
Feb 18, 2020 | News
The ICJ and IBAHRI welcome today’s ruling by the Istanbul 30th Assize Court that acquitted all defendants in the Gezi Park case for lack of evidence. The ICJ and IBAHRI have been observing all hearings of the trial.
“Today’s decision is welcome,” said Massimo Frigo, Senior Legal Adviser of the ICJ. “The factual and legal circumstances surrounding the case make clear that these defendants should have never been put to trial to begin with.”
Baroness Helena Kennedy QC, IBAHRI Director, commented: “We have watched this trial closely, with senior lawyers attending the process as observers. It is a case that should never have been brought, for those who faced trial suffered untold anguish. But such injustice has become all too common in Turkey, where the rule of law and human rights have lost meaning. We live in hope this augurs a return to sanity and due process.”
These protests, commencing in May 2013, were an effort by a group of environmentalists to save a park in central Istanbul from being re-zoned, but soon grew into nationwide demonstrations.
Police quelled the protests in Taksim Square through the use of tear gas and water cannons.
The sixteen defendants in the present trial were charged under the following articles of the Turkish Criminal Code: Article 312 (an attempt to overthrow the Turkish government or an attempt to prevent it from fulfilling its duties), Article 151 (damage to property), Article 152 (qualified damage to property), Article 174 (possession or exchange of hazardous substances without permission), Article 153 (damaging places of worship and cemeteries), Article 149 (qualified robbery), Article 86 (intentional injury), crimes under the Law on Firearms, Knives and Other Tools no. 6136 and crimes under the Law on Protection of Cultural and Natural Assets no. 2863.
The ruling follows a 2019 decision of the European Court of Human Rights brought by Turkish human rights defender Osman Kavala, one of the defendants in the present case.
Contact:
Massimo Frigo, Senior Legal Adviser, ICJ’s Europe and Central Asia Programme, t: +41 22 979 3805; e: massimo.frigo(a)icj.org
Additional information
The defendants in the case are Osman Kavala, Ali Hakan Altinay, Ayse Mücella Yapici, Ayse Pinar Alabora, Can Dündar, Çigdem Mater Utku, Gökçe Yilmaz, Handan Meltem Arikan, Hanzade Hikmet Germiyanoglu, Inanç Ekmekci, Memet Ali Alabora, Mine Özerden, Serafettin Can Atalay, Tayfun Kahraman, Yigit Aksakoglu and Yigit Ali Ekmekçi.

Feb 7, 2020 | News
The ICJ expresses concern at today’s physical assault of a lawyer and a journalist, who arrived in Grozny to take part in the trial of blogger Islam Nukhanov.
The ICJ called on the authorities of the Russian Federation and its Chechen local authorities to investigate the attack and ensure that those responsible be brought to justice.
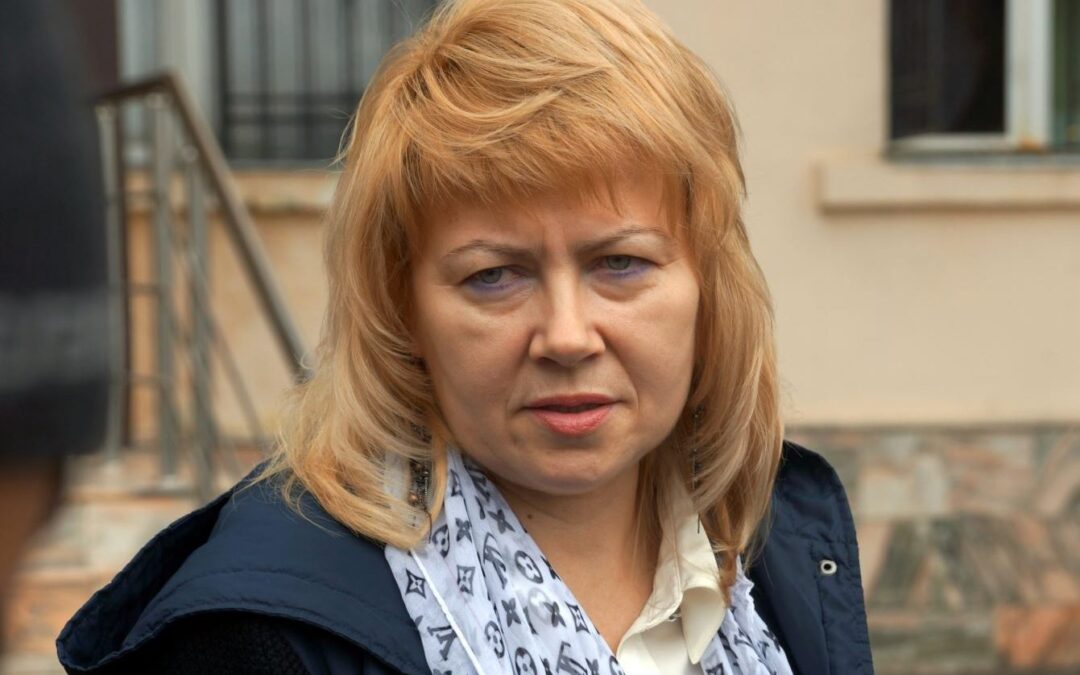
On 6 February, at around 22.00 lawyer Marina Dubrovina (photo) and Yelena Milashina, a journalist of Novaya Gazeta, a Russian newspaper, were beaten up by a group of young women in the lobby of the “Kontinent” Hotel in Grozny, Chechnya.
