Jul 23, 2019 | News
The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2019, does not adequately protect the rights of transgender people and should be revised to address the concerns of the transgender community and to conform with India’s international human rights obligations, the ICJ said today.
“The Transgender Bill as currently drafted still fails to fully protect the rights of transgender people including to self-identify, a right that has been upheld by the Indian Supreme Court,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ’s Asia Pacific Director.
“If Parliament passes the Bill in its current form, it will miss an important opportunity to introduce a law that respects, protects and fulfills the human rights of transgender people as required by the Supreme Court’s decision in NALSA and India’s international obligations,” he added.
The Government introduced the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2019, before the Parliament on 19 July 2019.
The current draft, fails to address key concerns that have been repeatedly raised by the transgender community and human rights organizations.
Critically, the Bill continues to mandate sex reassignment surgery for transgender people who seek to identify as male or female.
This requirement clearly contravenes the Supreme Court’s judgment in NALSA v. UOI, which guarantees the right to self-identification, without any need for medical intervention. Nor does the Bill make provision for reservations in employment or education despite a mandate by the Supreme Court in NALSA.
Among the problematic provisions are those which set out lighter sentences for criminal offences when committed against transgender people (including “sexual abuse”, “physical abuse”, “verbal and emotional abuse”, “economic abuse” and denial of “passage to a public place”); inadequate or missing definitions of offences; the retention of provisions that could be used to target transgender people for criminal prosecution; and the absence of mechanisms to enforce prohibitions on discrimination in the law.
The ICJ acknowledges that the draft of the Bill contains improvements over the version passed by the Lok Sabha in 2018.
The new draft removes the requirement for a screening committee to review applications for the issuance of a gender identity certificate. It also no longer criminalizes “compel[ing] or entice[ing] a transgender person” to engage in begging
The ICJ and other human rights organizations have recommended the deletion of these provisions in light of the well-documented historical abuse that such laws enabled by making it possible to target transgender persons, and the resulting effect of creating a specter of criminality around transgender identities.
“The Bill does include some important improvements over its 2018 version, such as the elimination of screening committees for the issuance of identity documents, and problematic criminal provisions relating to begging. However, it still falls significantly short from a constitutional and an international human rights perspective,” said Rawski.
“We urge the Parliament to address the deficiencies that remain – such as provisions on mandatory sex reassignment surgery, which contravene human rights law – before passing it into law,” he added.
The current session of Parliament will close on July 26, 2019 and may be extended by two-three days. If passed by the Lok Sabha, this Bill will be introduced in the Rajya Sabha (Upper House of the Parliament) for consideration.
The ICJ urges the Lok Sabha to reconsider the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill in accordance with the constitutional and international law obligations of the Indian state, and to ensure meaningful consultation with the transgender community in its lawmaking.
Contact
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia Pacific Region Director, e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org, t: +66 644781121
Maitreyi Gupta (Delhi), ICJ International Legal Adviser for India, e: maitreyi.gupta(a)icj.org, t: +91 7756028369
Read also
ICJ Briefing Paper on India: Legal and Jurisprudential Developments on Transgender Rights, SAATHII Vistaara Coalition. The paper analyses in detail the domestic judicial developments on transgender rights as well as the legislative process undertaken until the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2018 was passed on 17 December 2018.
ICJ Briefing Paper on The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2016, analyzes the 2016 Bill, its shortcomings, and India’s international obligations, as it is the basis of the 2018 Bill.
ICJ Briefing Paper on Implementation of NALSA Judgment discusses the 2014 April NALSA decision that affirmed that transgender people have the right to decide their self-identified gender. The paper analyses the responsibilities placed on Indian authorities, gaps in implementation, and India’s relevant international law obligations.
