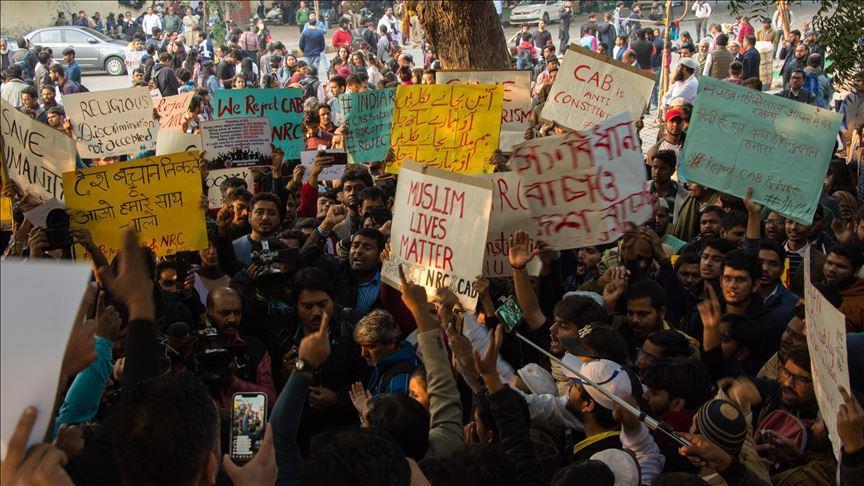Mar 10, 2020 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ and other NGOs today highlighted the discriminatory character of India’s Citizenship Amendment Act, and called for accountability for violence and excessive use of force in relation to protests against it, today at the Human Rights Council in Geneva.
The joint statement, delivered in a general debate, read as follows:
“India’s Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019 (CAA) arbitrarily excludes certain groups at risk of persecution, such as Muslims, from accessing an expedited path to citizenship, based on their religious affiliation.
The CAA is inconsistent with rule of law principles and international law, including the right to equality before the law and the right to non-discrimination, protected under human rights treaties such as the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination, to which India is a party.
The implementation of the National Register of Citizens (NRC) in Assam risks making 1.9 million persons stateless. A nationwide NRC will put more people at risk.
Our organizations urge the Indian government to amend the CAA to ensure that any path to citizenship provides for equal protection for persecuted persons, and does not discriminate on grounds such as religion or national origin.
We also urge India to develop a comprehensive refugee law that addresses the plight of persecuted minorities in a non-discriminatory manner, and to accede to the 1951 Refugee Convention and its 1967 Protocol.
We further call on India to respect the right to peaceful assembly, and to ensure accountability for those alleged to have instigated violence or used excessive force in relation to the nationwide protests against the CAA.”
The statement was delivered by ICJ on behalf also of Asian Forum for Human Rights and Development (FORUM-ASIA), CIVICUS – World Alliance for Citizen Participation, Human Rights Watch, International Service for Human Rights (ISHR), Minority Rights Group International, and World Organization against Torture (OMCT).
The statement can be downloaded in PDF format here: ICJ statement GD item 4 India (10-03-2020)

Feb 27, 2020 | Events, News
On 2 March, the ICJ and other NGOs will present discussion of the situation for human rights in India at a side event to the UN Human Rights Council in Geneva.
The event takes place Monday 2 March 2020, 14:00 – 15:00, in Room VII, Palais des Nations, Geneva.
In India, human rights defenders and civil society activists are facing escalating levels of harassment and restrictions. The systematic use of restrictive laws against critics and an ongoing clampdown on public gatherings and internet freedom now go beyond Jammu and Kashmir. A divisive and discriminatory citizenship law has sparked widespread protests across India. Protests against the law have been met with arbitrary arrests, excessive force and violence by the authorities, with at least 27 people killed and hundreds injured with impunity.
As the situation continues to deteriorate, this event will look at what action is needed by states, civil society and the United Nations to ensure an end to these human rights violations in the world’s largest democracy.
