May 30, 2018 | News
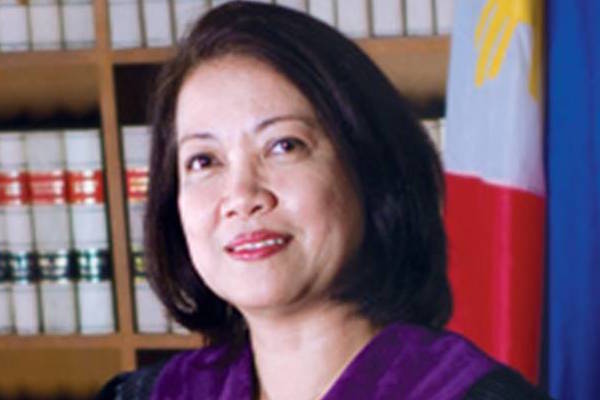
As Chief Justice Maria Lourdes Sereno filed a motion today to reconsider the Supreme Court’s 11 May 2018 decision to remove her from the Court, the ICJ expressed its grave concern that the proceedings in the case had contributed to an overall deterioration in the rule of law in the country.
Sereno’s removal comes on the heels of a series of public statements by President Rodrigo Duterte attacking the Chief Justice, including direct threats to seek her removal from the Court.
The ICJ and other national and international observers have repeatedly and publicly condemned these attacks.
Her removal, through the contrivance of a judicial ruling by a sharply divided Court, adds to the perception that the government institutions are unable or unwilling to safeguard the rule of law, and will attack the institutions that protect it.
“Preserving the independence of the judiciary in the Philippines is crucial at a time when the government is credibly alleged to have been engaged in widespread and systematic human rights violations, amounting to crimes under international law,” said Frederick Rawski, Asia Pacific Director for the ICJ.
“Given the perception of political interference and the potential impact of this case on the credibility of the judiciary as a whole, it is imperative that the Court swiftly and fairly consider the Chief Justice’s motion for reconsideration,” he added.
The removal decision came in response to a quo warranto petition filed by the Solicitor General, the government’s foremost counsel.
The petition sought to nullify her appointment on the grounds that she had failed to comply with disclosure requirements, despite the fact that her qualifications had already been certified as sufficient by the Judicial and Bar Council when her name was included in the short-list submitted to the president for consideration.
The decision superseded ongoing impeachment proceedings in the Congress.
The ICJ raised concerns that the decision could open the floodgates to similar attacks, not only against members of the Court, but to members of the judiciary and other bodies, such as the Philippine Commission on Human Rights.
It called on the Supreme Court to take care to ensure that any proceedings are conducted in line with the highest standards of judicial ethics, as reflected in the international standards such as the Bangalore Principles of Judicial Conduct.
The ICJ also reminded the government of the Philippines that under international standards – including the UN Basic Principles on the Independence of the Judiciary – the judiciary, including individual judges, must be able to conduct itself without “improper influences, inducements, pressures, threats or interferences, direct or indirect… for any reason.”
It is a responsibility of both the judiciary and the political branches of government to ensure that this principle is respected.
