
Dec 16, 2020 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
In an open letter, the ICJ today called on Indonesia’s COVID-19 Mitigation Task Force to provide detailed guidance to the Government of Indonesia, in taking actionable steps to implement gender responsive measures in the country.
Since the beginning of the outbreak of the pandemic, the mortality rate of Indonesia is reportedly among the highest in the world.
In addressing the pandemic, the Government has established regulations and repeatedly advised people to restrict social gatherings and stay at home. These measures have a particularly disparate impact on Indonesian women, exacerbating the pre-existing gender inequalities in Indonesia.
The ICJ has previously highlighted the challenges faced by women in its report “Living Like People who die slowly.” Similar concerns has been expressed by the UN Committee on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights.
The ICJ called the task force to take proactive and special measures to protect women workers in its COVID-19 response, in line with the recommendations of the UN Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women’s Guidance Note on COVID-19.
Specifically, the ICJ has recommended that it promote government responses to:
- Ensure that women receive basic needs support
- Provide more working opportunities for women to work from home
- Provide online counseling or mental health support for women workers
The ICJ considers that the failure to recognize the gender dynamics affecting women workers, particularly public health emergencies, limits the effectiveness of the overall Government’s response efforts and impedes the full realization of women’s human rights in Indonesia.
Download

Dec 15, 2020 | News
On 15 December 2020, the eighth anniversary of the enforced disappearance of Lao civil society leader Sombath Somphone, the ICJ joined 53 organizations and 19 individuals in reiterating its calls on the Government to reveal his fate and whereabouts and to investigate his and all other cases of alleged enforced disappearance in the country.
The statement condemned the Government’s ongoing failure to adequately investigate all allegations of enforced disappearance in Laos, which has been compounded by years of near complete lack of commitment to address this serious crime or provide an effective remedy or reparation to its victims and their families.
In June 2020, during the third Universal Periodic Review (UPR) of Laos, the Government refused to accept all five recommendations that called for an adequate investigation into Sombath’s enforced disappearance. The Government failed to support another eight recommendations that called for investigations into all cases of alleged enforced disappearances in Laos. Despite the government accepting that “the search for missing Lao citizens, including Sombath Somphone, is the duty of the Lao government”, it has failed to evidence any political will to effectively execute or fulfill this duty.
Sombath Somphone was last seen at a police checkpoint on a busy street in Vientiane on the evening of 15 December 2012. Footage from a CCTV camera showed that Sombath’s vehicle was stopped at the police checkpoint and that, within minutes, unknown individuals forced him into another vehicle and drove him away in the presence of police officers. CCTV footage also showed an unknown individual driving Sombath’s vehicle away from the city center. The presence of police officers at Sombath’s abduction and their failure to intervene strongly indicates State agents’ participation in Sombath’s enforced disappearance.
Lao authorities have repeatedly claimed they have been investigating Sombath’s enforced disappearance, but have failed to disclose any new findings to the public since 8 June 2013. They have not met with Sombath’s wife, Shui Meng Ng, since December 2017. No substantive information about the investigation has been shared by the authorities with Ng or Sombath’s family, indicating that, for all intents and purposes, the police investigation has been de facto suspended.
The statement reiterated a call for the establishment of a new independent and impartial investigative body tasked with determining Sombath’s fate and whereabouts, with the authority to seek and receive international technical assistance to conduct a professional and effective investigation in accordance with international standards. This is a call which multiple signatory organizations have been making since his enforced disappearance in 2012.
The statement further urged the Lao government to ratify the International Convention for the Protection of All Persons from Enforced Disappearance (ICPPED), which Laos signed in September 2008; incorporate its provisions into the country’s legal framework, implement it in practice, and recognize the competence of the Committee on Enforced Disappearances to receive and consider communications from or on behalf of the victims.
The full statement is available here.
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior Legal Adviser, e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org

Nov 26, 2020 | Advocacy, News
Today, the ICJ joined other NGOs in condemning the Thai police’s use of force against peaceful protesters marching to the national parliament in Bangkok on November 17, 2020.