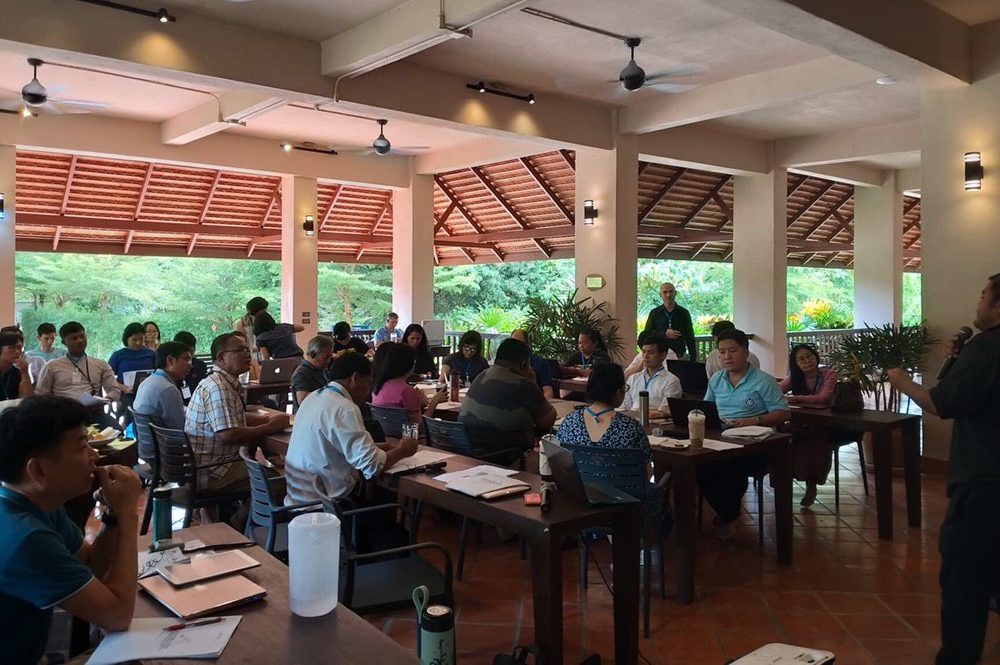

Jul 21, 2019 | News
Today, the ICJ hosted a discussion on Thailand’s legal frameworks on corporate accountability for outbound investments in Chiang Mai, Thailand. The forum was co-organized with Earth Rights International.
Lawyers, members of civil society organizations and academics from Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, and Thailand attended the discussion.
Participants discussed:
- corporate civil, criminal and administrative liability and in particular, the applicable laws governing the prosecution and adjudication of human rights abuses committed by Thai corporations and gaps in Thailand’s legal frameworks. The meeting also looked into recommendations to strengthen Thailand’s domestic laws to increase access to justice for victims of human rights abuses committed by Thai corporations in the context of their business activities abroad, particularly on issues such as: limited liability of shareholders and the “corporate veil” in relation to the responsibilities of Thai corporations, the complexity of laws governing joint ventures, and challenges in bringing state-owned enterprises to justice;
- jurisdiction of Thai courts in civil, criminal and administrative cases where de facto and de jure foreign subsidiaries of a Thai corporation were involved in wrongful acts or omissions abroad, and problems posed by statutes of limitation;
- tools for preventing human rights abuses by corporations such as Human Rights Due Diligence (HRDD), Transboundary environmental impact assessments (EIA), Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) measures, and the Duty of Care principle under tort law; and
- the role of other related actors to prevent and mitigate human rights risks, including the National Human Rights Commission of Thailand (NHRCT), National Contact Points (NCPs), financial institutions and securities institutions, and provided recommendations to strengthen mandates of such organizations which would allow them to provide better protection for individuals and communities who may be affected by outbound investments.
This discussion will provide the foundation for further work and analysis by the ICJ regarding Thailand’s legal frameworks on corporate accountability for outbound investments. It will also provide the basis for ICJ strategic advocacy at the national level.

Jul 19, 2019 | News, Op-eds
An opinion piece by Emerlynne Gil, Senior Legal Adviser, ICJ Asia-Pacific Programme.
