
Apr 2, 2021 | News
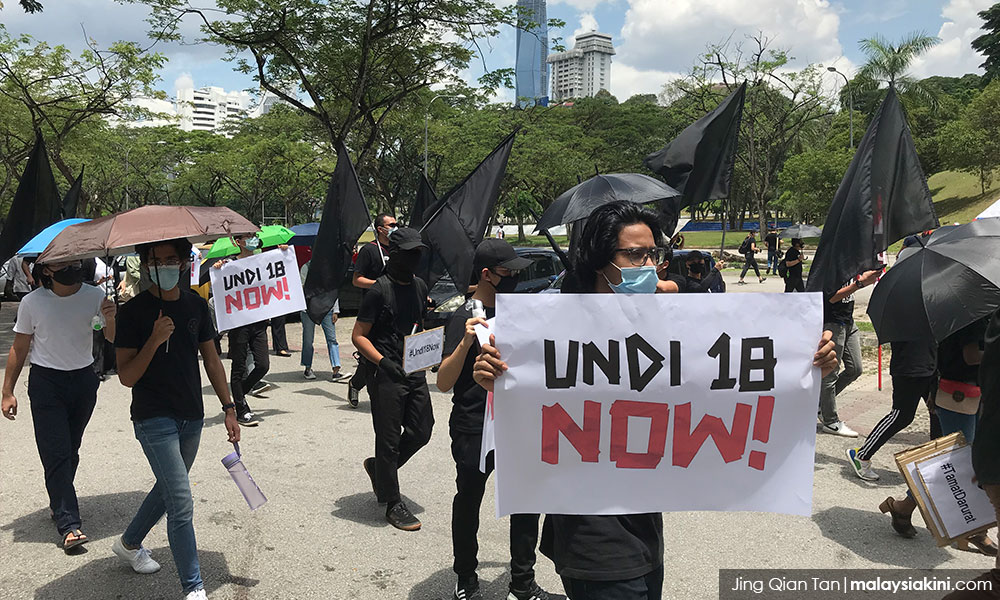
The ICJ today called on the Malaysian authorities to drop their criminal investigations of at least 11 participants in the peaceful Undi18 protests.
The Dang Wangi district police opened investigations against Dato’ Ambiga Sreenevasan, an ICJ Commissioner, and at least ten other individuals including Simpang Renggam MP Maszlee Malik, Petaling Jaya MP Maria Chin Abdullah, and Segambut MP Hannah Yeoh in relation to the wholly peaceful and socially distanced Undi18 protest rally held on 27 March 2021.
They are being investigated for alleged violations of section 9(5) of the Peaceful Assembly Act 2012 (‘PAA’) and Regulation 11 of the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases (Measures Within Infected Local Areas) (Conditional MCO) (No. 4) Regulations 2021 (‘MCO No. 4 Regulations’).
The ICJ said that the application of these laws against the protestors would not be consistent with international law and standards on freedom of expression and peaceful assembly.
The ICJ said that the investigations seem intended to harass and intimidate those who would exercise their rights to free expression and peaceful assembly.
If charged and convicted, violations of the PAA could result in a fine of up to RM$10,000 (approx. USD 2,410). Violations of the MCO No. 4 Regulations may result in a prison term of up to six months and/or a fine of RM$10,000 (approx. USD 2,410).
The ICJ reiterated its previous call for Malaysian legislators to reform the PAA, which imposes unjustifiably burdensome restrictions carrying excessive penalties on the exercise of freedom of expression and assembly.
Contact
Boram Jang, International Legal Adviser, Asia & the Pacific Programme, e: boram.jang(a)icj.org
Background
In July 2019, the Malaysian Parliament unanimously voted to lower the voting age from 21 to 18 years old.
On 25 March 2021, the Election Commission announced that it would postpone the implementation of this new rule from July 2021 to September 2022 at the latest. The Commission cited the COVID-19 lockdowns as a reason for the delay. This would affect the ability of 1.2 million people to vote, if elections are called later this year.
On 27 March 2021, hundreds of individuals gathered peacefully in front of Malaysia’ Parliament building to protest this delay. It was reported that the protestors were wearing face masks and trying to observe physical distancing, with some protestors donning full personal protective equipment.
