
Jan 9, 2013 | News
 Members of Sri Lanka’s Parliament should reject the impeachment motion to remove Chief Justice Shirani Bandaranayake, that will be put before Parliament on 10-11 January 2013, the ICJ said today.
Members of Sri Lanka’s Parliament should reject the impeachment motion to remove Chief Justice Shirani Bandaranayake, that will be put before Parliament on 10-11 January 2013, the ICJ said today.
The ICJ call comes after a three-member panel of the Supreme Court, in a decision issued on 1 January 2013, ruled that the impeachment procedure in Parliament was not constitutionally valid, finding that such procedures could only be established ‘by law’ enacted by Parliament. The Standing Orders governing the current impeachment investigative process are not considered ‘law’ under the Constitution of Sri Lanka.
“The assault on the independence of the Sri Lankan judiciary in recent months has brought Sri Lanka to the brink of a constitutional crisis,” said Sam Zarifi, ICJ’s Asia Director. “If the impeachment motion is passed in Parliament in defiance of decisions of the country’s judiciary, it will signal a massive breakdown in the rule of law and checks and balances.”
The ICJ stresses that in a democratic society operating under the rule of law, the principle of judicial review is paramount and judges have the ultimate authority to determine what the law provides.
Following the Supreme Court decision, the Court of Appeal quashed the findings of the Parliamentary Select Committee on 7 January 2013, claiming the PSC lacked authority to make such a finding.
In response to the Supreme Court decision, President Mahinda Rajapakse announced his intention to create a four-member panel on 7 January 2013 to review the Parliamentary Select Committee Report and comment on its constitutional validity. The identities of the panel members have not been revealed.
“Creating another ad hoc committee on an arbitrary basis to pronounce on the validity of the impeachment process in Parliament – a process already held to be improper by the apex Court – aggravates the insult to the judiciary and deepens the constitutional crisis,” Zarifi said. “Judges are not above the law, and should be subject to impeachment if they have engaged in serious misdeeds, but the faulty process used by the Parliamentary committee violated basic notions of due process and truth-seeking.”
Last month, the Bar Association of Sri Lanka unanimously passed a resolution calling on the President to reconsider the impeachment, warning that if principles of rule of law were disregarded in the removal process, the Bar would not formally welcome the new Chief Justice.
“This current crisis threatens to leave Sri Lanka with little or no means to hold State officials accountable for serious human rights violations,” Zarifi added. “This government has shown itself committed to imposing a climate of impunity in Sri Lanka. The Parliament should stop the country’s sad slide away from the rule of law.”
The ICJ released a 150-page report in early November 2012 focusing on impunity in Sri Lanka and highlighting the recent attacks on the judiciary as a key factor that has led to the erosion of State accountability mechanisms.
The impeachment process against Chief Justice Shirani Bandaranayake has been widely criticized for ignoring international standards and practice.
The ICJ in an earlier statement called on the Government of Sri Lanka to adhere to international standards and practice in the impeachment hearings.
The ICJ reiterates its call on the Government of Sri Lanka to take active measures to promote the independence of the judiciary and rule of law by adhering to international standards and practice in impeachment hearings.
CONTACT:
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Asia-Pacific Regional Director, Bangkok, t:+66 807819002; email: sam.zarifi(at)icj.org
Sheila Varadan, ICJ Legal Advisor, South Asia Programme (Bangkok), t: +66 857200723; email: sheila.varadan(at)icj.org
BACKGROUND:
The impeachment motion was initiated just days after the Chief Justice ruled against the Government on a controversial bill – the Divi Neguma Bill, under which the Minister of Economic Development (who is also the President’s brother, Basil Rajapakse) would have had control over a fund of 80 billion Sri Lankan rupees (611 million USD) with minimal accountability.
Attacks on the judiciary have been escalating since July 2012. A Government Minister Rishad Bathiudeen threatened a Magistrate in Mannar and then allegedly orchestrated a mob to pelt stones at the Mannar courthouse. In early October 2012, the ICJ condemned the physical assault on the secretary of the Judicial Service Commission, Manjula Tillekaratne.