Last week, the UN Human Rights Council adopted a resolution expressing concern over the human rights situation in the Philippines. It specifically expressed grave concern over the killings and disappearances arising from the drug war of the current administration.
Since 2016, when the government began its campaign against illegal drugs, there have been reports of thousands of killings of people who were allegedly involved in the drug trade and drug use.
Furthermore, in the recent report of Lawyers Rights Watch Canada (LRWC), there have been more than 40 lawyers killed under the current administration.
The resolution was, in fact, restrained in tone and content. Human rights groups like the ICJ had hoped that it would establish an international mechanism to investigate the killings and other human rights violations.
However, the Council held back and merely urged the Philippine government to “take all necessary measures to prevent extrajudicial killings and enforced disappearances”.
It also asked the Philippine government “to cooperate with the Office of the High Commissioner on Human Rights” and other international human rights mechanisms, and requested the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights to present a report to the Council for discussion in June 2020.
The Philippine government sent a big delegation to Geneva to lobby against the adoption of any resolution. During the informal consultations among States on this resolution, there were theatrics from the delegation, which walked out during the first consultation.
At the second consultation, nobody from the delegation attended, but former Ambassador Rosario Manalo, who also previously represented the Philippines in the ASEAN Intergovernmental Commission on Human Rights (AICHR), and is now a member of the UN Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women, was present.
Purporting to speak as a ‘human rights defender’, she launched an angry tirade against Iceland as the sponsor of the resolution and the other States who supported it.
She also called the Filipino human rights defenders in the room who were seated right next to her as ‘treacherous’, and accused them of peddling lies about the country.
The theatrics in Geneva did not serve the Philippine government well. In the end, the Council voted to adopt the resolution.
Now that it has been adopted, what does this mean for Filipinos? The UN Human Rights Council, like any international human rights body, has significantly limited ability to directly protect human rights on the ground.
Thus, while it has adopted this resolution, the Council will not have the power to actually stop the unlawful killings and other human rights violations being committed. The Council will be unable to compel the implementation of the recommendations in any resolution it adopts, where a State is unwilling to cooperate.
Hence, the Philippine government still holds the discretion on whether or not to implement the recommendations made by the Council.
This is where ordinary Filipinos come in. The people – as the eyes and ears on the ground – are indispensable to the work of international human rights bodies like the Human Rights Council.
The effectiveness of the Council in protecting human rights on the ground greatly relies upon the extent to which the people on the ground – including human rights defenders – are able to engage and work with them.
The information provided by the general public regarding the situation on the ground is very important to the work of international human rights mechanisms like the Council. This information gives these mechanisms a clearer and more accurate picture of the human rights situation in the country.
We should thus not be silent. We should continue pressing the government to implement the recommendations in this resolution. The key recommendation is that the government should investigate extrajudicial killings and enforced disappearances and hold the perpetrators accountable.
In its formal statement to the Council after adoption of the resolution a few days ago, the representative of the Philippine government at the Council vigorously claimed that the country has ‘fully functioning domestic accountability mechanisms’, ignoring the fact that authorities have been unwilling or unable to conduct effective investigation or prosecutions for any of the numerous allegations of unlawful killings.
Hence, we should press the government to demonstrate that its claim that domestic accountability mechanisms are functioning is true, and that it should then use these mechanisms by investigating the killings and disappearances and punishing the perpetrators.
It is a welcome development that the Human Rights Council passed this resolution on the human rights situation in the Philippines.
But the work does not end there. There is a symbiotic relationship between the actions of the people on the ground and the work of international human rights mechanisms like the Council.
It is now left to us to press our government for the implementation of the recommendations in the resolution.

Jul 18, 2019 | News
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) today welcomed the decision of the International Court of Justice (ICJ-CIJ for its acronym) upholding the right of consular access and notification for Indian national Kulbhushan Jadhav.
The Court determined that Pakistan had unlawfully denied Jadhav consular access before and after his summary trial by a military court.
