
Mar 16, 2021 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
Today, during a debate on the outcome of the Universal Periodic Review of Libya, the ICJ called on Lybian authorities to bring the country’s criminal legislation in line with international law, in particular by defining clearly crimes under international law.
The statement reads as follows:
“Madame President,
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) welcomes Libya’s acceptance of the recommendation to cooperate fully with the Independent Fact-Finding Mission on Libya and ensure that it has unfettered access throughout the country’s territory (148.7-8, 148.11-17).
The ICJ regrets that Libya has only taken note of – as opposed to accepting ‒ Estonia’s recommendation (148.80) to bring the Penal Code in line with international standards, and Libya’s rejection of Zambia’s recommendation (148.70) to define crimes under international law in Libya’s domestic legal system clearly.
Libyan domestic law fails to criminalize: arbitrary deprivation of life; torture and other ill-treatment; enforced disappearance; rape and other forms of sexual and gender-based violence; slavery; war crimes; and crimes against humanity, in line with international law and standards.
The ICJ further welcomes Libya’s acceptance of the recommendations (148.144-146, 148-149, 151-161, 165-166) to investigate effectively crimes under international law and bring perpetrators to justice.
The ICJ expresses concern, however, at the prevailing impunity in the country. Crimes under international law are not being effectively investigated and prosecuted, largely because of the absence of political will, inadequate resources, and the frequent threats against justice actors, particularly by armed groups.
The ICJ also regrets that Libya failed to accept the recommendations of: Ukraine (148.25); Costa Rica (148.31); Cyprus (148.32); France (148.33); the Holy See (148.34); Liechtenstein (148.35); Namibia (148.36); Portugal (148.37); Rwanda, Croatia and Slovakia (148.37); Argentina (148.38); Australia (148.39); Honduras (148.40); Iceland (148.41); Italy (148.42); and Latvia (148.43). These recommendations call on Libya to establish a moratorium on executions, and to accede to the Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights with a view to abolishing the death penalty. The death penalty constitutes a violation of the right to life and of the absolute prohibition of torture and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment.
I thank you.”
Contact:
Massimo Frigo, ICJ UN Representative, e: massimo.frigo(a)icj.org, t: +41797499949
Vito Todeschini, Legal Adviser, ICJ MENA Programme, e: vito.todeschini(a)icj.org

Mar 16, 2021 | Advocacy
This side event will take place on Tuesday 16 March 2021, from 14:00-15:00 (CET) at the 46th session of the UN Human Rights Council. For registration: https://bit.ly/3llCCMF
Minority Rights Group International and South Asia Collective, along with ICJ, OMCT, Article 19 and FORUM-ASIA, are hosting a side event at 46th session of the Human Rights Council, on hate speech and incitement in South Asia. The aim is to instigate discussion on the causes and consequences of hate speech in South Asia, in the hope of encouraging UN and its agencies to engage better on preventive and early warning actions in the region.
Speakers
- Fernand de Varennes – UN Special Rapporteur on Minority Issues
- Alice Wairimu Nderitu – UN Special Advisor on the Prevention of Genocide
- Haroon Baloch, Pakistan – Digital Rights Researcher, Bytes for All Pakistan
- Farah Mihlar, Srilanka – Lecturer, University of Exeter; Srilanka Minority Rights campaigner
- Shakuntala Banaji, India – Professor of Media, Culture and Social Change at London School of Economics
Moderator
- Joshua Castellino – Executive Director, Minority Rights Group International
Mar 15, 2021 | Advocacy, News
The ICJ and a group of Sri Lankan judges have agreed on the importance of taking effective measures to address discrimination and equal protection in accessing justice in the country.
On 6 and 13 March 2021, the ICJ, in collaboration with the Sri Lanka Judges’ Institute (SLJI), organized the National Judicial Dialogue on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women and Enhancing Women’s Access to Justice. This event was organized under the ‘Enhancing Access to Justice for Women in Asia and the Pacific’ project funded by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (SIDA).
