of CSOs, lawyers, MPs and village track administrators.
The workshop aimed to raise awareness of international standards and best practice of resettlement and development-based eviction and displacement among local community in order to mitigate potential adverse impact associated with the development of the Kyauk Phyu Special Economic Zone.
In the opening, Dr Daniel Aguirre, ICJ International Legal Adviser, outlined the essential role of lawyers and community members in safeguarding human rights and holding the State and investors accountable.
The discussion was led by international experts and experienced and committed leaders of Civil Society Organization.
Susanna Price from Australian National University highlighted key principles of the ADB’s Involuntary Resettlement Policy along with experiences from China, Cambodia and Indonesia.
U Hayman Oo, ICJ Legal Researcher, explained how the UN principles on Development-based Eviction and Displacement are applicable in the context of Myanmar and urged the participants to use these standards for their advocacy work.
U Myo Mrat Hein, the Director and lawyer of the Thazin Legal Aid Group, discussed important issues surrounding the national land acquisition legislation whilst Sean Bain, legal consultant at the ICJ give a brief overview of important provisions of the Myanmar SEZ Law (2014).
The other two guest local speakers shared their first-hand experiences of advocacy work and resettlement issues which occurred during the development of Dawai and Thilawa SEZ respectively.
Participants exchanged strategies and ideas to take preparatory steps to mitigate potential impacts of the KPSEZ in terms of protecting their economic, social and cultural rights, learning from Dawei and Thilawa, as well as from international standards which Myanmar recognizes.
The new Kyauk Phyu SEZ Management Committee, along with Dawai and Thilawa, was formed last month with over 30 members including international and local social and environmental experts.
In a meeting held in Nay Pyi Taw following the establishment of the SEZ Management Committee, Daw Aung San Su Kyi emphasized that the current three SEZs of the country are leading projects for Myanmar’s economic growth.
She also expressed concerns over the potential negative effect of these zones if not properly implemented.

Oct 25, 2016 | Events
The ICJ convenes today a roundtable at the United Nations gathering several stakeholders to discuss on a possible future treaty on business and human rights.
Tuesday 25 October, 2016
13:00 to 15:00 hrs
Room XXVII- Palais des Nations
The second session of the Open Ended Intergovernmental Working Group to elaborate a legally binding instrument on Transnational Corporations and other business enterprises in relation to human rights, offers the opportunity to significantly advance the process of establishing an effective treaty that assist in preventing and addressing business related human rights abuses. Advancing the process will require stakeholders to reach a common platform of understanding on some core concepts and foundational elements before textual details can be elaborated and negotiated.
The objective of the roundtable is to assist in this process by creating a space for various stakeholders to address issues of importance for the treaty process from diverse points of view with the goal of enhancing mutual understanding among stakeholders of concepts and element that can serve as the basis for possible agreement for the future. This panel has a multistakeholder nature with a view to create a space of dialogue and understanding among the most important actors of the process.
Moderator:
Mr Ian Seiderman, Legal and Policy Director, International Commission of Jurists
Speakers:
Mr Ariel Meyerstein- United States Council of International Business, representing the International Organization of Employers
Mrs Makbule Sahan, Legal Advisor, International Trade Union Confederation
Prof Douglas Cassel, School of Law, University of Notre Dame, Indiana, United States
Prof Surya Deva, member of the UN Working Group on Business and Human Rights
Mr Humberto Cantú Rivera, Researcher at University of Panthéon-Assas, Paris II
Mrs Debbie Stothard, Secretary-General, International Federation of Human Rights (FIDH)
icj-side-event-2nd-session-flyer (download the flyer)

Oct 20, 2016 | Advocacy, Analysis briefs, News
In a paper published today, the ICJ recommends a series of substantive elements that it considers as key to an effective treaty on business and human rights.
The ICJ is publishing this paper as the second session of the open ended intergovernmental working group on transnational corporations and other business enterprises with respect to human rights (OEIWG) will be held next week (24-28 October).
On 26 June 2014, the United Nations Human Rights Council (HRC) adopted Resolution 26/9 establishing an “open ended intergovernmental working group on transnational corporations and other business enterprises with respect to human rights” (OEIWG) with the mandate to “elaborate an international legally binding instrument to regulate, in international human rights law, the activities of transnational corporations and other business enterprises”.
The first session of the OEIWG took place from 6 to 10 July 2015.
The ICJ supports the objective of establishing an international legally binding instrument on transnational corporations and other business enterprises, with a focus on business accountability and access to effective remedies for human rights abuses by business enterprises.
There is a substantial international protection gap to be filled in this respect, on which the ICJ has previously commented extensively.
It is with a view to closing this gap and ensuring that international human rights law can optimally fulfil its protective function that the ICJ is engaging in the present treaty process.
The key elements in the ICJ paper are a contribution to the ongoing discussions about the future instrument, without being exhaustive as to such elements.
