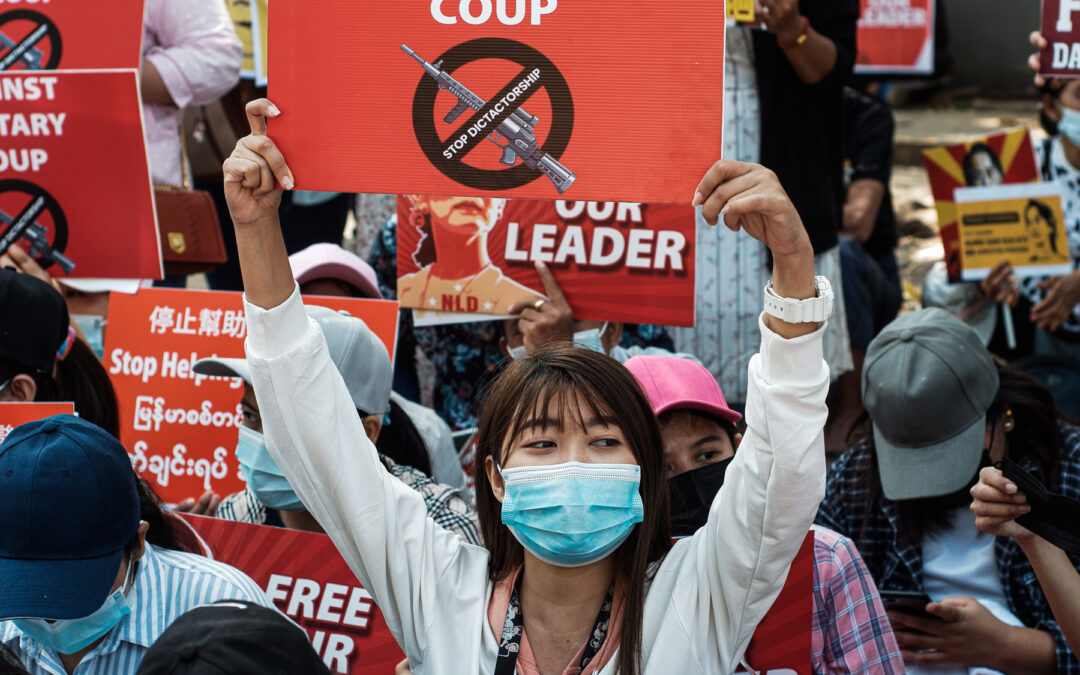

Mar 17, 2021 | News
Imposition of Martial Law in several areas of Myanmar subjects civilians to trial by military tribunals, a dangerous escalation of the military’s repression of peaceful protests, said the ICJ today.
“Use of martial law marks the return to the dark days of completely arbitrary military rule in Myanmar. It effectively removes all protections for protestors, leaving them at the mercy of unfair military tribunals.”
– Ian Seiderman, ICJ’s director of law and policy
On 14 March, the Myanmar military issued Martial Law Order 3/2021, covering a number of townships of different provinces in Myanmar. According to this order, military officials assume full authority from civilian officials, and civilians may be subjected to military tribunals for charges of 23 violations of the criminal code and other laws. The 23 crimes include many of the charges used most against peaceful protesters in the past month, including charges of ‘disrupting or hindering government employees and services’ and ‘spreading false news’ about the government, and ‘exciting disaffection towards the government.’
The Martial Law Order also assigns disproportionately severe sentences, including the death penalty and prison sentences with hard labor. Judgments of military tribunals are not subject to appeal, even if the death penalty is imposed.
“Martial law has been imposed in precisely the areas where the military have used unlawful and lethal force against peaceful protesters, and removes even the pretense of access to courts for the people whose rights have been violated systematically by the military, ” said Seiderman.
The ICJ’s detailed review of military courts has documented that they lack competence, independence and impartiality to prosecute civilians. International law provides that the jurisdiction of military tribunals must generally be restricted solely to specifically military offenses committed by military personnel.
“The military courts lack transparency, due process and judicial oversights. It leaves no possibility to appeal the sentences, including the death sentences that have been handed down by military generals, ” said Seiderman.
Since the military coup d’etat of February 1 and the declaration of a state of emergency, the military has enacted and amended legislation enabling ongoing gross human rights violations, including possible crimes against humanity. More than 200 people have been unlawfully killed, with 2,000 more injured as security forces have used excessive force to suppress peaceful protests.
