
Mar 18, 2015 | Non-legal submissions
The Colombian Commission of Jurists, an affiliate of the ICJ, made an oral statement to the UN Human Rights Council today, addressing threats to the independence of the judiciary in Bolivia.
The statement came in the discusson of Bolivia’s review by the Council universal periodic review procedure, in which Bolivia accepted recommendations on judicial independence, including to “guarantee the full independence of the judiciary system, in accordance with…international standards.”
In response, the ICJ and Colombian Commission of Jurists highlighted the disciplinary and criminal proceedings brought by the Legislative Assembly against three judges of the Constitutional Court at the end of last year. The proceedings were based solely on the disagreement of the political branches with an interim order issued by the Court in a case challenging the constitutionality of a new law to regulate notaries.
In the so-called “trial” conducted by the Legislative Assembly in December, Assembly Members’ statements demonstrated a manifest lack of impartiality. The Assembly extensively and arbitrarily limited the rights of the judges to present evidence and witnesses in their defence.
In the result, one judge was arbitrarily removed from office in January, and another resigned under the pressure. The Assembly also referred both of these women for criminal prosecution. Proceedings against a third judge were suspended only for health reasons.
As the Government had announced that it will seek radical reform of the judicial system during 2015. In light of recent events, the two organisations asked:
- How will Bolivia ensure that reforms are consistent with universal and regional standards on the role and independence of the judiciary?
- What role will Bolivian and international civil society and legal experts have in developing the reforms?
- Will reforms ensure a judicial selection procedure that is based on objective criteria and truly independent of the executive and legislative branches of government?
- Will consideration be given to transferring responsibility for discipline and removal procedures to a new independent and impartial body, with real guarantees of fairness, and clearly defined grounds for removal that exclude disagreement with rulings?
Ireland had also raised concern about independence and effectiveness of the judiciary in its oral statement.
The delegation of Bolivia mentioned in its opening statement its intention to convene a forum on judical reforms and put reforms to a referendum, but did not provie any details other than that various sectors of Bolivian society would be involved. During the opportunity given at the end of the session to respond to the questions from states and NGOs, the delegation of Bolivia chose not to address these issues.
Read also Bolivia: ICJ condemns removal and forced resignation of Constitutional Court judges by Legislative Assembly and links therein.
The full written statement may be downloaded in PDF format here: Bolivia-HRC28-UPR-Advocacy-non legal submission-2015-ENG

Mar 16, 2015 | Advocacy, Legal submissions
The ICJ has made further submissions to the UN Working Group on Arbitrary Detention on its elaboration of Draft Principles and Guidelines on habeas corpus.
In February 2015, the Working Group released for public input a revised set of ‘Draft Principles and Guidelines on remedies and procedures on the right of anyone deprived of his or her liberty by arrest or detention to bring proceedings before a court without delay, in order that the court may decide without delay on the lawfulness of his or her detention and order his or her release if the detention is not lawful’.
The ICJ’s submission welcomes the elaboration by the Working Group of the revised Draft Principles and Guidelines as a means of assisting States to enhance, in law and in practice, respect for the right to habeas corpus and especially welcomes certain aspects of the document. It suggests means of further improving the revised Draft Principles and Guidelines, concerning:
- The temporary nature of any derogating measures impacting upon the application of some procedural elements of the right to habeas corpus;
- The competence of courts to make orders for immediate release;
- The implementation of court orders for release;
- The public nature of judicial decisions following adjudication of habeas corpus petitions;
- Guarantees applicable to specialized tribunals;
- The right to legal aid and legal assistance;
- Confirming that the procedure must be available at all times and to all detained persons, including prisoners or war, as a remedy to protect non-derogable rights such as the prohibition against torture and ill-treatment; and
- The inadmissibility of evidence obtained by torture.
The Working Group will present its final draft to the Human Rights Council’s 30th regular session in September 2015.
Attachments
ICJ-WGAD-RevisedDraftPrinciplesAndGuidelines-3rdLegalSubmission-2015-EN (The ICJ’s latest submission in PDF)
WGAD-Habeas-RevisedDraftPrinciplesAndGuidelines-2015-EN (PDF)
Additional links for reference
The ICJ’s first written submissions to the Working Group in November 2013
The ICJ’s second written submissions to the Working Group in April 2014
Panel presentations at the September 2014 Global Consultation by ICJ staff Matt Pollard and Alex Conte

Mar 13, 2015 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The Colombian Commission of Jurists, an affiliate of the ICJ, today called for the UN Human Rights Council to uphold the use of civilian courts, rather than military tribunals, to try civilians and to adjudicate claims for human rights violations.