The ICJ has already published a paper focused on issues of scope of businesses to be addressed in the treaty, in particular the meaning or “transnational corporations (TNCs) and other business enterprises” a question which remains unresolved and is contentious in the OEIWG discussions.
The present paper will focus on the possible content of the prospective treaty.
universal-oewg-session-2-icj-submission-advocacy-analysis-brief-2016-eng (full text in PDF)
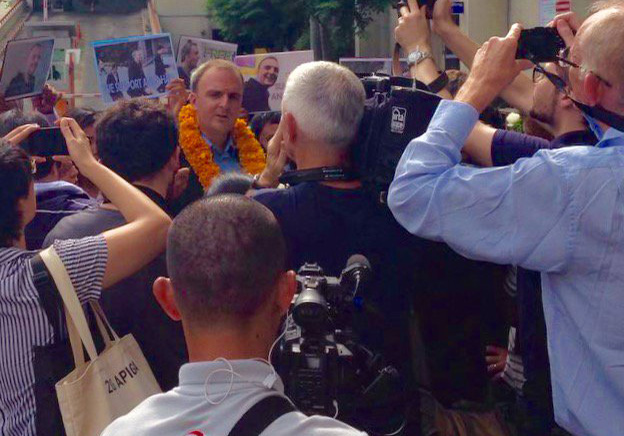
Sep 20, 2016 | News
The ICJ expresses its disappointment with today’s verdict criminalizing the work of human rights defender, Andy Hall, and calls upon Thailand to decriminalize defamation and amend the Computer Crime Act in line with international standards protecting freedom of expression.
This morning, Thailand’s Southern Bangkok Criminal Court found Andy Hall guilty of defaming a Thai fruit processing company under Article 328 of the Thai Criminal Code and violation of Article 14(1) of the Computer Crime Act, and sentenced him to a fine of THB 200,000 (USD$ 5,700) reduced to THB 150,000 (USD $4,300); and four years imprisonment, reduced to three years and suspended for two years.
Andy Hall has said he will appeal the verdict.
“Human rights defenders such as Andy Hall have the right to exercise freedom of expression in advocating for the protection and realization of human rights – a right that Thailand has a duty to protect,” said Kingsley Abbott, Senior International Legal Adviser at the ICJ.
“Unfortunately, there are numerous examples of criminal defamation and the Computer Crime Act being used against human rights defenders in Thailand, a practice that must end, including through a substantial reform of these laws,” he added.
The ICJ and Lawyers Rights Watch Canada submitted a joint amicus curiae brief in the proceedings, arguing that the imposition of harsh penalties such as imprisonment or large fines on a human rights defender risk having a ‘chilling effect’ on the exercise of freedom of expression, which Thailand is bound to protect pursuant to its international legal obligations.
The ICJ anticipates the arguments contained in the joint amicus will be considered on appeal.
“It is also disappointing that the Court did not appear to take into account the recent decision of the Phuket Provincial Court in the Phuketwan case, which found that the Computer Crime Act was not intended to be used in cases of alleged defamation,” said Abbott.
On 1 September 2015, the Phuket Provincial Court acquitted two journalists of criminal defamation and violations of the Computer Crime Act after the Royal Thai Navy complained the journalists defamed it when, on 17 July 2013, the journalists reproduced a paragraph from a Pulitzer prize-winning Reuters article that alleged “Thai naval forces” were complicit in human trafficking.
The criminal defamation proceedings brought against Andy Hall are among several that have been brought against human rights defenders in Thailand in recent years.
Others examples include the charges laid against activists Pornpen Khongkachonkiet, Somchai Homloar and Anchana Heemina in July 2016 for raising allegations of torture in the deep South; and those brought against activists protesting various development projects in Thailand which are allegedly having an adverse impact on communities.
Background
Today’s case is one of four criminal and civil proceedings (two criminal and two civil) a Thai fruit processing company, Natural Fruit Company Ltd., has brought against Andy Hall in relation to the report of a Finnish NGO, Finnwatch, published in January 2013, called Cheap Has a High Price.
Andy Hall’s research was included in the report which alleged that labour rights violations were taking place at Natural Fruit Company Ltd., whose employees included migrant workers from Myanmar.
In September 2015, a Thai Appeal Court upheld the dismissal of the other criminal defamation proceeding Natural Fruit Company Ltd. brought against Andy Hall. That proceeding is currently before the Supreme Court. Two civil proceedings are also before the Thai courts but have been suspended pending resolution of the two criminal proceedings.
The use of criminal defamation laws, carrying penalties of imprisonment, against human rights defenders reporting on alleged human violations, constitutes a violation of Thailand’s obligations under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), to which it is a state party.
thailand-verdict-andy-hall-case-news-press-release-2016-eng (full text in PDF)
thailand-verdict-andy-hall-case-news-press-release-2016-tha (full text in Thai, PDF)
Contact
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Director (Bangkok), t: +66 807819002; e: sam.zarifi(a)icj.org
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, t: +66 9 4470 1345, e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org