It emphasized that any “potential prejudice and the implications for the evidence and the right of defence of the accused should receive close scrutiny during the review and reconsideration.”
The Court categorically held that Article 36 of the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations (VCCR) “does not exclude from its scope certain categories of persons, such as those suspected of espionage,” as argued by Pakistan.
“The decision by the International Court today is a resounding affirmation that there can be no curtailment of the right to consular access by foreign nationals by States that are Party to the VCCR,” said Ian Seiderman, Legal and Policy Director of the ICJ.
“Consular access is essential to ensure a fair trial for foreign nationals and this human right must not in any way be made contingent upon the offence foreign nationals are charged with.”
The International Court called on Pakistan to give effect to the Court’s ruling by providing effective review and reconsideration of both his conviction and sentence, including by taking account of the principles of the right to a fair trial.
The ICJ has pointed out that Pakistan’s military justice system and procedures are incompatible with the right to a fair trial. Under international standards, military tribunals are never permissible in prosecutions against civilians for offences carrying the death penalty.
Since 3 March 2016, Kulbhushan Jadhav has been in custody of the Pakistani authorities. The circumstances of his arrest remain in dispute between the Parties.
India was informed of the arrest on 25 March 2016. On 10 April 2017, Pakistan’s military announced Kulbhushan Jadhav had been convicted and sentenced to death by a military court for “espionage and sabotage activities against Pakistan.”
India had brought the case against Pakistan before the International Court of Justice, alleging “egregious violations” of the VCCR by Pakistan because of the denial of consular access to Jadhav.
In response, Pakistan had primarily argued that Jadhav is a an Indian spy involved in acts of terrorism in Pakistan, and the VCCR is not applicable to spies or “terrorists” due to the inherent nature of the offences of espionage and terrorism.
“States around the world continue to use counter terrorism and national security as a justification to curtail human rights – the International Court of Justice’s affirmation that the protections under the VCCR are not conditional is hugely significant in this context,” said Ian Seiderman.
The International Court also held that it considered a continued stay of Jadhav’s execution as constituting “an indispensable condition for the effective review and reconsideration of the conviction and sentence.”
In May 2017, the Court had asked Pakistan to take all measures at its disposal to ensure that Jadhav is not executed pending the final decision in the proceedings.
The ICJ considers the death penalty a violation of the right to life and cruel, inhuman or degrading punishment and notes that a large majority of States, in repeated UN resolutions, have called on retentionist states to declare a moratorium on the practice with a view to abolition.
Background
In addition to the arguments regarding espionage and terrorism, Pakistan also relied on a bilateral agreement on consular access, signed by India and Pakistan in 2008, arguing that the agreement overrides the obligations under the VCCR. The International Court of Justice, however, rejected this argument, on the ground that, among other things, obligations under the VCCR may be enhanced or clarified by bilateral treaties, but cannot be diluted or undermined.
India had requested a number of other measures of relief from the Court, including the annulment of Kulbhushan Jadhav’s death sentence; a declaration that Kulbhushan Jadhav’s military trial was in violation of the VCCR and international human rights law, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR); a directive restraining Pakistan from giving effect to the death sentence; and a directive to release Kulbhushan Jadhav and ensure his safe passage to India.
However, in accordance with its jurisdictional competencies and prior precedents, the Court denied these remedies to India. As “appropriate reparation” in this case, the Court directed Pakistan to effectively review and reconsider Jadhav’s conviction and sentence “to ensure that full weight is given to the effect of the violation of the rights set forth in Article 36 of the Vienna Convention.”