A flyer for the event can be downloaded here in PDF format: UN-Event-India-2019

Jan 15, 2020 | News
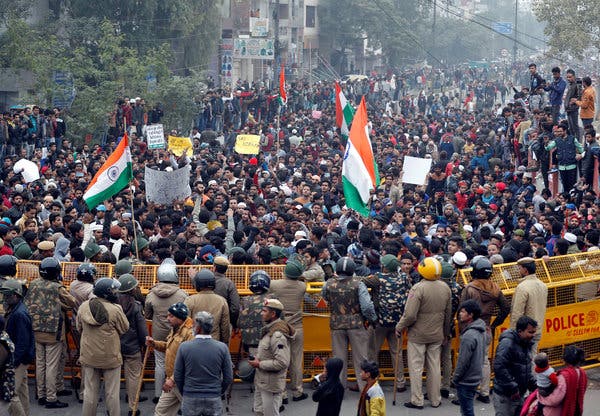
The Indian government must investigate the use of excessive and unlawful force by Uttar Pradesh police against demonstrators protesting the imposition of a discriminatory new law, the International Commission of Jurists said today in a briefing paper.
The briefing paper, based in part on firsthand interviews with witnesses and victims, documents the unnecessary, excessive and indiscriminate use of force in the state of Uttar Pradesh that have led to more than 19 deaths and several more critical injuries since 11 December 2019 as a result of use of firearms as well as teargas, water cannons, and baton charging by the police in response the ongoing protests against the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2020.
Section 144 of the Code of Criminal Procedure, which restricts right to assembly of more than 4 persons, has been imposed in Uttar Pradesh since December 19, 2019, thereby effectively preventing people from protesting. However, protests broke out in several cities in Uttar Pradesh despite the ban. While police authorities claim that the protestors initiated the violence, firsthand interviews with victims and witnesses and numerous other credible reports indicate that the police used force on peaceful protestors including lathis, teargas, bullets.
“The high death toll of peaceful protestors in Uttar Pradesh highlights the use of excessive force by the police, in contravention of international standards of policing and human rights. The state and federal governments must investigate any death or injury that occurs during protests by law enforcement officials and to ensure access to justice to victims and their families,” Sam Zarifi, ICJ Secretary General said.
Individuals reported that they had not been able to get their medico-legal certificates and victims’ families reported inability to access postmortem reports.
The right to life and freedom from ill treatment is protected under international law including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights to which India is a party and requires that when arbitrary deprivation of life occurs, there is accountability and reparation for victims.
The Allahabad High Court is hearing Shree Ajay Kumar v. State of Uttar Pradesh starting 16 January 2020, wherein it has taken suo moto cognizance of a letter sent by Ajay Kumar a lawyer in Bombay and has treated it as a basis for the commencement of a public interest litigation. The letter alleges that “the situation in the State of Uttar Pradesh is antithetical to core constitutional values and warrants interference of this Court.”
“A ruling that the Uttar Pradesh police violated protestors right to life by use of firearms and indiscriminate use of batons, teargas will serve as an important reminder to the police and the Indian State to respect the rights to life, freedom from ill-treatment and freedom of assembly and expression of protestors and that the use of such force against peaceful protestors will not be condoned by the State” said Sam Zarifi.
To download the full statement with additional background information, click here.
Contact
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Secretary General , e: sam.zarifi(a)icj.org
Maitreyi Gupta, International Legal Adviser for India, t: +91 7756028369 ; e: maitreyi.gupta(a)icj.org
Read also
ICJ Press Release: India: Discriminatory citizenship law passed by Parliament violates international and constitutional law, December 11, 2019
ICJ Press Release: India: Authorities must cease the excessive use of force and ill-treatment of Citizenship (Amendment) Act 2019 protestors, December 16, 2019
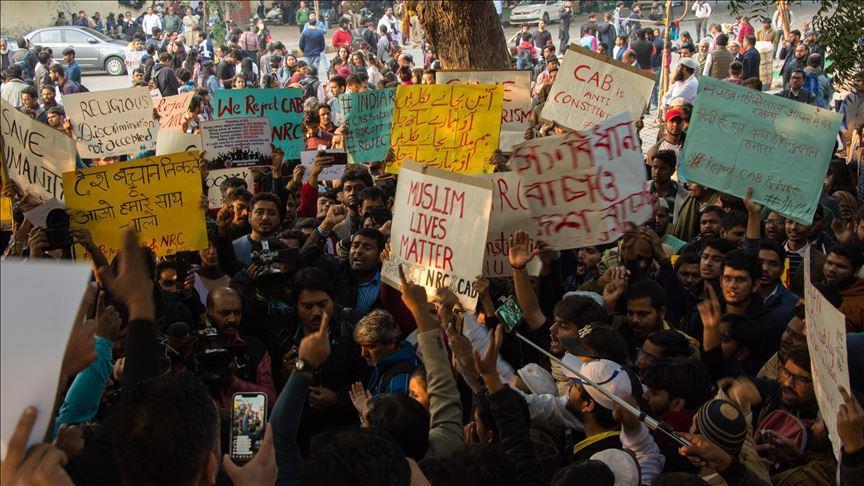
Dec 16, 2019 | News
The Indian Police Service and the paramilitary Central Reserve Police Force must desist from the use of unlawful force and ill-treatment against demonstrators protesting the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, the ICJ said today.