Background
On 14 March, the military-appointed State Administration Council, in accordance with Article 419 of the Constitution, enacted Martial Law Order 1/2021, imposing martial law in a number of areas in Yangon. The affected areas were further expanded through two other orders issued on 15 March, Martial Law Order 2/2021 and 3/2021. These orders transfer all power to the Military Commander in those areas. All local administration bodies have been placed under martial law, effectively giving military full control of all judicial and administrative processes.
The Order 3/2021 in particular is divided into six main sections with the most concerning provisions in relation to the list of crimes to be heard by military tribunals, and the proscribed punishments.
Contact
Osama Motiwala, ICJ Asia-Pacific Communications Officer, e: osama.motiwala(a)icj.org
Mandira Sharma: ICJ Senior Legal Adviser, e: mandira.sharma(a)icj.org
Mar 15, 2021 | Advocacy, News
The ICJ and a group of Sri Lankan judges have agreed on the importance of taking effective measures to address discrimination and equal protection in accessing justice in the country.
On 6 and 13 March 2021, the ICJ, in collaboration with the Sri Lanka Judges’ Institute (SLJI), organized the National Judicial Dialogue on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women and Enhancing Women’s Access to Justice. This event was organized under the ‘Enhancing Access to Justice for Women in Asia and the Pacific’ project funded by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (SIDA).
Twenty magistrates and District Court judges from around Sri Lanka, with judicial and legal experts from other countries, participated in this judicial dialogue which was conducted virtually due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The dialogue highlighted how Sri Lankan women continue to face a myriad of challenges including legal, institutional and cultural barriers when accessing justice. Gender biases and discriminatory behaviour prevalent in every aspect of justice delivery needs to be dealt with in order to effectively enhance women’s access to justice.
Boram Jang, ICJ International Legal Advisor remarked that “judiciaries have an important role to play in eliminating gender discrimination in justice delivery as it is a critical component in promoting women’s access to justice. In order to do so, the judges should be equipped with a full understanding of Sri Lanka’s obligations under the CEDAW and other human rights instruments.”
Honorable L. T. B. Dehideniya, Justice of the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka and Executive Director of the SLJI expressed hope that judicial dialogues such as this would “enhance the capacity of participant judges to use the international legal instruments, which Sri Lanka has ratified, in domestic judicial work especially with regard to the elimination of gender inequalities and biases.”
Ms. Bandana Rana, Vice Chair of the CEDAW Committee led a discussion with the judges on the application of the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), pointing out that “judges play a pivotal role in identifying the incongruences between existing laws and international human rights standards and ensuring that the full gamut of women’s human rights is retained in line with the CEDAW framework.”
Justice Ayesha. M. Malik, High Court Judge, Lahore, Pakistan affirmed the importance applying the right to access to justice under international human rights law and suggested strategies for reflecting these international standards in judicial decisions.
Attorney Evalyn Ursua addressed on gender stereotypes and biases in justice delivery and engaged the participants on how these could be effectively eliminated. She stated that “the judiciary as a part of the State has the obligation to eliminate gender discrimination.” She encouraged the judges to use the cultural power of law to change language and attitudes surrounding gender discriminatory behaviour and stigma.
The second day featured a discussion on the specific barriers that women in Sri Lanka face when they access justice. Hon. Shiranee Tilakawardane, former Justice of the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka led a discussion on the role and measures available to the judiciary as an institution to enhance access to justice for Sri Lankan women.
Justice Tilakawardane stated that “While theoretically, the Sri Lankan constitution enshrines equality before the law, in reality women continue to feel disadvantaged when they try to access justice” and added “the Sri Lankan judiciary can empower its women only when it understands, acknowledges and addresses the disadvantages they face owing to their gender.” She impressed upon the participant-judges that “ensuring equality is no longer a choice, nor is it merely aspirational, but a pivotal part of judicial ethics.”
The panelists on the second day surveyed the legal, institutional and cultural challenges faced by women at every step of the judicial process. The panel comprised of Prof. Savitri Goonesekere, Emeritus Professor of Law and Former member of the CEDAW Committee, Mrs. Farzana Jameel, P.C, Additional Solicitor General of the Attorney General’s Department and Mrs. Savithri Wijesekara, Executive Director of Women in Need.