Twenty magistrates and District Court judges from around Sri Lanka, with judicial and legal experts from other countries, participated in this judicial dialogue which was conducted virtually due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The dialogue highlighted how Sri Lankan women continue to face a myriad of challenges including legal, institutional and cultural barriers when accessing justice. Gender biases and discriminatory behaviour prevalent in every aspect of justice delivery needs to be dealt with in order to effectively enhance women’s access to justice.
Boram Jang, ICJ International Legal Advisor remarked that “judiciaries have an important role to play in eliminating gender discrimination in justice delivery as it is a critical component in promoting women’s access to justice. In order to do so, the judges should be equipped with a full understanding of Sri Lanka’s obligations under the CEDAW and other human rights instruments.”
Honorable L. T. B. Dehideniya, Justice of the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka and Executive Director of the SLJI expressed hope that judicial dialogues such as this would “enhance the capacity of participant judges to use the international legal instruments, which Sri Lanka has ratified, in domestic judicial work especially with regard to the elimination of gender inequalities and biases.”
Ms. Bandana Rana, Vice Chair of the CEDAW Committee led a discussion with the judges on the application of the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), pointing out that “judges play a pivotal role in identifying the incongruences between existing laws and international human rights standards and ensuring that the full gamut of women’s human rights is retained in line with the CEDAW framework.”
Justice Ayesha. M. Malik, High Court Judge, Lahore, Pakistan affirmed the importance applying the right to access to justice under international human rights law and suggested strategies for reflecting these international standards in judicial decisions.
Attorney Evalyn Ursua addressed on gender stereotypes and biases in justice delivery and engaged the participants on how these could be effectively eliminated. She stated that “the judiciary as a part of the State has the obligation to eliminate gender discrimination.” She encouraged the judges to use the cultural power of law to change language and attitudes surrounding gender discriminatory behaviour and stigma.
The second day featured a discussion on the specific barriers that women in Sri Lanka face when they access justice. Hon. Shiranee Tilakawardane, former Justice of the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka led a discussion on the role and measures available to the judiciary as an institution to enhance access to justice for Sri Lankan women.
Justice Tilakawardane stated that “While theoretically, the Sri Lankan constitution enshrines equality before the law, in reality women continue to feel disadvantaged when they try to access justice” and added “the Sri Lankan judiciary can empower its women only when it understands, acknowledges and addresses the disadvantages they face owing to their gender.” She impressed upon the participant-judges that “ensuring equality is no longer a choice, nor is it merely aspirational, but a pivotal part of judicial ethics.”
The panelists on the second day surveyed the legal, institutional and cultural challenges faced by women at every step of the judicial process. The panel comprised of Prof. Savitri Goonesekere, Emeritus Professor of Law and Former member of the CEDAW Committee, Mrs. Farzana Jameel, P.C, Additional Solicitor General of the Attorney General’s Department and Mrs. Savithri Wijesekara, Executive Director of Women in Need.
Contact
Osama Motiwala, Communications Officer – osama.motiwala@icj.org
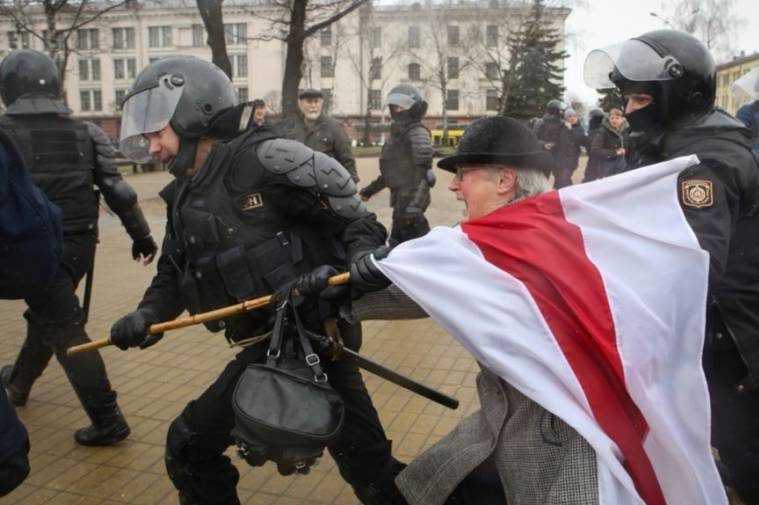

Mar 15, 2021 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
Today, the ICJ joined IBAHRI, Human Rights House Foundation and the OMCT in a statement before the UN Human Rights Council condemning human rights violations against lawyers in the country.
