Jun 26, 2024 | Advocacy, News
The ICJ recalls that, under international law, security forces must respect the principles of necessity and proportionality and that the use of lethal force is only permissible when strictly necessary to protect life.

Jul 14, 2022 | News
Sri Lanka’s President Gotabaya Rajapaksa should immediately submit his promised resignation and the Sri Lankan Parliament should immediately convene and follow a transition process in accordance with the Sri Lankan Constitution, said the International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) today.

Jun 4, 2021 | News
Colombian authorities should immediately stop law enforcement officials from using excessive force to respond to protests and withdraw the military from law enforcement functions, said the ICJ today.
Over the course of ongoing protests, largely against economic and social conditions, multiple human rights and other civil society organizations have documented widespread human rights violations, including instances of torture and ill-treatment, sexual violence, extrajudicial killings, and enforced disappearances.
“The reports of violence and excessive and often unnecessary use of force by law enforcement officials are part of a wider failure of the authorities to adopt effective measures to protect and guarantee the right to life and the right to peaceful protest” said Carolina Villadiego, ICJ legal adviser for Latin America.
According to Indepaz, a local Non-Governmental Organization, as of 30 May 2021, at least 71 people had been killed, likely unlawfully, in the context of the protests. The situation is particularly dire in Cali where in just one day, 28 May 2021, 13 people were reportedly killed. In addition, it has been documented that firearms and lethal force have been deployed against protestors, including indigenous persons, by armed individuals in Cali. In at least one incident, multiple video recordings show police officials were present during the shootings and took no action to stop the shootings or apprehend the armed individuals.
Police and other law enforcement officials have the obligation to defend the rights of people, including their right to protest, and to protect them from violence by others. Colombian law enforcement officials have not only violated their obligation to avoid use of unnecessary or excessive use of force against people, but in Cali, they seem to have failed to prevent criminal violence by armed individuals as well.
“There must be a prompt, thorough and impartial investigation into these violations with a view to holding accountable those responsible”, said Carolina Villadiego.
The ICJ is also deeply concerned with militarization of the response to the protests. On 28 May 2021, President Duque issued Decree 575 of 2021 that authorizes the intervention of military forces in at least eight departments out of thirty two in the country, to assist in the lifting of any kind of roadblocks and to prevent the installation of new blockades by protesters. The Decree fails to consider any limitation of the use of force by military forces in line with international law standards such as the UN Basic Principles on the Use of Force by Law Enforcement.
Additionally, the sweeping and overbroad scope of the Decree to involve the military forces in what are inherently law enforcement functions does not consider that they are not trained or designed to protect civilians during protests or scenarios of public order disruption.
The ICJ urges the Colombian Government to fully respect the UN Basic Principles and other international standards on the use of force and the intervention of military forces to control protests and demonstrations. In this regard, the Government must fully comply with the September 2020 ruling on measures to guarantee peaceful protests issued by the Colombian Supreme Court.
In the ruling, the Supreme Court identified serious violations regarding the intervention of law enforcement officials, especially police officials, in protests and demonstrations. The Court identified systematic violence against demonstrators, the existence of stereotypes and prejudice against those who criticize the government’s policies, and a lack of mechanisms to hold the officials accountable.
Consequently, the Court ordered several measures to address this situation and guarantee the right to peaceful protest, including adopting and implementing a protocol to regulate the use of force during protests and manifestations, in accordance with international human rights standards.
The ICJ also calls on the Colombian Government to guarantee the right to peaceful protest. As the UN Human Right Committee has clearly affirmed, the right to peaceful protest may entail the disruption of vehicular or pedestrian movement, which “may be dispersed, as a rule, only if the disruption is “serious and sustained””.
While the vast majority of protestors have acted peacefully, there have been some instances where they have not. The ICJ calls on all persons to avoid violence during the protests and condemns the crimes committed against police officials, including the killing of at least two police officers, the serious injuries suffered by one police officer after being hit by a Molotov cocktail, and the sexual violence suffered by a police woman.
The ICJ deplores the particular use of some roadblocks that have affected the delivery of essential medical services, as well as the fires at the courthouse in Tuluá and other public buildings. Any individual engaging in criminal behaviour must be impartially investigated and, if found guilty in a fair trial, brought to account.
Finally, the ICJ also urges the National Government to fully cooperate with the mission of the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights (IACHR) to Colombia that will take place from 8 June to 10 June 2021. The Government should respect and ensure the IACHR’s independence and autonomy during the visit.
Contacts:
Carolina Villadiego Burbano, Latin American Legal and Policy Adviser, email: carolina.villadiego(a)icj.org
Rocío Quintero M, Latin American Legal Adviser, email: rocio.quintero(a)icj.org