An oral statement to the UN Human Rights Council highlighted that:
- military tribunals should as a matter of principle have no jurisdiction to try civilians or to adjudicate claims of serious human rights violations;
- These matters should be the domain of civilian courts; and
- The jurisdiction of military tribunals should be restricted to specifically military offenses committed by military personnel.
The oral statement emphasised to the global reach of the issue, referring by way of example to the military commissions established by the United States of America at Guantánamo Bay, as well as recent negative developments in Colombia, Egypt, Thailand and Pakistan.
The statement noted that the Principles Governing the Administration of Justice Through Military Tribunals presented to the Commission on Human Rights by Emmanuel Decaux in 2006 (UN Doc E/CN.4/2006/58), are widely referenced, but have yet to receive full recognition by the Human Rights Council. The statement added its support to the calls by the Special Rapporteur on Independence of Judges and Lawyers, the Working Group on Arbitrary Detention, and others, for the Council to endorse and seek implementation of the Principles without further delay.
The statement responds to an expert consultation on the administration of justice through military tribunals convened by the Council (UN Doc A/HRC/28/32).
The full oral statement can be downloaded in pdf format here: Advocacy-HRC28-MilitaryCourts-OralStatement-2015
Said Benarbia, Director of ICJ’s Middle East North Africa Programme participated in the expert consultation.
His statement can be found here: MENA-Military Courts HRC28-Advocacy-2015-ENG (full text in PDF).
Thailand exercised its right of reply, which can be viewed in the UN webcast archive, here.
Mar 3, 2015 | Advocacy
Thirteen human rights organizations, including the ICJ, call on the United Arabe Emirates government to release the activists jailed following the UAE 94 trial.
On the second anniversary of the start of the mass “UAE 94” trial that imprisoned dozens of government critics and reform activists in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), including prominent human rights defenders, judges, academics, and student leaders, a coalition of 13 organizations calls on the UAE government to release immediately and unconditionally all those imprisoned solely for peacefully exercising their rights to freedom of expression and association following this grossly unfair trial, as well as those who remain detained or imprisoned for publicizing concerns about it.
The organizations also call on the authorities to ensure that the allegations of torture and other ill-treatment that the individuals were subjected to prior to and following their trial are promptly, independently, impartially and thoroughly investigated, that those responsible are held to account, and that the victims have access to effective remedies and to reparation.
The organizations share the serious concerns raised since 2011 by several UN human rights bodies and human rights organizations regarding the UAE government’s continuing pattern of harassment, secret, arbitrary and prolonged incommunicado detention, torture and other ill-treatment, enforced disappearances, and unfair trials targeting activists and those critical of the authorities, as well as its increasing use of national security as a pretext to clamp down on peaceful activism and to stifle calls for reform.
The space for dissent in the UAE is increasingly shrinking. The repression has been entrenched with the enactment in 2012 of the cybercrimes law, which the government has used to silence social media activists and others who support and defend freedom of expression online, and the enactment of the 2014 counter-terror law.
The vague and overly broad definition of terrorism in the 2014 law, which treats a wide range of activities, including those protected by human rights standards, as amounting to terrorism, may be used to sentence human rights defenders or critics of the government to lengthy prison terms or even death.
The organizations call on the UAE government, which currently is a member of the UN Human Rights Council, to adhere to its obligations to uphold human rights at home, including respecting the rights to freedom of opinion and expression, and to freedom of association and peaceful assembly.
The full statement can be found here in English and Arabic:
United Arab Emirates-Release activists convicted at the UAE94 trial-Advocacy-2015-ENG (full text in PDF)
United Arab Emirates -Release activists convicted at the UAE94 trial-Advocacy-2015-ARA (full text in PDF)
Read also:
UAE: Fear that Anti-Terrorism Law will be used to curtail human rights and target human rights defenders, Gulf Centre for Human Rights, Front Line Defenders, Cairo Institute for Human Rights Studies, Arabic Network for Human Rights Information, 13 December 2014,
Mass convictions following an unfair trial: The UAE 94 case, an ICJ report, October 2013,
United Arab Emirates: ICJ condemns blatant disregard of the right to a fair and public trial, ICJ, 12 March 2013
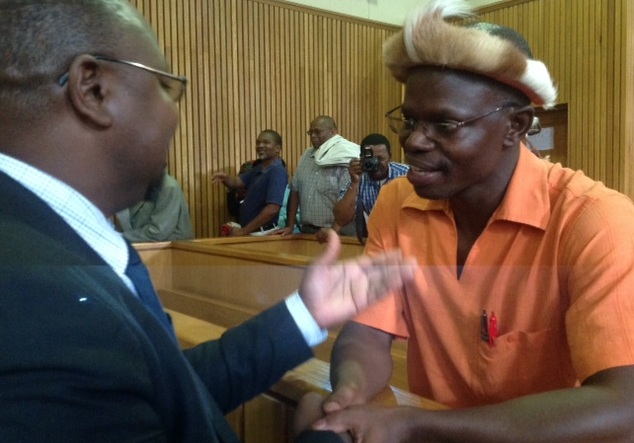

Feb 17, 2015 | News
Alleging a range of human rights violations by Swaziland in the cases of Thulani Maseko and Bheki Makhubu, leading legal advocates today filed a petition with the UN Working Group on Arbitrary Detention (UNWGAD) in Geneva.
