
Nov 7, 2023
Yesterday, the International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) and Amnesty International (AI) jointly submitted an amicus curiae legal brief to the Bangkok South Civil Court in a class-action lawsuit filed by two residents of Cambodian villages, representing at least 23 families out of a potential class of more than 700 affected families in the Oddar Meanchey Province, Cambodia, against Mitr Phol Sugar Corporation Ltd., a Thai company.
This lawsuit, based on Thai and Cambodian tort laws, alleges human rights abuses committed by Mitr Phol’s apparent subsidiary in Cambodia, Angkor Sugar Co. Ltd.
In 2008, Angkor Sugar Co. Ltd. was granted an economic land concession to operate an industrial sugar plant in Oddar Meanchey Province. The complaint alleges that after the concession was granted, Angkor Sugar Co. Ltd. colluded with local authorities to forcibly seize land held by individuals from local communities, resulting in the destruction of their houses, the burning of villages and crops, and physical harm to some villagers.
This marks the first-ever class-action lawsuit filed in Thai courts by plaintiffs from another country for abuses committed by a Thai company outside of Thailand.
Today, the Court held a session to examine the list of evidence submitted by both parties. The next appointment date will be on 27 March 2024 for the examination of evidence, after which the court will set the witness examination date.
The ICJ/AI amicus brief sets out the principal applicable international human rights law and standards, and comparative jurisprudence for the Thai court to consider in resolving this case. The organizations submit that the human rights responsibilities of a parent company, such as Mitr Phol, extend beyond its own conduct to include the activities of subordinate entities. To this end, Mitr Phol has a duty to exercise due diligence in monitoring and controlling their subsidiaries in Cambodia, whose conduct they may influence. Failure to carry out this due diligence should result in liability as a consequence of the actions of their subsidiaries.
The brief also highlights that under international standards, business enterprises have a responsibility to respect all internationally recognized human rights wherever they operate, such as the right to adequate housing.
The Thai court itself also has a duty that extends beyond the national borders of Thailand to ensure access to justice, effective remedy, and reparation for individuals from communities living in proximity to the operations of Thai companies and their subsidiaries in other countries when their rights are violated.
The need to apply international human rights standards is recognized by the government of Thailand, as evidenced in the adoption of its National Action Plan on Business and Human Rights, and is also recognized by Mitr Phol through the company’s Code of Conduct.
Background
Victims of corporate human rights abuses face multiple barriers in holding companies to account and securing access to justice.
Although this case is the first of its kind in Thai courts, in recent years, other cases involving human rights abuses committed by Thai state-owned enterprises abroad were brought to Thai courts by Thai citizens, but they ended with limited success. These cases included an unsuccessful lawsuit brought by Thai villagers against Thai governmental agencies regarding the construction of the Xayaburi Dam in Lao PDR and its transboundary environmental destruction affecting communities in Thailand.
The limitations identified encompass the legal nature of corporations, evidentiary challenges, conflict of laws, and statutes of limitation.
Despite calls from CSOs to initially address the weak implementation of the first NAP, Thailand’s Second National Action Plan on Business and Human Rights (2023-2027) was endorsed by the Thai Cabinet on 25 July 2023.
The NAP identifies ‘cross-border investment and multinational enterprises’ as one of the four key priority issues in the NAP. The Second NAP includes an action point that requests the Ministry of Justice to “study and recommend amendments to the laws or propose measures to ensure access to justice and effective civil, criminal and administrative remedies for local and overseas communities within the areas where companies or Thai state-owned enterprises operate and are affected by such operations.”
The submission in English can be downloaded here
The submission in Thai can be downloaded here
Further reading
Thailand: Barriers persist in access to justice for victims of human rights abuses involving Thai transnational corporations abroad – ICJ report
Contact
Sanhawan Srisod, ICJ Associate International Legal Adviser, e: sanhawan.srisod@icj.org

Nov 3, 2023 | News
Former Deputies and Mayors Face Prosecution and Prolonged Incarceration for Political Speech.