On 29 March 2021, 11 individuals were summoned for questioning for alleged violations under section 9(5) of the PAA and Regulation 11 of the MCO No. 4 Regulations.
On 30 March 2021, eight of them gave their statements at the Dang Wangi police station in Kuala Lumpur. Four others, including Dato’ Ambiga Sreenevasan, will give their statements on 2 April 2021.
Section 9(5) of the PAA imposes a requirement for a five-day notice of an assembly to the Officer in Charge of the Police District. Failure to do so may result in a fine not exceeding RM$10,000 (approx. USD$2,410). Section 21A also allows the police to issue compounds of up to RM$5,000 instead of a charge being proffered subject to the written consent of the Public Prosecutor.
Regulation 11 of the MCO No. 4 permits the gathering or involvement in a gathering subject to any directions issued by the Director General. Regulation 17 states that failure to comply may result in a fine not exceeding RM$1,000 (approx. USD$241), imprisonment for a term not exceeding six months, or both. Additional emergency laws have raised the potential fine that may be imposed to up to RM$10,000 (approx. USD$2,410).
Apr 1, 2021 | Agendas, Events, News
Migrants and asylum seekers must be provided adequate procedural guarantees in asylum procedures and in immigration detention, a group of experts and judges asserted during a seminar for Greek and Italian judges held by the ICJ, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna (SSSA), and Greek Council for Refugees (GCR) on 29-31 March.
Asylum applicants should have access to adequate information about the procedure and their entitlements in a language they understand, access to a reliable communication system with the authorities, the availability of interpreters, access to legal aid, and reasoned decisions, experts said during the seminar, held in the framework of the FAIR plus project. Speakers further emphasized that immigration detention must be subject to automatic review by an independent body with a power to release detainees, especially when removal is no more an option.
More than 30 judges from Italy and Greece came together for this event to discuss procedural guarantees for migrants and asylum seekers, related to the safe third country concept, the access to legal assistance and interpretation, safeguards related to immigration detention, and procedural guarantees in the asylum procedure, especially in the accelerated procedures.
A summary of the discussions
On the first day, the judges exchanged overviews of national systems and presented some specific questions regarding the Italian and the Greek systems. Following the discussion on the safe third country concept and its implementation in Greece, an Italian judge presented recent developments in the Italian case-law, and the role of the judge, country of origin information, accelerated procedures, the length of procedures and the question of credibility assessment.
On the second day, the discussion related to the impact of Covid-19 pandemic on the rights of migrants and asylum seekers took place. The situation in Greece and in Italy was described by judges, in particular in relation to the access to the asylum procedure, the lawfulness of detention, the right to health and the question of access to a personal hearing when some of the hearings take place electronically.
An overview of the situation of immigration detention in Italy and Greece was presented by an Italian lawyer and an expert from UNHCR Greece. Speakers highlighted that in cases when people cannot be returned, they should not be kept in detention without a legal basis.
Accelerated procedures in law and in practice in both countries have been introduced by UNHCR Greece and Italy were addressed through a case-study and discussion, covering mainly the specific needs in accelerated procedures, automatic suspensive effect of appeals, and time limits in the accelerated procedures.
Finally on the last day, two lectures were delivered by Ledi Bianku, a former judge of the European Court for Human Rights, and an Associate Professor at the University of Strasbourg. First, looking into the guarantees in asylum and migration proceedings, Ledi Bianku stressed the need to always provide asylum applicants adequate information about the procedure and their entitlements in a language they understand, access to a reliable communication system with the authorities, the availability of interpreters, access to legal aid, and reasoned decisions in order to provide access to an effective remedy. In the second part of his intervention, Mr. Bianku discussed the detention of migrants, where he stressed the need for automatic review of detention, especially when removal is no more an option, by an independent body with a power to release.
The FAIR plus project is a judicial training and cooperation project supported by the European Union’s Justice programme, focusing on four countries Ireland, Greece, Italy and the Czech Republic. The aim of the project is to contribute to better judicial protection of the fundamental rights of migrants across the EU. Within the project the ICJ and partners are drafting of training materials and relevant legal briefings, implement training of the existing judicial trainers in the target countries, conduct four national trainings, two transnational seminars, and an international roundtable. The project is implemented in collaboration with national partners: Immigrant Council of Ireland (ICI), Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna (SSSA), Greek Council for Refugees (GCR) and Forum for Human Rights (Czech Republic).
