Dec 7, 2019 | News
The ICJ called on the Indian government to conduct an independent and impartial investigation into the apparently unlawful killings by Telangana Police of the four men accused of raping and killing of Dr. Priyanka Reddy on November 27, 2019.
The men had been in police custody for over a week at the time of the killings.
“The rape and killing of Dr. Reddy is a heinous crime, and sadly only the latest in a pattern of rampant sexual violence that plagues India. The perpetrators of such acts must be held accountable,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia-Pacific Director. “However, the unlawful killing of suspects in custody helps no-one. It denies victims true justice, rewards unlawful behavior by the police, and generally undermines the rule of law.”
On November 27, Dr. Priyanka Reddy, a veterinarian, was returning home when she was gangraped. Her body was subsequently burned by the perpetrators. The next day, four suspects were arrested. According to the police, they remained in custody until Friday, 6 December, when all four were shot and killed after they allegedly attempted to take weapons from the police and tried to escape during a re-enactment at the crime scene. Details of the incident remain unclear, though it has the appearance of a custodial execution.
“The suspicious circumstances of these deaths in custody, and the history of the use of extrajudicial killings in India, demands a thorough, independent and impartial investigation,” said Rawski. “The nationwide alarm at the trend of sexual violence is completely warranted. However, celebrating the unlawful behavior of police will not ultimately protect women from sexual violence or address their lack of access to justice.”
Several Indian women’s rights activist groups have also condemned the killings. A statement by the All India Progressive Women’s Association’s statement pointed out that “This is not justice. This is a ploy to shut down our demand for accountability from the police, judiciary, governments, and justice and dignity for women.” The National Human Rights Commission of India has also called for an investigation into the circumstances of the killing.
According to international standards including the International Convention of Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), to which India is a party, States have a duty to investigate allegations of extrajudicial executions with due diligence and good faith, regardless of whether or not there is a formal complaint. The investigation of extrajudicial, summary or arbitrary executions must be thorough prompt, impartial and independent, towards establishing the crime committed and prosecuting those responsible for the crimes. This has been reiterated by the Supreme Court of India, which has condemned encounter killings, and set out guidelines for their investigation.
The ICJ urges the Indian Government to conduct a thorough and impartial investigation into the killings by the police, in line with the Supreme Court’s decisions, and India’s constitution and international obligations. The ICJ calls upon the courts to ensure that police officials who conduct unlawful killings are held accountable. It also calls upon the Government to take immediate steps to address the lack of an effective response from police personnel to allegations of rape and sexual violence, and to take effective lawful measures to prevent the unacceptable attacks upon victims of rape and other sexual violence seeking a remedy in the courts.
Contact
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia-Pacific Director, t: +66 64 478 1121; e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org
Maitreyi Gupta, ICJ India Legal Adviser, t: +91 77 560 28369 e: maitreyi.gupta(a)icj.org

Nov 26, 2019 | News
Three exceptional women – Huda Al-Sarari, Norma Ledezma and Sizani Ngubane – are the finalists for the 2020 Martin Ennals Award, a demonstration of the leading position now occupied by women in the defence of human rights. The ICJ is member of the MEA Jury.
In Yemen, Huda Al-Sarari has exposed and challenged the existence of secret prisons and many cases of torture.
In Mexico, Norma Ledezma is fighting against femicides and disappearances.
In South Africa, Sizani Ngubane is fighting for access for women to education and to land.
Three women nominated: a first
Each year, the Martin Ennals Award rewards human rights defenders from around the world who distinguish themselves by their strong commitment to promoting human rights – often at the risk of their own lives.
In 2020, for the first time the Jury nominated three women who defend the fundamental rights of their communities in sensitive contexts.
“The Martin Ennals Foundation is proud to recognize the courageous work of three women. For the 2020 edition, our Jury’s choice reflects the ever-greater global impetus of individuals – whatever their gender – who are committed to respect for human rights and women’s rights in particular,” said Isabel de Sola, Director of the Martin Ennals Foundation.
“The finalists for the 2020 Martin Ennals Award work on different continents, but all three have in common their resilience, determination, a tremendous rigour and, finally, the positive and concrete impact of their work,” added Hans Thoolen, Chairman of the Jury.
In Yemen, where the conflict has been ongoing since 2005, Huda Al-Sarari, a Yemeni lawyer, unveiled the existence of several secret detention centres where the worst violations of human rights were committed: torture, disappearances or even extrajudicial executions.
In South Africa, women face discrimination, the worst expression of which is widespread gender violence. In rural communities, they frequently have their land expropriated and are deprived of access to education and justice. Sizani Ngubane founded an organization of more than 50,000 women from rural areas in her country and has fought successfully for over 40 years for the recognition of their rights.