On 6 November 2012, a motion to initiate impeachment proceedings was brought against Chief Justice Shirani Bandaranayake. The motion contained fourteen charges relating to the non-disclosure of financial assets and improper conduct of a Chief Justice. On 8 November 2012, the Chief Justice’s lawyers responded to four of the fourteen charges, claiming that all operative bank accounts had been disclosed and only those accounts which were closed or held no funds were not declared.
On 6 December 2012, the Chief Justice and her team of lawyers walked out of the impeachment hearing in protest over the denial of a fair hearing.
On 8 December 2012, a majority of the Parliamentary Select Committee comprising government representatives found the Chief Justice guilty of four charges out of the fourteen allegations. The Committee’s released its findings despite the Supreme Court’s request in late November 2012 that hearings be delayed until it could determine the constitutionality of the proceeding.
Photo by vikalapa
Dec 13, 2012 | News
Following recent attacks against the independence of the judiciary in several Central American countries, the ICJ issued today a strong position statement (in Spanish).
La CIJ ante los últimos acontecimientos que afectan seriamente la independencia de los differentes poderes judiciales en países de la región centroamericana, expresa:
- Durante el año 2012, la CIJ ha constatado que los diferentes gobiernos y autoridades de los países de Centroamérica han realizado actos que afectan seriamente la independencia judicial. En Honduras, el miércoles 12 de diciembre, la Asamblea Legislativa procedió a destituir a cuatro magistrados de la Sala Constitucional de la Corte Suprema de Justicia, sin tener facultades o atribuciones para un acto de esta naturaleza. Esta destitución nos sitúa frente a un escenario similar al del Golpe de Estado de junio de 2009;
- En El Salvador, se han dado hechos similares; durante todo el año 2012, la Asamblea Legislativa y otros grupos del poder político, han pretendido desarticular la Sala Constitucional de la Corte Suprema de dicho país, debido al contenido de sus sentencias; en Costa Rica hace unas semanas, también la Asamblea Legislativa se negó a ratificar en su cargo a un magistrado de la Sala Constitucional de la Corte Suprema de Justicia, alegando que los fallos de dicha sala creaban una “situación de ingobernabilidad” y que ese acto era un “llamado de atención para el resto de los magistrados”, siendo la primera vez que el Organismo Legislativo se negó a ratificar en su cargo un nuevo mandato de un magistrado del alto Tribunal;
- En Guatemala, tanto el Presidente de la Cámara Penal de la Corte Suprema de Justicia como la Fiscal General, vienen siendo objeto de ataques a su independencia por parte de abogados defensores de las personas acusadas, por la función positiva que han cumplido en la lucha contra la impunidad en casos de graves violaciones a los derechos humanos cometidas durante el conflicto armado;
La CIJ considera que todos estos hechos constituyen injerencias y ataques a la independencia del Poder Judicial; tratándose de magistrados de diferentes Cortes Supremas y de una Fiscal General, estos actos evidencian por sí mismos, la precariedad de la garantía de independencia judicial en dichos países. A esta situación, hay que agregar que varios de los países mencionados, carecen de sistemas de carrera judicial y de mecanismos de protección adecuados para garantizar a los funcionarios el ejercicio independiente de la función jurisdiccional; además, en ellos existen fenómenos de impunidad generalizados y de cuerpos ilegales, aparatos clandestinos de seguridad y crimen organizado.
Frente a estos hechos, la CIJ recomienda:
- Que las autoridades estatales concernidas con los hechos arriba mencionados, se abstengan de interferir en el ámbito de la independencia de los poderes judiciales, ya que de lo contrario, estarían incumpliendo sus obligaciones internacionales sobre respeto a la independencia de poderes, establecidas en la Convención Americana sobre Derechos Humanos y en el Pacto Internacional de Derechos Civiles y Políticos;
- Que se tomen las medidas necesarias para asegurar la independencia de jueces, magistrados y fiscales como corresponde en un Estado de Derecho;
- Que los estados relacionados establezcan mecanismos de protección para jueces, magistrados, fiscales y demás operadores de justicia, a fin de salvaguardar su integridad y garantizar el ejercicio de la función jurisdiccional independiente;
- Que los estados concernidos impulsen procesos de creación o fortalecimiento de carreras judiciales de conformidad con los estándares internacionales;
- Que se fortalezcan los poderes judiciales y otras entidades del sector justicia, a fin de lograr la efectiva protección de los derechos humanos incluida la lucha contra la impunidad.
