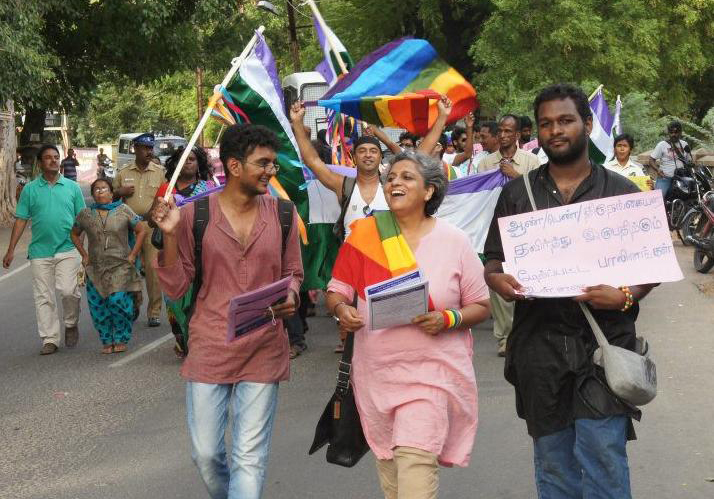Jul 26, 2018 | News, Op-eds
An opinion piece by Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior Legal Adviser in Bangkok, Thailand.
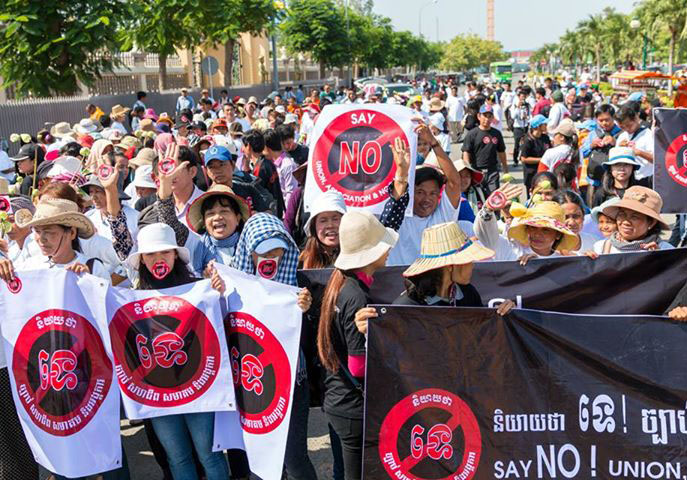
Over recent decades, international observers have tended to view the human rights and political situation in Cambodia as a series of predictable cycles that does not warrant too much alarm.
The conventional wisdom has been that Prime Minister Hun Sen and his government routinely tightens their grip on the political opposition and civil society in advance of elections before relaxing it again after victory has been secured.
But that analysis is no longer valid.
The reason is simple: During the course of ensuring it will win the national election scheduled for this Sunday (29 July), Hun Sen’s ruling Cambodian People’s Party (CPP) has, since the last election, systematically altered the country’s constitutional and legal framework – and these changes will remain in place after the election has passed.
Through the passage of a slew of new laws and legal amendments inconsistent with Cambodia’s obligations under international law, and the frequent implementation of the law to violate human rights, the legal system has been weaponized to overwhelm and defeat the real and perceived opponents of the CPP, including the political opposition, the media, civil society, human rights defenders and ordinary citizens.
This misuse of the law is a significant development in the history of modern Cambodia and represents a determined move away from the vision enshrined in the historic 1991 Paris Peace Agreements that ended years of conflict and sought to establish a peaceful and democratic Cambodia founded on respect for human rights and the rule of law.
And it risks cementing the human rights and rule of law crisis that now exists within Cambodia for years to come.
To facilitate the closure of civil society space, and contrary to international law and standards, in 2015 the Law on Associations and Non-Governmental Organizations (LANGO) was passed, which requires the mandatory registration of all NGOs and Associations, provides the government with arbitrary powers to deny or revoke registration, and places a vaguely worded duty on NGOs and associations to “maintain their neutrality towards political parties”.
