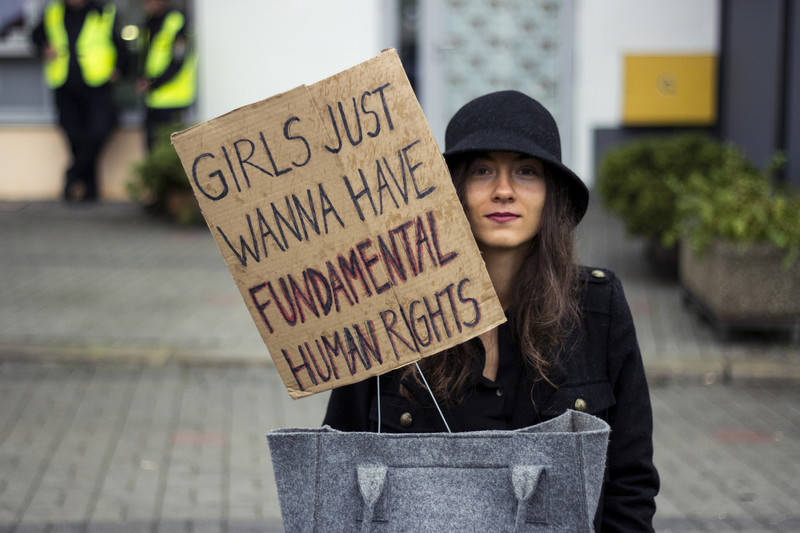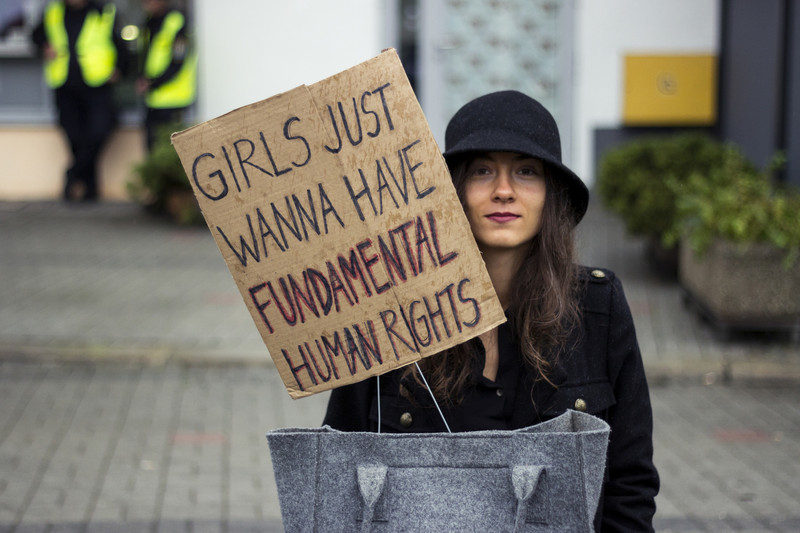May 12, 2020 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ has written to the Commissioner for Human Rights and the Rapporteurs on Turkey of the Parliamentary Assembly to alert them to the continued detention of Selahattin Demirtaş and Osman Kavala despite rulings by the European Court of Human Rights.
The International Commission of Jurists recalled that in both the Demirtaş and Kavala cases the European Court of Human Rights, in finding a violation of article 18 ECHR, determined that the detention of the applicants had been ordered in pursuance of an ulterior purpose than those allowed by article 5.1 ECHR.
That purpose was silencing of human rights and other activists, stifling pluralism and limiting freedom of political debate and utilizing pre-trial detention as a method of arbitrary punishment.
The Turkish government is however not releasing the applicants on the ground that the Chamber judgments have not yet become final.
Meanwhile, the authorities have initiated new investigations against both Demirtas and Kavala, and issued new detention orders on similar though not identical charges as those reviewed in the Court’s judgments, with the apparent intent not to implement the ECtHR judgments.
The ICJ considers that these developments may be seen as integral to the ulterior purpose identified by the Court in its Kavala and Demirtaş decisions. Under these conditions, both Kavala and Demirtaş may expect their arbitrary detention to be continued for an unlimited period of time through arrest orders based on fabricated investigations.