Contact
Osama Motiwala, Communications Officer – osama.motiwala@icj.org
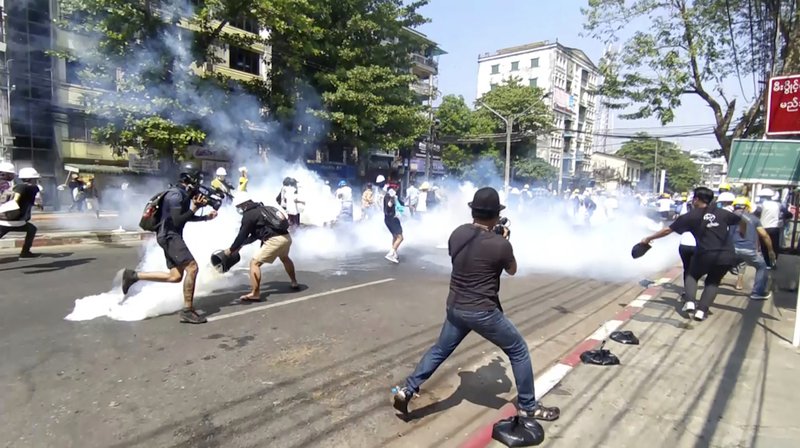

Mar 4, 2021 | News
The escalating killing of peaceful protestors by Myanmar’s security forces should be independently investigated as possible crimes against humanity, said the ICJ today on the eve of a closed-door UN Security Council session on the situation.
According to reliable information provided to the ICJ, security forces have unlawfully killed approximately 50 unarmed people – including at least five children – in more than 10 cities on different days since the military overthrew the civilian government on 1 February 2021. On 3 March, at least 38 people were reported killed by security forces.
In addition, numerous protestors have been injured and a total of 1,498 people have been arrested, charged or sentenced in relation to the military coup, according to The Assistance Association for Political Prisoners (AAPP).
“As the scale of the violence continues to increase, seemingly as part of a systematic, centralized policy to use lethal force against peaceful protestors, it is hard to escape the conclusion that Myanmar’s security forces are perpetrating crimes against humanity,” said Kingsley Abbott, Director of Global Accountability and International Justice at the ICJ. “This underscores the urgent need for all states, including the permanent members of the UN Security Council, to stop shielding the Myanmar military and work together towards opening avenues to justice for the Myanmar people.”
The UN Security Council will meet this Friday for a closed-door session at the request of the United States which is President of the Council in March 2021.
“The UN Security Council should immediately refer Myanmar to the International Criminal Court for a full independent and effective investigation,” added Abbott.
In addition to acts that may constitute murder as a crime against humanity, security forces have also reportedly committed acts which, when committed in a widespread and systematic manner, would amount to other crimes against humanity, including imprisonment, torture, and enforced disappearance – all of which also go towards supporting the existence of an attack.
“These killings and other crimes under international law are a direct result of the culture of impunity that has been allowed to persist in Myanmar for decades,” added Abbott. “All states should support the different accountability initiatives underway, including the Independent Investigative Mechanism for Myanmar which is collecting evidence for use in future legal proceedings.”
“It is long past time for perpetrators of serious human rights violations in the country to be brought to justice before the International Criminal Court or in any national jurisdictions willing and able to exercise universal jurisdiction.”
Background
On 12 September 2018, following an independent investigation, the United Nations Independent International Fact-Finding Mission on Myanmar called for Myanmar’s military to be “…investigated and prosecuted in an international criminal tribunal for genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes” concerning alleged violations in Shan, Kachin and Rakhine States and elsewhere throughout the country.
Under general international law, including customary international law and treaties and statutes of international criminal courts, crimes against humanity must be prosecuted. The authoritative definition of crimes against humanity is contained in the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (ICC).
Under Article 7 of the Rome Statute, for killings to amount to crimes against humanity, they must be committed as part of a widespread or systematic attack directed against any civilian population, with knowledge of the attack. According to the elements of crimes of the Rome Statute, “’Attack directed against a civilian population’ in these context elements is understood to mean a course of conduct involving the multiple commission of acts referred to in Article 7, paragraph 1, of the Statute against any civilian population, pursuant to or in furtherance of a State or organizational policy to commit such attack. The acts need not constitute a military attack. It is understood that ‘policy to commit such attack’ requires that the State or organization actively promote or encourage such an attack against a civilian population.”
