
Jul 17, 2020 | Multimedia, Noticias
La CIJ continuó apoyando la realización de una serie de conversatorios online acerca de los desafíos que enfrentan los sistemas de justicia latinoamericanos en el marco de la emergencia generada por la COVID -19.
Recientemente se realizaron cuatro nuevos conversatorios que abordaron temas relacionados con los planes de apertura de los sistemas judiciales, los procesos de reforma a la justicia que estaban en marcha antes de la emergencia, los desafíos de la justicia virtual, y los impactos de la pandemia en los derechos de las mujeres en prisión.
Esta iniciativa fue organizada por un grupo de mujeres de América Latina que trabaja en temas de justicia en la región, y también fue apoyada por la Fundación para el Debido Proceso Legal, la Fundación Construir (Bolivia), la Fundación Salvadoreña para el Desarrollo Económico y Social (El Salvador), la Fundación Tribuna Constitucional (Bolivia), el Instituto de Defensa Legal (Perú), el Observatorio de Derechos y Justicia (Ecuador), y la Fundación para la Justicia y el Estado Democrático del Derecho (México).
Los videos de las sesiones están disponibles en español en los siguientes enlaces:
Conversatorio 1: Planes de apertura de los sistemas judiciales durante la pandemia
Conversatorio 2: Procesos de reforma a la justicia y pandemia
Conversatorio 3: Desafíos de la justicia virtual
Conversatorio 4: Mujeres en prisión

Jul 11, 2020 | News
The Malaysian authorities must immediately put an end to their increasing attacks on freedom of expression, especially the media, international non-governmental organisations the ICJ, Amnesty International, CIVICUS: World Alliance for Citizen Participation said today.
Laws incompatible with international human rights law and standards, including the Sedition Act 1948 and Section 233 of the Communications and Multimedia Act (CMA) 1998, are being used to limit free speech and press freedom and should be repealed by the legislature.
In the latest move in the ongoing clampdown on criticism and other expression, authorities have targeted those involved in making the documentary “Locked Up in Malaysia’s Lockdown,” by news broadcaster Al Jazeera and its 101 East series – which reported on the authorities’ arrests of migrant workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Al-Jazeera is being investigated for sedition and defamation, and has also been accused of breaching the Communications and Multimedia Act by the Malaysian authorities.
On 3 July 2020, Al Jazeera on its 101 East Stream published a documentary that investigated the arrests, detention, and ill-treatment of refugees and undocumented migrant workers during the outbreak of COVID-19 in Malaysia. The documentary highlighted raids conducted by authorities; the inhumane conditions of detention; and the situation of migrant workers who fear arrest. Those detained were found to be held in cramped facilities, while migrant workers at risk of detention suffered from a severe lack of adequate food. The documentary also highlighted the chilling effect the government crackdown has had on the migrant worker community, who fear for their lives and safety.
Rather than addressing the concerns raised in the documentary, the government has instead sought to question the reporters involved, and pursue migrant workers who spoke with Al Jazeera. By initiating a public campaign against migrants and refugees and publishing personal details of the migrant workers who were featured in the report, the authorities have also placed the lives and safety of those interviewed in jeopardy.
The government’s subsequent threats to revoke the visas of foreign workers appears intended to intimidate other migrant workers from speaking up about human rights violations, including mistreatment. These actions have contributed to a worrying rise in intolerance towards freedom of expression, including critical views.
Amnesty International, CIVICUS World Alliance for Citizen Participation, and the ICJ consider these actions as forms of harassment and intimidation of the media, migrant workers, and others exercising their right to freedom of expression, including criticism or dissent.
The use of the Sedition Act 1948, Section 233 of the Communications and Multimedia Act, and criminal investigations against the media set a dangerous precedent and are incompatible with international law and standards. These laws place restrictions on the exercise of freedom of expression that are overly broad, unnecessary and disproportionate, and inconsistent with rule of law and human rights principles.
We reiterate their our previous calls on the Government of Malaysia to abolish both laws, which have historically been used to silence voices of those challenging government policy.
Background
Since the COVID-19 pandemic emerged earlier this year, the Malaysian government has launched a crackdown on refugees, asylum-seekers and migrant workers, carrying out a series of raids on settlements in Kuala Lumpur and Selangor. Most notably, raids were carried out as Labour Day operations on 1 May 2020, but also continued afterwards.