Feb 22, 2021 | Advocacy, News
On 13 and 20 February 2021, the ICJ, jointly with Centre for Civil and Political Rights (CCPR Centre), held two consultative sessions on international law and standards relating to the right to freedom of expression, peaceful assembly and the use of force in law enforcement operations.
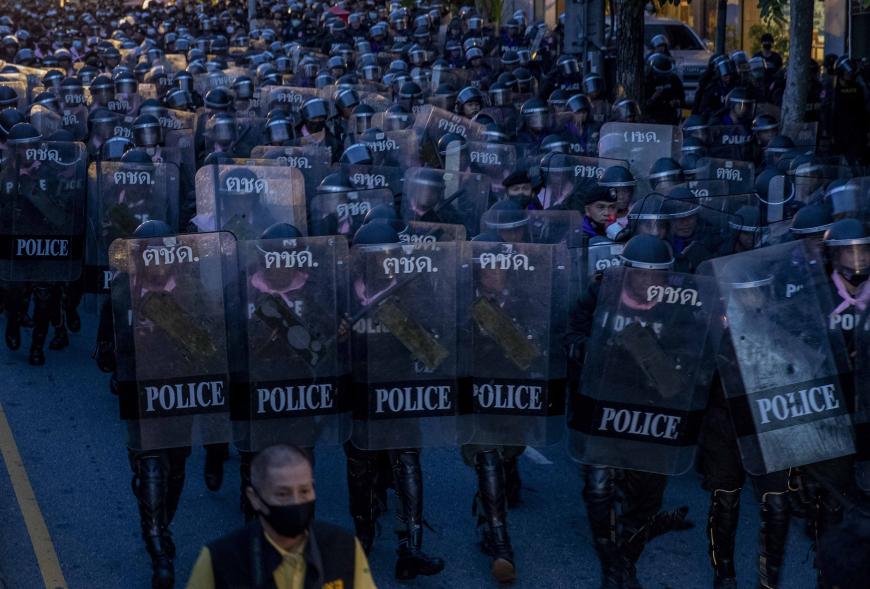
The discussions took place against the backdrop of recent widescale protests in Thailand, in which people exercising the rights to peaceful assembly and freedom of expression were met with sometimes unlawful force by security units.
Twenty-five Thai and international lawyers, civil society representatives and academics attended both discussion sessions, some participants in person and others online.
The 13 February session focused on relevant international law and standards relating to the rights to freedom of expression, peaceful assembly and the use of force in law enforcement operations, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), to which Thailand is a party, The sessions were led by Daisuke Shirane, CCPR Centre Asia Pacific Coordinator; Badar Farrukh, OHCHR Regional Office for South-East Asia Human Rights Officer; and Chonlathan Supphaiboonlerd, ICJ Associate Legal Adviser.
Participants considered the exercise in practice of the rights to freedom of expression and information, rights that have recently been unduly restricted in Thailand. Such restrictions were said to have resulted in violations of the rights of individuals who increasingly rely on online platforms, particularly social media platforms such as Facebook and Twitter, to share information on the protests and to express their opinions on the reform movement.
The session included a Q&A session with Christof Heyns, former member of the UN Human Rights Committee and Special Rapporteur on summary, arbitrary and extrajudicial executions. The discussion focused on the scope of the right of peaceful assembly, COVID-19 related restrictions, the State’s duty to facilitate peaceful assembly, and the international legal requirements of legality, necessity and proportionality on State’s response against the protesters.
In the 20 February consultation, Aram Song, attorney of the MINBYUN-Lawyers for a Democratic Society from South Korea, shared with the participant his experiences representing victims of human rights violations arising from police responses to protesters. He discussed the unlawful use of force and the constitutionality of regulations and ordinance that restricting the right to expression and peaceful assembly in the courts. Thereafter, Gayoon Baek, Chief Secretary of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission of the Republic of Korea, gave her views on how to conduct advocacy through international human rights mechanisms to ensure the right to freedom of expression and peaceful assembly.
This workshop is part of the ICJ’s ongoing efforts to bring existing Thai laws in compliance with international laws and standards that regulating the right to freedom of expression and peaceful assembly.
Further reading
Thailand: ICJ co-hosts round-table on right to peaceful assembly