The ICJ further reiterated the importance of enabling access to alternatives to detention for all pre-trial detainees who may be at risk because of COVID-19 if they do not pose a current threat to public safety, regardless of the nature of the offences with which they have been charged. It stressed that, since Mr. Demirtaş and Kavala, along with many politicians and human rights defenders accused of security related offences in Turkey, do not pose a threat to public safety, they should be released as soon as possible.
ICJ-Letter-DemirtasKavala-PACERapporteurs-2020-eng (download the letter to the PACE Rapporteurs)
ICJ-Letter-KavalaDemirtas-CommissionerHR-2020-eng (download the letter to the Commissioner for Human Rights)

May 1, 2020 | Advocacy
The ICJ, the International Bar Association’s Human Rights Institute (IBAHRI), and the Centre for Civil and Political Rights (CCPR Centre) today published a legal opinion by ICJ Commissioner Professor Sarah Cleveland, on compliance of Kazakhstan’s Draft Law on the Procedure for Organising and Holding Peaceful Assemblies, with the Republic of Kazakhstan’s international human rights obligations.
“Excessive restrictions on freedom of peaceful assembly in Kazakhstan have been of significant concern to the UN Human Rights Committee, the Venice Commission of the Council of Europe, and other human rights bodies for many years,” said Sarah Cleveland.
“Kazakhstan now has an important opportunity to bring its law into compliance with its international human rights obligations, but the draft law currently being considered does not achieve this.”
The Opinion finds that the proposed legislation includes of number of restrictions on freedom of assembly that are fundamentally contrary to Kazakhstan’s human rights obligations, including (1) excessive notification and approval requirements; (2) excessive authority to ban an assembly; (3) a prohibition on spontaneous assemblies; (4) restriction of assemblies to specific locations; (5) preferential treatment for assemblies organized by the government; (6) a prohibition against foreigners, refugees, stateless persons from organizing or participating in assemblies, (7) excessive obligations on organizers and participants; and (8) excessive sanctions for organizers and participants. The timing and process for adopting a law that so fundamentally impacts domestic compliance with core human rights obligations itself raises serious human rights concerns, given the limited ability of civil society organizations and the general public to participate in a robust public debate regarding the law during the quarantine.
In light of these serious human rights concerns, the IBAHRI, the ICJ and the CCPR Centre urge the Senate and/or the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan to halt consideration of the Draft Law, and to seek guidance from the OSCE/ODIHR Panel of Experts on Freedom of Assembly and Association, the Office of UN High Commissioner on Human Rights, and/or the Venice Commission regarding how the current law on freedom of peaceful assembly might be revised consistent with Kazakhstan’s international human rights obligations.
Kazakhstan-Assembly Law Opinion-Advocacy-2020-ENG (full text in PDF)

Apr 22, 2020 | News
In a joint letter to EU Member States, the ICJ and other human rights NGOs have urged them to recognize the grave implications for human rights and the rule of law, of the Hungarian government’s recent emergency measures.
Ahead of the Council of the EU videoconference of EU Affairs Ministers to discuss the response to COVID-19, Amnesty International, International Federation for Human Rights (FIDH), Human Rights Watch, the ICJ, Open Society European Policy Institute and Reporters Without Borders (RSF) urged the Council to take immediate steps to protect the principles enshrined in Article 2 of the Treaty on European Union (TEU), and the rights enshrined in the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights. This is particularly needed in light of the already deteriorated state of the rule of law and human rights in Hungary, which warranted the activation, in September 2018, of the procedure laid down in Article 7.1 TEU.
The organisations urged the member states of the European Union to:
- include in the agenda of the upcoming session of the EU General Affairs Council an Article 7.1 TEU hearing on the situation in Hungary, including recent developments in relation to the COVID-19 outbreak, and address to the government of Hungary, as a matter of urgency, concrete recommendations to safeguard respect for the rule of law and human rights in the country, that the Hungarian government must implement by a set deadline;
- commit to assessing the implementation of the recommendations in a timely manner in order to reach a determination under Article 7.1 TEU and, should conditions warrant it, move forward under Article 7.2 TEU.
- ensure enhanced monitoring of the Hungarian government’s use of EU funding, including funds aimed at supporting member states during the public health crisis.
The organisations urged both the Council and the Commission to cooperate with each other, and with the European Parliament and national parliaments, to ensure a coordinated, consistent and effective response to the situation.