The joint statement delivered during the debate on the outcome of the UPR of Belarus reads as follows:
“The IBAHRI, the International Commission of Jurists, the Human Rights House Foundation and the OMCT would like to echo concerns that have been raised during the UPR review and are reflected in the UPR outcome document.
We strongly condemn the numerous, widespread human rights violations committed in the aftermath of the 2020 Belarus Presidential election, in particular:
- First – The disproportionate use of force by security forces against peaceful protestors, the arbitrary arrest and detention of thousands of people, systematic torture and ill-treatment following arrest or during detention, reports of enforced disappearances and denied access to a lawyer.
- Second – The systematic control of the executive over the judiciary and the court system. The judiciary continues to selectively use legislation to intimidate dissenting voices and tightly controls the licensing and activities of lawyers working under threat of being targeted.
- Third – The Illegal and arbitrary restrictions to fundamental rights and freedoms, including the right to peaceful assembly, free expression and access to information. From violent targeting of journalists and the media, to state sanctioned internet shutdowns resulting in censorship.
Therefore, we urge Belarus to:
- Immediately and unconditionally release all individuals arbitrarily detained and stop any practices of torture and ill-treatment of detainees;
- Undertake impartial, independent, effective and prompt investigations into allegations of human rights abuses;
- Bring perpetrators to justice, ensuring effective remedy and reparation for victims;
- Allow professionals – including legal and media professionals – to conduct their work without fear of targeting;
- Ensure respect and practice for all human rights, including free expression, online and offline, providing unconstrained access to information for all; lastly
- Adopt all necessary measures to prevent further human rights violations, without delay.”
Contact:
Massimo Frigo, ICJ UN Representative, e: massimo.frigo(a)icj.org, t: +41797499949
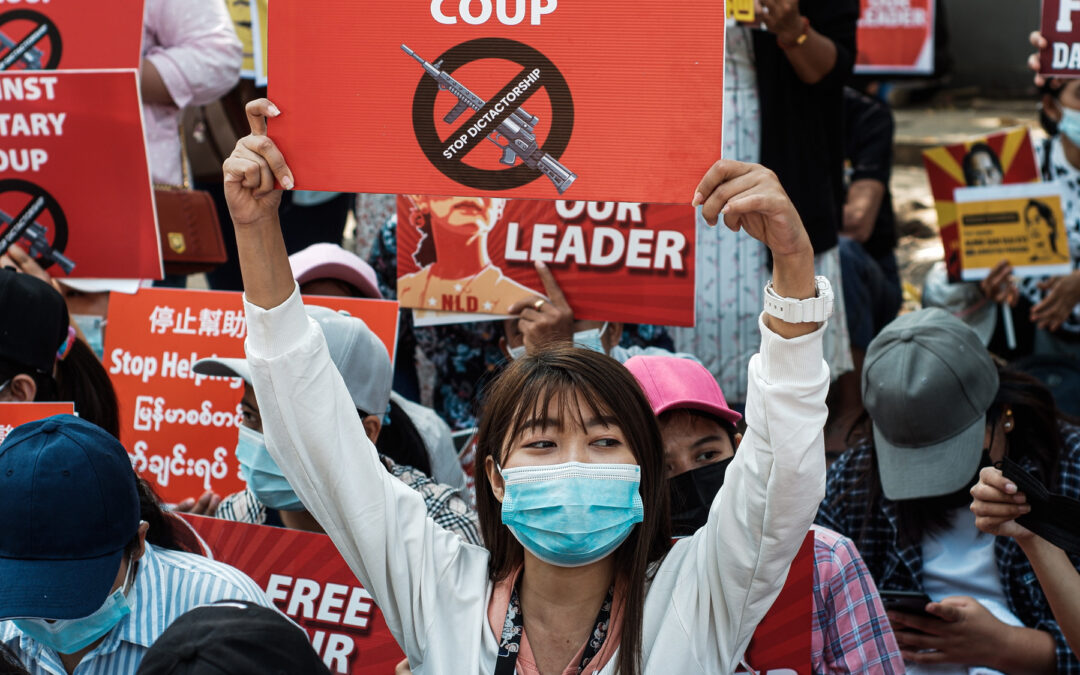

Mar 15, 2021 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
Today, during a General Debate, the ICJ called on the UN Human Rights Council to condemns a set of laws amendend by the military governmentn in Myanmar and restricting human rights, and to demand the return to of Myanmar civilian rule respecting the rule of law.
The statement reads as follows:
“Madame President,
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) condemns the illegitimate attempts to “amend” several laws by the Military appointed Myanmar’s State Administration Council (SAC) following its unlawful seizure of power on 1 February 2021.
