Jun 29, 2015 | News
The ICJ calls on the UN Human Rights Council and the Security Council to respond to the findings of the Independent Commission of Inquiry on the 2014 Gaza Conflict, and fully implement all its recommendations.
This should be done with a view to ensuring accountability, including effective remedy and reparation, for all violations of international humanitarian law and human rights abuses committed by the Israeli Defence Forces (IDF) and by Palestinian armed groups, the ICJ says.
The ICJ further calls on the Human Rights Council to establish an independent mechanism to monitor the implementation of the Commission’s recommendations by both parties.
“Israeli and Palestinian authorities must break the chronic cycle of impunity in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. All credible evidence of war crimes, such as the Commission of Inquiry has highlighted, must be properly investigated,” said Said Benarbia, Director of the ICJ MENA Programme.
“No one who is responsible, whether military or civilian and regardless how high their office, can be allowed to escape justice,” he added.
The Report published last week, and discussed today at the Human Rights Council, documents serious violations of international law and human rights abuses committed during the conflict, such as indiscriminate attacks, including disproportionate attacks, and direct attacks against civilians and against civilian objects that are not justified under the International Humanitarian Law.
The Commission found that artillery and other explosive weapons had been used in densely populated areas, that entire neighborhoods in Gaza had been destroyed, and that unguided rockets had been used.
As indicated by the Commission, some of those acts may constitute war crimes.
To date, both Israeli and Palestinian authorities have failed to meet their obligations under international law to effectively investigate the violations and to prosecute anyone criminally responsible.
Investigations and criminal proceedings initiated by the IDF’s Military Advocate General (MAG), which is also involved in the planning and execution of the IDF’s military operations, fall short of international standards including in relation to independence and impartiality.
No criminal investigations into violations and abuses committed by Palestinian armed groups appear to have been initiated by the Gaza authorities.
The ICJ calls on both authorities to provide for effective, independent and impartial investigation mechanisms in line with international standards.
Absent such reforms, international justice mechanisms can and should fill accountability and remediation gaps where domestic authorities are unwilling or unable to effectively administer justice.
“Israeli and Palestinian authorities must reform the framework for their current investigations and prosecutions. They must also fully cooperate with international accountability mechanisms, including the preliminary examination initiated by the International Criminal Court,” Benarbia said. “The aim throughout must be to make known the truth about the violations, to identify and hold those responsible to account, to ensure victims’ rights, and to prevent any recurrence.”
Contact:
Theo Boutruche, Legal Adviser of the ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, tel: +33 670735747, e-mail: theo.boutruche(a)icj.org
POT-UN Report Gaza -News-Press release-2015-ARA
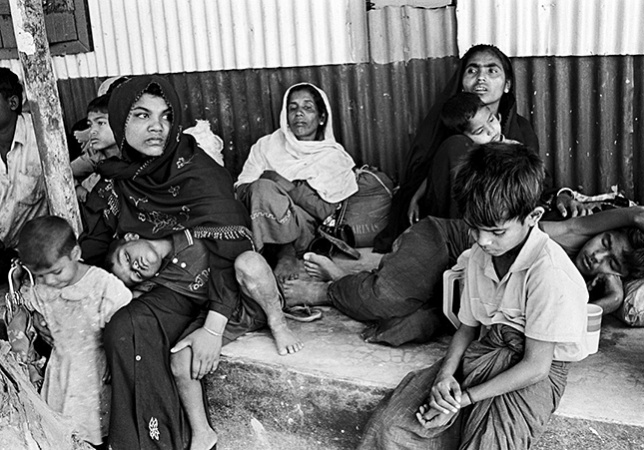

May 27, 2015 | News
Representatives of 17 countries gathering in Bangkok on 29 May to discuss the humanitarian crisis involving thousands of Rohingya and Bangladeshis adrift in the Andaman Sea must adopt a regional response that complies with international human rights law and standards, said the ICJ today.
“The countries in ASEAN should work with each other and the international community to immediately save the lives of thousands of Rohingya and Bangladeshi people now trapped on ‘floating coffins’, and to address the human rights disaster in Rakhine state that helped create and foster this crisis,” said Sam Zarifi, ICJ’s Asia director.
“It’s essential that the participants of this meeting use this opportunity to establish a response that complies with international law and standards on human rights, the treatment of refugees and migrants, and people in distress on the sea,” he added.
The government of Thailand called the “Special Meeting on Irregular Migration in the Indian Ocean” to provide a forum for countries affected by this crisis.
The main countries involved in this crisis, Myanmar, Bangladesh, Thailand, and Malaysia, have not signed on to the Refugee Convention or to the Convention relating to the Status of Stateless Persons.
“Now they have to scramble to come up with a sensible and humane response,” Zarifi said.
“ASEAN countries have hidden behind the notion of ‘noninterference’ to turn a blind eye to the persecution of Rohingya in Myanmar, to the growth of criminal smuggling and human trafficking networks, and the increasing demand for undocumented laborers,” he added.
“But this crisis shows that problems in one country can and will quickly spread to the others unless ASEAN can provide a rights-compliant regional response.”