In response to these raids, the Office of the UN High Commissioner on Human Rights (OHCHR) denounced the crackdowns on migrant workers and journalists on 21 May. Migrant workers fear for their safety and there have been reports of suicide amongst them.
Amid growing concerns about the crackdown, the government has increasingly sought to silence criticism.
On 7 July, refugee aid worker Heidy Quah was questioned by police for posting a statement on the raids and the treatment of migrant and refugee children on social media. Her lawyer confirmed that she is being investigated under the Penal Code for criminal defamation and the Communications and Multimedia Act for the ‘improper use of network facilities or network service’.
Since the Perikatan Nasional government assumed power, numerous investigations have been launched against individuals who have criticized government actions. Since February 2020, a journalist has been investigated by police for reporting on immigration raids; a member of parliament was investigated for criticising the May parliamentary session for not permitting debates; and a large number of ordinary Malaysians have been convicted for a variety of social media postings, including for criticising the enforcement of quarantine orders under the Movement Control Order (MCO).
In another recent attack on media freedom, on 2 July 2020, contempt of court charges were filed against Steven Gan, editor-in-chief of online news outlet Malaysiakini, over comments that were posted by readers that were allegedly critical of the judiciary. The Federal Court will next hear the case on 13 July. If convicted, Gan faces an unlimited prison sentence or fine.

Jul 10, 2020 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ and the World Organization against Torture (OMCT) today highlighted a range of human rights violations, including of freedom of association and assembly, in India’s repression of peaceful protests and the impact of COVID-19 measures in the country.
The joint statement “OMCT and ICJ welcome the Report of the Special Rapporteur on the rights to freedom of peaceful assembly and association and echo his concerns over the intensity and seriousness of the threats to the enjoyment of these rights, including the impact of current Covid-19 pandemic on the already fragile civic space.
We are particularly alarmed over the increasingly violent repression of dissent in India and the arbitrary detention and harassment of activists and human rights defenders by the state in relation to their participation in peaceful protests against the Citizenship Amendment Act 2019 (CAA), the National Population Register and the National Register of Citizens.
The repression of anti-CAA protests has been brutal, with the police reportedly using excessive force against demonstrators, including firing indiscriminately into crowds, using teargas and water cannons, beating bystanders and detaining and torturing protesters, including children. At least 31 persons were killed during these protests and scores were injured. No impartial and transparent investigations into the violence have been conducted to this day.
Reportedly fabricated charges of sedition, murder, and terrorism under repressive anti-terror and national security laws – such as the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act and the National Security Act – have been filed against activists and human rights defenders participating in the protests. Those arrested and detained include Gulfisha Fatima, Natasha Narwal, Devangana Kalita, Khalid Saifi, Meeran Haider, Shifa ur Rehman, Isharat Jahan, Dr. Kafeel Khan, Sharjeel Imam, Akhil Gogoi and Asif Iqbal. They are still in prison despite repeated calls for their release by national and international human rights groups and the United Nations.
Severe restrictions on freedom of peaceful assembly and association have been imposed in the framework of the Covid-19 emergency. These include blanket shutdown of internet services and the imposition in several areas of Section 144 of the Criminal Procedure Code, a colonial law banning public protests and gathering of more than five people. While appreciating India’s efforts to prevent the spread of Covid-19, we remind the government that restrictions must meet the requirements of legality, necessity and proportionality and shall not be abused to muffle dissent.
We call on the Government of India to take urgent steps to ensure that its people enjoy the rights to express dissent and to participate in peaceful protests without fear of being arrested, brutally beaten, tortured or killed. The right to life and from the prohibition of torture and other ill treatment as well as the rights to freedom of expression, association and assembly are protected under international law including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights to which India is a party.
We further call for a thorough, prompt, transparent and impartial investigation into allegations of unlawful use of force by police, and for the immediate release of all unjustly detained activists and HRDs.”
Jun 22, 2020 | News
Today, the ICJ, the Regional Office of the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) for Central Asia and the Nationwide Movement “Yuksalish” are holding an Expert Discussion on the impact of COVID-19 on access to justice for economic, social and cultural rights (ESC rights) in Uzbekistan and comparative experiences from Europe and Central Asia.
The Fifth Expert Discussion, Access to justice in times of COVID-19, will address issues including access to a lawyer and access to court.