The Indian authorities must also hold police and other public officials accountable for the human rights violations arising from these police actions, the ICJ added.
“The violent tactics that police have used over the past several days in Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, and other Indian states must cease and the government must address the legitimate concerns raised by the public about the discriminatory impacts of both the Citizenship Amendment Act and National Register of Indian Citizenship,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia Pacific Director.
“Any officials who use excessive force, including the unlawful or disproportionate use of pellet guns or tear gas cannons against unarmed student protestors, must be fully and impartially investigated and held accountable for their actions,” he added.
In its operations policing the demonstrations, the ICJ called on the authorities to abide by Indian Constitutional guarantees and international legal obligations on human rights.
These protect persons from torture and ill-treatment and the rights to freedom of expression, association and assembly.
They also require that police refrain from using unnecessary and disproportionate force and never use potentially lethal force unless to protect against an imminent threat to life.
The ICJ also called on the authorities to ensure that any person detained not be subjected to torture or other ill-treatment; have prompt and confidential access to counsel; and that those injured or otherwise provided with access to medical services.
“The police need to respond to prevent acts of violence, but they must use force only when strictly necessary. Potentially lethal force is only justifiably employed in self-defence or in defence of others against an imminent threat of death or serious injury,” said Rawski.
“If arrests need to be made, they must be done without exception in accordance with the law, respecting the rights of detainees to have access to legal counsel, to be free of torture and other ill-treatment of any kind, and to receive needed medical treatment,” he added.
The ICJ said that the authorities must undertake prompt, independent, impartial and thorough investigation of all allegations of unlawful use of force, with a view to holding accountable any responsible authorities and providing an effective remedy and reparation to victims.
Background
In response to the passage of the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019, protests erupted all over the country, including in Assam, Tripura, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, Delhi, West Bengal, Kerala, and Hyderabad.
In Delhi and Uttar Pradesh, yesterday, members of the police and Central Reserve Police Force forced their way onto the campuses of Jamia Milia University and the Aligarh Muslim University in response to protests against the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019.
At Jamia Milia University, the police and Central Reserve Police Force used tear gas cannons upon students who had been reportedly protesting peacefully. Police entered the university library and beat students who were there studying for their exams. The police detained (and subsequently released) some 50 students. Some reported being beaten while in detention, held for over six hours in a locked police station, and denied access to lawyers and family. Medical attention was also reportedly denied to some injured students.
At Aligarh Muslim University, the police and Central Reserve Police Force reportedly demolished the gates, and used tear gas, pellet guns, and lathi (wooden sticks) charge. They were said to have entered student hostels, wherein they reportedly caused damage to one room which had students inside it. According to a lawyer at the University, at least one’s student whereabouts is unknown and some 50 students and others have reported been injured, some severely. Some were reportedly taken to the hospital by the police.
The Citizenship (amendment) Act, 2019 amends the Citizenship Act, 1955, which governs questions of citizenship and aspects of lawfulness of migration status in India. The Act gives protected status to Hindu, Sikh, Jain, Parsi, Buddhist and Christian migrants from Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh, all Muslim-majority countries, who entered India on or before 31 December 2014. Similarly situated Muslims are categorized as “illegal migrants”.
The Bill provides to the above-mentioned religious communities and countries an expedited route of citizenship giving them the opportunity to be eligible for citizenship by naturalization if they have lived or worked in India for six years, as opposed to twelve years, as otherwise required. The Bill controversially excludes from its ambit certain ethnic and religious groups, such as Muslims, in violation of international law and standards protecting against discrimination.