Contact
Emerlynne Gil, Senior International Legal Adviser for Southeast Asia, t: +662 619 8477 (ext. 206) ; e: emerlynne.gil@icj.org

May 26, 2018 | News
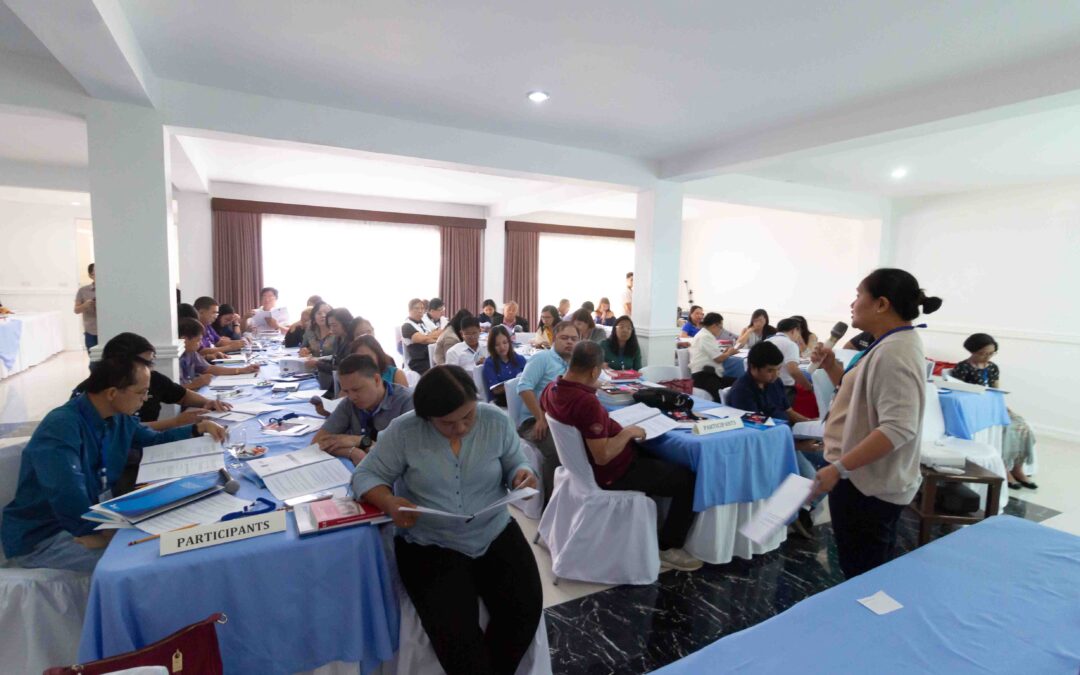
Today, the ICJ and the Integrated Bar of the Philippines (IBP) concluded a two-day workshop on eliminating gender discriminatory attitudes and behaviours towards women with a commitment to step up efforts on the protection of rights of women in the country.
Participants at the workshop were lawyers from IBP’s legal aid committees from the Eastern and Western Visayas Regions.
The workshop was held in Bohol from 25 to 26 May 2018.
“Legal aid providers are at the frontline of assisting women in accessing justice,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ’s Regional Director for Asia and the Pacific.
“It is critical that they are able to immediately detect discriminatory conduct against the women they are assisting and help in eliminating such discrimination,” he added.
Recourse to gender stereotypes in the administration of justice widespread in the Philippines and they impact women’s access to justice.
Participants at the workshop noted, in this respect, examples such as the belief that women, unlike men, are weak in the physical and cognitive sense, and the ‘virtuous-or-good-woman-versus-bad-woman-or slut’ stereotype that are still reflected in law and court decisions in Philippines.
It was noted that the UN Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women had emphasized that “stereotyping and gender bias in the justice system have far-reaching consequences for women’s full enjoyment of their human rights.”
The discussions during the two-day workshop also focused on strengthening the capacity of legal aid providers to further enhance access to justice of women whose loved ones and relatives had been extra-judicially killed.
Atty. Abdiel Dan Fajardo, National President of the IBP addressed the ongoing extrajudicial killings and culture of impunity in the Philippines that affects women particularly.
He said: “Without combatting the culture of impunity, legal aid lawyers cannot enhance access to justice for women. Therefore, it is high time to bolster the knowledge and awareness of legal aid lawyers in combatting impunity that affect women and their children.”
It was recalled that the remarks of the UN Special Rapporteur on extrajudicial, summary, or arbitrary executions, Agnes Callamard, in her report to the Human Rights Council in 2017, stressed that women are particularly affected by the extrajudicial killing of their partners and other family members.
The Special Rapporteur noted that in the Philippines, since majority of the victims are men, their female partners, “by virtue of their gender-based roles, are left to confront the associated stigma, fear, insecurity and economic deprivation, in addition to the burdens of identifying and burying their dead loved ones and seeking justice.”