Please find the agenda here.

Apr 1, 2021 | News
The conviction of political activists Martin Lee, Margaret Ng, Jimmy Lai, Lee Cheuk-yan, Albert Ho, Leung Kwok-hung, Cyd Ho for their role in organizing public protests in 2019 delivers a massive blow to human rights and the rule of law in Hong Kong, said the ICJ.
“These convictions are the latest attack on the already weakened standing of the rule of law and democracy in Hong Kong,” said Ian Seiderman, the ICJ’s Legal and Policy Director.
The defendants were convicted by West Kowloon Magistrates’ Court on joint charges of organizing an unauthorized assembly under section 17A(3)(b)(i) of the Public Order Ordinance Cap. 245 and knowingly taking part in an unauthorized assembly under section 17A(3)(a) of the same Ordinance. Two other defendants, Au Nok-hin and Leung Yiu-chung, pleaded guilty in February before the trial began. They face up to five years in prison. Their sentences will be handed down at a later date.
“These prosecutions and convictions constitute persecution of human rights defenders, journalist, and politicians through abusive legal process. The unauthorized assembly provisions of the Public Order Ordinance has been used to silence lawful expressions of on matters of public concern,” said Ian Seiderman.
The Hong Kong SAR, though not the rest of the People’s Republic of China, is legally bound by the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), which guarantees to the right to freedom of assembly and expression. The ICCPR continues to be in force in Hong Kong by virtue of Article 39 of the Basic Law. The United Nations Human Rights Committee has repeatedly expressed concern that charging people under the Public Order Ordinance against peaceful protesters in Hong Kong stands to violate their human rights under the ICCPR.
The ICJ has previously pointed out that imposing criminal charge on people exercising their right of peaceful assembly who fail to comply with a procedural requirement, such as notification, unduly restricts freedom of peaceful assembly by adding unnecessary barriers to public gatherings. Furthermore, the sentencing guidelines of the Ordinance, which include the possibility of a peaceful participant of a public assembly being sentenced to five years in prison if the organizers fail to comply with the notification requirement, are extreme, disproportionate and open to abuse.
Background
On 12 August 2019 the Civil Human Rights Front (CHRF) submitted a Notification of Intention to hold a public meeting and procession, informing the police of the intention to hold a public assembly on 18 August 2019 starting from Victoria Park and ending at Chater Road, and a second public assembly at Chater Road. The police objected to the public procession from the Park to Chater Road. The CHRF appealed against the police decision and after an appeal hearing convened by the Appeal Board on 16 August 2019, the Board upheld the police decision and dismissed the appeal lodged by CHRF.
The CHRF held a press conference on 17 August 2019 wherein they said the police had not arranged for the dispersal of crowds from Victoria Park so pro-democracy legislators and other influential activists would be assisting the crowds to disperse safely to nearby MTR stations. On 18 August 2019 during the public assembly at Victoria Park and the defendants carried a long banner out of Victoria Park Gate 17 and led a procession of people to Chater Road, Central. The route taken followed the previously proposed route of the banned public procession. The procession finished at Chater Road with the defendants laying the long banner down on the road.
Contact
Boram Jang, International Legal Adviser, Asia & the Pacific Programme, e: boram.jang(a)icj.org
See also

Mar 31, 2021 | News
Today, the ICJ submitted recommendations to Thailand’s Office of the Council of State concerning the Draft Act on the Operation of Not-for-Profit Organizations B.E. … (‘Draft Act’), which is scheduled for public consultation between 12 and 31 March 2021.
The ICJ urged that the Draft Act be repealed in its entirety or substantially revised in order to ensure compliance with Thailand’s international legal obligations.
The ICJ is concerned that the law, if adopted, would pose onerous and unwarranted obstacles to many civil society organizations in Thailand, including human rights NGOs, in carrying out their work. In its submission, the ICJ underscores the imprecise and overbroad language of the draft law, which would allow for abusive and arbitrary application by the Thai authorities on “Not-for-Profit Organizations” (NPOs). In particular, it provides for discriminatory restrictions on organizations that receive foreign funding.
“It is well-established in international law and standards that any registration of NPOs should be voluntary and that no law should outlaw or delegitimize activities in defence of human rights on account of the origin of funding,” said Ian Seiderman, ICJ’s Legal and Policy Director.