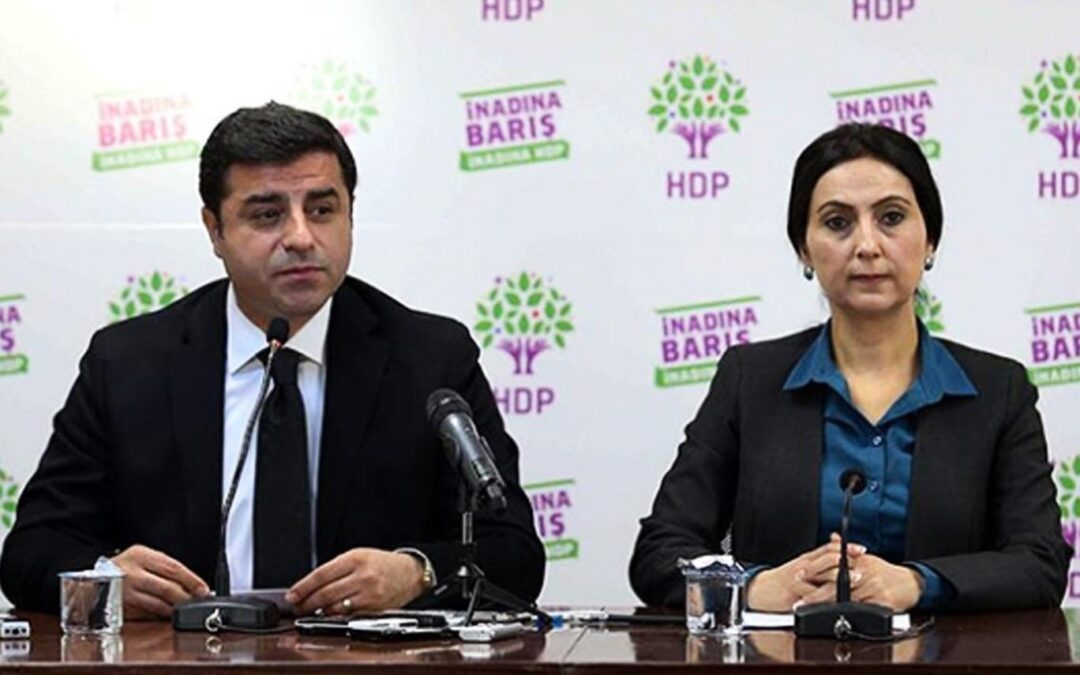
The Turkish government should abide by international law and implement the binding judgments of the European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) by immediately releasing politicians Selahattin Demirtaş and Figen Yüksekdağ, who formerly co-chaired the opposition Peoples’ Democratic Party (HDP), four rights organizations said today.
The four nongovernmental organizations—Human Rights Watch, the Turkey Human Rights Litigation Support Project, the International Commission of Jurists, and the International Federation for Human Rights—made their call on the seventh anniversary of the politicians’ wrongful imprisonment.
“The seventh anniversary of the unlawful incarceration of Selahattin Demirtaş and Figen Yüksekdağ is a stark reminder of the Erdoğan presidency’s willingness to use detention for political ends to silence democratically elected opposition politicians representing millions of Kurdish and leftist voters in Turkey,” said Hugh Williamson, Europe and Central Asia director at Human Rights Watch. “In defying the binding ECtHR judgments ordering the politicians’ release, Turkey is flagrantly violating its legal obligations under the European Convention on Human Rights and international law more broadly.”
On November 4, 2016, months after being stripped of their parliamentary immunity, Demirtaş, Yüksekdağ and eight fellow members of parliament from the HDP were arbitrarily detained and placed in pretrial detention, with four others incarcerated over the following five months. At the time, the HDP held 10.7 percent of seats in Turkey’s parliament and was backed by over five million voters. While the 12 other deputies whose cases are covered in the ECtHR judgments are no longer in detention, Demirtaş and Yüksekdağ remain incarcerated.
All the former parliamentarians have been repeatedly prosecuted in individual proceedings based exclusively on their exercise of their right to freedom of expression, protected under international law. This included their political speeches and activities, which did not involve or advocate violence. When a mass trial was opened against them in 2021, many of those ongoing individual case files were merged. The vague and wide-reaching accusations against them in this trial include allegations of “undermining the unity and territorial integrity of the State” (separatism) and even “murder.” These accusations relate to their support for protests that mainly took place in cities in southeast Turkey between October 6 and 8, 2014. The politicians have been held responsible for all offences allegedly committed over the course of these protests, which were organized against the brutal siege of the Kurdish-majority northern Syrian town of Kobane by the extremist armed group Islamic State (also known as ISIS). During the protests, 37 people reportedly died.
The evidence against the politicians, on the basis of which Demirtaş and Yüksekdağ are currently detained, consists of two social media postings supporting protests over the Kobane siege sent from the HDP Twitter account, together with the politicians’ nonviolent political speeches, lawful activities, and witness statements against them added to the case file years later that raise serious questions of credibility.
