
Jul 8, 2021 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
Today, the ICJ made an intervention during a debate on the outcome of the Universal Periodic Review of Lebanon before the UN Human Rights Council.
Mar 15, 2021 | Advocacy, News
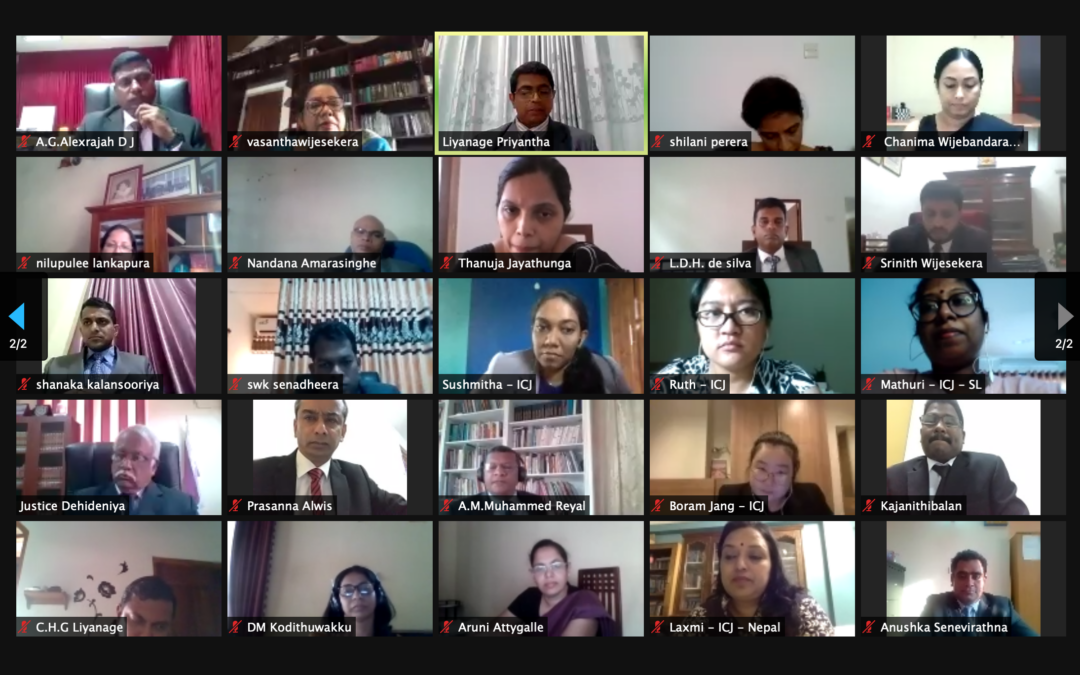
The ICJ and a group of Sri Lankan judges have agreed on the importance of taking effective measures to address discrimination and equal protection in accessing justice in the country.
On 6 and 13 March 2021, the ICJ, in collaboration with the Sri Lanka Judges’ Institute (SLJI), organized the National Judicial Dialogue on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women and Enhancing Women’s Access to Justice. This event was organized under the ‘Enhancing Access to Justice for Women in Asia and the Pacific’ project funded by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (SIDA).
Twenty magistrates and District Court judges from around Sri Lanka, with judicial and legal experts from other countries, participated in this judicial dialogue which was conducted virtually due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The dialogue highlighted how Sri Lankan women continue to face a myriad of challenges including legal, institutional and cultural barriers when accessing justice. Gender biases and discriminatory behaviour prevalent in every aspect of justice delivery needs to be dealt with in order to effectively enhance women’s access to justice.
Boram Jang, ICJ International Legal Advisor remarked that “judiciaries have an important role to play in eliminating gender discrimination in justice delivery as it is a critical component in promoting women’s access to justice. In order to do so, the judges should be equipped with a full understanding of Sri Lanka’s obligations under the CEDAW and other human rights instruments.”
Honorable L. T. B. Dehideniya, Justice of the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka and Executive Director of the SLJI expressed hope that judicial dialogues such as this would “enhance the capacity of participant judges to use the international legal instruments, which Sri Lanka has ratified, in domestic judicial work especially with regard to the elimination of gender inequalities and biases.”
Ms. Bandana Rana, Vice Chair of the CEDAW Committee led a discussion with the judges on the application of the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), pointing out that “judges play a pivotal role in identifying the incongruences between existing laws and international human rights standards and ensuring that the full gamut of women’s human rights is retained in line with the CEDAW framework.”