The ICJ calls on all ASEAN Member States and Bangladesh to become parties to key international treaties, such as the 1951 Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees and its 1967 Protocol, the Convention relating to the Status of Stateless Persons, and the 1979 International Convention on Maritime Search and Rescue (SAR).
The SAR encourages parties to enter into search and rescue agreements with neighboring states to ensure that assistance be provided to any person in distress at sea regardless of the nationality or status of such a person or the circumstances in which that person is found, and provide for their initial medical or other needs, and deliver them to a place of safety.
A draft ASEAN Convention Against Trafficking in Persons Especially Women and Children (ACTIP) and a corresponding Regional Plan of Action (RPA) for the Convention’s operationalization have yet to be endorsed by ASEAN leaders, and no copies of the drafts have been released to the public.
The ICJ calls on ASEAN to make this draft Convention and RPA public and hold consultations with civil society organizations, especially those that work with trafficked persons on which governments so frequently rely as service providers.
The ICJ also points out that certain ASEAN Member States have critical roles to play as integral components to the regional efforts addressing the current crisis.
It is clear that discriminatory policies and actions in Myanmar have significantly contributed to this regional humanitarian crisis, the ICJ says.
The ICJ adds that the Rohingya are forced to flee their homes because of ethnic conflict and the policies of the Myanmar government.
“The government has persecuted the Rohingya, refused to extend basic citizenship rights to them and in fact has recently passed legislation to entrench discrimination against the Rohingya such as the Protection of Race and Religion laws,” said Zarifi.
“These are some of the so-called ‘root causes’ that have displaced thousands within Rakhine State and driven the Rohingya to the sea and to the territory of neighboring countries. It is no longer possible to cite ‘sovereignty’ as an excuse for silencing regional discussions about these serious human rights concerns,” he added.
The ICJ has called on Myanmar to scrap laws that discriminate against minorities and to actively prosecute acts of violence fuelled by discrimination as well as crimes of hate speech.
The ICJ has also urged Myanmar to undertake every effort to improve basic living conditions for the Rohingya and Arrakhanese population in Rakhine State by enhancing respect for and protection of their economic, social, and cultural rights.
The ICJ also called on Thailand to assume its natural role as a key stakeholder in resolving this crisis.
“Thailand’s full commitment to a coordinated regional human rights based response is crucial,” Zarifi further said. “Thailand’s convening of a regional meeting is a welcome step, but as the meeting’s name suggests, Thailand still views this problem as primarily one of migration and trafficking, instead of as a serious human rights crisis that demands a human rights-based regional response.”
Thailand has recently committed to provide humanitarian assistance to migrants and refugees on board the boats.
However, the ICJ emphasized that Thailand and other countries must go further and rescue individuals in distress at sea and allow those who arrive on their shores to expeditiously and safely disembark.
Rather than pushing them back, involuntarily returning them, detaining them or applying other punitive measures, they should be provided with adequate and humane reception conditions and necessary medical care in the country.
Thereafter, with the aid of experts, their further protection and assistance needs must be individually and accurately determined and then addressed, consistent with international standards.
“The Thai government’s response that a naval vessel will be used as a floating administrative center for people already adrift in the waves, and that not even those in need of medical assistance will be allowed onshore, is simply callous and in violation of Thailand’s international obligations,” concluded Zarifi.
Additional information:
Eight ASEAN Member States will be attending the “Special Meeting on Irregular Migration in the Indian Ocean”: Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Vietnam, and Thailand. Singapore and Brunei Darussalam are not taking part in the meeting.
Also present will be representatives of Afghanistan, Australia, Bangladesh, India, Iran, New Zealand, Pakistan, Papua New Guinea, and Sri Lanka; the United States of America and Switzerland will participate as observers.
Three international organizations, namely the UN Refugee Agency (UNHCR), the UN Office of Drugs and Crimes, and the International Organization of Migration will also join the meeting.
Contact:
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Regional Director for Asia and the Pacific, t: +66807819002 ; e: sam.zarifi(a)icj.org

May 13, 2015 | News
The ICJ today condemned the decisions of the governments of Indonesia and Malaysia to turn away and push back boats carrying hundreds of Bangladeshis and Rohingyas, including women and children, out to sea.
The ICJ emphasized that the increase in the number of Rohingya arrivals in Indonesia and Malaysia underscores the need to address the root causes that drive these people to set off on these perilous journeys, including the longstanding human rights abuses to which Rohingyas are subjected.
The decision by the two governments to return the boats to sea came after the arrival of about 2,000 people, mostly believed to be Rohingya and Bangladeshi nationals, onto the shores of Malaysia and Indonesia earlier this week.
“This should be a wake-up call to ASEAN that human rights is not an internal affair of one Member State,” said Sam Zarifi, ICJ’s Regional Director for Asia and the Pacific.
“Had there been action on the part of ASEAN early on to protect the rights of Rohingyas in Myanmar, this looming humanitarian crisis would not have happened,” he added.
The large majority of Rohingyas have fled Myanmar because of the discrimination and deadly violence they face there as members of a religious minority.
Many of them had no choice but to resort to callous smugglers.
