
Dec 21, 2020 | News
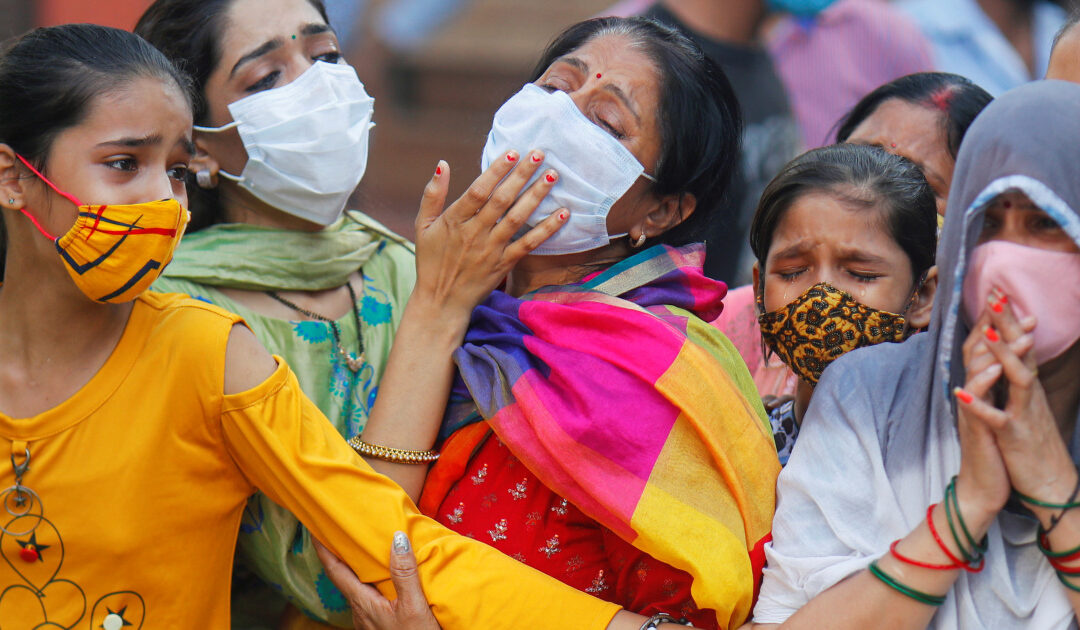
We are all about to celebrate the festive season. For a large number of people, there will be little to celebrate. Rule of Law & Human Rights violations are taking place, daily, unaccounted for and affecting their lives.
Here are some example:
- Failure to access healthcare of all people in India, Libya and South Africa;
- Enacting effective bans on abortion in some states in the USA;
- Failure to adequately tackle skyrocketing domestic violence around the globe during lockdown;
- Rights of refugees, stateless persons and destitute migrants being trampled on worldwide;
- LGBT minorities refused access to shelters;
- Ban on sexual education in Poland;
- Hungary’s prohibition of legal gender recognition;
- Curtailing of due process and fair trial rights;
- … and more
For almost a year, the ICJ has been on the front lines to document, advocate and provide efficient legal tools for civil society and the legal community to stop these abuses.
Please click on Donate, as little as 5 US$, to support ICJ fight against these repeated attacks on the most basic of Human Rights.
Dec 21, 2020 | News
Today, the Lebanese Center for Human Rights (CLDH) and the ICJ held a joint webinar on migrants and refugees in Lebanon. The organizations addressed the situation of migrant workers and refugees including their legal and social status and the violations to which they are exposed.
The ICJ and CLDH called on the Lebanese authorities to adopt and enforce just, fair and effective legal and policy frameworks to address the entry and stay of refugees and migrants in Lebanon, and ensure the protection of their human rights in full compliance with Lebanon’s obligations under international law, particularly their non-refoulement obligations.
The ICJ launched its recent report Unrecognized and Unprotected: The Treatment of Refugees and Migrants in Lebanon, which undertakes an assessment of the Lebanese legal framework governing the treatment of migrants and refugees in the country, including their entry and stay.
The report concludes that the legal and policy gaps, together with the executive’s excessive and unchecked powers in shaping and implementing migration-related policies, have led to serious violations to refugees’ and migrants’ human rights in Lebanon.
The ICJ presented the findings and key recommendations of its report, which included urging the Lebanese government to ensure that no individual is transferred to a country where he or she faces a real risk of persecution or other forms of serious harm, such as torture or other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment.
Procedural obstacles preventing migrant workers and refugees from accessing justice, such as lacking residency papers, were examined by CLDH.
