Jul 1, 2016 | Feature articles, News
A feature article by U Hayman Oo, ICJ Legal Researcher in Yangon, Myanmar.
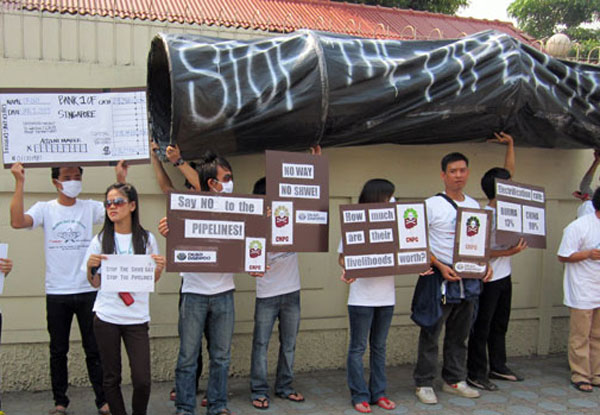
In a recent meeting with Chinese ambassador to Myanmar and villagers, organized in Kyauk Phyu, a villager from Gone Shein Village asked the ambassador to help address the damages caused to their farmland by the Shwe Gas Pipeline Project that began five years ago.
She also expressed doubts that the Kyauk Phyu Special Economic Zone (Kyauk Phyu SEZ) would benefit villagers amid all the unresolved disputes.
Given such disputes, local people are not optimistic about the upcoming development of the Kyauk Phyu SEZ.
They perceive that the project will be a ‘loss’ rather than a ‘gain’ for them.
Most of the local population of farmers fear that the project will be a disaster to their livelihood along with massive land losses.
On a recent trip to Kyauk Phyu by the International Commission of Jurists (ICJ), community members, including local MPs and lawyers, reported their concerns that a second round of such abuses will be experienced, this time even worse, during development of the Special Economic Zone planned for the area, despite promises from the Government that the development will be environmentally sustainable and bring socio-economic benefits to the region.
In fact, Special Economic Zone can contribute to the country’s economy and help benefit the welfare of its people – but only if sound policies of sustainable development in compliance with human rights are in place.
Otherwise, massive economic projects of this kind risk large-scale adverse environmental, social and human rights impacts.
Kyauk Phyu residents know very well how foreign investments can be harmful for the community when investors fail to comply with local laws as well as international standards, because of their experience with the Shwe Gas Project, a Myanmar-China pipeline.
The Gas Pipeline project was notorious for reported labour abuses, and claims of inadequate compensation for land confiscation, arrest and detention of community leaders and loss of community livelihoods and environmental degradation.
Villagers still frequently take to the street demanding for the damages caused to their farmland to be addressed, in the absence of a proper grievance mechanism.
With these prevailing experiences in mind, local residents were alarmed when authorities reportedly measured about 250 acres for the SEZ around Kathapray, Krat Tein, and Thaing Chaung village tracts in Kyauk Phyu, raising more concerns of land acquisition and compensation.
Locals complain that there was no transparent discussion over compensation for this potential land acquisition.
Villagers from Pyai Sate Kay village reportedly lost about 40 acres of farmland to the construction of a reservoir.
Although, the compensation were made for 5.1 acre of farmland, the rest of grazing land was not compensated according to a report from a villager.
There were also complaints that the compensation was neither a current market price nor a sufficient amount of money for them to be able to buy a similar size of land for cultivation.
He also complained that the Government promised to provide replacement land, but that this has not yet happened.
A total of over 70 acres of land was also apparently acquired for another reservoir under construction near Thai Chaung village.
Compensation was only paid for the farmland acreas occupied for the construction excluding land affected by the access to the reservoir.
“We were compensated but the land we lost were not measured properly. The amount paid was only on the basis of approximation. The land we lost should have been measured carefully to pay for the compensation,” said Ko Tun Nu from Thaing Chaung village.
It is reported that these reservoirs were constructed with the purpose of water supply for the SEZ project.
Furthermore, villagers from Ohn Taw and Pyai Sate Kay also reportedly lost a total of 220 acres of land when it was allocated for construction of a police station between the villages.
Although generally the purpose of the security force stationed there is for the security of the township, local people suspect that this increased security presence is instead in preparation to meet the security demands for the planned SEZ project.
There has apparently been no discussion over compensation. It is also questionable whether this volume of land is necessary for the construction of a police station.
According to the Special Economic Zone Law 2014, the Ministry of Home Affairs is responsible for land acquisition in the area of a SEZ in accordance with existing laws and regulations.
It also imposes duties on the investors and developers to bear the expenses of compensation and relocation and to ensure that the standard of living of affected persons does not fall below their original living standard.