The biggest blow to the political opposition has been the amendment last year of the Law on Political Parties (1997), amended twice within four months, which empowers the Supreme Court to dissolve parties, and four election laws, which permits the redistribution of a dissolved party’s seats in the country’s senate, national assembly, and commune and district councils.
Last November, the Supreme Court, presided over by a high-ranking member of the CPP, used the amended Law on Political Parties to dissolve the main opposition party, the Cambodia National Rescue Party (CNRP), which had received just under 44% of the vote – or about 3 million votes – in communal elections held in June 2017.
After the CNRP’s dissolution, the amended election laws were then used to redistribute CNRP seats at every level of government, from the commune to the senate, to the CPP and minor parties.
To silence the media, the country’s media and taxation laws have been invoked – local radio stations have been ordered to stop broadcasting Radio Free Asia and Voice of America “in order to uphold the law on media” and the independent Cambodia Daily was forced to close after being presented with a disputed US $6.3 million tax bill which the Daily claimed was “politically motivated” and not accompanied by a proper audit or good faith negotiations.
To curb the exercise of freedom of expression, the Constitution has received vaguely worded amendments placing an obligation on Cambodian citizens to “primarily uphold the national interest” while prohibiting them from “conducting any activities which either directly or indirectly affect the interests of the Kingdom of Cambodia and of Khmer Citizens”.
Meanwhile individual journalists, members of the political opposition including the CNRP’s leader, Kem Sokha, human rights defenders and an Australian documentary filmmaker have been charged with any number of a kaleidoscope of crimes ranging from intentional violence and criminal defamation to treason and espionage.
And Cambodia lacks an independent and impartial judiciary.
In 2014, three “judicial reform laws” were passed which institutionalized the prosecution and judiciary’s lack of independence from the executive.
At the same time, the government perversely uses the doctrine of the “rule of law” to justify its actions.
Just hours after the Supreme Court dissolved the CNRP, Hun Sen announced that the decision was made “in accordance with the rule of law.”
When members of the diplomatic community and senior UN officials meet government officials to express concern at the increasing misuse of the law they receive an absurdist legal lecture on the “importance of the rule of law”.
What is happening in Cambodia is the opposite of that.
The International Commission of Jurists, UN authorities and others have been defining the rule of law since the Universal Declaration of Human Rights was pronounced in 1948.
All agree that that the rule of law entails passing and implementing laws consistent with a country’s international human rights obligations.
It is time for the international community to recognize that a frank and fresh analysis of the situation in Cambodia is urgently required which acknowledges the way the country’s underlying legal and constitutional framework has been deliberately altered, and the way in which this will impact the country adversely long past this month’s election.
This acknowledgment must be accompanied by a coherent and, where possible, joint, plan of action that clearly sets out, with a timeline, what is required to bring Cambodia back on track with the agreed terms of the Paris Peace Agreements – including necessary legal and justice sector reforms – and the political and economic consequences for not doing so.
As long as Hun Sen’s Government deploys increasingly sophisticated justifications for its repressive actions, a more refined, multilayered and vigorous response from the international community is required – grounded on a proper application of the rule of law and Cambodia’s international human rights obligations.