The statement reads:
We, the undersigned organizations, condemn the Thai police’s unnecessary and excessive use of force against peaceful protesters marching to the national parliament in Bangkok on November 17, 2020. We are concerned that authorities could employ similar measures when facing protesters who have declared they will march to the Siam Commercial Bank headquarters on November 25.
On November 17, police set out barriers and barbed wire to prevent a peaceful march organized by pro-democracy movements from reaching the parliament. Protesters planned to protest outside the parliament as members of parliament and senators debated seven different proposals for constitutional amendments, including an amendment proposed by the lawyers’ non-governmental organization iLAW (Internet Law Reform Dialogue), which was supported by the People’s Movement and its allies. Police refused to let protesters through the barriers, and when the demonstrators acted to breach those barriers, police crowd control units used water cannons laced with purple dye and an apparent teargas chemical, as well as teargas grenades and pepper spray grenades, to forcibly disperse thousands of demonstrators, including students, some of whom are children. Water cannons were first used at approximately 2:25 pm and police continued their efforts to disperse protesters, with constant use of water cannons, teargas and pepper spray into the evening.
Police also failed to prevent violence between pro-democracy protesters and royalist “yellow shirts” near the Kiak Kai intersection, near the parliament. Initially, riot police separated the two groups. However, video posted on social media later showed police officers informing the royalist protesters that they would withdraw and seconds later they vacated their position between the two groups. During the ensuing skirmishes, both sides were filmed throwing rocks and wielding clubs. Live broadcasts included sounds that appeared to be gunfire.
The Erawan Medical Centre reported that there were at least 55 protesters injured, mostly from inhaling teargas. It also reported that there were six protesters who suffered gunshot wounds. The injured included children: a kindergartener and elementary school students.
Although some pro-democracy protesters engaged in violent conduct in responding to royalist protesters, we emphasize that the overwhelming number of protesters were entirely peaceful. Furthermore, we wish to emphasize that while specific participants of an assembly who engage in violence are subject to a response that is lawful, strictly necessary and proportionate, they also retain all other human rights including the right to life, to security of person and to freedom from torture and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment.
International human rights law, as expressed in the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), which Thailand acceded to in 1996, protects the rights to freedom of expression (article 19) and peaceful assembly (article 21). But Thai authorities have routinely enforced censorship and stifled public assemblies, meetings, and discussions about human rights, political reforms, and the monarchy’s role in society.
In General Comment 37, which sets out the content Thailand’s legal obligations in guaranteeing the right of peaceful assembly, the United Nations Human Rights Committee—the body responsible for interpreting and applying the ICCPR—made clear that there is a presumption in favor of considering assemblies to be peaceful. Isolated acts of violence by individuals should not be attributed to others, to the organizers, or to the assembly as such. While the right of peaceful assembly may in certain cases be limited, the onus is for the State to justify any restrictions, which must pass the tests of legality, legitimacy, and necessity and proportionality.
Read the full statement in English and Thai.