La CIJ continuará cumpliendo con su mandato de promover y garantizar la independencia de jueces, abogados y fiscales; en ese sentido, le dará seguimiento a estas situaciones y continuará observando y proponiendo soluciones a esta problemática.
Para mayor información :
Ramón Cadena Rámila, Director de la Comisión Internacional de Juristas para Centro América, t + 502 30441818

Dec 12, 2012 | Multimedia items, News, Video clips
 The ICJ 17th World Congress closed today with the adoption of a landmark Declaration on Access to Justice and Right to a Remedy in international human rights systems.
The ICJ 17th World Congress closed today with the adoption of a landmark Declaration on Access to Justice and Right to a Remedy in international human rights systems.
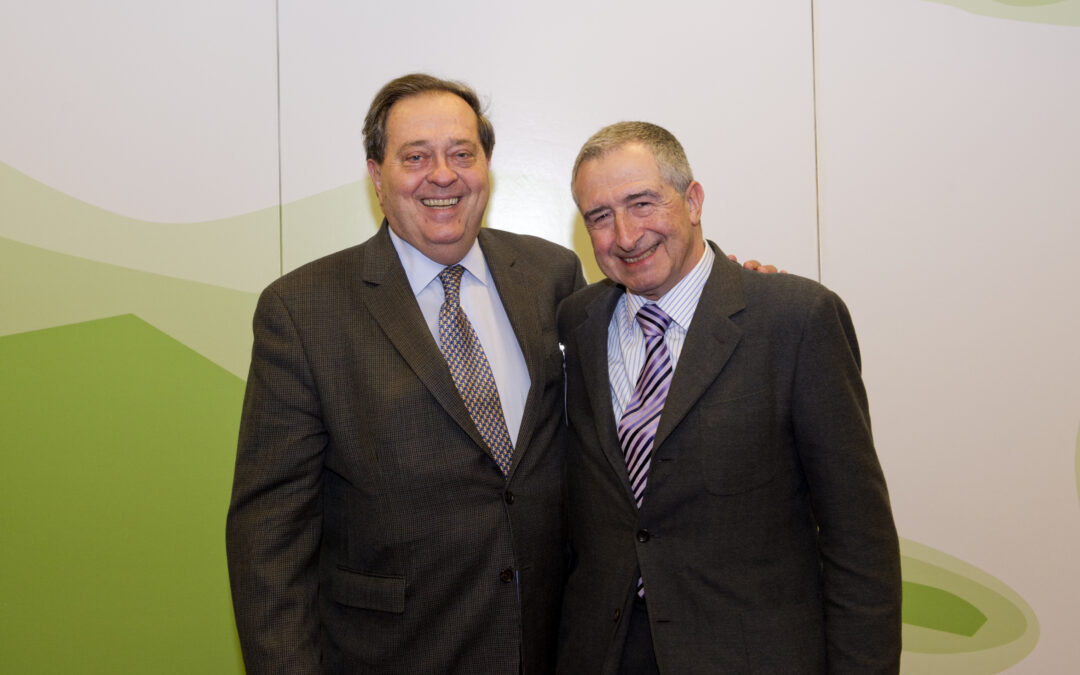
In his final speech at the closing of the Congress, Sir Nigel Rodley, the new ICJ President (photo above, on the right, with Pedro Nikken, outgoing ICJ President) said:
“The ICJ has always been the world’s leading organization of lawyers working for the Rule of Law and human rights. At the ripe young age of 60, it is at the height of its prestige and authority.”