The new NLD-led Government has inherited ample land-related problems and has prioritized dealing with these issues.
On May 5th, the Government formed the ‘Central Committee for the Review of the Acquisition of Farmland and Other Land’ in order to combat nation-wide land disputes.
The Committee’s responsibilities include investigation of compliance with existing laws by relevant authorities.
The President has also instructed that all land acquisition cease until all existing land disputes are resolved.
In addressing those issues, it is important that international standards such as Basic Principles and Guidelines on Development Based Eviction and Displacement are integrated into national policies and regulations.
Only then will such projects ensure the protection of the rights and livelihood of communities and the promotion of responsible business in the country.
Myanmar-Kyauk Phyu SEZ-News-Op-eds-2016-BUR (Full text in Burmese, PDF)
Nov 25, 2015 | Advocacy
AI y la CIJ apoyan la propuesta de creación de una Comisión Bicameral de la Verdad, la Memoria, la Justicia, la Reparación y el Fortalecimiento de las Instituciones de la Democracia en el país.
Esta comisión tratará de identificaciar las complicidades económicas y financieras en relación con violaciones de los derechos humanos y crímenes de derecho internacional cometidas durante la última dictadura militar, entre 1976 y 1983.
El trabajo de esta Comisión puede ser una contribución muy importante a la obtención de la verdad, justicia y reparación para las víctimas de la dictadura y sus cómplices económicos.
Sin embargo, esta iniciativa no debe reemplazar ni dilatar la actividad de la justicia ordinaria.
Argentina-Declaracion conjunta AI ICJ Complicidad economica-Advocacy-2015-SPA (full text in PDF)

Jun 24, 2015 | News
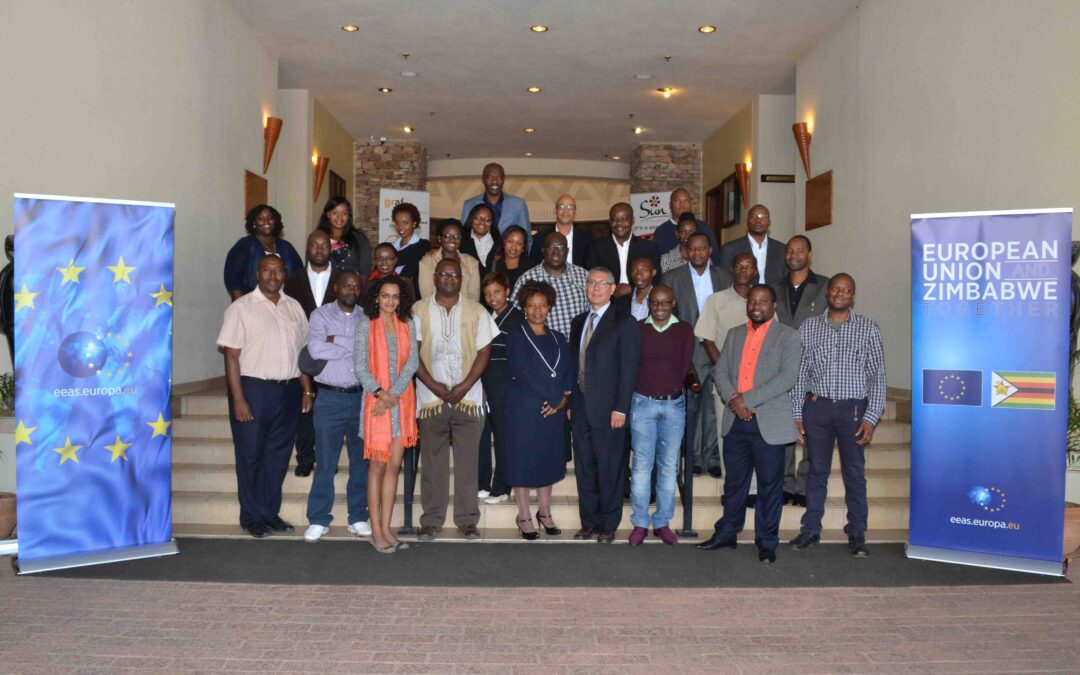
The workshop took place from 22-24 June in Victoria Falls and had a special focus on children’s rights as a particularly vulnerable group.
Its primary objective was to create a pool of jurists and activists with the knowledge and ability to undertake strategic litigation before national or regional courts in the interest of victims of human rights abuse by business enterprises in the Southern/Eastern Africa region.
To this end the meeting brought together legal practitioners and Human Rights Defenders involved in human rights legal accountability of business enterprises.
