
Mar 28, 2018 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ today submitted a report to the UN Committee against Torture, calling for recommendations to be made on prevention of and accountability for continued recourse to torture and ill-treatment in Tajikistan.
The ICJ’s submission is made ahead of consideration by the Committee against Torture in April to May 2018 of Tajikistan’s third periodic report on the implementation of its obligations under the Convention against Torture and Other Forms of Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment.
The ICJ’s report draws from an earlier study on Achieving Justice for Gross Human Rights Violations in Tajikistan and calls on the Committee against Torture to make recommendations concerning:
- The obligation to adequately sanction torture;
- The obligation to prevent torture and other forms of ill-treatment, including in places of detention;
- The obligation to investigate allegations of torture and ill-treatment;
- The use of amnesties and pardons for torture;
- The prohibition against the use of evidence obtained by torture;
- The right to complain about torture and ill-treatment; and
- The right of victims to effective remedies and reparation.
Tajikistan-CAT-Advocacy-AlternativeReport-2018ENG (download the ICJ’s submission, in PDF)
Mar 22, 2018 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
Today, the ICJ together with Forum for Human Rights submitted written information to the Committee against Torture ahead of its examination of the periodic report of the Czech Republic.
The two organisations argue that the Czech Republic violates Articles 2, 14 and 16 of the Convention Against Torture, by not ensuring access to a lawyer for children below the age of 15 (the age of criminal responsibility) in the pre-trial stage of juvenile justice proceedings.
1273 children younger than 15 were part of these pre-trial stage proceedings in the Czech Republic in 2017 without access to procedural guarantees, including legal counsel, unlike children aged 15-18 have under national legislation.
Children below the age of criminal responsibility do not benefit from such procedural rights and therefore, during the police questioning, they are typically left without any legal assistance and presence of a lawyer who neither can deter the police from resorting to ill-treatment or other abuses, nor work as a protection for police officers in case they face unfounded allegations of ill-treatment.
This situation constitutes a violation of the obligation to prevent torture or acts of cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment which do not amount to torture under Articles 2 and 16 of the CAT. Additionally, the Czech Republic fails to ensure access legal counsel for the purposes of an effective remedy under Article 14 of the CAT.
The joint submission aims to inform the 63rd session of the Committee Against Torture in April-May 2018 during which the Sixth periodic report of the Czech Republic will be examined.
Read the full joint submission here:
Czech-Republic-Joint-writteninformation- against-torture-2018-ENG (Full text in ENG, PDF)
Mar 14, 2018 | News
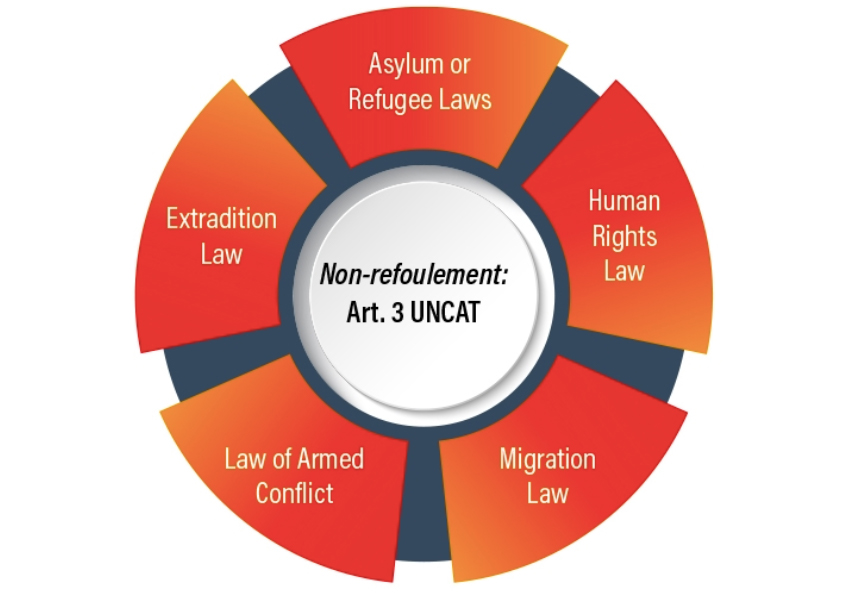
The new CTI tool on non-refoulement covers:
- constitutional and legislative provisions;
- national procedures;
- procedural rights to be guaranteed to those facing deportation or expulsion;
- training; and
- visa and stay arrangements for when return is prohibited.