Contact
Ian Seiderman: ICJ Legal and Policy Director, e: ian.seiderman(a)icj.org
Frederick Rawski: ICJ’s Asia Pacific Region, e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org
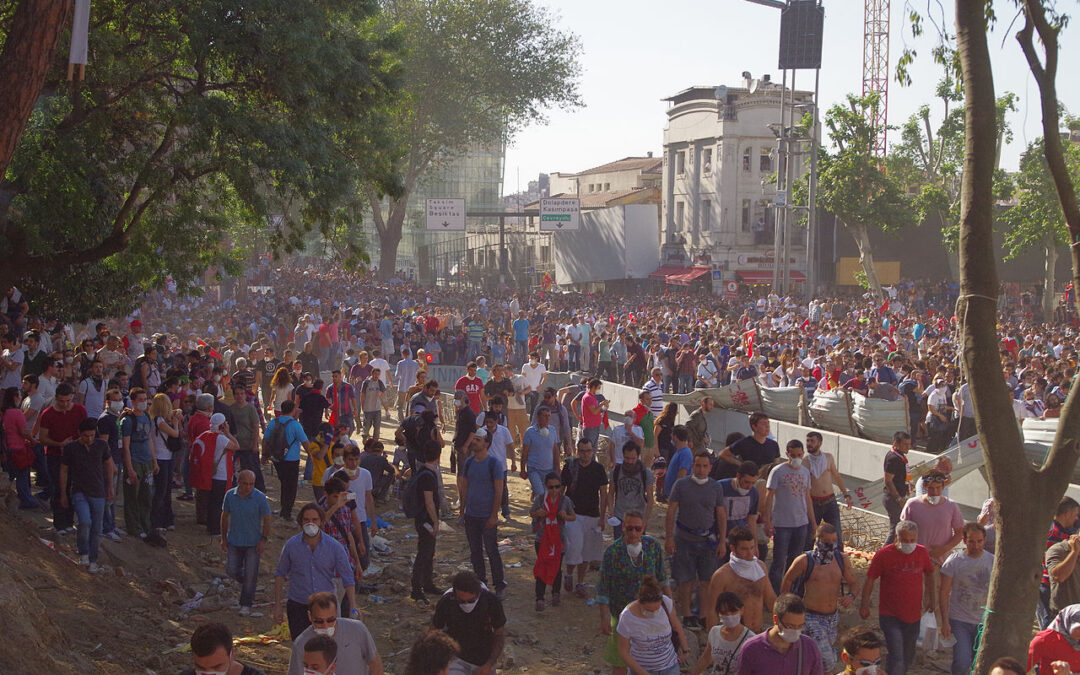

Jul 18, 2019 | News
The ICJ and the International Bar Association’s Human Rights Institute (IBAHRI) have jointly sent international observers to attend the second hearing of the criminal trial on the “Gezi Park” protest at the Silivri Prison Courthouse in Istanbul, scheduled to take place on 18 and 19 July 2019.
The ICJ and IBAHRI observers will be monitoring a trial hearing before İstanbul 30th Assize Court with prinicipal defendant Osman Kavala, and 15 others; Ali Hakan Altınay, Ayşe Mücella Yapıcı, Ayşe Pınar Alabora, Can Dündar, Çiğdem Mater Utku, Gökçe Yılmaz, Handan Meltem Arıkan, Hanzade Hikmet Germiyanoğlu, İnanç Ekmekci, Memet Ali Alabora, Mine Özerden, Şerafettin Can Atalay, Tayfun Kahraman, Yiğit Aksakoğlu and Yiğit Ali Ekmekçi.
The observers will report directly to the IBAHRI and ICJ Secretariats on the proceedings following the mission.
The Gezi Park protests began in May 2013 as an effort by a group of environmentalists to save a park in central Istanbul from being rezoned, but soon turned into nationwide demonstrations.
The protest was quelled by police with the use of tear gas and water cannons against the protesters in Taksim Square. Following a six-year investigation into the events, the 657-page indictment issued by the Istanbul Chief Public Prosecutor’s Office was accepted by the 30th A Court in Istanbul on 4 March 2019.