The webinar, facilitated by CLDH’s Executive Director Fadel Fakih, commenced with opening remarks from Said Benarbia, Director of the ICJ’s Middle East and North Africa Programme, and Wadih Al-Asmar, President of CLDH. Attendees included civil society, lawyers, and members of the Lebanese Bar association.
Underscoring that Lebanon is obligated to protect the rights of refugees and asylum seekers despite not being a State party to the 1951 Refugee Convention, as these rights are guaranteed by other international conventions ratified by Lebanon including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the UN Convention against Torture and other Cruel, Inhuman and Degrading Treatment or Punishment (UNCAT), Al-Asmar called on the Lebanese State to abandon its repressive security approach towards refugee populations, and to abolish the exploitative Kafala sponsorship system.
Benarbia addressed how normative gaps, together with restrictive provisions of the 1962 Law of Entry and Exit, including those criminalizing “irregular entry,” undermine the right of refugees to an individual examination of their asylum claim, their right to liberty and security of person, and their right to an effective legal remedy for human rights violations.
He pointed out that laws and policies impacting on migrants and refugees should be adopted and implemented by legally constituted civilian authorities, subject to legislative oversight and judicial review.
CLDH members Hasna Abdul Reda and Rabih Keyrouz focused on the obstacles that continue to impede migrant workers and refugees from accessing justice in Lebanon. CLDH Programme Manager, Josiane Noun, presented CLDH’s Legal Aid Programme and support services that the organization has made available to migrant workers and refugees.
Kouakou Adjo Delphine, representing the Alliance of Migrant Domestic Workers in Lebanon, discussed the challenges domestic migrants face in accessing justice for human rights violations.
The conference concluded with an open discussion between panelists and participants where possible solutions to enhance the protection afforded to migrant workers and refugees in Lebanon were discussed.

Dec 18, 2020 | Agendas, Events, News
The ICJ and the Greek Council for Refugees (GCR) today hold the first part of the online training for Greek judges and lawyers on asylum procedures and detention of third country nationals as a part of the FAIR PLUS project.
The training brings together experts from the Greek Administrative Court of Appeal, Administrative Court of First Instance, European Court of Human Rights, GCR, ICJ and academics for a discussion on administrative detention on third-country nationals with a focus on the current situation in Greece.
Among the topics to be discussed today are domestic remedies to detention of third-country nationals; as well as deportation and detention of third country nationals in light of the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR), EU law and Greek constitutional and European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) case-law regarding immigration detention.
The second part of the training, on fair and effective asylum procedures, is planned for 15 January 2021, and will focus on Directive 2011/95/EE (inclusion clause in refugee protection status); asylum procedure and procedural guarantees; case-law of the CJEU on asylum and common issues of asylum applications – credibility and safe third country.
This is the third training delivered as part of this project, the first two having been held in person this January in Dublin and last December in Pisa.
See the agenda for both parts of the training in English and in Greek.
This training is a part of FAIR PLUS project. It was carried out with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents are the sole responsibility of ICJ and do not necessarily reflect the views of the European Union.

Dec 17, 2020 | News
The ICJ and the Human Rights Joint Platform released today a joint statement, calling attention to a variety of obstacles faced by those seeking access to justice for human rights violations in Turkey.
The statement includes 13 recommendations to the Turkish government to ensure the justice system can uphold human rights.
In Turkey, victims of human rights violations remain unable to access justice, particularly effective remedies and reparation for violations of their rights, and there is little accountability of the State or State authorities for what are often serious violations.
Access to Justice has suffered by the immense damage done to the justice system in Turkey in recent years. The systematic undermining of judicial independence, and of the work of prosecutors and lawyers, through the widespread practice of arbitrary arrest and detention, unfounded prosecutions and dismissals of legal professionals as well as other human rights defenders, have fatally undermined the capacity of the justice system to provide reliable protection for human rights.
The Joint Statement is the fruit of three years of intensive work on access to justice for human rights violations in Turkey by the ICJ and IHOP.
During the last three years, the two organizations had the opportunity to gather the views of a wide range of stakeholders, including civil society, judges, lawyers, prosecutors, government officers, international experts, international organizations, human rights defenders and victims of human rights violations. The conclusions by ICJ and IHOP are a reflection of these opinions.
Drawing on this work and their decades-long experience in access to justice, the ICJ and IHOP have outlined the measures needed to begin to restore effective access to justice in Turkey.
The Joint Statement is part of the REACT project: implemented jointly by ICJ and IHOP, this project seeks to support the role of civil society actors in turkey in ensuring effective access to justice for the protection of human rights. This project is funded by the European Union. The views portrayed here do not necessarily reflect the opinion of the EU.