The event will present an opportunity to national and international experts, including lawyers, judges, members of UN human rights bodies, civil society, and other experts to debate questions of fundamental importance for ensuring access to justice and the protection of human rights in Uzbekistan.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has put new challenges before justice institutions around the world, including in Uzbekistan. These measures affected access to lawyers and courts judiciary therefore impeding full access to justice. This event will present an opportunity to discuss the solutions of States from around the globe about their responses to the pandemic. We believe that sharing experience among judges, lawyers and international experts from around the world will enrich the National debate and give an impulse for further development and the independence of the judiciary in Uzbekistan” said Akmal Burkhanov, Chairperson of the Nationwide movement “Yuksalish”.
“The pandemic became the so-called “maturity test” for the justice system and many of the urgent issues should be resolved in the light of the anti-COVID-19 measures taken. Therefore, I would also see the pandemic as an opportunity. The opportunity for transforming, changing for the better the functioning of traditional courts, provided that a high quality of justice and respect for individual rights are at the forefront of all changes,” pointed Eduards Stiprais, EU Ambassador to Uzbekistan.
Ryszard Komenda, Regional Representative of the UN Office for Human Rights for Central Asia quoted the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, Michelle Bachelet, who stated that “in order to cope effectively with the pandemic states may need to introduce certain restrictions on the exercise of certain human rights, however, such restrictions need to be necessary, proportionate, and non-discriminatory”. Mr. Komenda noted that “the impact of the regulations on lockdown affected the day-to-day work of courts and lawyers. From the perspective of international human rights standards, it is crucial that the right of individuals to an operative and independent judicial system, in particular the right to an effective remedy, habeas corpus guarantees and access to a lawyer of one’s choosing are strictly adhered to”.
“Our fifth Expert Discussion on economic and social rights, is devoted to addressing the major problems people have in getting access to justice and defending their rights during the global COVID-19 pandemic,” said Sam Zarifi, the ICJ Secretary General.
“The ICJ has documented how around the world the pandemic has severely affected peoples’ right to health, to food, to water, to education and to sanitation, and we have also seen the additional difficulties facing people with lower income and access to the levers of power.”
“We aim to discuss how international law and national best practices can help the judiciary and legal system alleviate some of the human rights issues arising from Covid-19 in Uzbekistan, and maybe even build a more responsive and accountable system after the pandemic.”
Background:
The Expert Discussions on ESC rights aim to raise awareness about the implementation of international law and standards on ESC rights by the national justice system, to facilitate access to justice in relation to ESC rights and promote effective use of international law on ESC rights at the national level. Each Expert Discussion is attended by international and national experts.
The first discussion was held in September 2018 on international standards in labour rights. The second meeting, held in December 2018, concerned judicial application of the principle of non-discrimination; the third meeting, held in March 2019, was dedicated to the rights of people with disabilities, and the forth meeting, held in October 2020, discussed the right to adequate housing in Uzbekistan.
Uzbekistan ratified the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) in 1995.
The Expert Discussions are organized by the ICJ within the framework of the “Advancing Civil Society in Promoting economic, social and cultural rights (ESCR) Standards in Uzbekistan (ACCESS)” Project funded by the EU through the European Instrument for Democracy and Human Rights (EIDHR).