In Mexico, the civil population is paying a high price for the weakness of the rule of law which is underpins widespread violence and impunity. Women are the primary victims, with more than 3,500 femicides committed each year. Norma Ledezma, who is the mother of one of the victims, puts all her energy into supporting families seeking access to justice in the state of Chihuahua.
The finalists were selected by a jury made up of representatives of ten of the world’s leading human rights organizations: the ICJ, Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch, Human Rights First, International Federation for Human Rights, World Organisation Against Torture, Front Line Defenders, EWDE Germany, International Service for Human Rights and HURIDOCS.
The 2020 Martin Ennals Award will be given to one of the three finalists on 19 February 2020 at a livestreamed public ceremony. The event is hosted by the City of Geneva which, as part of its commitment to human rights, is a longstanding supporter of the Award.
Contact
Olivier van Bogaert, Director Media & Communications, ICJ representative in the MEA Jury, t: +41 22 979 38 08 ; e: olivier.vanbogaert(a)icj.org
Chloé Bitton, Communications Manager, Martin Ennals Foundation, t +41 22 809 49 25 e: cbitton(a)martinennalsaward.org
Universal-MEA2020bios-News-2019-ENG (full bios of finalists, in PDF)
Universal-MEA2020bios-News-2019-ARA (full story and bios of finalists in Arabic, PDF)

Nov 25, 2019 | Multimedia items, News, Video clips
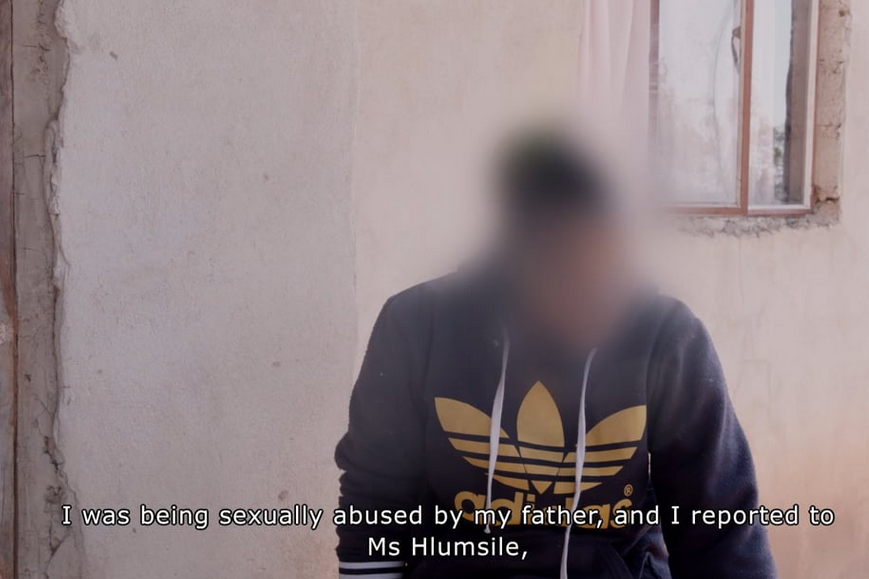
The ICJ just launched a 15 minute documentary showing contributions by the ICJ and local human rights defenders in bringing the Sexual Offences and Domestic Violence (SODV) Act to pass in Mbabane, Eswatini.
The documentary was launched at an SODV Act media training held with the Cooperation for the Development of Emerging Countries (Cospe) and the Editor’s Forum. The training was aimed at taking a human rights-based approach to understanding the Act, following pushback from those who have expressed the view that parts of the Act are an as an affront to Swazi tradition and culture.
In an effort to combat the various challenges presented by SGBV, the Kingdom of Eswatini introduced the Sexual Offences and Domestic Violence (SODV) Act in 2018. The Act complies with its commitments under international and regional human rights law to fight the scourge of SGBV in the country.
The documentary highlights the way in which the Act is expected to be instrumental in combatting the scourge of sexual and gender-based violence, as well as areas in which it has been contested. The documentary was well-received by participants of the training and opened up an engaging dialogue about its usefulness.
The media is at the forefront of informing public discourse about the Act and it is hoped that this training provided some much-needed clarity around the Act.
Watch the documentary:
Contact
Khanyo Farisè (Legal Associate): e: Nokukhanya.Farise(a)icj.org
Shaazia Ebrahim (Media Officer): e: shaazia.ebrahim(a)icj.org

Nov 7, 2019 | News
Today, the ICJ published an Arabic translation of Practitioners’ Guide N°12 on Women’s Access to Justice for Gender-based Violence.
The Guide is designed to support legal practitioners and human rights defenders involved or interested in pursuing cases of gender-based violence.
It provides information about regional and international law and standards relevant to gender-based violence, advice on implementing these standards as part of domestic law reform and examples of existing good practice in seeking protection for women.