ICJIHOP-JointStatement-2020-ENG (download the statement in English)
ICJIHOP-JointStatement-2020-TUR (download the statement in Turkish)
Dec 16, 2020 | News
Dialogue between Swazi Women Human Rights Defenders and CEDAW Committee Members highlights the obstacles faced by local women in the enjoyment of their human rights.
On 14 December 2020, the ICJ and the Southern Africa Human Rights Defenders Network (SAHRDN) facilitated a fruitful dialogue between Swazi Women Human Rights Defenders (WHRD) and members of the UN Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women (the CEDAW Committee) on the key human rights concerns facing Swazi women and possible advocacy strategies to address them.
The CEDAW Committee monitors State parties’ compliance with and implementation of their human rights obligations under the UN Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (the Convention), by which Eswatini is bound.
In light of the Eswatini government’s failure to submit a report to the CEDAW Committee, as required under the Convention, more than 20 Swazi WHRDs’ organizations had a preparatory meeting on 8 December to discuss and prioritize the human rights concerns they wished to bring to the CEDAW Committee members’ attention.
They hoped that, by coming together and agreeing on these issues, they may raise awareness and put pressure on the Eswatini government to comply with its obligations under the Convention, including by promptly submitting the country’s overdue report.
In the wake of this preparatory meeting, on 14 December Swazi WHRDs briefed the CEDAW Committee members about the most critical human rights violations faced by women in Eswatini. This meeting was broadcasted live on Facebook.
The dialogue focused on the Eswatini authorities’ failure to implement their human rights obligations under the Convention, including the previous Concluding Observations of the CEDAW Committee.
High rates of teenage pregnancy, women’s inadequate access to education, healthcare and adequate housing, and ways in which customary and religious laws are used to justify discrimination against them were among the key human rights concerns affecting women discussed during the dialogue.
Watch the animation on CEDAW

Dec 15, 2020 | News
On 15 December 2020, the eighth anniversary of the enforced disappearance of Lao civil society leader Sombath Somphone, the ICJ joined 53 organizations and 19 individuals in reiterating its calls on the Government to reveal his fate and whereabouts and to investigate his and all other cases of alleged enforced disappearance in the country.
The statement condemned the Government’s ongoing failure to adequately investigate all allegations of enforced disappearance in Laos, which has been compounded by years of near complete lack of commitment to address this serious crime or provide an effective remedy or reparation to its victims and their families.
In June 2020, during the third Universal Periodic Review (UPR) of Laos, the Government refused to accept all five recommendations that called for an adequate investigation into Sombath’s enforced disappearance. The Government failed to support another eight recommendations that called for investigations into all cases of alleged enforced disappearances in Laos. Despite the government accepting that “the search for missing Lao citizens, including Sombath Somphone, is the duty of the Lao government”, it has failed to evidence any political will to effectively execute or fulfill this duty.
Sombath Somphone was last seen at a police checkpoint on a busy street in Vientiane on the evening of 15 December 2012. Footage from a CCTV camera showed that Sombath’s vehicle was stopped at the police checkpoint and that, within minutes, unknown individuals forced him into another vehicle and drove him away in the presence of police officers. CCTV footage also showed an unknown individual driving Sombath’s vehicle away from the city center. The presence of police officers at Sombath’s abduction and their failure to intervene strongly indicates State agents’ participation in Sombath’s enforced disappearance.
Lao authorities have repeatedly claimed they have been investigating Sombath’s enforced disappearance, but have failed to disclose any new findings to the public since 8 June 2013. They have not met with Sombath’s wife, Shui Meng Ng, since December 2017. No substantive information about the investigation has been shared by the authorities with Ng or Sombath’s family, indicating that, for all intents and purposes, the police investigation has been de facto suspended.
The statement reiterated a call for the establishment of a new independent and impartial investigative body tasked with determining Sombath’s fate and whereabouts, with the authority to seek and receive international technical assistance to conduct a professional and effective investigation in accordance with international standards. This is a call which multiple signatory organizations have been making since his enforced disappearance in 2012.
The statement further urged the Lao government to ratify the International Convention for the Protection of All Persons from Enforced Disappearance (ICPPED), which Laos signed in September 2008; incorporate its provisions into the country’s legal framework, implement it in practice, and recognize the competence of the Committee on Enforced Disappearances to receive and consider communications from or on behalf of the victims.
The full statement is available here.
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior Legal Adviser, e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org