Jul 26, 2018 | News
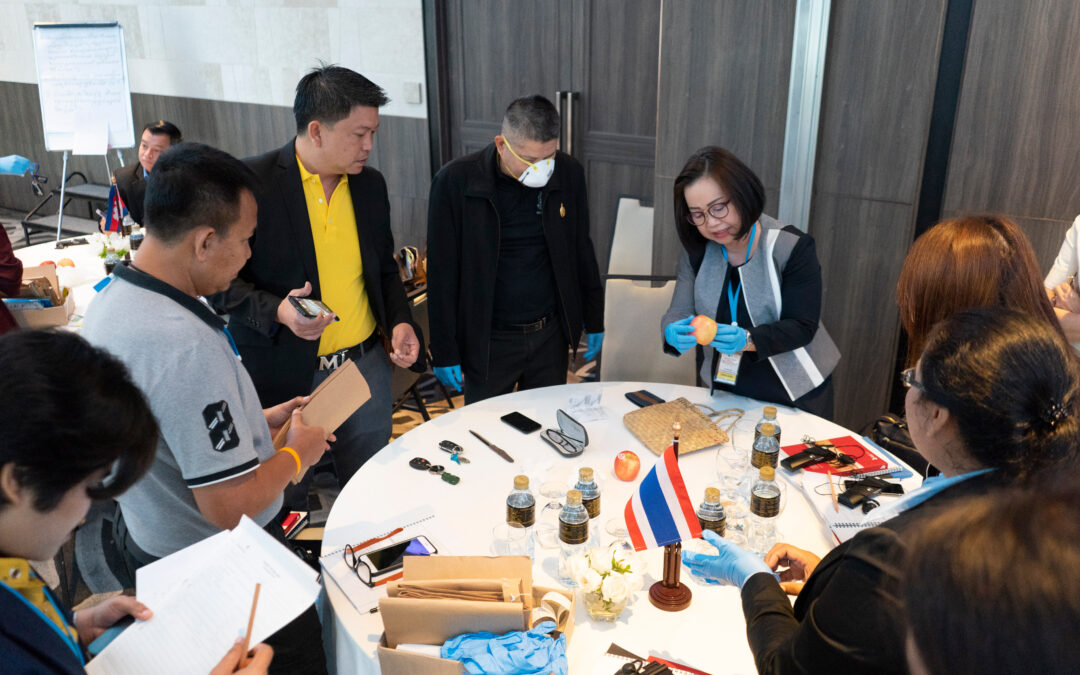
From 24 to 26 July 2018, the ICJ co-hosted a workshop for authorities from Thailand, Cambodia, and Myanmar.
The theme of the workshop was on conducting investigations of potentially unlawful deaths and enforced disappearance in accordance with international human rights law and standards.
The workshop was co-hosted with Thailand’s Ministry of Justice, the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) and the New Zealand Embassy in Bangkok.
The participants included 25 criminal investigators, public prosecutors and representatives of the Cambodian Ministry of Justice and the Thai Ministry of Justice.
The event commenced with opening remarks by James Andersen, Deputy Head of Mission, Embassy of New Zealand in Bangkok; Aim-orn Siangyai, Deputy Director General of Thailand’s Rights and Liberties Protection Department, Ministry of Justice; Frederick Rawski, Asia Pacific Regional Director, ICJ; and Shivani Verma, Human Rights Officer, OHCHR Regional Office for South-East Asia.
Kingsley Abbott, Senior Legal Adviser at the ICJ, gave a summary of the international human rights legal framework that applies to the investigation of unlawful deaths and enforced disappearance.
He then provided an outline of the revised Minnesota Protocol on the Investigation of Potentially Unlawful Death (2016), which was launched in Thailand on 25 May 2017 and which formed the core of the materials used at the workshop.
Other speakers included Glenn Williams, Detective Inspector, Field Crime Manager, New Zealand Police National Headquarters, who addressed the investigation process including crime scene management; Sean Buckley, International Investigator, who addressed witness interviews; Shivani Verma of the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights who addressed Witness Protection; and Dr. Pornthip Rojanasunan, Adviser of Thailand’s Central Institute of Forensic Science (CIFS), who addressed the issue of forensic pathology.
This workshop followed three workshops the ICJ co-hosted between 5 to 8 December 2017 and 30 May to 1 June 2018 in Thailand on the investigation of potentially unlawful deaths and enforced disappearance for lawyers from Thailand and India, academics and State authorities from Thailand, Cambodia, Myanmar and Nepal.