“Led by one of the world’s most experienced international human rights lawyers, Wilder Tayler, of Uruguay, the ICJ is now on a firm footing with a strong secretariat in Geneva – the city of human rights – and an increasing number of offices in key countries and regions of the world.”
“So, the ICJ is well-placed to make an even more significant contribution meeting such challenges as the serious problem of assaults on the independence of judges, lawyers, and prosecutors.”
“There is no justice if people don’t have access to it. The ICJ Congress, with its vast range of eminent expertise, from the ICJ Commissioners, national sections representatives, and guests, adopted a landmark Declaration on Access to Justice and Right to a Remedy in international human rights systems.”
“The focus was how to make international regional human rights systems more able to respond to the needs of those who cannot secure justice at home. There was special urgency bearing in mind the attempts of governments to weaken the systems’ ability to call these same governments to account.”
Sir Nigel Rodley, ICJ President, talks about the Declaration:
To download the text of the full declaration click on the links below:
ICJ 17th World Congress-Declaration and opening speeches-2012 (full text in pdf)
ICJ 17th World Congress-Declaration-2012 (full text in pdf)
ICJ 17th World Congress-Declaration-2012-FR (full text in pdf)
Photo by David Rouge

Dec 6, 2012 | News
The impeachment process against Chief Justice Shirani Bandaranayake ignores international standards and practice, says the ICJ.
The ICJ urges the government of Sri Lanka to take immediate steps to uphold the independence of the judiciary and adhere to international standards and practice on the removal of judges.
Today, the Chief Justice and her team of lawyers walked out of the impeachment hearing in protest over the denial of a fair hearing.
Protests supporting and opposing the impeachment process erupted on Tuesday 4 December 2012 as the Chief Justice appeared before the Parliamentary Select Committee for the second time.
Over two hundred judges, several hundred lawyers, trade union leaders and a large number of religious dignitaries assembled to show their support for the Chief Justice.
Opposition members of parliament publicaly called on the Government to adhere to principles of fair trial and due process in the impeachment process.
Reportedly the Chief Justice has been denied the right to cross-examine potential witnesses and has not been provided full disclosure of the allegations against her.
The Parliamentary Select Committee has also denied the request for a public hearing and prohibited observers from attending.
“Parliament is pushing ahead with an impeachment process that fails to adhere to fundamental principles of due process and fair trial,” said Sam Zarifi, ICJ Asia Pacific Director. “The Chief Justice’s impeachment is part of a relentless campaign waged by the Rajapaksa Government to weaken the judiciary. An independent judiciary is the principle check on the exercise of executive and legislative powers – vital to the functioning of a healthy democracy.”
As recalled by the United Nations Special Rapporteur on the independence of judges and lawyers in a statement last month, international standards require that judges be removed only in exceptional circumstances involving incapacity or gross misconduct.
A cornerstone of judicial independence is that tenure of judges be secure.
“Any process for removal must comply with all of the guarantees of due process and fair trial afforded under international law, notably the right to an independent and impartial hearing,” Zarifi added.
The United Nations Human Rights Committee, in its 2003 concluding observations on Sri Lanka, expressed concern that the procedure for removing judges under Article 107 and the complementary Standing Orders of Parliament was not compatible with Article 14 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights.
The Parliamentary Select Committee, presiding over the impeachment hearings is composed exclusively of members of parliament, the majority of which are drawn from the Government coalition. No members of the judiciary are permitted to sit on the Select Committee.
Comparatively in India, an impeachment hearing is presided over by a three-member committee comprised of a Supreme Court justice, a Chief Justice of any High Court and an eminent jurist.
In South Africa, a judge may only be removed after a hearing by the Judicial Service Commission, a body composed of members of the judiciary.
In Canada, all removal proceedings are conducted by the Judicial Council, a body composed of 38 chief and associate chief justices of the superior courts and chaired by the Chief Justice of Canada.
The United Nations Special Rapporteur on the independence of judges and lawyers warned against the misuse of disciplinary proceedings as a reprisals mechanism against independent judges.
The timing of the impeachment motion raises questions. The impeachment motion was initiated just days after the Chief Justice ruled against the Government on a controversial bill – the Divi Neguma Bill – before Parliament.