Justice Ayesha. M. Malik, High Court Judge, Lahore, Pakistan affirmed the importance applying the right to access to justice under international human rights law and suggested strategies for reflecting these international standards in judicial decisions.
Attorney Evalyn Ursua addressed on gender stereotypes and biases in justice delivery and engaged the participants on how these could be effectively eliminated. She stated that “the judiciary as a part of the State has the obligation to eliminate gender discrimination.” She encouraged the judges to use the cultural power of law to change language and attitudes surrounding gender discriminatory behaviour and stigma.
The second day featured a discussion on the specific barriers that women in Sri Lanka face when they access justice. Hon. Shiranee Tilakawardane, former Justice of the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka led a discussion on the role and measures available to the judiciary as an institution to enhance access to justice for Sri Lankan women.
Justice Tilakawardane stated that “While theoretically, the Sri Lankan constitution enshrines equality before the law, in reality women continue to feel disadvantaged when they try to access justice” and added “the Sri Lankan judiciary can empower its women only when it understands, acknowledges and addresses the disadvantages they face owing to their gender.” She impressed upon the participant-judges that “ensuring equality is no longer a choice, nor is it merely aspirational, but a pivotal part of judicial ethics.”
The panelists on the second day surveyed the legal, institutional and cultural challenges faced by women at every step of the judicial process. The panel comprised of Prof. Savitri Goonesekere, Emeritus Professor of Law and Former member of the CEDAW Committee, Mrs. Farzana Jameel, P.C, Additional Solicitor General of the Attorney General’s Department and Mrs. Savithri Wijesekara, Executive Director of Women in Need.
Contact
Osama Motiwala, Communications Officer – osama.motiwala@icj.org
Sep 8, 2020 | Advocacy, News
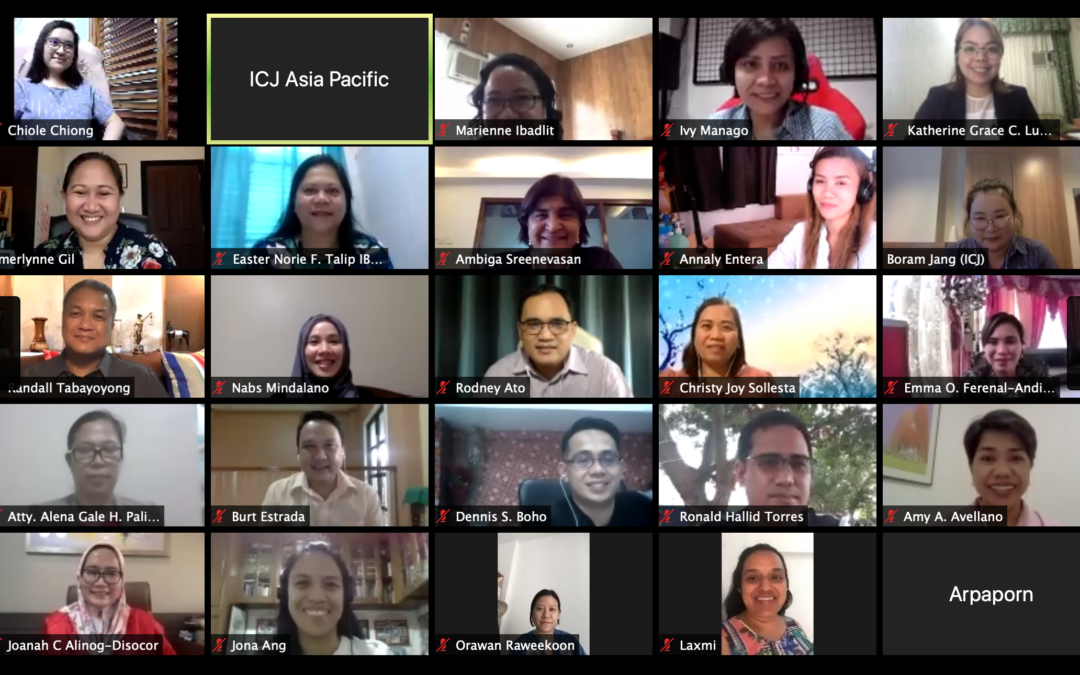
On 29 August and 5 September, the ICJ collaborated with the Integrated Bar of the Philippines (IBP) to hold a webinar series for legal aid providers in the Philippines on eliminating gender discriminatory attitudes and behaviors towards women.