Generally speaking, “widespread” refers to the geographical scope of the attack and the number of victims, but not exclusively. “Systematic” refers to the organized nature of the acts of violence and the improbability of their random occurrence.
Myanmar is not a State Party to the Rome Statute of the ICC. However, the ICC is investigating crimes committed against the Rohingya minority as part of waves of violence in Rakhine State in 2016 and 2017 where one element or part of the crime was committed inside Bangladesh, which is a party to the Rome Statute. The ICC would be able to conduct a full investigation of the situation in Myanmar if the UN Security Council used its Chapter VII powers to refer the matter to the ICC pursuant to Article 13(b) of the Rome Statute.
Universal jurisdiction refers to the legal concept that States have the authority, and in some cases the obligation, to bring proceedings in relation to certain crimes, including crimes against humanity, because they are so serious it does not matter where the crimes were committed or the nationality of the perpetrators or the victims. States are generally entitled to exercise jurisdiction for serious under crimes under international law.
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Director of Global Accountability and International Justice; e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org
Sam Zarifi, ICJ’s Secretary General, sam.zarifi(a)icj.org
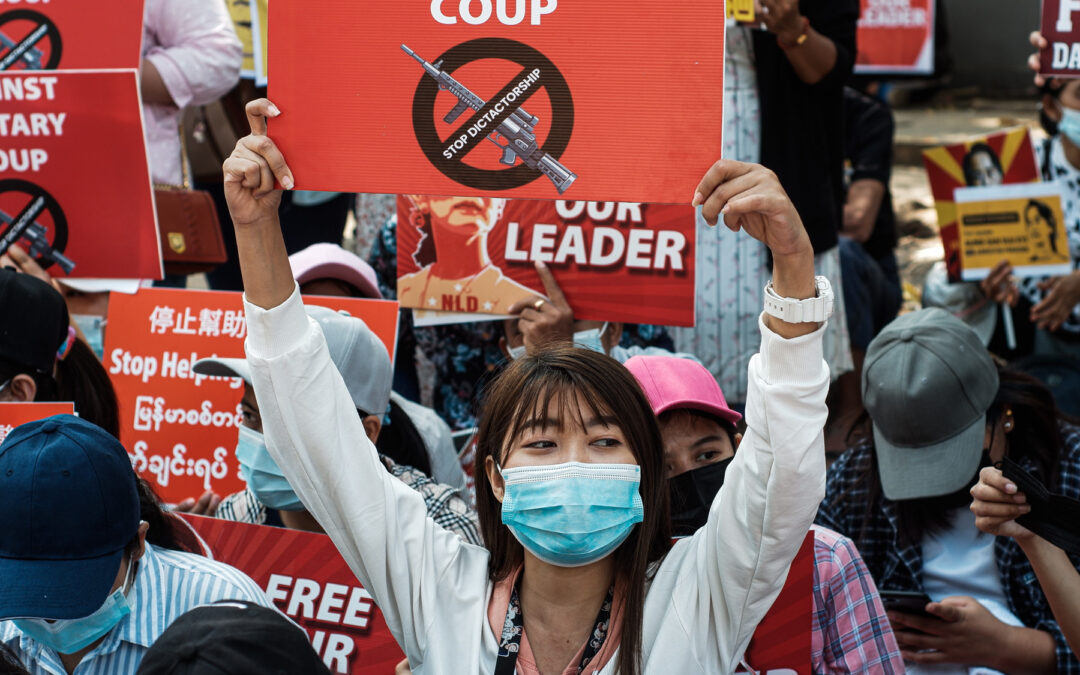

Mar 2, 2021 | News
Myanmar’s military government should reverse its post-coup d’etat revisions of legal protections for human rights in the country, the ICJ and Human Rights Watch said today.
Myanmar’s State Administration Council (SAC), appointed by the country’s military after it overthrew the elected civilian government on February 1, 2021, has dictated key revisions to the country’s legal system that criminalize even peaceful protests, and enable violations of the right to privacy and arbitrary arrests and detention. The changes were made through orders signed by the commander-in-chief, Sr. Gen. Min Aung Hlaing, on behalf of the SAC, and outside the parliamentary process.