The implementation of the Amended Law Protecting the Privacy and Security of Citizens (2017) would undermine the democratic process, criminalize peaceful protests and remove various human rights protections. It would provide for broad and unchecked power to the military to arrest anyone without a warrant and aim to remove basic protections, including the rights to be free from arbitrary detention and from warrantless surveillance and search and seizure.
The amendments to the Penal Code and the Criminal Procedural Code have made non-bailable certain offenses, specifically targeting persons criticizing the coup or the military junta, as well as those encouraging others to support the “Civil Disobedience Movement.”
In addition, Amendments made to other existing laws, such as the Ward and Tract Administration Law and Electronic Transactions Law, allow for search and seizure at night without arrest warrant and allow for the silencing of critical voices against the coup and human rights violations of the military, in violation of international standards.
The ICJ calls on the Council to adopt a resolution, which, among other things, univocally condemns and demands the repeal of these laws and the return to of Myanmar civilian rule respecting the rule of law.
Thank you.”

Mar 12, 2021 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
Today, the ICJ delivered a statement to the UN Human Rights Council calling for accountability for crimes against humanity committed in Myanmar during the Interactive Dialogue on the report by the UN Special Rapporteur on the situation of human rights in Myanmar.
The statement reads as follows:
“Madame President,
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) welcomes the recent report of the Special Rapporteur on the situation of human rights in Myanmar.
The widespread gross violations of human rights documented in the report – including extrajudicial killings, arbitrary arrests and detention- underscore the need for urgent measures of accountability to redress these and to deter further violations.
ICJ has documented further evidence that the unlawful crackdown against peaceful protestors have continued to worsen leading to more extrajudicial killings. More than 50 people have already been unlawfully killed and several hundreds have been severely injured.
Hundreds of others have been arbitrarily arrested and detained, with some subjected to torture and ill-treatment. As the scale of violations continues to increase in many parts of the country, these attacks have become systematic and widespread, and must be investigated as crimes against humanity.
The ICJ therefore supports the recommendations made by the Special Rapporteur, including for referral of the situation to the ICC.
The ICJ urges the Council to adopt a resolution that would strengthen and support the IIMM’s work to collect and preserve evidence for accountability; and to extend the mandate of the Special Rapporteur, including to ensure the immediate, full and unrestricted monitoring of the situations and prompt and effective implementation of their recommendations.
Thank you.”
Contact:
Massimo Frigo, ICJ UN Representative, e: massimo.frigo(a)icj.org, t: +41797499949