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, Senior International Legal Adviser, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Office, t: +66 94 470 1345, e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org

Jul 24, 2018 | Events, News
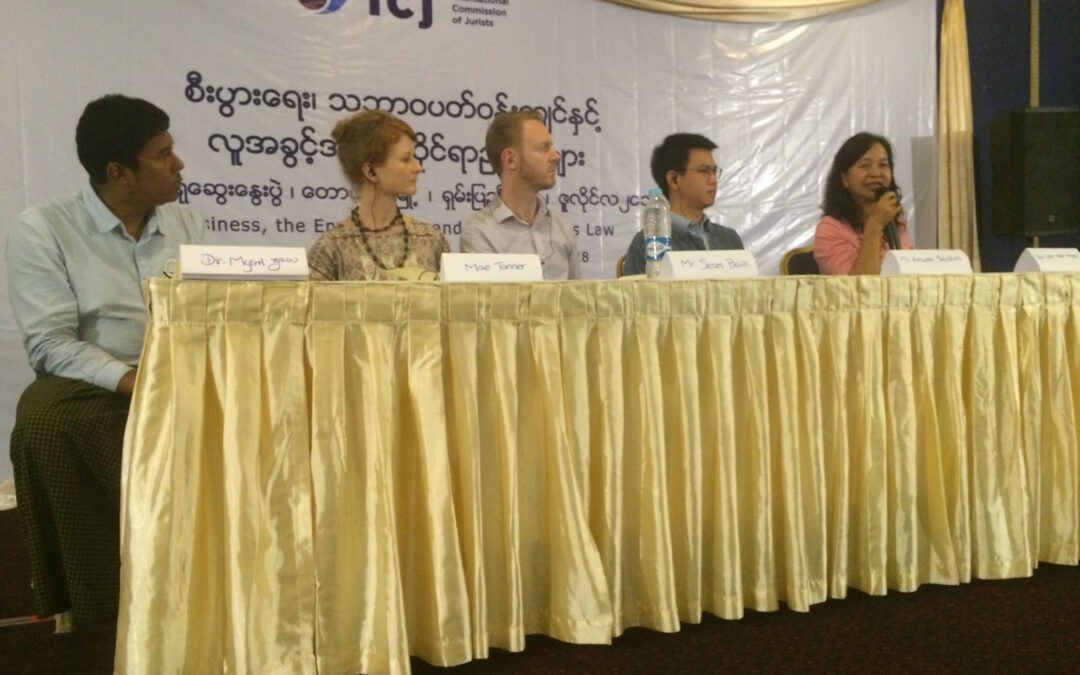
On 22 and 23 July the ICJ convened a workshop on Business, the Environment and Human Rights Law in Taunggyi, the capital of Myanmar’s Shan State.
This followed meetings between the ICJ’s legal advisers and the Shan State High Court and also with the State Advocate General on 13 July, to discuss rule of law developments.
The workshop aimed to identify ways to address the impacts of business activities on human rights and the environment, through legal advocacy including strategic litigation, and to provide a forum for cooperation and experience sharing among participants.
More than 50 lawyers, parliamentarians, human rights defenders and civil society representatives attended from Shan, Kayah and Mon states – provinces that together border Thailand, Laos and China.
An overview of the investment context was provided by Dr Myint Zaw of Paung Ku Myanmar, who also shared lessons from environmental activism in Myanmar.
As well as highlighting weaknesses in domestic law and policy, he presented concerns around lack of transparency and information sharing between the legislature and executive branches of government.
Australian lawyer and ICJ consultant Mae Tanner gave an overview of international human rights law and standards relevant to business activities and environmental protection, particularly emphasizing the obligations assumed by Myanmar in ratifying the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights.
She offered insights as to how UN mechanisms can be used by civil society to advance their advocacy on business and human rights in Myanmar.
Senior Advocate U Myint Thwin drew on his extensive litigation experience to share perspectives on the complex and confusing array of land laws in Myanmar and emphasized the importance of legal knowledge and training to combat corruption and achieve accountability.
The ICJ’s legal adviser Mr Sean Bain outlined the domestic laws relevant to investment and environmental protection in Myanmar and highlighted some key provisions that offer protection against human rights violations and abuses.
He noted the government’s stated aim of promoting the rule of law in Myanmar and emphasized the importance of demanding accountability, transparency and justice in this context.
Amarin Saichan, lawyer with Thai NGO EnLAW, shared experiences of pursuing strategic litigation to address unlawful and harmful business activities in Thailand, stressing the need for creativity in using the law to seek justice and accountability.