“As Myanmar’s military increasingly relies on excessive force and intimidation to quell peaceful protests against its coup, it is trying to give a veneer of legality to its actions by subverting existing protections in the legal system.”
“These revisions, which violate the principle of legality and Myanmar’s international obligations, in no way excuse or legitimate the widespread violations of human rights now taking place in Myanmar.”
– Ian Seiderman, ICJ’s Director of Law and Policy.
Since the coup on February 1, the military junta has:
- arbitrarily suspended sections of the Law Protecting the Privacy and Security of Citizens (2017), removing basic protections, including the right to be free from arbitrary detention and the right to be free of warrantless surveillance and search and seizure;
- amended the Penal Code to create new offenses and expand existing offenses to target those speaking critically of the coup and the military, and those encouraging others to support the “Civil Disobedience Movement”;
- amended the Ward and Tract Administration Law to reinstate the requirement to report overnight guests;
- amended the Code of Criminal Procedure to make the new and revised offenses non-bailable and subject to warrantless arrest; and
- amended the Electronic Transactions Law to prevent the free flow of information and criminalize the dissemination of information through cyberspace, including expression critical of the coup or the acts of the junta.
Under international legal standards, any restrictions on human rights must be strictly necessary to protect a legitimate interest and proportionate to the interest being protected, even in times of public emergency or for legitimate national security purposes (conditions that do not apply in Myanmar currently). The orders issued by the SAC fail to meet that standard, as they will arbitrarily interfere with the exercise of rights protected under international law, including freedom of expression, freedom of peaceful assembly, the right to liberty, and the right to privacy. Certain rights, such as the rights to bodily integrity and nondiscrimination, are not subject to restriction.
“By stripping the people of Myanmar of their basic rights, the military is once again demonstrating its disdain for international human rights protections,” said Linda Lakhdhir, Asia legal advisor at Human Rights Watch. “The junta cannot justify the oppression of Myanmar’s inhabitants through the unilateral creation of arbitrary new laws.”
Contact
Osama Motiwala, ICJ Asia-Pacific Communications Officer, e: osama.motiwala(a)icj.org
Mandira Sharma: ICJ Senior Legal Adviser, e: mandira.sharma(a)icj.org
Analysis of Legal Code Changes
Law Protecting the Privacy and Security of Citizens (2017)
On February 13, the State Administration Council arbitrarily suspended sections 5, 7 and 8 of the Law Protecting the Privacy and Security of Citizens, eroding basic protections for individuals.
Section 5 required the presence of two witnesses whenever the police enter a residence for the purposes of search or seizure “to ensure that there is no damage to the privacy or security of the citizen.” The suspension of that protection significantly raises the risk of abuses during searches and arrests.
Section 7 required a court order for any detention of more than 24 hours. Suspension of the provision will facilitate violations of international law, which provides that any person detained on a criminal charge be promptly taken before a judge.
Section 8 provided protections of an individual’s right to privacy by prohibiting search and seizure, surveillance, spying, or any investigation affecting the privacy, security, and dignity of the individual without a court order – protections that the junta has removed. Under international law no one shall be subjected to arbitrary interference with their privacy, family, home or correspondence.
Penal Code Amendments
On February 14, the SAC announced amendments to the Penal Code that could lead to criminal liability for thousands of demonstrators exercising their rights to free expression of their views, and anyone publicly criticizing the military coup d’etat through any means.
The SAC inserted a new provision, section 505A, that could be used to punish comments regarding the illegitimacy of the coup or the military government, among others. The new section would criminalize comments that “cause fear,” spread “false news, [or] agitates directly or indirectly a criminal offense against a Government employee.” Violation of the section is punishable by up to three years in prison.
Section 505(a) previously made it a crime to publish or circulate any “statement, rumor or report” “with intent to cause, or which is likely to cause, any officer, soldier, sailor or airman, in the Army, Navy or Air Force to mutiny or otherwise disregard or fail in his duty.” It has been replaced with much broader language clearly designed to penalize those encouraging members of the civil service of the security services to join the Civil Disobedience Movement.
Under the revised provision, any attempt to “hinder, disturb, damage the motivation, discipline, health and conduct” of the military personnel and government employees and cause their hatred, disobedience or disloyalty toward the military and the government is punishable by up to three years in prison.