If the bill passed, the Minister of Economic Development (who is also the President’s brother Basil Rajapakse) would have had control over a fund of 80 billion Sri Lankan rupees (611 million USD).
Attacks on the judiciary have been escalating in recent months. In July 2012, Government Minister Rishad Bathiudeen threatened a Magistrate in Mannar and then allegedly orchestrated a mob to pelt stones at the Mannar courthouse.
In early October, the ICJ condemned the physical assault on the secretary of the Judicial Service Commission, Manjula Tillekaratne.
In early November, the ICJ issued a report, Sri Lanka’s Crisis of Impunity, documenting how the erosion of state accountability and judicial independence, has led to a crisis of impunity in Sri Lanka.
The ICJ calls on the Government of Sri Lanka to take active measures to promote the independence of the judiciary and rule of law by adhering to international standards and practice in impeachment hearings.
Contact:
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Asia-Pacific Regional Director, (Bangkok), t:+66(0) 807819002; email: sam.zarifi@icj.org
Sheila Varadan, ICJ Legal Advisor, South Asia Programme (Bangkok), t: +66 857200723; email: sheila.varadan@icj.org

Nov 23, 2012 | News
 The ICJ expressed its grave concerns regarding the new Constitutional Declaration issued by President Mohamed Morsi on 22 November.
The ICJ expressed its grave concerns regarding the new Constitutional Declaration issued by President Mohamed Morsi on 22 November.
The President’s unilateral imposition of a constitutional framework on the Egyptian people, under which Constitutional Declarations, decisions, laws and acts taken by the President are shielded from any judicial review, undermines basic rule of law principles.
“Rather than establishing the rule of law and meeting the democratic aspirations of the Egyptian people, President Morsi perpetuates the practices of the old regime by denying the rights of Egyptians to fully participate in the conduct of public affairs and to challenge executive decisions and actions”, said Said Benarbia, ICJ Senior Legal Advisor for the MENA Programme. “The Egyptian authorities must change course to ensure that the new Constitution is in line with international rule of law and human rights principles, and that the drafting and adoption process is transparent and inclusive.”
Under the Declaration, the President has arrogated to himself sweeping powers “to protect the goals of the revolution, including by tearing down the structure of the former regime, excluding its symbols in the state, society and the judiciary, and purging the Sate institutions”. All decisions taken by the President, since he took office and until a new Constitution is adopted and a People’s Assembly is elected, are characterized as “final and binding and cannot be appealed by any way or to any entity. Nor shall they be suspended or cancelled and all lawsuits related to them and brought before any judicial body against these decisions are annulled”.
The ICJ also expresses its concern about the impact of the new Constitutional Declaration and the decision of President Morsi to dismiss the Prosecutor General on the independence of the judiciary.
Under international standards, all disciplinary, suspension or removal proceedings against members of the judiciary must be determined in accordance with well-established procedures that guarantee the right to a fair and transparent hearing and to an independent review.
Only an independent body can ensure the fairness of these proceedings, the ICJ stresses.
In a report published last week, the ICJ described how the Egyptian authorities have failed to ensure the drafting of a new Constitution in compliance with international principles of inclusive participation and transparency. The report concludes that the draft Constitution conflicts with Egypt’s obligations under international human rights law.
Contact:
Saïd Benarbia, Middle East & North Africa Senior Legal Adviser, ICJ, t +41 22 979 3817; e-mail: said.benarbia(at)icj.org
Alice Goodenough, Middle East & North Africa Legal Adviser, ICJ, t +41 22 979 3811; e-mail: alice.goodenough(at)icj.org

 Members of Sri Lanka’s Parliament should reject the impeachment motion to remove Chief Justice Shirani Bandaranayake, that will be put before Parliament on 10-11 January 2013, the ICJ said today.
Members of Sri Lanka’s Parliament should reject the impeachment motion to remove Chief Justice Shirani Bandaranayake, that will be put before Parliament on 10-11 January 2013, the ICJ said today.