The ECtHR determined in three judgments—two pertaining to Demirtaş in November 2018 and December 2020, and one to Yüksekdağ and 12 others in October 2022—that their detention on the basis of speeches and social media postings was a politically motivated move to silence them, “stifling pluralism and limiting freedom of political debate, the very core of the concept of a democratic society.” The court found that their rights to liberty, to freedom of expression, and to be elected had been violated. The facts forming the basis on which Demirtaş and Yüksekdağ are detained and were prosecuted for in the 2021 mass trial are substantially the same as those contained in the proceedings which the ECtHR found to be insufficient grounds for their detention.
“Despite the European Court ruling that the grounds to justify Yüksekdağ and Demirtaş’s detention were insufficient, the Ankara public prosecutor in April 2023 requested their conviction on numerous alleged offences concerning their political speech, which may result in their life imprisonment without parole,” said Temur Shakirov, interim director of the International Commission of Jurists’ Europe and Central Asia Programme. “This underscores the ultimate political motives behind the ongoing case targeting the two and reinforces doubts about the fair administration of justice in the country.”
After Demirtaş and Yüksekdağ’s detentions in November 2016, Turkey held a landmark referendum and several crucial election campaigns. The April 16, 2017 constitutional referendum introduced a system of governance concentrating power in the hands of the president. It was followed by the June 24, 2018 presidential election in which Demirtaş ran as a candidate from his prison cell against President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, the March 31, 2019 local elections, and, most recently, the May 14-28, 2023 parliamentary and presidential elections.
“With two prominent figures of the opposition in detention, the country has been deprived of a significant measure of meaningful democratic debate and fair elections around these crucial campaigns,” said Reyhan Yalçındağ, vice president of the International Federation for Human Rights. “With the March 2024 local elections fast approaching, the Committee of Ministers and the other Council of Europe bodies need to use all available means to ensure the end of the continuing violations of Demirtaş’s and Yüksekdağ’s rights, including their rights to participation in public affairs, which is also a violation of the rights of millions of voters.”
The Council of Europe’s Committee of Ministers, responsible for overseeing member states’ implementation of ECtHR judgements, has issued six decisions and two resolutions calling on Turkey to release Demirtaş from detention. At its December 5-7 session this year, the Committee of Ministers will for the third time examine Turkey’s failure to implement the judgment pertaining to Yüksekdağ and release her from detention.
The four nongovernmental organizations have made a joint submission to the Committee of Ministers asking it to issue a decision in December calling for the release of Yüksekdağ.
“Turkey has ignored the Committee’s numerous decisions and interim resolutions calling for Demirtaş’s immediate release. This refusal to comply with Turkey’s international obligations has been repeated in the case of Yüksekdağ,” said Ayşe Bingöl Demir, director of the Turkey Human Rights Litigation Support Project. “The Committee must intensify its scrutiny against Turkey in relation to these cases without further delay, and this must include the triggering of infringement proceedings, in line with the route rightly followed in the case of the imprisoned rights defender Osman Kavala.”
Eighteen other elected former party officials and mayors from the HDP and an affiliated party, the Democratic Regions Party, are also currently detained. Among them is the prominent former elected mayor of Diyarbakır, Gültan Kışanak, detained since October 25, 2016, and Sebahat Tuncel, former co-chair of the Democratic Regions Party, detained on November 6, 2016. Kışanak’s pretrial detention has exceeded the legal limit of seven years under Turkish law, notwithstanding that seven years’ pretrial detention is a flagrant violation of international human rights law. The detentions of the politicians are blatantly arbitrary and politically motivated, and those imprisoned should be immediately released, the organizations said.
Press release in Turkish: Turkey Demirtas and Yuksekdag press release TURKISH
Nov 2, 2023 | News
The International Commission of Jurists renews its call for an immediate ceasefire in the Gaza Strip following the most recent Israeli attacks on the densely populated Jabalia refugee camp in northern Gaza on 31 October and 1 November 2023.
According to the Gaza Health Ministry, the two strikes killed at least 195 people. The Israel Defence Forces (IDF) claimed that the 31 October airstrike targeted and killed Ibrahim Biari, a claim Hamas denied. The IDF further claimed that Biari was one of the Hamas commanders responsible for the 7 October attacks in Israel.
Intentionally directing an attack against civilians or civilian objects or intentionally launching an attack knowing it will cause disproportionate civilian harm is a war crime. The Office of the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights expressed concern that these attacks may be “disproportionate attacks that could amount to war crimes”.