This workshop gathered together a selected group of human rights advocates from Malawi, Zambia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Uganda, Kenya and Tanzania working on cases relating to business’ human rights abuse.
In East and Southern African countries mining represents a significant part of the national economies and annual GDP.
Tanzania, Malawi, Zambia, South Africa, Botswana and Mozambique have seen the inflowing investments grow in recent years, but it is not clear that this trend has meant improvements in the realization of human rights, especially economic and social rights.
Child labour is endemic, and its occurrence in tobacco plantations subject children to additional hazards to their health and wellbeing.
Mining and oil exploration creates problems to local communities who are not properly consulted or benefit from the activity and usually bear the brunt of environmental degradation and pollution associated with those extractive industries.
Business enterprises are in many instances complicit with State’s violations of human rights.
The meeting also sought to provide legal and other tools to community representatives and litigators who want to start strategic litigation in the public interest.
This flows from the realisation that effective remedy and reparation for victims of business human rights abuses, especially in a transnational context, remains elusive as ever and confronts a series of legal and procedural obstacles.
Access to effective remedy and justice is a priority objective in the context of work relating to the human rights responsibilities of business enterprises.

Jun 1, 2015 | News
The ICJ conducted a two-day workshop on “Business and Human Rights” in Kyauk Phyu, Rakhine State on 30-31 May. The event was attended by 40 participants representing civil society organizations in Sittwe, Kyauk Phyu, Ann and Ponna Kyaunn.
It also included members from the township and district courts, township police force and members of parliament, focused on investment in Rakhine state in the absence of credible and transparent mechanisms to prevent human rights abuses.
The workshop occurred against the backdrop of myriad longstanding human rights issues in Rakhine State, including the humanitarian crisis confronting the state’s Rohingya population.
The State has also witnessed ongoing government repression of the State’s ethnic Rakhine population in response to demands for autonomy and their opposition to unregulated development of the State’s ample natural resources, including extensive gas deposits, at the expense of their livelihoods and rights.
The development of gas fields in the State has been fraught with human rights violations, including of forced labour and forced eviction of thousands of farmers from their lands.
As discussed during the workshop, since Myanmar’s relative opening up, the government has continued to invite and approve of foreign investors to develop resource extraction projects in Rakhine State, while locals resist the potential harmful effects of such projects on their livelihoods, properties and environment.
In 2013, hundreds of villagers protested against the adverse impacts of the Shwe gas pipeline construction – a large scale natural gas project developed by Daewoo International of South Korea in a joint venture with Myanmar Oil and Gas Enterprise.
Daewoo has once again ventured into Rakhine State, proposing a coal power plant in Kyaukphyu township, that could have adverse effects on the economic and environmental landscapes in local communities.
During ICJ’s previous trips to Sittwe and Kyaukphyu, local civil society activists had asked for information on responsible investment and national and international standards relating to displacement, land confiscations, and environmental and social impact assessments.
In the first day of the workshop, U Kyaw Min San, ICJ’S National Legal Adviser, led the discussion on fundamental citizen rights guaranteed in Myanmar legislation as well as an analysis of the land laws in Myanmar.
Daniel Aguirre, ICJ’s International Legal Adviser, gave an overview of international human rights law and the role of States and business corporations in protecting and respecting economic, social and cultural rights.
Vani Sathisan, ICJ’s International Legal Adviser, provided a legal analysis of Myanmar’s law on Special Economic Zones (SEZ), highlighting how the law fails to guarantee the protection of human rights and the environment while providing tax reliefs and exemptions, as well as land leases, to win over investors and developers.
On the second day, Daw Tin Tin Wai, Private Sector Policy Officer from Oxfam GB and a Campaign Officer from EarthRights International shared their experiences from Dawei SEZ and Thilawa SEZ, respectively.
They shared that lack of consultations with local communities and large-scale land confiscations through intimidation and threats occurring in the two SEZs reflected flaws in the government and judiciary to protect human rights and provide for access to remedy.
The workshop included a group discussion among the participants focusing on the role of local and international non-governmental organizations in Kyauk Phyu, Ponna Kyunn and Sittwe, the current situation of Kyauk Phyu SEZ and Ponna Kyunn industry zone and land issues related to such development projects.
Hayman Oo, ICJ’s Legal Researcher, facilitated the discussion, which served to highlight the specific themes around which the CSOs were organizing their advocacy and research.
At the closing dinner, U Kyaw Min San extended the ICJ’s appreciation to all the local CSOs for their participation and active engagement, and reiterated the ICJ’s support to work with community-driven organizations to work on recommendations to the government and businesses on transparency, prior consent and consultation, and compensations, and to push for a more rights-compliant approach to investments in Kyaukphyu.