There is also a section on non- refoulement in the extradition context.
The purpose of this and other CTI Implementation Tools is to inspire other States to take action through exchanges of good practices.
The tool also provides timely and practical information and advice for States in light of the recently released UN Committee against Torture’s General comment on the implementation of Article 3 of the Convention in the context of Article 22.
Some of the laws mentioned in this tool detail the powers that can be exercised by State authorities to remove a person and the constraints on those powers, as well as the relevant administrative and judicial procedures to be followed. National legislation has also detailed the rights of persons within those procedures (photo).
The tool was developed for the CTI by the ICJ with the support of the University of Bristol’s Human Rights Implementation Centre.
CTI’s series of UNCAT Implementation Tools are available here.

Feb 27, 2018 | Events, News
The ICJ, in collaboration with the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights Regional Office for South-East Asia (OHCHR), and the Centre for Civil and Political Rights, organised a workshop for lawyers from southeast Asia, on engaging with UN human rights mechanisms.
The two-day workshop provided some thirty lawyers from Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam, and Lao PDR with knowledge, practical skills and expert advice about UN human rights mechanisms, with the participants themselves sharing their own experiences and expertise.
In addition to explaining what the UN mechanisms are and how they work, the workshop discussed how lawyers can use the outputs of UN human rights mechanisms in their professional activities, as well as how to communicate with and participate in UN human rights mechanisms in order to ensure good cooperation and to best serve the interests of their clients.
Sessions were introduced by presentations by the ICJ’s Main Representative to the United Nations in Geneva and OHCHR officials, followed by discussions and practical exercises in which all participants were encouraged to contribute questions and their own observations.
A special discussion of effective engagement of lawyers with Treaty Bodies was led by Professor Yuval Shany, a member of the Human Rights Committee established to interpret and apply the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR).
The workshop also aimed to encourage the building of relationships and networks between the lawyers from across the region.
The workshop forms part of a broader project of awareness-raising and capacity-building for lawyers from the region, about UN mechanisms.
A similar workshop was held in January 2017 for lawyers from Myanmar.
The project has also published (unofficial) translations of key UN publications into relevant languages, and is hosting lawyers in a mentorship programme in Geneva.
More details are available by contacting UN Representative Matt Pollard (matt.pollard(a)icj.org) or by clicking here: https://www.icj.org/accesstojusticeunmechanisms/

Feb 26, 2018 | Events
On 28 February 2018, the ICJ is holding a workshop on combatting sexual and gender-based violence (SGBV) in Swaziland, in cooperation with Women and Law in Southern African – Swaziland (WLSA Swaziland) and the Swaziland Action Group Against Abuse (SWAGAA).
The workshop, held as part of the ICJ’s Global Redress and Accountability Initiative, will consider the prevalence of SGBV in Swaziland, and contributing factors, and will focus on the extent to which perpetrators of such violence are, and can be, held accountable in law and in practice and the means by which victims of SGBV may better access effective remedies and reparation.
Participants will also discuss opportunities for engagement with UN mechanisms on addressing SGBV in the Kingdom of Swaziland.
The workshop is set against the backdrop of urgent recommendations adopted by the UN Human Rights Committee in 2017 on the combatting of violence against women, in respect of which Swaziland must report to the Committee by July 2018.
It comes ahead of Swaziland’s anticipated report, also due in July 2018, to the UN Committee on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women which in 2014 also adopted several recommendations on the combatting of violence against women.
The workshop also comes as national debates continue on the enactment of the Sexual Offences and Domestic Violence Bill, which Swaziland had committed to enact without delay at its 2016 Universal Periodic Review.
Workshop Agenda