Both women suffered injuries to the face and body. Dubrovina and Milashina had come to Grozny to observe the trial of Islam Nukhanov, a blogger from the town of Kogalzm in the Tumen Oblast of the Russian Federation, charged with possession of a weapon, who has been detained by Chechen police since November 2019 after he posted a video on YouTube, with footage allegedly taken near the residence of the head of the Chechen Republic, Ramzan Kadyrov.
On 7 February, neither Dubrovina nor Milashina was admitted to the courtroom where Nukhanov was tried, due to the public and the media reportedly being excluded from the hearing.
The ICJ urges the federal and local authorities of the Russian Federation, to investigate the attack against Dubrovina and Milashina in a prompt and independent manner.
Measures should be taken to ensure that lawyers, especially when exercising their professional duties, are protected against such attacks.
Furthermore, Islam Nukhanov’s trial should be held in public, unless and until the authorities demonstrate that the circumstances of his trial require that the public and the media be excluded from it, consistent with relevant international fair trial standards.
Background
Islam Nukhanov, 27, is a blogger of Chechen origin was apprehended on 1 November 2019 in Grozny after he posted a video clip where he filmed streets and houses in Grozny, allegedly, near the residence of the head of the Chechen Republic Ramzan Kadyrov. Since his apprehension, Nukhanov has been in detention.
In 2018, the ICJ expressed concern at allegations that the arrest and detention of Oyub Titiev, the head of the Chechen branch of the Russian human rights organisation Memorial, was carried out as retaliation for his human rights activity.
In 2016, the ICJ expressed concern at the reported resignations of federal judges in the Chechen Republic of the Russian Federation following apparent pressure by the acting Head of the Republic Ramzan Kadyrov who had suggested that resignation would be the “most correct decision of their lives”
The ICJ is concerned at the regular attacks on lawyers and human rights defenders in Chechnya, which are systemic and may have the purpose of intimidating those who wish to defend human rights in the Chechen Republic of the Russian Federation.
The UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers provide that “where the security of lawyers is threatened as a result of discharging their functions, they shall be adequately safeguarded by the authorities”.

Feb 5, 2020 | Advocacy, News, Open letters
ICJ Commissioners and Honorary Members today denounced the rapidly escalating rule of law crisis in Poland, after a new law was passed that would result in harassment of judges upholding the independence of the judiciary.
A group of 44 ICJ Commissioners and Honorary Members, including senior judges, lawyers and legal scholars from around the world said in their statement “it is clear that the separation of powers, the independence of the judiciary, and the capacity of Polish judges to uphold the rule of law are now severely compromised. Judges’ freedom of expression, association and assembly are under immediate threat.”
The statement
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ), its Centre for the Independence of Judges and Lawyers (CIJL) and the undersigned Commissioners and Honorary Members of the ICJ are alarmed at the rapidly escalating rule of law crisis in Poland.
It is clear that the separation of powers, the independence of the judiciary, and the capacity of Polish judges to uphold the rule of law are now severely compromised. Judges’ freedom of expression, association and assembly are under immediate threat.
The passing by the Sejm on 23 January of the amendments to the laws on the judiciary, and their signing into law on 4 February, means that judges will be prohibited from questioning the legitimacy or institutional independence of any Polish court, even where its members have been appointed through a politically controlled process, in violation of EU and international law. Judges will face disciplinary action for denying the validity of any judicial appointment.
This law is an attempt to prevent any Polish court from upholding the independence of the judiciary, in the face of repeated legislative and government attacks on judicial independence in recent years.