The SAC also significantly broadened the “treason” provisions in section 124 of the Penal Code. Section124A, which already criminalized comment that “bring into hatred or contempt” or “excite disaffection against” the government, was expanded to include comments relating to the defense services and defense services personnel, effectively criminalizing any criticism of the military or military personnel. Violation of the section is punishable by up to 20 years in prison.
The newly added section 124C imposes a prison term of up to 20 years on anyone who intends to “sabotage or hinder the performance of the Defense Services and law enforcement organizations who are engaged in preserving the stability of the state.” This provision would criminalize efforts to encourage security forces to join the Civil Disobedience Movement or permit unauthorized protests.
Finally, under section 124D, a person can be sentenced up to seven years in prison if they hinder a government employee from carrying out their duties. This provision is so broad that any actions of protesters could be interpreted as preventing security personnel or defense service officers from performing their duty.
Code of Criminal Procedure
On February 14 the junta amended the Code of Criminal Procedure Amendment Law to make offenses under sections 505A, 124C and 124D non-bailable and subject to arrest without a warrant.
Ward or Village Tract Administration Law (13/2/21)
The amendments to the Ward or Village Tract Administration Law (13/2/21) further increase the military’s ability to conduct surveillance on people’s movements, in particular on human rights defenders seeking shelter away from their own homes. Amendments to section 17 of the Act require all overnight guests from other wards or villages to be reported to the ward or village tract administrator, who are authorized by section 13 to “take action” against any who “failed to inform the guest list.” Section 27 reintroduces criminal sanctions for failing to report overnight guests. Such provisions existed under previous military governments and were deeply resented.
Electronic Transactions Law (Law No 7/ 2021)
On February 15, the junta also amended the Electronic Transactions Law to include, among others, provisions that had been proposed in the draft Cybersecurity Law.
As was true under that much-criticized draft law, the amended Electronics Transactions Law permits government agencies, investigators, or law enforcement to access personal data in relation to “cyber-crimes,” “cyber misuse” or any criminal investigation.
The amendments also include several provisions (articles 38(d) and (e)) that provide criminal penalties for “unauthorized” access to online material and that could be used to prosecute whistle blowers, investigative journalists, or activists who use leaked material for their work.
Section 38B criminalizes “obtaining, disclosing, using, destroying, modifying, disseminating, or sending someone’s personal data to anyone else without approval,” with one to three years in prison. While the protection of the right to privacy online is important, this provision goes well beyond legitimate protections on privacy and imposes arbitrary restrictions on freedom of expression.
In particular, “personal data” is defined in a manner so broad as to include virtually any information associated with a person. The law is therefore impermissibly vague and overbroad, as it would likely prevent even the disclosure of information about anyone involved in alleged human rights violations, including by human rights defenders and journalists.
Section 38C criminalizes the creation of “misinformation or disinformation with the intent of causing public panic, loss of trust or social division on cyberspace,” and provides for imprisonment of one to three years in addition to fines. These provisions are similarly vague and overbroad and unnecessarily and disproportionately limit the exercise of expression online, including criticism of the coup and the military junta.
***
Download the full statement here.

Mar 1, 2021 | News
The Nepal government should immediately withdraw an ordinance that undermines the independence of constitutional human rights bodies and rescind recent appointments that were made without consultation or parliamentary approval, the ICJ, Human Rights Watch, and Amnesty International said today.
These government actions undermine public trust and confidence in the integrity of the judiciary and other constitutional bodies such as the National Human Rights Commission and the Election Commission. The illegitimate appointments process is not simply an abstract irregularity but will lead to ineffective and weak implementation of critical mandates to protect human rights and other rule of law objectives, the groups said.
“The government’s actions are a severe dent in Nepal’s long struggle for a rule of law-based constitution, which was finally adopted in 2015 to guarantee human rights,” said Meenakshi Ganguly, South Asia director at Human Rights Watch. “It is sad to see some of the same politicians who drafted the Constitution playing fast and loose with the charter just a few years later.”
On December 15, 2020, President Bidya Bhandari endorsed an executive ordinance to amend the law governing the Constitutional Council, which makes appointments to the judiciary, the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), and other constitutional bodies including the Election Commission. Under the Constitutional Council Act, five out of six members must be present, but under the ordinance a simple majority is sufficient. Because one seat on the council is vacant the quorum has been reduced to three.