The full letter is available here: CSO Letter to GAC -rule of law in Hungary April 2020
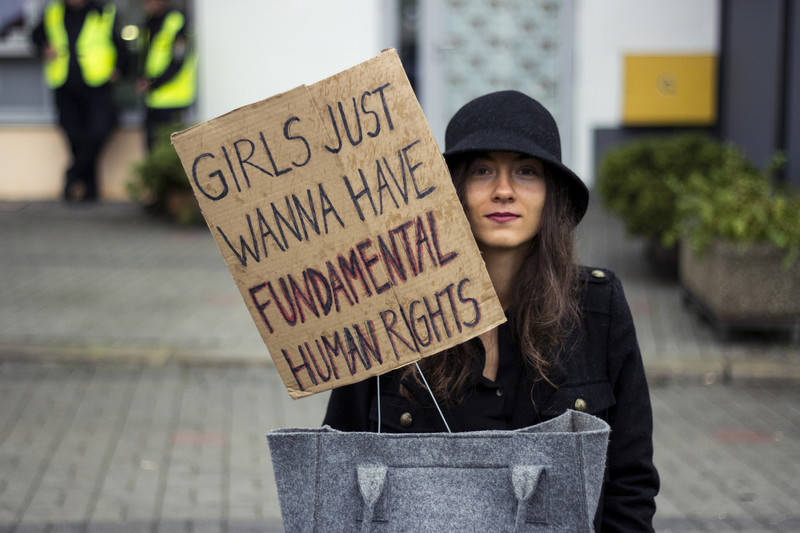
Apr 14, 2020 | Advocacy, News
The ICJ and 108 other organizations are deeply concerned by relentless attempts to roll back sexual and reproductive rights in Poland.
On 15 and 16 April Poland’s Parliament will again debate two draft bills that would severely limit access to safe abortion care and would criminalize the provision of sexuality education.
If enacted into law these bills would place women’s and adolescents’ health and well-being at risk and violate Poland’s international human rights obligations.
Full statement, in PDF: Poland-COVID-19 Abortion bill-Advocacy-2020-ENG)
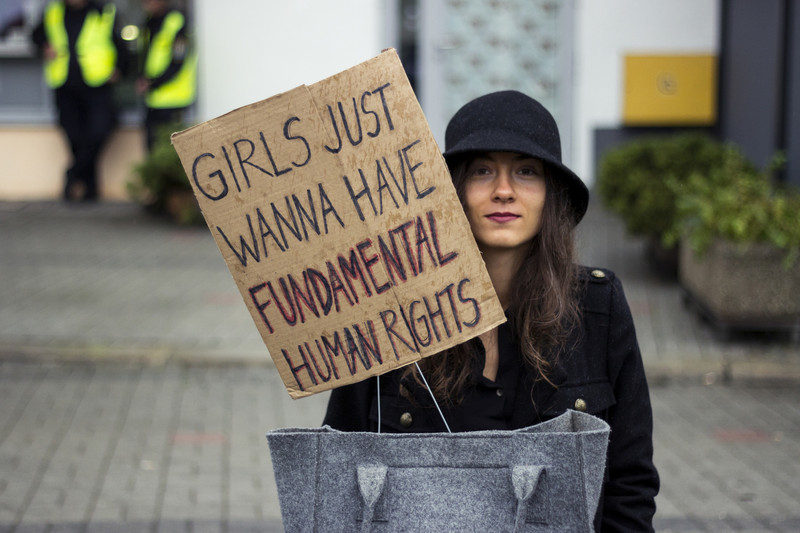
Apr 9, 2020 | Advocacy, News
A joint statement signed by the ICJ and 102 other organizations.
The COVID-19 pandemic and public health crisis is presenting grave challenges for health care systems across Europe.
As European countries work to address the pandemic, protect their populations, and meet the increased demand on health care workers and health care facilities it is vital that they adopt measures to safeguard the health, human dignity, physical and mental integrity, and reproductive autonomy of women and girls in the region.
In many countries the lack of government measures to guarantee individuals’ safe and timely access to essential sexual and reproductive health services, goods, and information during the pandemic is of particular concern.
