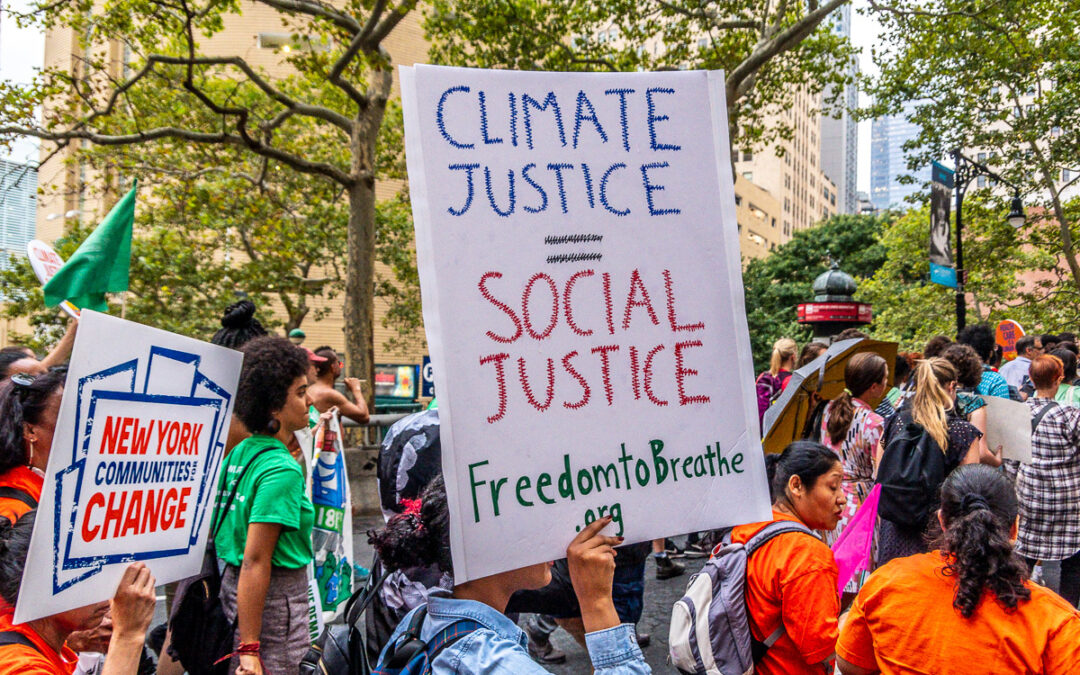

Dec 17, 2021 | Advocacy, Legal submissions
The ICJ submitted today a contribution to the work of a Council of Europe Committee drafting a recommendation on human rights and the protection of the environment.
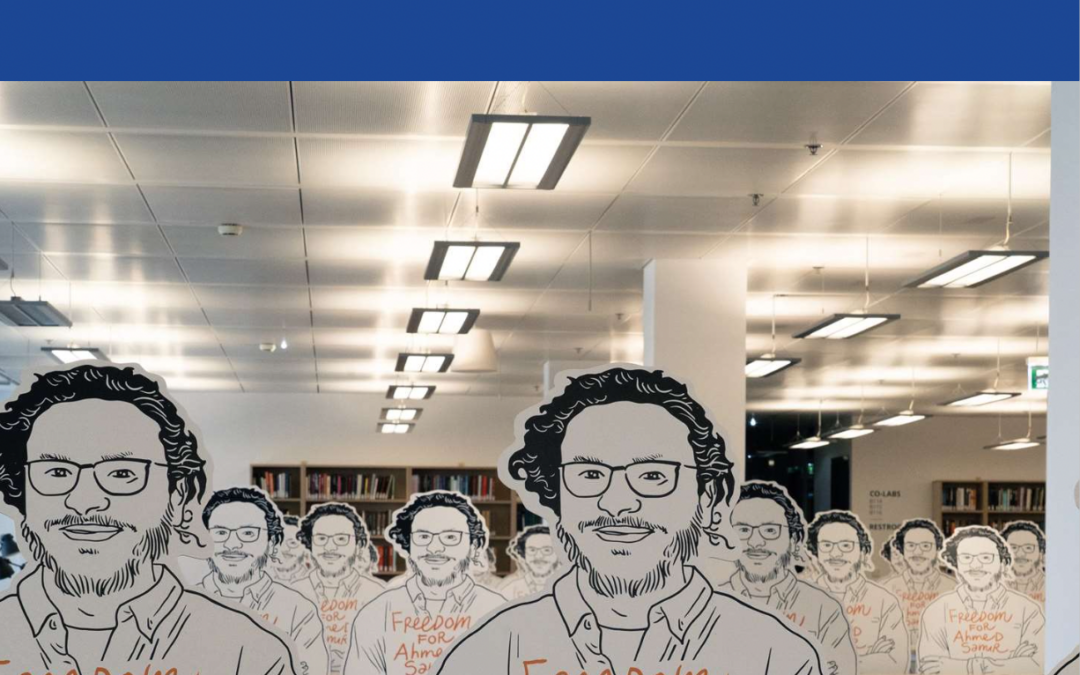

Nov 26, 2021 | News, Publications
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) has summarized the conclusions of a new report about the case of Ahmed Samir Santawy issued by the Egyptian Commission on Rights and Freedoms (ECRF) in a briefing paper released today.

Nov 22, 2021 | News, Non-legal submissions
During a recent visit to Eswatini from 2 to 5 November 2021, the International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) engaged with civil society organizations, lawyers, the Swaziland Human Rights Commission and government officials on the local human rights record. The ICJ subsequently filed a submission to the ACHPR documenting its findings, and supported the drafting of a separate submission by the Foundation for Socio-Economic Justice (FSEJ) in Swaziland. These submissions draw on the ICJ’s human rights work on Eswatini over more than a decade, as well as on the FSEJ’s continued human rights advocacy and monitoring in context of the current pro-democracy protests.
Nov 1, 2021 | News
The Sri Lankan judiciary must overcome gender stereotypes to improve women’s access to justice in the country, said participants at a workshop organized by the ICJ and the Legal Aid Commission of Sri Lanka on 30 and 31 of October.

Oct 28, 2021 | News
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ), the Council of Bars and Law Societies of Europe (CCBE), Lawyers for Lawyers (L4L), European Association of Lawyers (AEA-EAL), Helsinki Foundation for Human Rights (HFHR) and the Centre for Constitutionalism and Human Rights of the European Humanity University (CCHR EHU) and the Human Rights Embassy (HRE) (“the undersigned organisations”) call on the Bar Association of Belarus to reverse its decisions to disbar lawyer Natalia Matskevich and to end the practice of disbarment of lawyers for carrying out their professional duties in line with international law and standards on the role of lawyers.