The Guide (Arabic version here) also addresses the practical issues that are faced by women who have been subject to gender-based violence and the steps that are necessary to secure their access to justice in practice. It considers women’s experiences of the criminal justice system and reflects on how the justice system deals with women’s safety and need for access to services beyond legal assistance.
Download
Universal-Womens accesss to justice-Publications-Practitioners’ Guide Series-2019-ARA (full guide, in PDF)

Nov 3, 2019 | News
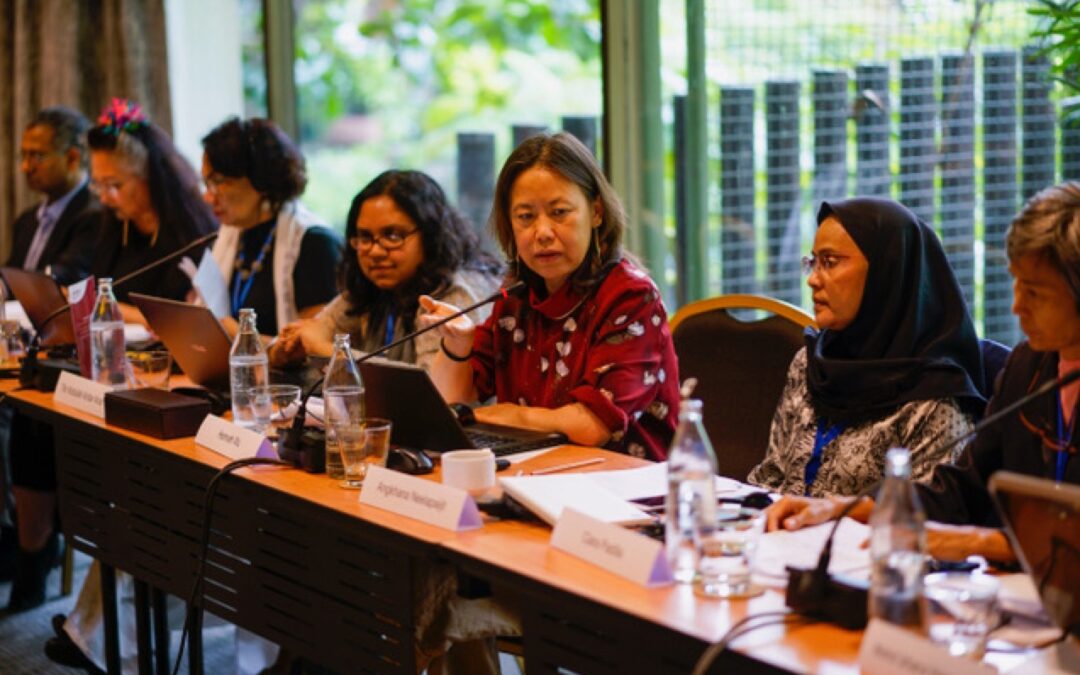
Bangkok, Thailand – From 1 to 2 November 2019, ICJ in collaboration with the UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) and the Ralph Bunche Institute for International Studies, hosted a consultation on gender and the right to freedom of religion or belief with the UN Special Rapporteur on Freedom of Religion or Belief, Dr. Ahmed Shaheed.
The primary objective of the consultation was to provide a forum for human rights defenders, particularly women and human rights defenders belonging to sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics (SOGIESC) minorities to share their perspectives on laws, practices and anti-rights strategies based on religion or belief that discriminate against women and SOGI groups and individuals in Asia. The consultation was attended by at least fifty-two (52) human rights defenders from all over Asia.
Emerlynne Gil, ICJ’s Senior International Legal Adviser, in her opening address, emphasized that gender equality and the right to freedom of religion or belief should not be viewed as inimical to each other. She said, “Women and individuals belonging to sexual orientation and gender identity minorities should also be able to being to a faith or religion of their choice, or religion into which they are born and they should continue to belong to the religion or belief without being discriminated against by the faith or religious community.”
The consultation included discussions on the domestic contexts and legal frameworks in relation to freedom of religion and the rights of women and SOGIESC minorities, including in relation to the right to health. The participants considered challenges faced by women and SOGIESEC minorities when religious leaders act as justice actors were also discussed. The consultation, while highlighting the good practices in advancing the rights of women and SOGIESC minorities, also explored existing challenges and tensions in respect of achieving gender equality.
At the conclusion of the consultation, Dr. Shaheed noted the diversity of the participants in the room, who came from all over Asia. He emphasized that “in order to engage more effectively and strategically, it is imperative that we improve our literacy in relation to the human rights framework and of religion in order to better understand its intersectionality.”
Contact
Sushmitha Thayanandan, National Legal Advisor, Sri Lanka (ICJ) e: sushmitha.thayanandan(a)icj.org