The American Bar Association’s Center for Human Rights, the global law firm Hogan Lovells and the ICJ jointly produced a petition calling for the UNWGAD to issue an opinion regarding the lawfulness of the continued incarceration of Thulani Maseko, an internationally recognized human rights lawyer and feature writer for The Nation magazine.
“The consequences of this arbitrary action against Thulani Maseko have not only violated his rights and exacted a heavy personal toll, but have also highlighted the rule of law deficit in Swaziland,” said Wilder Tayler, ICJ’s Secretary General. “Thulani Maseko has been denied his right to express an opinion on public affairs and the administration of justice, guaranteed under international law and affirmed in the UN Basic principles on the Role of lawyers.”
Thulani Maseko and journalist Bheki Makhubu were charged with two counts of contempt of court emanating from articles published in February and March 2014, in which they questioned circumstances surrounding the arrest of a government vehicle inspector.
They were sentenced to two years of imprisonment, without the alternative option of a fine at the end of a trial largely condemned by leading international rights groups as unfair and not complying with international standards on the right to a fair trial.
Some of the fair trial guarantees that have been breached, according to the legal petition filed with the UNGWAD, include the right to be tried by an independent and impartial tribunal; right to a public hearing; right to a legal counsel; right to the presumption of innocence; right to bail; and right to protection of the law.
“The use of contempt of court proceedings to suppress the right to freedom of expression is a violation of international human rights law,” said Marc Gottridge, partner at Hogan Lovells. “The right to freedom of expression is guaranteed in the Swazi constitution and international law, including treaties to which Swaziland is a party.”
“The general failings of the Swazi judiciary with respect to independence and impartiality makes it reasonable to conclude that there cannot be an effective domestic remedy for Thulani Maseko,” he added.
Contact:
Arnold Tsunga, Director, ICJ Africa Regional Programme, t +27 716 405 926 or +41 762 399 032, e arnold.tsunga(a)icj.org,
Matt Pollard, Senior Legal Adviser, ICJ, Centre for Independence of Judges and lawyers, t +41 22 979 38 12, e matt.pollard(a)icj.org
Marc Gottridge, Partner Hogan Lovells, t +1 212 918 3000, e marc.gottridge(a)hoganlovells.com
Ginna Anderson, Senior Counsel, Center for Human Rights, American Bar Association, t +1 202 442 3438, e ginna.anderson(a)americanbar.org
Background:
Thulani Maseko was arrested on 17th March 2014 following a warrant of arrest that was issued by the Chief Justice Michael Ramodibedi on his own motion.
This was after he had written an article titled “Where the Law Has No Place” criticising the courts for the way that a fellow Swazi citizen Mr Gwebu Bhantshana had been arrested and detained and the wider implications of that case on the rule of law in Swaziland.
Save for 3 days in April 2014 when he was released following Judge Mumcy Dlamini’s judgment declaring his arrest and detention wrongful and illegal, Thulani has been in custody since his initial arrest. Mr. Maseko was initially held at Sidwashini Correctional facility before he was taken to Big Bend Correctional facility, where he is currently lodged.
Further background material can be found here:
http://www.americanbar.org/news/abanews/aba-news-archives/2014/04/statement_of_jamesr.html
https://www.icj.org/swaziland-icj-condemns-the-harsh-prison-term-imposed-on-thulani-maseko-and-bheki-makhubu/
https://www.icj.org/swaziland-icj-condemns-the-conviction-of-celebrated-human-rights-lawyer-and-prominent-journalist-on-charges-of-contempt-of-court/
https://www.icj.org/swaziland-icj-concerned-at-detention-of-human-rights-lawyer-and-journalist/
Download the petition:
Swaziland-Maseko WGAD Petition-Advocacy-2015-Eng (full text in PDF)
The lawyers at Hogan Lovells US LLP who worked on this petition are Marc Gottridge, Dianne Milner, Allison Holt and Hans H. Hertell.