He also raised concerns around the use by government of strategic litigation against public participation in Thailand and explained how Thai lawyers are using the courts to guarantee the right protest against harmful development projects.
Participants had the opportunity to discuss how the strategies they shared could be used in the context of issues faced by their communities.
These included human rights and environmental concerns raised by energy and extractive projects, restrictions on shifting agriculture, and violations of the right to freedom of expression and assembly faced by communities who oppose state-backed developments.
They considered advocacy strategies for four case studies selected by participants from across Shan, Kayah and Mon states.
Throughout the workshop speakers and participants highlighted the importance of cooperation between civil society and lawyers, and the need to use Myanmar’s legal system more proactively as part of their broader advocacy strategies.
This workshop is part of the ICJ’s ongoing support to lawyers and civil society in Myanmar.

Jul 15, 2018 | News
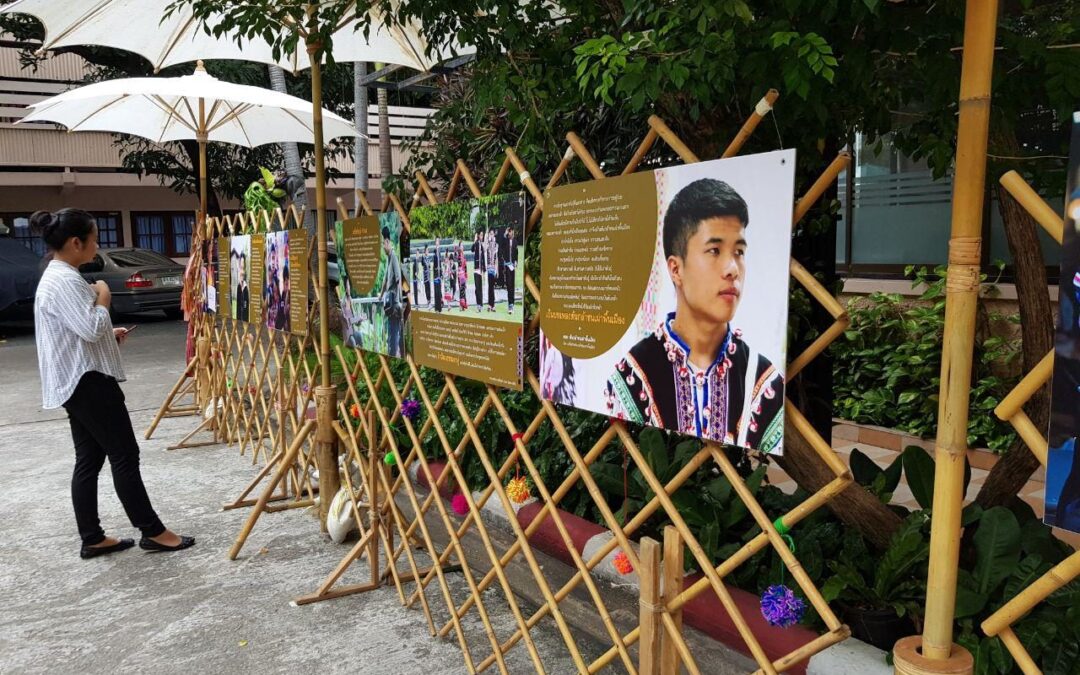
On 14 July 2018, the ICJ co-organized a discussion on extrajudicial killings in Thailand, focusing on the cases of Chaiyaphum Pasae and Abe Saemu.
The discussion was held at the Student Christian Centre in Bangkok.
Chaiyaphum Pasae, a Lahu youth activist, was killed by a military officer in the Chiang Dao district of Thailand’s northern Chiang Mai province in March 2017. The killing took place during an attempt to arrest him as an alleged drug suspect. Officials claimed Chaiyaphum Pasae had resisted arrest and was subsequently shot in “an act of self-defence”.