To download the full statement with additional background information, click here.
Contact
Maitreyi Gupta, ICJ India Legal Adviser, t: +91 77 560 28369 e: maitreyi.gupta(a)icj.org
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia-Pacific Director, t: +66 64 478 1121; e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org

Dec 11, 2019 | News
The ICJ today condemned The Citizenship (Amendment) Bill 2019 passed by the Rajya Sabha (upper house of the Indian Parliament) on 11 December 2019, after the Lok Sabha (lower house of the Parliament) adopted it on 9 December.
The ICJ calls on India to reconsider and repeal, or substantially amend, the Bill to bring it in line with international legal obligations and Indian Constitutional principles.
“The implementation of this proposed legislation would violate core principles of non-discrimination, equal protection of the law and freedom of religion, guaranteed under international law and the Indian Constitution,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ’s Asia Director.
The Bill amends the Citizenship Act, 1955, which governs questions of citizenship and aspects of lawfulness of migration status in India. While it purports to provide protection and shelter to religious groups such as Hindus and provides them paths to citizenship, it excludes from its ambit certain religious groups such as Muslims.
The Bill gives protected status to Hindu, Sikh, Jain, Parsi, Buddhist and Christian migrants from Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh, all Muslim-majority countries, who entered India on or before 31 December 2014. Similarly situated Muslims are categorized as “illegal migrants”.
Furthermore, the Bill provides to the above-mentioned religious communities and countries an expedited route of citizenship giving them the opportunity to be eligible for citizenship by naturalization if they have lived or worked in India for six years, as opposed to twelve years, as otherwise required.
“The Citizenship (Amendment) Bill creates two tiers of citizenship and migration status in India based on religion, with Muslims relegated to the lower end,” added Rawski. “This Bill, which entrenches discriminatory practices into law, must not be implemented unless substantially amended to provide for equal protection for persons of all religions or other status.”
The legal framework for citizenship identified by this Bill is incompatible with bedrock rule of law and democratic principles. It is highly discriminatory and arbitrary, and manifestly fails to satisfy the State’s obligations under international human rights law, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), to which India is a party.
The arbitrary inclusion of some groups while excluding others violates Article 14 of the Indian Constitution and Article 26 of the ICCPR. India’s international obligations require that its regulation of citizenship under domestic law be compliant with the principle of non-discrimination, equality before the law, and equal protection of the law without discrimination on the grounds of, inter alia, race, religion, or ethnic or national origin. This Bill, which provides for differentiated criteria for citizenship and other legal protection based on membership of religious group, complies neither with international law nor Indian constitutional law.
The arbitrary inclusion of some groups while excluding others would only be permissible under Article 14 of the Indian Constitution and Article 26 of the ICCPR if the classification is founded on an intelligible differentia between the group excluded and the group that is included, and (ii) the differentia has a rational relation to the objects sought to be achieved by the Act.
The Bill claims religious persecution as the ground of reasonable classification, but then arbitrarily excludes several similarly situated and widely persecuted religious minorities such as Ahmediya Muslims and Shia Muslims from Pakistan and Bangladesh, Rohingyas from Myanmar, Hazaras from Afghanistan from its protective ambit. It therefore does not meet these criteria under the Indian Constitution and international law.
The adoption of the Bill comes as the Ministry of Home Affairs of the Indian Government issued a directive on August 8, 2017 to state governments to “identify and deport” 40,000 Rohingya refugees from Myanmar, which has led to deportation of 7 Rohingya men to Myanmar already.
In addition, the Indian Government has indicated that it will pursue nationwide National Register of Indian Citizens, which will likely exclude numerous people, many also Muslim, who should be recognized as Indian Nationals. A similar exercise undertaken in Assam earlier this year was an arbitrary and discriminatory process that rendered some 1.9 million people stateless. This violates international law and standards which protects the right to nationality and safeguards against statelessness.
Contact
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia-Pacific Director, t: +66 64 478 1121; e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org
Maitreyi Gupta, ICJ India Legal Adviser, t: +91 77 560 28369 e: maitreyi.gupta(a)icj.org