Violators of the Draft Act would risk having their registration revoked. The Draft Act also imposes liability of criminal punishment on those who operate without registration with imprisonment not exceeding five years or fined not exceeding 100,000 THB (approx. 3,200 USD), or both.
“In cases of registration revocation, the legal recourse available for NPOs to challenge such decisions involves lengthy and burdensome administrative and judicial proceedings, which would normally take years to reach a conclusion. Proceedings of this kind will be untenable for some organizations and will deal a fatal blow to the essential work of many human rights defenders,” said Ian Seiderman.
The Draft Act also provides sweeping powers to government authorities to monitor activities, search and seize electronic data of NPOs without any court warrant, in violation of the rights to privacy.
Background
Thailand is a State party to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), which requires States to respect and protect, inter alia, the right to freedom of association, expression, peaceful assembly, the right to take part in the conduct of public affairs, the right to privacy and the right to an effective remedy. Thailand may impose limitations on NPOs only in narrow circumstances and subject to strict conditions as set out in the ICCPR.
On 23 February 2021, Thai Cabinet approved in principle the Office of the Council of State’s proposal to enact a law aims to provide oversight on NPOs’ operations.
The draft law is currently under consideration of the Council of State for legal review. Public consultation is currently carried out by the Office, only via their online platform. Members of the public were expected to have registered any concerns about the Draft Act through the website of the Office, by post or by email, between 12 to 31 March 2021 – a considerably tight period of time.
The draft law will then be resubmitted to the Cabinet, then presented to the Parliament.
Download
Recommendations in English and Thai (PDF)

Mar 30, 2021 | News
The ICJ today called for the reform of the country’s law on contempt of court to prevent their abuse and for the withdrawal of the contempt action filed against human rights lawyer Charles Hector.
Charles Hector faces potential contempt of court charges over a letter he sent to an officer of the Jerantut District Forest Office, as part of trial preparation. He is currently representing eight inhabitants of Kampung Baharu, a village in Jerantut, Pahang, in their civil lawsuit against two logging companies, Beijing Million Sdn Bhd and Rosah Timber & Trading Sdn Bhd.
The companies applied for leave to commence contempt of court proceedings against Charles Hector and the defendants. They claim that his letter violates an interlocutory injunction order prohibiting the villagers and their representatives from interfering with or causing nuisance to their work.
“Charles Hector is being harassed and intimidated through legal processes for carrying out his professional duties as a lawyer and gathering evidence in preparation for trial. The Malaysian authorities must act to protect human rights lawyers from sanctions and the threat of sanctions for the legitimate performance of their work,” said Ian Seiderman, the ICJ’s Legal and Policy Director.
The harassment of Charles Hector through legal processes violates international standards such as the UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers that make clear that lawyers must be able to perform their professional functions without intimidation, hindrance, harassment or improper interference.
Contempt of court, whether civil or criminal, may result in imprisonment and fines. Malaysia’s contempt of court offense is a common law doctrine and not codified statutorily.
“Fear of contempt charges stands to cast a chilling effect on the work of human rights lawyers and defenders. This further reinforces how Malaysia’s contempt of court doctrine needs to be urgently reformed as it is incompatible with international human rights law and standards,” said Seiderman.
The ICJ calls for the reform of Malaysia’s contempt of court doctrine to ensure clarity in definition, consistency in procedural rules and sentencing limits pertaining to criminal contempt cases. This reform should be in line with recommendations by the Malaysian Bar that the law of contempt be codified statutorily to provide clear and unequivocal parameters as to what really constitutes contempt.
Background
In September 2019, the two logging companies reportedly obtained approvals from the Jerantut District Forest Office to carry out logging in the Jerantut Tambahan Forest Reserve. The eight villagers are from a community many of whose residents have been protesting against the logging. The villagers depend on the forest reserve for clean water and their livelihoods.
On 14 July 2020, the companies filed a writ of summons against the eight villagers in the Kuantan High Court. The writ stated that the plaintiffs had applied for an injunction order to stop the defendants from preventing the companies’ workers from carrying out their works and spreading “false information” online.
On 5 November 2020, the companies successfully obtained an interlocutory injunction order. It was reported that the injunction order prohibits the defendants and their representatives from interfering with the approval given to the plaintiffs by the District Forest Office or causing nuisance to the work of the plaintiffs in any manner whatsoever, including physically, online or by communication with the authorities.