The Constitutional Council met the same day with a newly reduced quorum. Three council members made 38 nominations to vacant positions on constitutional bodies at that meeting. They included all five seats on the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), as well as nominations to bodies established to protect the rights of Dalits, women, and marginalized minorities, and to investigate corruption allegations.
Under the Constitution, appointments to these key institutions are supposed to be vetted by parliament. However, parliament was abruptly dissolved on December 20, five days after the appointments were announced. The nominees were sworn in on February 3, 2021, despite legal challenges in the Supreme Court to the constitutionality of the nominations and the dissolution of parliament. On February 23, the Supreme Court ruled that the dissolution of parliament was unconstitutional.
“In a context where repeated calls for institutional reforms have gone unheeded for decades, this move by the government further weakens the effectiveness of constitutional bodies that are supposed to be beacons of hope for victims of human rights violations and abuses,” said Mandira Sharma, senior international legal adviser at ICJ. “Independence, impartiality and legitimacy are preconditions for these bodies to effectively and efficiently deliver their mandates.”
Nepal’s Human Rights Commission, until recently, had played an important role in calling for accountability, including by releasing the names of people allegedly responsible for serious human rights violations such as torture and extra-judicial killing and recommending that they should be prosecuted. It is currently graded ‘A’ by the Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) for its compliance with the Paris Principles, which were adopted by the UN General Assembly as the basic standards governing the mandate and operation of effective national human rights organizations. Core among the Paris Principles is that a national human rights institution must be independent and that its independence must be guaranteed by law. The organizations are concerned that following the new appointments the commission no longer meets those standards.
Among the other constitutional bodies to which new commissioners have been appointed in the same manner are the Election Commission and the Commission for the Investigation of Abuse of Authority (CIAA), Nepal’s anti-corruption agency. The Election Commission is seen by many people as playing an important role in efforts to achieve a society based on the rule of law and respect for human rights , while the CIAA has the authority to bring corruption cases against politicians.
Numerous appointments have also been made to commissions with mandates to protect the rights of people from vulnerable groups, including the National Women’s Commission, National Dalit Commission, and National Inclusion Commission. Many of these positions had lain vacant for years.
At least two Supreme Court petitions have been filed challenging the ordinance amending the Constitutional Council Act, and the new appointments to constitutional bodies. The chief justice, Cholendra Shumsher Rana, who sits on the constitutional bench of the Supreme Court, participated in the three-member Constitutional Council meeting that made the disputed nominations, and he administered the oath of office to the new commissioners on February 3.
“The doubts over the independence and integrity of the NHRC and other commissions will endanger the protection of human rights in Nepal,” said Dinushika Dissanayake, Deputy South Asia Director of Amnesty International. “The government must immediately reverse these appointments and start a new process in consultation with the civil society and rights holders in Nepal.”
The Accountability Watch Committee, a group of prominent human rights defenders in Nepal, issued a statement on February 12 announcing that they would not “cooperate and engage with the NHRC and other constitutional bodies until the Supreme Court’s decision.” Accountability Watch also called upon “the United Nations, diplomatic missions in Nepal and international organizations not to give legitimacy and cooperate with this appointment process which is currently sub-judice at the Supreme Court of Nepal.”
Foreign donor agencies that have previously engaged with the NHRC, and with the other commissions affected by this process, should stand clearly for a proper, open, and transparent appointments process that is based on international standards, Human Rights Watch, ICJ, and Amnesty International said.
Download the statement in English and Nepali.
Contact
In London, Meenakshi Ganguly (English, Bengali, Hindi): gangulm(a)hrw.org
In Colombo, Dinushika Dissanayake (English): dinushika.d(a)amnesty.org
In Kathmandu, Mandira Sharma (English, Nepali): mandira.sharma(a)icj.org

Mar 1, 2021 | Advocacy, News
Between December 2020 and February 2021, the ICJ co-hosted a series of workshops for government authorities, medical professionals and lawyers in the southern border provinces of Thailand on how to conduct investigations into alleged unlawful killings and enforced disappearances.
Thailand’s southern border provinces of Pattani, Yala, Narathiwat and four districts of Songkhla have been affected by a longstanding ethno-nationalist insurgency, which has involved conflict between certain Malay groups and Thai military and security forces. Special security laws have been enacted and applied to the deep south. Over recent years, there are reports of widespread human rights violations, including violations of due process and fair trial rights, torture, ill-treatment while in custody, arbitrary detention and extrajudicial killings continue to emerge. Investigations into these allegations, prosecutions of perpetrators and provision of remedies and reparations to victims remain slow.