Women and girls – this statement refers to women and girls, as the majority of individuals who are needing abortion care identify as such but it equally applies to all individuals who may become pregnant and need abortion care or other sexual and reproductive health care – are facing significant restrictions in safely accessing essential sexual and reproductive health services, particularly timely abortion care, post abortion care, and emergency contraception.
Such restrictions disproportionately impact individuals belonging to marginalized groups, including women living in poverty, women with disabilities, Roma women, undocumented migrant women, adolescents, and women at risk or who are survivors of domestic and sexual violence.
These restrictions also create unnecessary risks of exposure to COVID-19 for women and girls and their families as well as for health care providers.
Particularly grave barriers are arising for women and girls living in European countries where abortion care is illegal or severely restricted, and where as a result they must travel to other countries to access legal care or must obtain abortion medication from outside their own jurisdiction.
These issues can also arise in those European countries where individuals are forced to go through burdensome or harmful administrative processes to access abortion care or where they may have difficulty finding doctors in their country willing to provide care.
We applaud those governments that have moved swiftly to safeguard access to essential time- sensitive sexual and reproductive health care during this time, in particular through ensuring access to telehealth and early medical abortion from home.
We call on all other European governments to follow suit and to follow the guidance of medical and public health experts.
We call on the six European countries (Andorra, Liechtenstein, Malta, Monaco, Poland and San Marino) where abortion is illegal or severely restricted to urgently reform these laws, which place women’s health and lives at risk.
Limitations on travel and transport now compound the impact of these highly restrictive laws. Individuals in these countries may no longer be able to travel abroad or to obtain medication for abortion sent by post from medical providers in other countries. As a result, they face heightened risks to their health and wellbeing.
We call on those countries where abortion is legal but where clinical services are unavailable or difficult to access due to a range of barriers, including medically unnecessary requirements that oblige individuals to take multiple or unneeded trips to health care facilities or undergo mandatory hospitalization, to urgently eradicate those barriers and ensure access to services.
Urgent steps should also be taken to ensure that refusals of care because of private beliefs by doctors do not jeopardize timely access to legal abortion care.
In accordance with human rights obligations3 and the recommendations of medical experts4 the following measures should be adopted, and at a minimum remain in place for the duration of the COVID-19 pandemic:
- Ensure that abortion is treated as essential and time-sensitive health care and guarantee access to care in a timely manner.
- Authorize and make available in a timely manner telehealth consultations for anyone who is seeking abortion care or information. Specific measures should be adopted to ensure that telehealth consultations are free or low cost and easily accessible for marginalized groups.
- Guarantee timely access to early medical abortion throughout each jurisdiction and allow doctors to prescribe the necessary medication via telehealth consultation.
- Allow individuals to take all abortion medication at home. Requirements in some European countries that one pill must be taken in the physical presence of a doctor or in a health care facility should be removed.
- Remove mandatory waiting periods prior to abortion as well as mandatory counselling requirements or ensure counselling can be conducted through telehealth consultation.
- Authorize primary care doctors and midwives to provide early medical abortion.
- Adopt health system safeguards to guarantee access to care in cases where early medical abortion is not possible or is contraindicated, for individuals who need abortion care later in pregnancy or post-abortion care, or who may need to visit a health care facility for other reasons. Travel in such cases should be deemed essential and permitted even where governments have otherwise restricted free movement.
- Where a doctor’s authorization is required, this should be limited to one doctor. Requirements for multiple doctors’ approval of an abortion should be removed.
- Guarantee timely access to prenatal testing and psychosocial support where requested.
- Guarantee an adequate number of providers willing and able to provide abortion care throughout the country and widely publicize information on how women can identify health care professionals willing and available to provide abortion care. Urgently ensure that refusals of care by doctors do not jeopardize access to abortion care in a time of crisis.
- Widely disseminate information on those changes to SRHR policies and health care services that are being made in the context of COVID-19 responses.
- Ensure access to contraception including emergency contraception, including through authorizing telehealth consultations and provision of emergency contraception over the counter in pharmacies without a prescription.
Finally, we call on all policy makers across the European region to reject proposals that purport to restrict access to safe abortion care during the COVID-19 pandemic. These disingenuous proposals simply serve to exacerbate the current public health crisis and have negative effects on the health, lives, and wellbeing of women and girls.
Download the full statement with additional information and the list of signatories