On 17 December 2020 Charles Hector sent a letter on behalf of his clients to Mohd Zarin Bin Ramlan, an officer of the Jerantut District Forestry Office, seeking clarifications on a letter sent by the office on 20 February 2020.
The logging firms contend that the letter violated the injunction order. In January 2021, the companies filed an ex parte application for leave to commence contempt of court proceedings against Charles Hector and the eight villagers.
The hearing was postponed until 25 March 2021 at the Kuantan High Court. On 25 March 2021, the plaintiff’s lawyer opposed the presence and participation of Charles Hector’s lawyer on the grounds that it was an ex parte application, which was contested by Charles Hector’s lawyer. The Court decided to adjourn the hearing to 6 April 2021.
Contact
Boram Jang, International Legal Adviser, e: boram.jang(a)icj.org

Mar 29, 2021 | News, Publications, Reports, Thematic reports, Uncategorized
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) has published a new report Accessing Economic and Social Rights in Uzbekistan: An Analysis of Selected Laws and Practices. In the report, it considers aspects of Uzbekistan’s implementation of its obligations to respect, protect and fulfil economic, social and cultural (ESC) rights through laws and policies as well as through access to justice and remedies for those who allege that their ESC rights have been violated.
Analysing the general legal framework for protection of these rights, the report considers in more detail particular challenges in Uzbekistan, in respect of the right to adequate housing, the right to health, and rights in the workplace.
In the report, the ICJ concludes that in-depth reforms of the justice system are still needed to ensure effective remedies for ESC rights violations in practice, including through genuine independence of the judiciary and regular application of international human rights law in and by the courts.
In general, the use of international law in the Uzbekistan justice system remains weak and underdeveloped. International law is to a high degree theoretical for most legal practitioners, an approach that appears to have its roots in legal tradition and culture, lack of political will and a lack of concrete programmes of measures to make progress in this regard. In practice, judges, prosecutors and lawyers continue not to be exposed to international law on ESC rights, and usually do not apply it in their work directly.
The report concludes that in Uzbekistan the justiciability of ESC rights is not always accepted, as some ESC rights are not seen as rights whose violation could or should be remedied through and by the courts. Rather, many actors see guarantees of non-discrimination or aspects of the right to health or education as benefits which are not of a justiciable nature. Lawyers, sharing a similar legal mindset and background, do not tend to demonstrate the necessary legal activism in pursuing judicial remedies in such cases.
The report contains five chapters. Chapter 1 of the report outlines the general issues which are essential to ensure access to justice for ESC rights in Uzbekistan. Chapter 2 is dedicated to issues related to the right to housing, its international legal aspects and national implementation. Chapter 3 discusses issues related to the right to health while Chapter 4 describes the aspects of the protection of the right to work internationally as well as in Uzbekistan. In Chapter 5, the report sets out conclusions and recommendations on access to justice as well as the measures to protect specific rights addressed in the report.
The publication of the report marks the conclusion of a three-year project, ACCESS, of the International Commission of Jurists (ICJ), which has worked to advance civil society engagement for the protection of ESC rights in Uzbekistan. It draws on several discussions in Uzbekistan, as well as on legal research carried out throughout the project.
Please see the report below:
In English: Accessing Economic and Social rights in Uzbekistan: an analysis of selected laws and practices
In Russian: Доступ к экономическим и социальным правам в Узбекистане: анализ законодательства и практики
In Uzbek: Ўзбекистонда иқтисодий ва ижтимоий ҳуқуқларни баҳолаш: айрим қонунлар ва амалиёт таҳлили
Please see the executive summaries below:
In English: Accessing Economic and Social rights in Uzbekistan: an analysis of selected laws and practices. Executive summary
In Russian: Доступ к экономическим и социальным правам в Узбекистане: анализ нормативно-правовых актов и практики. Резюме отчета.
In Uzbek: Ўзбекистонда иқтисодий ва ижтимоий ҳуқуқлардан фойдаланиш имкониятлари: алоҳида норматив-ҳуқуқий ҳужжатлар ва амалиёт таҳлили.Ҳисоботнинг қисқача мазмуни