This is directly contrary to the obligations of judges under the EU treaties to apply EU law, and would therefore lead to violations of Poland’s EU law obligations. It would also lead to violations of Poland’s obligations under international human rights law, since it would require judges to act contrary to their duty to uphold the right to a fair hearing before an independent and impartial tribunal.
As the Venice Commission noted in its recent opinion on the amendments, they are clearly “designed to have a nullifying effect” on recent judgments and resolutions of the Court of Justice of the EU and the Polish Supreme Court, which have called into question the validity of recent judicial appointments. As such, they do severe damage to the rule of law in Poland.
These developments follow recent legislation which has politicised the National Council of the Judiciary (NCJ) and imposed executive control of the appointment process for judges of the Supreme Court, court presidents and other judges. A powerful new Extraordinary Chamber as well as a Disciplinary Chamber of the Supreme Court, appointed under this new system, has further entrenched political control of the judiciary.
The ICJ, its undersigned Commissioners and Honorary Members, applaud the continued resolute defence of the rule of law by sections of the Polish judiciary. This has been evident in the resolution of the Supreme Court (Civil, Criminal, Labour and Social Security Divisions) of 23 January which found that recent judicial appointments meant that some Polish courts were not sufficiently independent to be legitimately constituted.
We deplore the response by President Adrzej Duda in which he suggested that judges opposing the judicial reforms on the judiciary acted out of improper self-interest.
The undersigned ICJ Commissioners and Honorary Members affirm their solidarity with Polish judges, in particular those who are currently facing abusive disciplinary or criminal proceedings for carrying out their judicial functions in accordance with the principle of judicial independence, or for exercising their freedom of expression, association or assembly as a means to defend the rule of law.
We recall that international human rights law and international standards on the judiciary require all branches of government to respect the independence of the judiciary. Furthermore, they recognise that judges have rights to freedom of expression and association and that they have a particularly important role in contributing to discussions on issues of the functioning of the judicial system and the rule of law, especially in defending the independence of the judiciary.
We call on the international community to respond to the Polish rule of law crisis in a manner appropriate to the gravity of the situation, before the damage to the Polish legal system becomes further entrenched.
In particular, we call on the European Union to urgently advance proceedings concerning Poland under Article 7 TEU, in light of the clear breach of EU law and EU fundamental values entailed by the new law, in conjunction with previous reforms, and by the government’s open defiance of decisions of the Court of Justice of the EU and the Polish Supreme Court.
Poland-Commissioners-Statement-Advocacy-Open-Letter-2020-ENG, (full text with all signatories, PDF)

Feb 4, 2020 | News
Today, the ICJ has observed the trial in court proceedings against lawyer Amanzhol Mukhamediarov before the Yesil District Court in Nur-Sultan. Mukhamediarov, Chair of the Committee on the rights of lawyers of the Kazakhstan Bar Association, is facing disbarment following a lawsuit of by the Ministry of Justice of Kazakhstan.
Along with the case against Erlan Gazhymzhanov, who faces disbarment on the same set of facts, this case may raise issues of interference with freedom of expression of lawyers and possible interference in their work. This prompted ICJ to send a mission to observe court proceedings.
This hearing is observed on behalf of the ICJ by a lawyer from the Geneva Bar Association (Switzerland), Ms Xeniya Rivkin, as part of the International Cooperation Initiative project between the ICJ and the Geneva Bar Association.
The observer will carry out an assessment of the case based on the observation of the hearing in light of the materials of the case and the international law and standards on the role and independence of lawyers.
Read also
ICJ trial observation manual
Kazakhstan: ICJ observes hearing in lawyer’s disbarment case
Kazakhstan: frivolous disbarment proceedings against prominent lawyer Sergey Sizintsev should be immediately dropped, ICJ says
Kazakhstan: ICJ alarmed at government interference in legal profession
Jan 24, 2020 | News
Today, the ICJ has conducted a trial observation in disbarment proceedings against lawyer Yerlan Gazymzhanov before the Saryarkyn Court of Nur-Sultan.
Erlan Gazymzhanov is facing disbarment following a lawsuit brought by the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The lawyer is accused of violating court rules by publishing on a social network an archive video from the hearing in a case in which he alleged inappropriate behaviour by the judge.
The case raises issues of the lawyer’s freedom of expression and possible improper interference in his work.
The ICJ will carry out an assessment of the case and its compliance with international standards following its observation of the proceedings.
Another lawyer, Amanzhol Mukhamedyarov is facing a disbarment lawsuit on the same allegations.
Mukhamedyarov’s case will be heard in separate proceedings on 4 February in Esil district court of Nursultan.