Abe Saemu, from the Lisu hill tribe, was killed by a military officer in February 2017 in the Chiang Dao district of Chiang Mai province in an attempt to arrest him on allegations of drug coffences. Officials claimed Abe Saemu had resisted arrest and was killed in “self-defence”.
During the discussion, ICJ’s National Legal Adviser Sanhawan Srisod addressed the audience to set out the international law and standards that apply to investigating potentially unlawful deaths, including the rights of victims and family members, referring to the standards set out in the revised Minnesota Protocol on the Investigation of Potentially Unlawful Death (2016), which was launched in Thailand on 25 May 2017.
Participants in the event included members of the families of Chaiyaphum Pasae and Abe Saemu, the lawyers in both of their cases, interested members of the public, media representatives, students and academics.
The discussion opened with an art exhibition and Lahu dance show by the Save Lahu group. Human Rights Commissioner Angkhana Neelapaijit then made a presentation on challenges in seeking accountability for extrajudicial killings in Thailand.
A panel discussion on the latest updates in the cases of Chaiyaphum Pasae and Abe Saemu followed, moderated by Pranom Somwong from Protection International.
The panel included relatives of Chaiyaphum Pasae and Abe Saemu; Ratsada Manuratsada, a lawyer representing the families in both cases and Krissada Ngamsiljamras, a representative from the National Human Rights Commission of Thailand.
A second panel considered challenges on the administration of criminal justice in the context of unlawful deaths.
Moderated by Pratubjit Neelapaijit of UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, the panel included Malee Sittikreangkrai (Chiang Mai University); Sumitchai Hattasan (Human Rights Lawyers’ Association); Namtae Meeboonsalang (Provincial Chief Public Prosecutor, Office of the Attorney-General); Kritin Meewutsom (Forensic doctor, Ranong Hospital); and Sanhawan Srisod (ICJ).
The event was conducted in collaboration with Cross Cultural Foundation (CrCF); Protection International (PI); UN OHCHR; Human Rights Lawyers’ Association (HRLA); Thai Volunteer Services (TVS); Dinsorsee Creative Group; Center for Ethnic Studies and Development, Chiang Mai University (CESD); Legal Research and Development Center, Chiang Mai University (LRDC) and Network of Indigenous Peoples in Thailand (NIPT).
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, Senior Legal Adviser, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Office, kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org

Jul 13, 2018 | News
The Sri Lankan Government should reconsider and reverse its decision to bring back the death penalty for drug related offences, the ICJ said today.
On 10 July, the Sri Lankan Cabinet unanimously approved an action plan to implement the death penalty for “drug smugglers”.
According to the spokesperson of the Cabinet, 19 people convicted for “large scale drug offences” who “are still involved in drug trafficking…from within prisons” would initially be those initially designated for execution.
Sri Lanka has had a moratorium on the death penalty for over four decades.
The last execution carried out in the country was in 1976.
“The resumption of executions of convicted drug offenders would constitute a violation of the right to life under international law,” said Ian Seiderman, ICJ’s Legal and Policy Director.
”And, based on experience around the globe, it will not in any way serve the purported objective of tackling the problems of drug-related crime in Sri Lanka,” he added.
Article 6 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), which Sri Lanka acceded to in 1980, guarantees the right to life and requires that states that have not yet abolished the death penalty must restrict capital punishment to only the “most serious crimes”.
The UN Human Rights Committee, the supervisory body for the ICCPR, considers that the death penalty may never be used for drug offences.
The extraordinarily retrograde measure of resuming executions following a 42-year moratorium would also constitute a violation of article 6, which contemplates at least progressive movement towards abolition.
The UN General Assembly has repeatedly adopted resolutions emphasizing that that the use of the death penalty undermines human dignity and calling on those countries that maintain the death penalty to establish a moratorium on its use with a view to its abolition.
In 2016, an overwhelming majority of 117 UN Member States – including Sri Lanka – voted in favor of a worldwide moratorium on executions as a step towards abolition of the death penalty.
“At least 150 countries have now either abolished the death penalty in law or practice,” added Seiderman.
The ICJ considers the death penalty to be a violation to the right to life and the right not to be subjected to cruel, inhuman or degrading punishment.