The first workshop was organized between 21 and 22 December 2020 in Songkhla province for authorities from Thailand’s southern border provinces. The event focused on how investigations into unlawful deaths should be conducted in accordance with international human rights law and standards, with a particular focus on the revised Minnesota Protocol (2016), which the ICJ assisted in producing.
The workshop was co-hosted with Thailand’s Ministry of Justice, the Embassy of New Zealand in Bangkok, and the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR). The participants included 48 judges, public prosecutors, police investigators, representatives of the Ministry of Justice’s Department of Special Investigation (DSI), the National Anti-Corruption Commission (NACC), the Narcotics Control Board (ONCB) and observers from the Internal Security Operations Command (ISOC) Region 4 Forward.
The second workshop was organized on 23 and 24 December 2020 in Pattani province for medical professionals in the same region. The event introduced participants to the international human rights law and standards governing the effective investigation and documentation of torture and other ill- treatment, including the revised Minnesota Protocol (2016) and the Istanbul Protocol (1999), and emphasized the important role of medical professionals in the documentation of torture.
The workshop was co-hosted with Thailand’s Ministry of Justice and the OHCHR. The participants included 28 medical professionals from district and military hospitals and detention centres.
Between January and February 2021, the ICJ also developed training videos for defence lawyers and civil society representatives in the southern border provinces. The videos focused on the use of forensic evidence in cases of alleged unlawful killings and how international human rights law and standards, particularly the revised Minnesota Protocol (2016) and ICJ’s Practitioners’ Guide No. 14, can assist defence lawyers when preparing for criminal proceedings and challenging the forensic evidence of prosecution witnesses.
The project was jointly implemented with the OHCHR, Cross-Cultural Foundation, Muslim Attorney Centre Foundation and the Embassy of New Zealand in Bangkok. Participants included 21 defence lawyers and civil society representatives from Thailand’s southern border provinces.
Speakers at the three workshops included:
- Amornrat Lekvichai, Thailand’s Institute of Forensic Science;
- Badar Fafukh, Human Rights Officer, OHCHR Regional Office for South-East Asia;
- Duangsamorn Chudeechan, Thailand’s Institute of Forensic Science;
- Duarte Nuno Vieira, Full Professor, Faculty of Medicine, University of Coimbra and Chairman of the Scientific Advisory Board of the International Criminal Court;
- Gisle Kvanvig, Head of UN Police Secretariat, Norwegian Center for Human Rights;
- Howard Varney, Senior Programme Advisor, International Center for Transitional Justice;
- Ivar Fahsing, Expert on investigation and Human Rights, Norwegian Center of Human Rights;
- Porntip Rojanasunan, member of the Expert Advisory Panel of the revision of the Minnesota Protocol;
- Sanhawan Srisod, ICJ Associate Legal Adviser;
- Stephen Cordner, Professor Emeritus, Department of Forensic Medicine, Monash University and editor of the Forensic Science sections of the 2016 Minnesota Protocol;
- Steve Wood, Senior Liaison Officer and Regional Coordinator, New Zealand Police National HQ;
- Stuart Casey-Maslen, Honorary Professor, Faculty of Law, University of Pretoria and Research Coordinator of the Minnesota Protocol;
- Thomas Wenzel, Full Professor, Faculty of Medicine, University of Vienna; and
- Vitit Muntarbhorn, Professor Emeritus, Faculty of Law, Chulalongkorn University and Former ICJ Commissioner.
The workshops are part of the ICJ’s ongoing efforts under the Global Accountability Initiative to ensure the domestic implementation of international law and standards on the investigation of potentially unlawful deaths and enforced disappearances.
In Thailand, since 2017, the ICJ has held several national and regional-level workshops on the same topics with justice sector actors, defence lawyers and civil society representatives.
Contact
Sanhawan Srisod, ICJ Associate Legal Adviser, Asia & the Pacific Programme, e: sanhawan.srisod(a)icj.org
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Director, Global Redress and Accountability; e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org
See also
Thailand: launch of the revised Minnesota Protocol