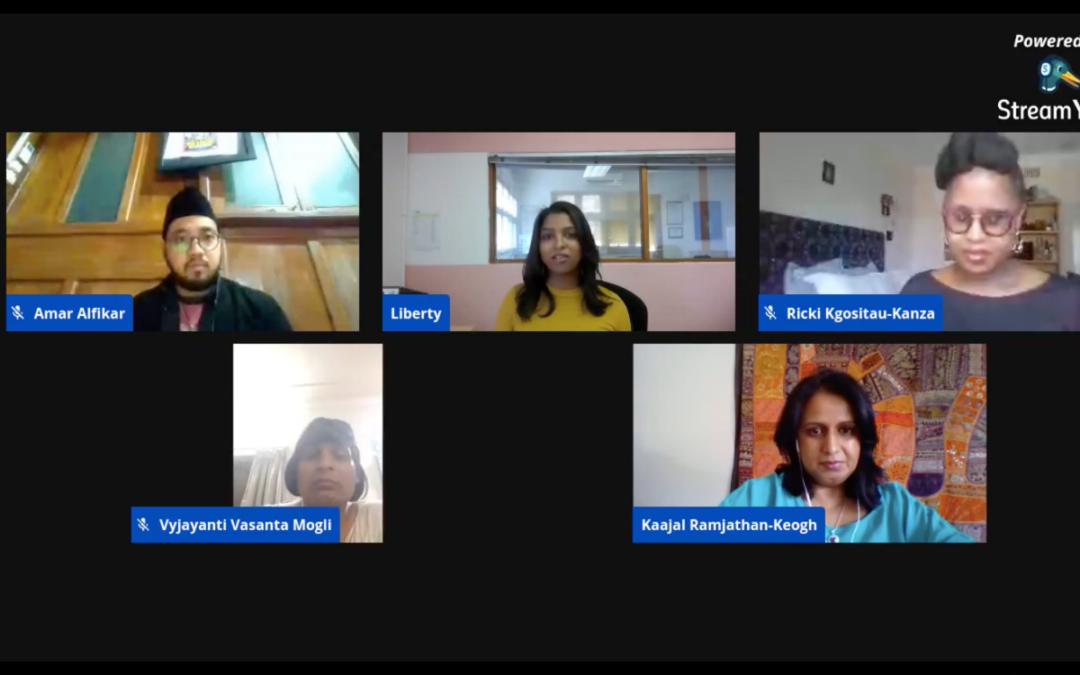
Nov 19, 2020 | News
On 18 November 2020, the ICJ hosted a Facebook Live with four transgender human rights activists from Asia and Africa. It highlighted the stark reality between progressive laws and violent lived realities of transgender people.
The 20th November 2020 marks the Transgender Day of Remembrance (TDOR), the day when transgender and gender diverse people who have lost their lives to hate crime, transphobia and targeted violence are remembered, commemorated and memorialized.
The discussions focused on their individual experiences of Transgender Day of Remembrance in their local contexts, the impact of COVID-19 on transgender communities and whether laws are enough to protect and enforce the human rights of transgender and gender diverse people.
The renowned panelists were from four different countries, Amar Alfikar from Indonesia, Liberty Matthyse from South Africa, Tshepo Ricki Kgositau-Kanza from Botswana and Vyjayanti Vasanta Mogli from India. The panel was moderated by the ICJ Africa Regional Director, Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh.
The panel aimed to provide quick glimpses into different regional contexts and a platform for transgender human rights activists’ voices on the meaning of Transgender Day of Remembrance and the varied and devastating impacts of COVID-19 on transgender people.
The speakers discussed the meaning that they individually ascribe to Transgender Day of Remembrance. A common theme running across the conversations was that it is not enough to highlight issues and concerns of the transgender community only on this day. Instead, these discussions should be part of daily conversations about the human rights of transgender people at the local and international level.
Liberty Matthyse discussed the importance of remembering the transgender persons who have lost their lives over the past years, and added:
“South Africa generally is known as a country which has become quite friendly to LGBTI people more broadly and this, of course, stands in stark contradiction to the lived realities of people on the ground as we navigate a society that is excessively violent towards transgender persons and gay people more broadly.”
Amar Alfikar describes his work as “Queering Faiths in Indonesia”. This informs his understanding of what Transgender Day of Remembrance means in his country and he believes that:
“Religion should be a source of humanity and justice. It should be a space where people are safe, not the opposite. When the community and society do not accept queer people, religion should start giving the message, shifting the way of thinking and the way of narrating, to be more accepting, to be more embracing.”
It was clear from the discussions that a lot of the issues that have become prominent during the COVID-19 pandemic, have not arisen due to the pandemic. In fact, the COVID-19 pandemic has had the effect of a magnifying glass, amplifying existing challenges in the way that transgender communities are treated and driven to margins of society. Speaking about the intersectionality of transgender human rights, Vyjayanti Vasanta Mogli said:
“I don’t think LGBT rights or transgender rights exist in isolation, they are part of a larger gamut of climate change, racial equality, gender equality, the elimination of plastics, and all of that.”
The panelists had different opinions on whether it is enough to rely on the law for the recognition and protection of the human rights of transgender individuals.