The defendants are to be charged under Turkish Criminal Code Article 312 (attempt to overthrow the Turkish Government or attempt to prevent it from fulfilling its duties), Article 151 (damage to property), Article 152 (qualified damage to property), Article 174 (possession or exchange of hazardous substances without permission), Article 153 (damaging places of worship and cemeteries), Article 149 (qualified robbery), Article 86 (intentional injury); crimes under the Law on Firearms, Knives and Other Tools no. 6136, and crimes under the Law on Protection of Cultural and Natural Assets no. 2863.
The total sentence asked for by the prosecution for these offences amounts to approximately 47,520 years imprisonment.
Contact:
Massimo Frigo, Senior Legal Adviser, t: +41 22 979 38 05 – e: massimo.frigo(a)icj.org

Jul 17, 2019 | News
On 16 July 2019, the European Court of Human Rights found Russia’s refusal to register associations set up to promote and protect the rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people to violate the rights to freedom of association and to be discriminatory on the grounds of sexual orientation.
The Court’s judgment was informed by a third party intervention submitted jointly by the ICJ, the European Human Rights Advocacy Centre (EHRAC) and ILGA-Europe on 29 July 2016.
The cases were brought by Russian individuals and non-profit organizations (Rainbow House, Movement for Marriage Equality and Sochi Pride House) (Zhadanov and others v. Russia).
The organizations’ registration requests were refused by the authorities and the domestic courts because of formal irregularities in their applications and because their aim was to promote LGBT rights.
In a unanimous judgment, the Court reiterated the importance for individuals to be able to join together to act collectively and establish legal entities. Rejecting as “unconvincing” the Government’s assertion that the applications were refused on procedural grounds, the Court found that in order to obtain registration the organizations would have had to renounce their aims of promoting LGBT rights: “Those grounds touched upon the very core of the applicant organisations and affected the essence of the right to freedom of association”.
Referring to Russia’s submission that the organisations were refused registration to prevent social or religious hatred and disorder, the Court reminded States that they have a positive duty to guarantee the proper functioning of associations, even when they annoy or give offence.
In the present case, rather than taking steps to enable the organizations to carry out their activities without fear of violence, the authorities instead “decided to remove the cause of the tension and avert a risk of disorder by restricting the applicants’ freedom of association”.
The Court therefore found the refusal to register the organizations was not necessary in a democratic society (in breach of Article 11 ECHR).
Having found that the decisive ground for refusing the organizations’ applications for registration was their aim of promoting LGBT rights, the Court held that the applicants had suffered a difference in treatment based on their sexual orientation which could not be reasonably or objectively justified (in breach of Article 14 ECHR in conjunction with Article 11).
EHRAC, ILGA-Europe and ICJ’s joint intervention, drafted by Jeremy McBride QC of Monckton Chambers (UK), focused on the extent of legitimate restrictions on the right to freedom of association for the protection of morals, arguing that it was impossible to protect individual rights if citizens were unable to create associations to defend common interests and needs.
It submitted that any restrictions on this right should be strongly justified and legitimate aims which permitted interference should be interpreted narrowly.
“This judgment reaffirms the vital importance for individuals to be able to group together and organize themselves around shared causes. States must act positively to ensure that this right is meaningful, particularly when people belong to vulnerable or marginalised minority groups or hold unpopular views,” said Joanne Sawyer, Lawyer, EHRAC.
“We are very pleased with European Court’s pioneering judgment confirming the vital right to freedom of association for those promoting rights of LGBTI people. This judgment sends a key message to LGBTI activists in Russia and other countries across Europe who are facing similar discriminatory restrictions – refusal to register associations cannot be justified on the ground of protection of morals,” said Arpi Avetisyan, Senior Litigation Officer, ILGA-Europe.
“The ICJ welcomes the Court’s conclusion that Russia’s refusal to register associations established to promote and protect the human rights of LGBT people cannot be justified on the grounds of protecting moral values or the institutions of the family and marriage,” added Livio Zilli, ICJ Senior Legal Adviser.