Dr Stefan Stobl, a lawyer from Munich (Germany) and a member of the ICJ Section Germany, observed today’s hearing on behalf of the ICJ.
Additional information:
Read ICJ’s trial observation manual
The ICJ has previously expressed concern about increasing restrictions on the independence of lawyers in Kazakhstan:
Kazakhstan: frivolous disbarment proceedings against prominent lawyer Sergey Sizintsev should be immediately dropped, ICJ says
Kazakhstan: ICJ alarmed at government interference in legal profession
Kazakhstan: the ICJ calls to immediately drop prosecution of lawyer Bauyrzhan Azanov

Jan 9, 2020 | Agendas, Events, News
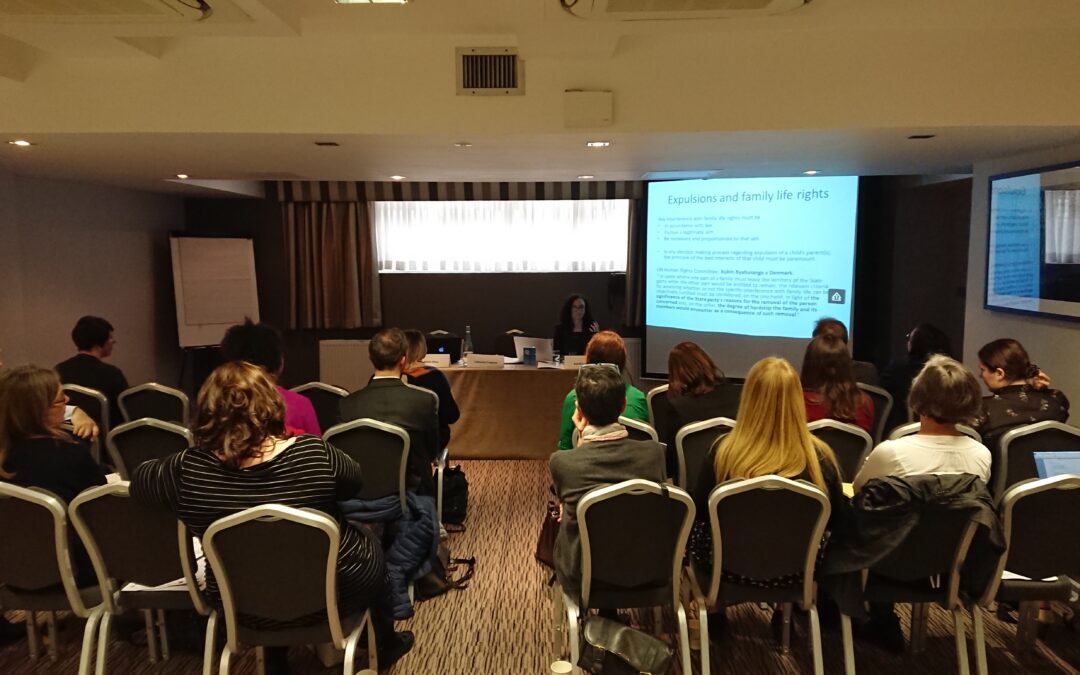
Today, the ICJ and Immigrant Council of Ireland (ICI) are holding a 2-day training seminar for judges and lawyers in Dublin, Ireland, on the rights of migrants, in particular the right to family life and due process in asylum proceedings.
The participants consist of about 30 judges and judicial assistants from the International Protection Appeals Tribunal (IPAT) administrative decision makers (IPO/INIS), and legal professionals.
During the two days of training, experts from the European Court of Human Rights, the UK Immigration Tribunal, Trinity College Dublin, the Immigrant Council of Ireland and the ICJ will deliver the training, bringing international human rights and EU law perspectives to the discussion on the Irish context.
Among the issues discussed will be – on day 1 – the right to private and family life in migration, including, and recent developments at the ECtHR, and right to private and family life in the national context as well as best interests of the child determination and family life rights in return decisions. On day 2 discussion will focus on procedural rights and remedies in the context of international protection,. Issues discussed will include due process rights in asylum procedures, safe third country concept, and credibitity assesments and vulnerability in international protection applications.
In parallel, a training for 20 social care professionals working with migrant children is being delivered.
This is the second national training under the FAIR PLUS project, following the first training held last December in Pisa.
See the full agenda here.
This training is a part of FAIR PLUS project. It was carried out with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents are the sole responsibility of ICJ and do not necessarily reflect the views of the European Union.