Gaza’s Health Ministry maintains that the number of Palestinians killed since 7 October has surpassed 9,000 and the Committee on the Rights of the Child has expressed concern that more than 3,500 children have been killed.
The ICJ considers that an immediate, durable and fully respected ceasefire by all sides, and an immediate cessation of hostilities in the Gaza Strip, including direct, indirect and disproportionate attacks on civilians and civilian objects, are necessary to stop further loss of civilian life.
According to the Independent International Commission of Inquiry on the Occupied Palestinian Territory, including East Jerusalem, and Israel, there is already clear evidence that war crimes may have been committed in Israel and Gaza since 7 October.
In this regard, the ICJ notes the visit by the Prosecutor of the International Criminal Court, Karim Khan KC, to the Rafah Crossing on the Gaza-Egypt border on 29 October 2023 and, in particular, commends his commitment to investigate the ongoing attacks, and his call for all further attacks to cease immediately. The Prosecutor confirmed that his Office has an ongoing investigation with jurisdiction over the Palestine situation, including current events in Gaza.
In light of the above, the ICJ considers that, only an immediate ceasefire will prevent war crimes, and prevent the risk of crimes against humanity and genocide.
The ICJ calls upon Palestinian armed groups to adhere to their obligations under international humanitarian law, including by releasing all hostages in their custody, and urges the IDF, particularly its military advocate generals, to ensure full respect for international humanitarian law in the conduct of hostilities.
Contact:
Said Benarbia, Director, ICJ’s Middle East and North Africa Programme, email: said.benarbia@icj.org
Katherine Iliopoulos, Legal Adviser, ICJ’s Middle East and North Africa Programme, email: katherine.iliopoulos@icj.org
Oct 19, 2023 | News
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) condemns the strike on al-Ahli hospital in the Gaza Strip on 17 October 2023, which according to the Palestinian Health Ministry killed more than 500 Palestinian civilians, mainly women and children, and injured hundreds more.
“Civilians and hospitals must be protected at all times”, said Said Benarbia, Director of the ICJ’s MENA Programme. “Intentional attacks on hospitals may amount to war crimes under international humanitarian law and must cease immediately”, added Benarbia.
Palestinian sources have said that the massacre was caused by an Israeli air strike. The Israeli Defence Forces have denied any responsibility, claiming that it was caused by a failed rocket launch by Palestinian armed groups.
Under the Geneva Conventions and customary international humanitarian law, States have an obligation to investigate war crimes with a view to bringing alleged perpetrators to justice.
The ICJ calls on the Office of the Prosecutor of the International Criminal Court (ICC) to allocate the necessary resources to respond to the escalating situation in Israel and Gaza with a view to investigating and establishing criminal responsibility for alleged war crimes and other violations of international humanitarian law committed by both parties.
According to the ICC Prosecutor Karim Khan, the ICC has jurisdiction over potential war crimes committed by Palestinian armed groups in Israel and Israelis in the Gaza Strip, even though Israel is not a State party. In 2015, Palestine acceded to the ICC Statute. In 2021, the Court ruled that its jurisdiction “in the Situation in Palestine extends to the territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely Gaza and the West Bank, including East Jerusalem.”
On 12 October the Israel Defence Forces (IDF) ordered the entire population of northern Gaza, that is, more than 1 million people, to evacuate to southern Gaza within 24 hours in advance of a likely military ground offensive.
On 14 October, the World Health Organization (WHO) strongly condemned Israel’s repeated orders for the evacuation of 22 hospitals in the Gaza strip, and called on Israeli authorities to protect health facilities, health workers, patients and civilians.
“The Israeli evacuation order was issued in the absence of safe passage or a safe destination. It may amount to a transfer of parts of the population of the occupied territory, a war crime under the ICC Statute and a serious violation of international humanitarian law”, said Benarbia.
Under international humanitarian law, hospitals and other medical facilities are considered to be protected civilian objects. Unless they are used for military purposes, they shall be protected at all times and may not be the object of attack.
Under international humanitarian law, all parties to an armed conflict have an obligation to distinguish between military and civilian targets and to take all feasible precautions to protect civilians from attacks and from the effects of military operations. Indiscriminate attacks on civilians and civilian objects, including those perpetrated using weapons that are indiscriminate by nature, amount to breaches of international humanitarian law. Intentionally directing attacks against civilians amounts to war crimes under the under the Statute of the ICC and customary international law.
Furthermore, the ICJ is deeply concerned by reports of the use of white phosphorus by Israel in other military operations in Gaza and Lebanon.
