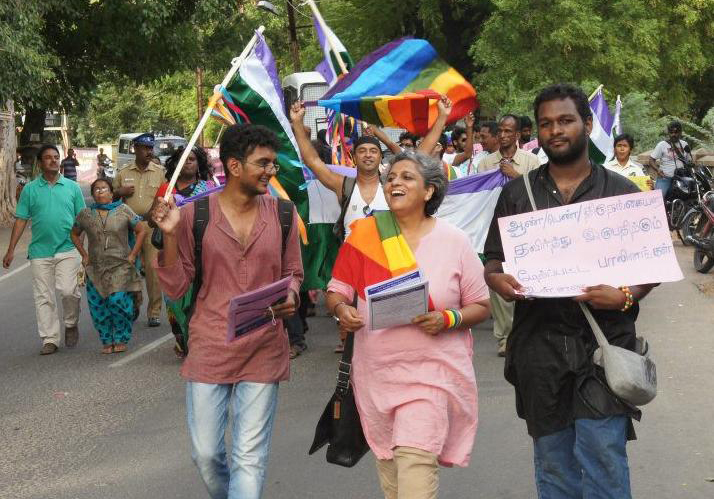Jul 15, 2020 | Advocacy, Multimedia items, News, Video clips
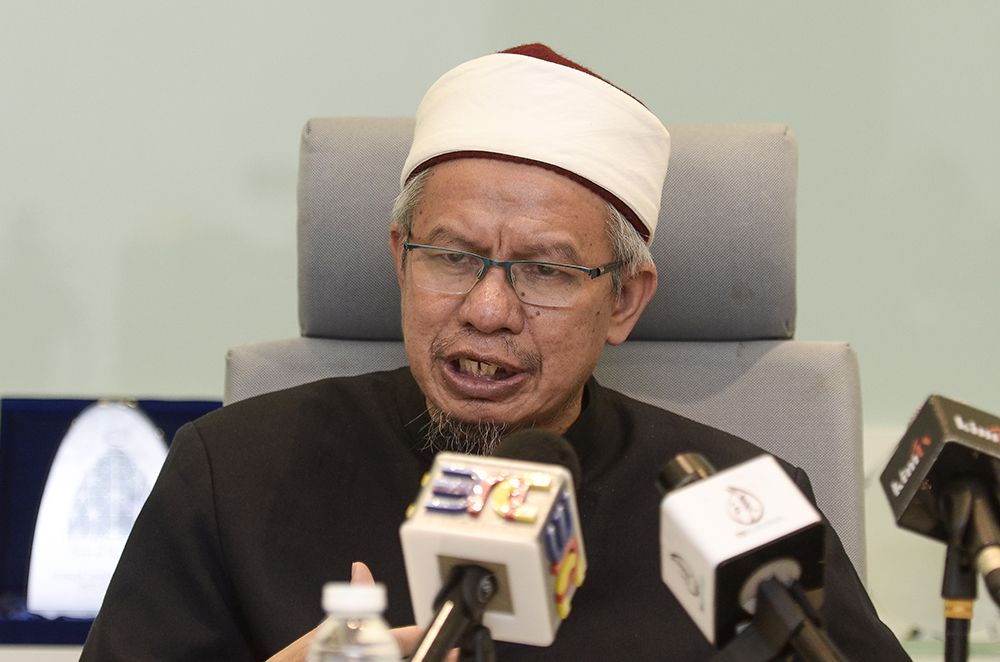
The ICJ today condemned the order issued by Zulkifli Mohamad Al-Bakri, Malaysia’s Minister in charge of religious affairs, to the Federal Territories Islamic Religious Department (Jawi) to take action against the transgender community.
The ICJ called on the Minister to rescind the order immediately and take steps to ensure non-discrimination and equal protection of all persons in Malaysia, including LGBTI persons.
On 10 July 2020, Zulkifli Mohamad Al-Bakri announced in a social media post that he had given the Jawi authorities “full licence to carry out its enforcement actions” against transgender persons in Malaysia. He elaborated that his order would beyond arresting transgender persons but would also extend to providing them “religious education” so that they would “return to the right path”.
“This unacceptable transphobic and homophobic attack from a government official highlights the societal prejudices and the lack of legal protections against discrimination faced by transgender persons in Malaysia,” said Ambiga Sreenavasan, a prominent Malaysian lawyer and Commissioner of the ICJ.
“Instead of ensuring that the human rights and dignity of all persons are respected and protected, the Minister, through his statement, is going in the complete opposite direction by advocating state action against persons belonging to sexual orientation and gender identity minorities,” added Ambiga Sreenavasan. “The Minister is legitimizing harassment, discrimination and violence against transgender people, and increasing violations of their human rights.”
Across the country in 13 states and the federal territories, a “male” who “poses” as a woman or wears the clothing of a “woman” may be subjected to criminal liability under state-level religious enactments. Consensual same-sex sexual relations are criminalized as “unnatural offences” in both secular civil law and religious state-level laws. These “offences” carry heavy penalties in the form of fines, imprisonment and corporal punishment in the form of caning, which constitutes impermissible cruel, inhuman or degrading punishment under international law and standards.