The common denominator, however, was that the laws as they stand have a long way to go before fully giving effect to the right of equality before the law and equal protection of the law without discrimination of transgender people.
Tshepo Ricki Kgositau-Kanza, who was a litigant in a landmark case in Botswana in which the judiciary upheld the right of transgender persons to have their gender marker changed on national identity documents, explained the challenges with policies which, on their face, seem uniform:
“Uniform policies… are very violent experiences for transgender persons in a Botswana context where the uniform application of laws and policies is binary and arbitrarily assigned based on one’s sex marker on one’s identity document which reflects them either as male or female. Anybody in between or outside of that kind of dichotomy is often rendered invisible and vulnerable to a system that can easily abuse them.”
This conversation can be viewed here.
Contact
Tanveer Jeewa, Communications Officer, African Regional Programme, e: tanveer.jeewa(a)icj.org

Nov 14, 2020 | Advocacy, News
On 12-13 November 2020, the ICJ co-hosted a discussion on “Thailand’s National Action Plan on Business and Human Rights: 1-Year Progress Review” in Bangkok. The forum was co-organized with other 11 organizations.
Participants on the first day included some 95 individuals representing populations affected by business operations from all regions of Thailand and members of civil society organizations. The considered reviewed the progress that has been made by Thailand over the past year towards fulfilling its commitments in the four priority issues in its First National Action Plan on Business and Human Rights (NAP): (1) Labor; (2) Land, environment and natural resources; (3) Human rights defenders; and (4) Cross border investment and multi-national enterprises.
Several participants noted a lack of any evident and tangible progress in the NAP implementation and questioned the effectiveness of the NAP because it does not have the status of a law but is merely a resolution from the Council of Ministers. They further expressed concern at the lack of a comprehensive monitoring system in place to monitor NAP and its achievement according to the key recommendations aligned with the UN Guiding Principle on Business and Human Rights, and on legal harassment and intimidation faced by human rights defenders.
In the session regarding cross border investment and multi-national enterprises, the ICJ participants led the discussion regarding challenges to hold Thai companies accountable for human rights abuses which took place abroad. The participants looked into several obstacles to accessing to justice for victims of business-related human rights abuses in the context of cross-border investment. The discussion was based on the ICJ’s work and analysis in the draft report on the human rights legal framework of Thai companies operating in Southeast Asia, which is expected to be launched in December 2020.
Comments and recommendations raised by participants on the first day were presented to representatives from the Ministry of Justice, Thailand National Human Rights Commission, Global Compact Network Thailand and UN agencies, in the public seminar on the second day. The outcomes of the discussion and recommendations will also be submitted to the NAP Monitoring/Steering Committees, chaired by Director-General of Rights and Liberties Protection Department, Ministry of Justice.
Background
On 29 October 2019, the Cabinet approved and adopted the First National Action Plan on Business and Human Rights (2019-2022), making Thailand the first country in Asia to adopt the stand-alone NAP.
The NAP emphasizes the duties of State agencies to review and amend certain laws, regulations and orders that are not in compliance with human rights laws and standards and ensure their full implementation; ensure accessibility of mechanisms for redress and accountability for damage done to affected communities and individuals; overcome the barriers to meaningful participation of communities and key affected populations; and strengthen the role of businesses to “respect” human rights on a variety of key priority issues.
The event was co-hosted with:
- International Organization for Migration (IOM)
- Community Resource Centre Foundation (CRC)
- Asian Forum for Human Rights and Development (FORUM-ASIA)
- EarthRights International (ERI)
- The Mekong Butterfly (TMB)
- International River (IR)
- Spirit in Education Movement (SEM)
- Thai Extra-Territorial Obligations Working Group (Thai ETOs Watch)
- Green Peace Thailand
- Green South Foundation
- Business and Human Rights Resource Center (BHRRC)
Further reading
Thailand’s Legal Frameworks on Corporate Accountability for Outbound Investments
Thailand: ICJ co-hosts discussion on National Action Plan on Business and Human Rights