The ICJ urges Sri Lanka to reinstate its moratorium on executions and take steps towards taking all necessary measures to abolish the death penalty.
Contact:
Ian Seiderman, ICJ’s Legal and Policy Director, email: ian.seiderman(a)icj.org
Reema Omer, ICJ’s International Legal Advisor, South Asia, email: reema.omer(a)icj.org
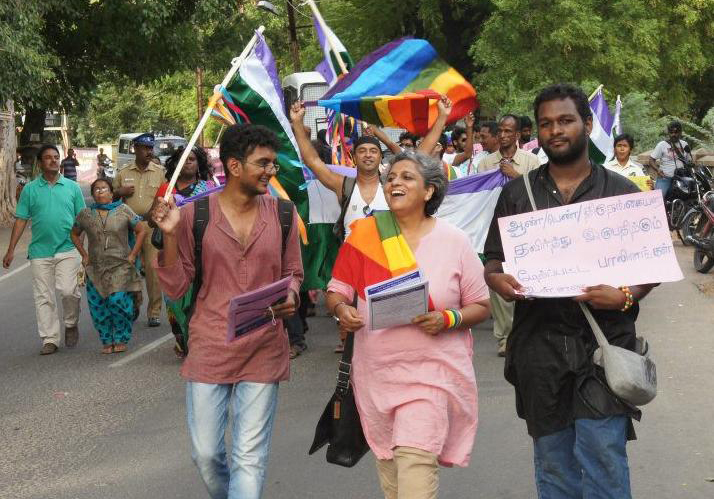
Jul 10, 2018 | News
The SC is set to reconsider the criminalization of consensual same-sex relationships between adults, in response to a writ petition with significant ramifications for addressing the full range of human rights violations based on sexual orientation or gender identity in India said the ICJ.
The Indian Supreme Court commenced hearing the case, Navtej Singh Johar v. Union of India, which is joined with five connected cases, today, concerning the constitutional validity of the criminalization of consensual same-sex relations between adults under Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code in response to writ petitions filed by several LGBTI individuals.
Section 377 criminalizes “carnal intercourse against the order of nature”. Section 377 is a relic of the British colonial penal code and is replicated in several former British colonies even though it was it was finally repealed in Northern Ireland in 1982, following repeals in Scotland in 1980 and England and Wales in 1967.
“Hopefully, the Indian Supreme Court will follow and build upon the strong precedent set by the Delhi High Court in the Naz Foundation v. Govt. of NCT of Delhi that declared Section 377 and the criminalization of consensual same-sex relationships to be in violation of the Indian Constitution as well as international law in 2009,” said Sam Zarifi, ICJ’s Secretary General.
“There are real grounds for optimism as the Indian Supreme court as recently as August 2017 handed a landmark judgment in Justice K.S. Puttaswamy and Another v. Union of India and Others that declared the right to determine one’s sexual orientation and gender identity as core to the right of privacy,” he added
The ICJ has documented how section 377 has created a climate in which arbitrary arrest, extortion, harassment and blackmail of LGBTI persons in India thrives.
“The Indian judiciary’s decision to read down section 377 in Naz Foundation v. Govt. of NCT of Delhi, which was then overruled by the Supreme Court, has been used by several other jurisdictions, such as Trinidad and Tobago as support for putting an end to criminalization of same-sex relationships. So the outcome of this petition before the Indian Supreme Court is of significance not just to people in India, but to the fight against discrimination around the world,” Zarifi said.
“But even a good decision by the Indian Supreme Court will not end the discrimination against people on the basis of their sexual orientation or gender identity in India. It’s time for the Indian Parliament to repeal section 377 in its entirety and engage in a wide-ranging review to consider which gaps, if any, need to be filled, for example with respect to acts constituting rape or other sexual offences,” he added.
Contact:
Maitreyi Gupta (Delhi), International Legal Adviser for India, t: +91 7756028369 ; e: maitreyi.gupta(a)icj.org
India-Supreme Court and Section377-News-press release-2018-ENG (full story with additional information, in PDF)