Members of IBP’s legal aid committees from the Eastern and Western Mindanao Regions participated in these webinars, focused on gender stereotypes and discriminatory practices that exist in the legal profession and in the work of legal aid providers who directly engage with women when they seek justice.
Dato Ambiga Sreenevasan, ICJ’s Commissioner from Malaysia, addressed the promotion and protection of women’s human rights in the context of the legal profession: “While conditions for women have improved, there is still work to be done to achieve equality between men and women in the legal profession. At the entry level, things appear to be going well, but we must look also at women’s opportunities throughout their legal career and question why it is the case that some areas are still male-dominated.”
Mikiko Otani, ICJ’s Commissioner from Japan and a member of the UN Committee on the Rights of the Child, spoke about how gender stereotypes and gender discrimination hinder women from accessing justice. “The Bar should be at the forefront of advocating for improvement in legal structures that would help eliminate gender discrimination,” she said.
The Philippines had previously featured as one of the top ten performers in addressing gender disparities, as measured by the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Index. However, it has recently fallen to rank 16th out of 153 countries. Emerlynne Gil, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, acknowledged various measures adopted by the Philippines to implement the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), such as the adoption of the Anti-Violence Against Women and Children Act and the Magna Carta for Women. She noted, however, that the Philippines still must do a great deal more.
“The existing culture of impunity and lack of effective remedies for women to access the justice system are just some of the difficult challenges the country faces that prevent it from achieving this goal,” Emerlynne Gil said.
The webinar series also featured a discussion on specific challenges faced by women when accessing justice during the COVID 19 pandemic and in the context of the “drug war” in the Philippines. The lawyers discussed their role and also that of the Bar as an institution to immediately identify and eliminate these gender stereotypes to ensure their clients’ right to access to justice.
Judge Amy Alabado Avellano, a Regional Trial Court judge in the Philippines led this discussion. Attorney Burt Estrada, IBP Executive Vice President, and Attorney Marienne Ibadlit, former IBP Governor for Western Visayas, also held a dialogue with the lawyers on how the IBP as a professional association for lawyers in the Philippines could contribute towards enhancing access to justice for women in the country.
Contact
For questions and clarifications, please contact Ms. Emerlynne Gil, Senior International Legal Adviser, t: +662 619 8477 (ext. 206); e: emerlynne.gil(a)icj.org.

Jul 5, 2020 | News
The ICJ hosted live interviews with human rights defenders from Asia, Africa and Latin America to mark Pride Month, which is celebrated during the month of June in various parts of the world. The interviews took place from 22 June to 3 July 2020.
In total, 13 human rights defenders from 11 countries spanning three continents, who are working to uphold the human rights of of lesbians, gay, bisexual, transgender (LGBT) individuals, were interviewed.
The interviews discussed existing legal systems that discriminate on the basis of sexual orientation, gender identity and expression (SOGIE) and the impacts of COVID-19 on existing activism, .
The interviews aimed to provide quick snapshots of different country and regional contexts and a platform for LGBT activist voices on the varied and devastating impacts of COVID-19 on LGBT people.
Debunking cultural myths
In many countries around the world where people are criminalized or stigmatized as a result of harmful steretypes and prejudice on the grounds of their real or imputed SOGIE, public discourse tend to cast LGBT relationships and identities as threats to culture, religion or beliefs and the future of the nation. These interviews endeavoured to interrogate and debunk cultural and regional myths surrounding SOGIE identities as ‘Western’ constructs.
In a response to homosexuality being said to be ‘unAfrican’, Kutlwano Pearl Magashula, executive officer for program functions at the Other Foundation from Botswana, said:
“Utterances that suggest that homosexuality is unAfrican enforce stigma and violence and serve to carve deep roots in the consciousness of people around the world that breed discrimination and treating people differently.”
Devastating impacts of COVID-19 on LGBT people
Important impacts of COVID-19 on LGBT people were highlighted by different speakers, ranging from a loss of livelihood, vulnerability to violence at home and in public spaces, as well as challenges in accessing healthcare.
“There is violence against transgender women sex workers. The police arrest them, yell at them and shoot at them with rubber bullets. This is a recent episode here in Colombia and it is terrible. If they don’t work, they don’t have money to buy food and pay the rent. It is a difficult scenario,” Dejusticia researcher Santiago Carvajal Casas from Columbia said.