Contact:
Dilfuza Kurolova, ICJ Legal consultant, t: +998 90 9050099 ; e: dilfuza.kurolova(a)icj.org
Agenda:
English version
Russian version
Uzbek version
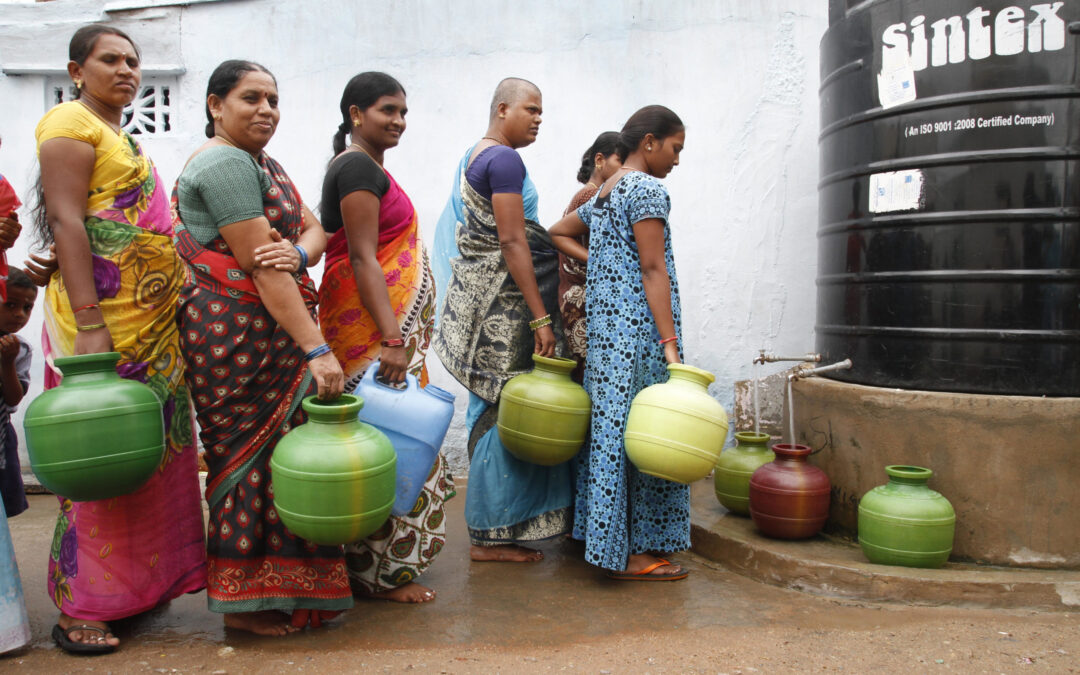

May 28, 2020
The Indian Government has fallen short of its obligations to guarantee the right to water during the COVID-19 pandemic, the ICJ said in a briefing paper released today.
There is the need for frequent hand washing to protect from, and prevent the spread of, COVID-19. However, for many people, particularly those living in poverty, water of adequate quality and quantity is either unavailable, inaccessible or only intermittently available. This increases the risk of transmission of COVID-19. Indian authorities’ failure to meet their obligations to address this situation results in violation of the rights to water and sanitation, life and health. It also presents a significant public health risk.
In a briefing paper, the ICJ answers the following questions in the context of some of the human rights concerns that have arisen as a consequence of lack of access to adequate water during the COVID-19 pandemic:
- What are the principal concerns regarding the right to water in India?
- What are India’s legal obligations to guarantee the right to water?
- What issues must the Indian authorities address to meet its obligation to guarantee the right to water during COVID-19?
- What does the International Commission of Jurists recommend?
The ICJ calls upon Indian authorities to undertake the following:
- Immediate and Emergency Water Provision:
- Urgently enact and implement enforceable policies and strategies on the provision of emergency water in all water-scarce areas for all people during the COVID-19 pandemic. Such access should be provided regardless of legal tenure, notification status of an informal settlement or any other factor or circumstance. In particular, this must include:
- Provision and cleaning of public hand-washing facilities, soap, other cleaning materials and hand sanitizer on a continuous basis during the COVID-19 pandemic;
- Clear instructions for state governments on the permissible means of providing water and a minimum quantity and quality of water to be provided per household;
- A waiver of water charges for all persons below a specified income level during the COVID-19 pandemic; and
- A cessation of all water disconnections during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Legal Enforcement:
- Finalize the enactment of enforceable national legislation on access to water which is compliant with India’s obligations in terms of the right to water;
- In the absence of such a law, clarify the legally binding nature of advisories, policies, orders and guidelines issued in relation to access to water in general and access to emergency water during the COVID-19 pandemic in particular; and
- Create and ensure effective operation of water supply helpline for effective and prompt redress of grievances and responses to emergency water needs.
- Monitoring and Information Circulation
:
- Establish independent monitoring mechanisms, with effective participation by community members and civil society organizations, state human rights institutions, and other members as maybe deemed relevant by the Government; and
- Provide regular, accurate, evidence-based information on the spread of COVID-19 to the general public (including via public television and radio) on hygiene measures that are effective in curbing the spread of COVID-19.
Earlier, the ICJ has published briefing papers on the Right to Food and Right to Housing in India, on 27 April and 7 May respectively, urging India to take immediate steps to guard against the “hunger crisis” and “housing crisis”. The ICJ has also highlighted the human rights violations faced by stranded internal migrant workers in India
Infographic
Download the Right to Water Infographic here.
Contact
Download
India-Right-to-Water-COVID-19-Briefing-Paper-2020-ENG (PDF)