At the Bohol workshop, ICJ and IBP also signed a Memorandum of Agreement to commence joint work on strengthening the IBP’s National Center for Legal Aid (NCLA).
May 17, 2018 | Feature articles, News
South Asian States must repeal laws that discriminate against LGBTI persons, and must respect, protect and fulfill the full range of their human rights, the ICJ said today on International Day Against Homophobia and Transphobia (IDAHO-T).
These rights include the right to equality before the law and equal protection of the law for all without discrimination, to which LGBTI persons are entitled due to their inherent dignity as human beings.
Across South Asia, discriminatory laws have enabled socially constructed gender and sexual norms to foster and perpetuate intimidation, harassment, threats of violence and violence against lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) persons, due to animosity, hostility and hatred motivated in whole or in part by their actual or perceived sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and/or intersex status.
Under international law, including the International Bill of Rights, that is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the two Covenants – the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights – discrimination on the grounds of sexual orientation and/or gender identity is prohibited.
In this context, the Office of the UN High Commissioner of the Human Rights has underscored five core international human rights law obligations for States: (1) protecting individuals from homophobic and trans-phobic violence; (2) preventing torture and cruel, inhuman, and degrading treatment of LGBTI persons; (3) decriminalizing homosexuality; (4) prohibiting discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity; and (5) respecting the freedom of expression, association and peaceful assembly of LGBTI persons.
Under international human rights law, the principle of non-discrimination includes the right to determine one’s sexuality, sexual orientation, and gender identity and gender expression.
Contrary to their international human rights law obligations in this respect, States’ policing of gender and sexuality has created a pattern of stigma, harassment and violence.
For example, consensual same-sex sexual relations remain criminalized in seven out of eight countries in South Asia – Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka – based on colonial era laws, such as S. 377 of the Penal Codes of Pakistan, India, Maldives and Bangladesh, and similar legal provisions in Sri Lanka and Bhutan, that criminalize “carnal intercourse against the order of nature”.
While the enforcement of these laws rarely lead to actual criminal convictions and sentences of imprisonment, their mere continued existence creates an ominous and ongoing threat against and criminalizes entire sectors of the populations in these countries.
This, in turn, gives rise to a climate that encourages and is ripe for extortion, harassment and blackmail of LGBTI persons, by the police, as well as non-State actors, including the general public and even their own families.
While there have been some progressive developments, discrimination, violence and other human rights abuses against LGBTI people – both at the hands of State and non-State actors – remain rampant in South Asia.
Hence, on IDAHO-T, the ICJ renews its call on all South Asian Governments to repeal discriminatory laws against LGBTI persons, including laws that criminalize consensual same-sex sexual relations.
In addition, the organization urges all South Asian Governments to enable transgender persons’ right to self-identification of their gender, and to enact legislation that establishes prior, free, full, informed, genuine and consistent consent for any medically unnecessary interventions on intersex persons.
Contact
Maitreyi Gupta, ICJ International Legal Adviser in India, t: +91 7756028369; e: maitreyi.gupta@icj.org
Full text in ENG (PDF): India-IDAHO-T call-News-Feature article-2018-ENG

May 14, 2018
Today, the ICJ issued a mid-term submission on Nepal’s implementation of the recommendations it had received during the second cycle of the UPR review in 2015.
In its submission, the ICJ raised specific concerns about the Government of Nepal’s failure to fulfill its stated commitment to implement the recommendations it had received. The recommendations discussed in the ICJ submission, many of which restated existing legal obligations of Nepal, related to four areas:
i) Transitional justice
ii) Legislative framework to address serious human rights violations
iii) Accountability for past human rights violation
iv) International mechanisms
View the ICJ’s full submission here: Nepal-UPR report-Advocacy-Non Legal Submission-2018-ENG

Apr 16, 2018 | News
On the fourth anniversary of the apparent enforced disappearance of Karen activist, “Billy,” the ICJ repeats its calls for the Department of Special Investigations (DSI) to assume responsibility for effectively investigating the case.