“Israel must refrain from using white phosphorus, and any other means and methods of warfare that are inherently indiscriminate or that cause superfluous injury or unnecessary suffering”, added Benarbia.
White phosphorus has the potential to cause civilian harm due to the severe burns it causes and its lingering long-term effects on survivors. While it is not per se a prohibited weapon under international humanitarian law, its use in densely populated areas, such as the Gaza Strip, is prohibited as it violates the international humanitarian law requirement that parties to the conflict take all feasible precautions to avoid civilian injury and loss of life.
The ICJ also condemns the continued detention by Palestinian armed groups of approximately 200 hostages.
“Hostage-taking is prohibited under international humanitarian law, and those detained must be released immediately”, said Benarbia.
The ICJ also reiterates calls by the United Nations Secretary General, WHO and others for the establishment of a humanitarian corridor to enable humanitarian aid to enter the Gaza Strip.
Contact:
Said Benarbia, Director of the ICJ’s Middle East and North Africa Programme, email: said.benarbia(at)icj(dot)org

Oct 16, 2023 | News
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) condemns the arbitrary detention and criminal prosecution of three lawyers who had been defending the prominent opposition figure, Alexei Navalny.
“These criminal proceedings, constituting persecution of lawyers, severely compromise the administration of justice in Russia and undermine the ability of all lawyers to defend their clients’ human rights and uphold the rule of law”, said Temur Shakirov, interim Director of ICJ Europe and Central Asia Programme.
On 13 October 2023, Vadim Kobzev, Alexey Liptser and Igor Sergunin – who had been acting as Navalny’s defence lawyers — were arrested and detained at Basmanny District Court in Moscow on charges of purportedly participating in an “extremist community”, with a potential sentence of up to six years’ imprisonment if convicted. As such, the criminal proceedings against Vadim Kobzev, Alexey Liptser and Igor Sergunin amount to persecution.
The charges are reportedly based on accusations that the three lawyers facilitated Navalny’s communication with the outside world while in detention.
Moreover, another lawyer representing Navalny, Alexander Fedulov, apparently fearing being arrested, was forced to flee the country following the arrest of his three colleagues.
The arrest and detention of the three lawyers and Fedulov’s flight significantly disrupt Navalny’s ability to defend himself through the assistance of qualified, independent legal counsel of choice, and his ability to challenge the criminal convictions and sentences, which led to his detention since 2022 as a result of a series of criminal cases against him widely believed to be politically motivated.
“The detention of Navalny’s lawyers is likely to constitute part of a wider strategy to isolate him even further. Moreover, it sends a chilling message to anyone wishing to defend human rights and political activism”, said Shakirov. “This is contrary to the right of lawyers to practise their profession freely, and it denies Navalny his right to legal representation, a fair trial guarantee protected under international human rights law binding on the Russian Federation”.
The ICJ stresses that the harassment and arbitrary detention of lawyers contravene the Russian Federation’s obligations under international law, including under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers. They affirm the crucial role of lawyers in upholding the rule of law and protecting human rights. It is crucial to ensure that lawyers can perform their legitimate professional functions without intimidation, hindrance, harassment, or improper interference, as guaranteed under the Basic Principle on the Role of Lawyers.
“The ICJ calls on the Russian Federation: to immediately stop this flagrant violation of the guarantees afforded to lawyers under international human rights law; for an end to these persecutory criminal proceedings; for all charges against Vadim Kobzev, Alexey Liptser and Igor Sergunin to be dropped; and for them to be immediately released”, added Shakirov.
Furthermore, the ICJ urges the Russian authorities to cease the persecution and harassment of lawyers and to take steps to ensure a safe environment where lawyers can operate without fear of reprisal for their work.
Background:
According to the UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers, governments must ensure that lawyers are able to perform all of their professional functions without intimidation, hindrance, harassment or improper interference and must not face sanctions for discharging their duties in accordance with professional standards and ethics (Principle 16). Furthermore, lawyers must not be identified with their clients or their clients’ causes as a result of discharging their functions. (Principle 18).
The UN Basic Principles also specify that lawyers like others have a right to freedom of expression and in particular the right to take part in public discussion of matters concerning the law, the administration of justice and the promotion and protection of human rights” (Principle 23)
The arrest of the three lawyers has prompted a call for a strike within the Russian legal community to demonstrate against the hostile environment within which lawyers in the Russian Federation operate, particularly those defending human rights and representing political activists.