However, a recent crackdown on human trafficking in both Thailand and Malaysia has spooked smugglers who, in order to avoid arrest, have abandoned boatloads adrift at sea instead of taking them ashore.
It is reported that approximately 6000 Rohingyas and Bangladeshi are now on boats adrift in the Andaman Sea in poor and overcrowded conditions.
“The decisions of the Indonesian and Malaysian governments constitute an abject failure of their duty to increase search-and-rescue efforts at sea and to provide humanitarian relief to those in need. Moreover, pushing these people back out to sea is a life-endangering practice and in no way does it provide a safe and effective solution,” said Zarifi.
Under international law, the act of pushing those boats back to the high seas constitutes a collective expulsion and may constitute a violation of the principle of non-refoulement.
Such a practice is also likely to lead to violations of the right to seek and enjoy asylum from persecution, of the right not be subjected to torture and other ill-treatment, and of the right to life.
On 29 May 2015, senior officials and representatives from at least 6 ASEAN member states will be in Thailand to have a “Special Meeting on Irregular Migration in the Indian Ocean”.
“ASEAN member states must ensure that any regional decision taken on this issue will be one that adequately and meaningfully protects the lives of people who embark on those desperate journeys across the Indian Ocean,” added Zarifi.
The ICJ urges ASEAN member states to stop the practice of returning boatloads of asylum-seekers and migrants to the sea and to immediately adopt effective regional measures in line with international human rights standards.
The ICJ also urges ASEAN to strengthen its regional human rights mechanism so that it would be able to effectively address violations of human rights in the region.
Contact:
Emerlynne Gil, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, in Bangkok, email: emerlynne.gil(a)icj.org or mobile: +66 84 092 3575
Picture: EPA/Zikri Maulana

Apr 30, 2015 | News
The ICJ welcomes yesterday’s adoption, by the UN Working Group on Arbitrary Detention, of the Working Group’s “Basic Principles and Guidelines on Remedies and Procedures on the Right of Anyone Deprived of His or Her Liberty by Arrest or Detention to Bring Proceedings Before Court”.
Under its resolution 20/16 (2012), the UN Human Rights Council requested the Working Group to prepare draft basic principles and guidelines on habeas corpus. The Working Group set out a first draft set of principles and guidelines ahead of its global consultation on the subject in September 2014. From 2 to 5 February 2015, the Working Group met to continue its elaboration of the Basic Principles and Guidelines, resulting in the adoption of a second draft. The Working Group adopted its final iteration of the document at the conclusion of its session on 29 April 2015. The Basic Principles and Guidelines will be presented to the Human Rights Council during the Council’s 30th regular session, to be held from 14 September to 2 October 2015.
The ICJ welcomes the Basic Principles and Guidelines as a means of assisting States to enhance, in law and in practice, respect for the right to habeas corpus. It especially welcomes certain aspects of the document, including:
- Paragraph 68, in which applicable qualifications are set out to any derogating measures to accommodate constraints on the application of some procedural elements of the right to habeas corpus;
- Principle 6 and Guideline 4 which reaffirm that habeas corpus petitions must be heard by courts that bear all characteristics of competence, independence and impartiality (paras 27, 70 and 72(a)), that competence includes the power to order immediate release if detention is fund to be arbitrary or unlawful (para 27), that immediate implementation of such orders is required (para 71(c)) and that courts must give reasoned and particularized decisions (para 71(d));
- Guideline 7, in which it is provided that individuals are entitled to take proceedings multiple times (paras 81 and 82), that expediency is required, including in cases of subsequent challenges, and especially in cases alleging, among other things, torture or ill-treatment (para 83) and that authorities remain obliged to ensure regular review of the continuing need for detention (para 84);
- Principle 9 and Guideline 8 concerning legal representation and legal aid;
- The clarifications in Principle 10 and Guideline that persons able to bring proceedings include counsel, family members or other interested parties, whether or not they have proof of the consent of the detainee (paras 34 and 92) and that no restrictions may be imposed on a detainee’s ability to contact such persons (para 35);
- The express recognition in Guideline 12 that information obtained by torture or other forms of ill-treatment may not be used in evidence;
- Guideline 13 concerning disclosure and limitations applicable to any non-disclosure of information on security or other grounds;
- Guideline 14, reflecting authorities’ obligation to justify the need and proportionality of detention;
- Principle 15 and Guideline 16 (on remedies), reflecting the overarching right to remedies and reparation (paras 43), the need for authorities to give immediate effect to an order for release (para 44) and the right to compensation, restitution, rehabilitation, satisfaction and guarantees of non-repetition (paras 109-112); and
- Principle 16 concerning the application of Article 9(4) of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) alongside international humanitarian law (paras 45 and 47), the application of Article 9(4) to civilians in an international armed conflict (para 47), the application of habeas principles to prisoners of war (para 48), and the question of administrative detention or internment in the context of a non-international armed conflict (para 49).
The ICJ has engaged in all stages of the Working Group’s elaboration and consultations. It made written submissions in November 2013, April 2014 and March 2015. Its staff, Matt Pollard and Alex Conte, gave panel presentations at the September 2014 global consultation.