To date no progress has been made to establish the fate of Billy and the DSI has declined to take up the matter.
Pholachi “Billy” Rakchongcharoen was last seen on 17 April 2014 in the custody of Kaeng Krachan National Park officials.
At the time of his apparent enforced disappearance, Billy had been working with ethnic Karen villagers and activists on legal proceedings the villagers had filed against the National Park, the Wildlife and Plant Conservation Department, the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment, and the former Chief of Kaeng Krachan National Park concerning the alleged burning of villagers’ homes and property in the National Park in 2010 and 2011.
“The very reason the DSI was created was to investigate complex cases of this kind, including where Government officials may be implicated in gross human rights violations that amount to crimes under international law,” said Kingsley Abbott, Senior International Legal Adviser with the ICJ.
“If the DSI continues to refuse to open a special investigation after four years of little apparent progress by the police, the DSI will risk being perceived as contributing to the pervasive culture of impunity that exists within Thailand,” he added.
This week, Billy’s wife, Phinnapha Phrueksaphan, advised the ICJ that the last time the DSI had discussed Billy’s investigation with her and her family was over a year ago.
The ICJ was further informed that on 9 April 2018, Phinnapha submitted a letter to the Director-General of the DSI seeking updates on the progress of Billy’s case and clarification as to why the DSI had not accepted Billy’s case for a special investigation.
“Thailand has a clear legal duty to continue to investigate the case until Billy’s fate or whereabouts are established and to ensure that the investigative process and any outcomes are transparent – which is especially important to victims’ families who play a crucial role in investigations,” added Abbott.
On 23 May 2017, Thailand established a Committee consisting of 18 officials, including from the DSI, to formulate policies for the prevention of acts of torture and enforced disappearance, and to investigate and provide remedies in accordance with the Convention against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment (CAT), to which Thailand is a party, and the International Convention for the Protection of All Persons from Enforced Disappearance (ICPPED), which Thailand has signed but not yet ratified.
On 26 June 2017, the Committee reportedly stated that it would consider past, pending and new cases of enforced disappearance, including the case of Billy.
However, the Committee has yet to demonstrate effectiveness in efforts to implement Thailand’s international human rights obligations.
“While any steps Thailand takes towards accountability for allegations of torture, ill-treatment and enforced disappearance is welcome, the Committee should not be seen as a meaningful substitute for establishing these as crimes under domestic law,” Abbott said.
Thailand-Billy disappearance 4th year-News-web story-2018-ENG (Full story in PDF)
Thailand-Billy fourth-News-webstory-2018-THA (Thai version, in PDF)
Further Reading
Billy’s case
ICJ, ‘Launch special investigation into enforced disappearance of “Billy”’, 6 August 2015
ICJ, ‘Strengthen efforts to solve the apparent enforced disappearance of “Billy”, 16 April 2015
ICJ, ‘“Disappearance” of Billy demands special investigation’, 17 July 2014
ICJ, ‘Thai authorities must urgently investigate Billy’s ‘disappearance’’, 28 April 2014
Draft Act criminalizing torture and enforced disappearance
ICJ and Amnesty International, Open letter to Thailand’s Minister of Justice on the amendments to the Draft Prevention and Suppression of Torture and Enforced Disappearances Act, 12 March 2018
English
Thai
ICJ and Amnesty International, Recommendations to Thailand’s Ministry of Justice on the Draft Prevention and Suppression of Torture and Enforced Disappearances Act, 23 November 2017
Human Rights Committee review of Thailand
ICJ and Thai Lawyers for Human Rights and Cross-Cultural Foundation, Joint follow-up submission to the UN Human Rights Committee, 27 March 2018
UN Committee against Torture review of Thailand
ICJ and Thai Lawyers for Human Rights, Joint submission to the UN Committee against Torture, 29 January 2018
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, email: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org