Pre-existing inequalities and landmark wins
Personal experiences of ‘life after’ important wins from around the world were shared. Some important gains from the decriminalization of consensual same-sex sexual relationships in Botswana and India, as well as the recent legalization of same-sex marriage in Taiwan must be celebrated. However, many of these wins may remain illusory for people who have been discriminated against on the basis of class, caste and other status inequality, or are without social support, especially in the face of COVID-19.
“What we really need is social protection, we need a safety-net for all those who are close to the poverty line and who are likely to go below the poverty line because of disasters like the COVID-19 epidemic or catastrophic out of pocket healthcare expenditures. We definitely need accessible healthcare for everyone and livelihood.” – Dr. L Ramakrishnan, public health professional and Vice-President of SAATHII, India
Watch the Facebook lives below:
Kutlwano Pearl Magashula, Executive Officer for Program Functions at the Other Foundation, on the board of LEGABIBO as the vice-chairperson and co-founder of the autonomous feminist collective Black Queer DocX (Botswana)
Busisiwe Deyi, Commissioner of CGE/ Lecturer of Jurisprudence (South Africa)
Letlhogonolo Mokgoroane, lawyer activist and podcaster (South Africa)
Lini Zurlia, advocacy officer at ASEAN SOGIE Caucus (ASEAN/Indonesia)
Yee Shan, member of Diversity Malaysia (Malaysia)
Sirasak Chaited, human rights campaigner, LGBT+ and sex worker rights activist (Thailand)
Santiago Carvajal Casas, Dejusticia researcher (Colombia)
Sih-Cheng (Sean) Du, Director of Policy Advocacy at Taiwan Tongzhi (LGBTQ+) Hotline Association (Taiwan)
Neeli Rana, transgender activist (Pakistan)
Riska Carolina, The Indonesian Plan Parenthood Association (IPPA) member (Indonesia)
Hla Myat Tun, Deputy Director from Colors Rainbow and Co-Director at &PROUD (Myanmar)
Dr. L Ramakrishnan, Vice President Saathii, activist, public health professional (India)
Nigel Mpemba Patel, Associate editor at the South African Journal on Human Rights and research consultant at ILGA World (Malawi)
***
Cover photo by Violaine Biex-Colors Rainbow, Myanmar.

Jan 18, 2020 | Advocacy, News
From 16 to 17 January 2020, the ICJ, in collaboration with the National Police Commission (KOMPOLNAS), UN Women, and the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) organized a Seminar on Eliminating Gender Discriminatory Practices for the Police.
It was held in Bogor, Indonesia and gathered 30 law enforcement officers from Indonesian provinces that are reported to have the highest rate of incidents of violence against women.
Frederick Rawski, ICJ’s Asia and the Pacific Regional Director, stressed to participants that, “Police officers are the first point of contact for women who try to access justice for violations committed against them. It is important therefore for these officers to be well-trained on gender sensitivity and women’s human rights.”
“Only 40 percent of women speak out on violence, and only 10 percent of these report to the police because they are often blamed for the violence they experience or humiliated by those who should protect them,” added Ms. Doreen Buettner, Programme Specialist on Access to Justice of UN Women.
Indonesia is a State Party to the Convention on Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), having ratified it on 13 September 1984. It has established a gender mainstreaming mechanism under Presidential Instruction No. 9 of 2000 on Gender Mainstreaming in National Development, which obliges all government representatives and agencies, including the police, to mainstream gender in their work in order to eliminate gender-based discrimination.
Ms. Poengky Indarti, Commissioner from the National Police Commission (KOMPOLNAS), stressed that “Gender-responsive police training should not a one-time thing, we need to institutionalize the training for it to be sustainable.”
At the seminar, the discussions were aimed at strengthening the understanding of the members of police officers on women’s human rights, and the importance of eliminating gender stereotyping in their work to enhance access to justice for women.
Ms. Siti Aminah, Commissioner of the National Commission of Violence Against Women in Indonesia (Komnas Perempuan) and Professor Meg Garvin, Executive Director of the National Crime Victim Law Institute (NCVLI) and Clinical Professor of Law at the Lewis & Clark Law School facilitated discussions on common gender stereotypes in Indonesia and strategies, protocols and good practice relating to all aspects of responses to incidents of violence against women.
Contact
Ruth Panjaitan, National Legal Advisor for Indonesia, International Commission of Jurists, e: ruthstephani.panjaitan(a)icj.org
Resources
To access pictures from the event, click here.