The ICJ stressed that these laws served to institutionalize systemic discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity and expression, while also creating barriers for LGBT people when seeking justice. They provide state authorities with expansive power to police gender identities, expressions and sexual orientations of people.
The ICJ notes that experiences of severe stigma, marginalization, and violence committed by families, communities, and State actors lead to immense health risks and mental health disparities of transgender individuals.
The ICJ is also deeply concerned about the Minister’s plan to require members of the transgender community to undergo religious conversion therapy. Numerous studies have shown how religious conversion therapy and related practices are causing real harm not only to transgender people, but also to lesbian, gay, and bisexual individuals.
The ICJ calls on the Government of Malaysia to abide by its obligations under international law and follow through with its commitment to human rights, by ensuring that transgender people and all persons are legally protected against discrimination, and that they are able to live free from prejudice, harassment, and violations of their human rights.
Contact
Emerlynne Gil, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, e: emerlynne.gil(a)icj.org
Background
In 2019, the Human Rights Commission of Malaysia (SUHAKAM) released a report on Transgender Persons in Kuala Lumpur and Selangor. Many of the transgender people interviewed for this report said that they constantly face arbitrary arrests, discrimination in obtaining employment, and even discrimination in obtaining housing because of their gender identity. A large majority of those interviewed experienced violence because of their gender identity.

Jun 8, 2019 | Multimedia items, News, Publications, Reports, Thematic reports, Video clips
The Indian Government must give effect to recent rulings of the Supreme Court and end discrimination and other human rights violations and abuses based on real or perceived sexual orientation, gender identity and expression, the ICJ said today at the Delhi launch of its new report on the conditions of LGBTQ people in India.
The ICJ’s 152-page report Living with Dignity: Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity-Based Human Rights Violations in Housing, Work, and Public Spaces in India details human rights violations suffered by LGBTQ persons in their family homes, workplaces, and public spaces including streets, public toilets, public transport and shopping centres.
Following on the Supreme Court’s decisions in NALSA and Navtej, which strongly affirmed the human rights of LGBTQ persons, the report identifies legal and policy challenges, as well as structural barriers that prevent them from enjoying the full range of human rights.
”Despite the promise of recent jurisprudence, the Indian government has not consistently met its constitutional and international obligations to guarantee the rights of LGBTQ persons,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia Director.
“The ICJ encourages the Indian State to build on existing efforts to protect these rights to ensure full compliance with the right to live with dignity in terms of the Indian Constitution and international human rights law,” he added.
The Living with Dignity report identifies a wide range of violations and abuses of rights in the context of housing, work and public spaces.
Human rights violations associated with housing included discrimination in accessing rental accommodation, harassment and violence by landlords and by families, and arbitrary evictions.
The report sets out instances of discrimination in the workplace, at all stages of employment, and throughout the formal and informal sectors.
It also documents obstacles faced by LGBTQ persons seeking access to public spaces, including discriminatory policing, gendered toilets and transport, harassment and abuse by State officials, and discriminatory targeting through the application of public nuisance, sex work and anti-beggary laws.
The report offers a set of recommendations meant to make existing law and policy more protective of LGBTQ persons’ rights and calls for the amendment or repeal of certain existing laws.
“There is no single law or policy solution to ending long-standing and systemic discrimination. But legal and policy reforms are essential to addressing the abuses suffered by LGBTQ persons and these must include the effective, inclusive and meaningful participation of a diverse range of LGBTQ individuals and advocacy groups,” Rawski said.
The report also recommends the convening of a nationwide consultation geared towards the enactment of a comprehensive anti-discrimination law prohibiting discrimination on the grounds of sexual orientation and gender identity as is required by international human rights law.
In a preface to the report, ICJ Commissioner and former Chief Justice of the Delhi High Court, Justice Ajit Prakash Shah, indicates his hope that the report will “be used as a tool by lawyers, human rights defenders and policymakers” and “contribute to enhancing public discourse on LGBTQ rights, as well as broader issues of discrimination and the rule of law in India”.
Download
Report: Living with Dignity: Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity-Based Human Rights Violations in Housing, Work, and Public Spaces in India (English)
Executive Summary (English)
Infographics
SOGIE-based Human Rights violations in Housing
SOGIE-based Human Rights violations at Work
Barriers experiences by LGBTQ people in accessing Public Spaces
Contact
Maitreyi Gupta (Delhi), ICJ International Legal Adviser for India, e: maitreyi.gupta(a)icj.org, t: +91 7756028369
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia Pacific Region Director, e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org, t: +66 644781121
Read also
Briefing Paper on Navtej Singh Johar et al. v. Union of India and Others, July 2018.
Unnatural Offences”: Obstacles to Justice in India Based on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity, February 2017.
ICJ Briefing Paper on Implementation of NALSA Judgment, 2016.
Watch the video
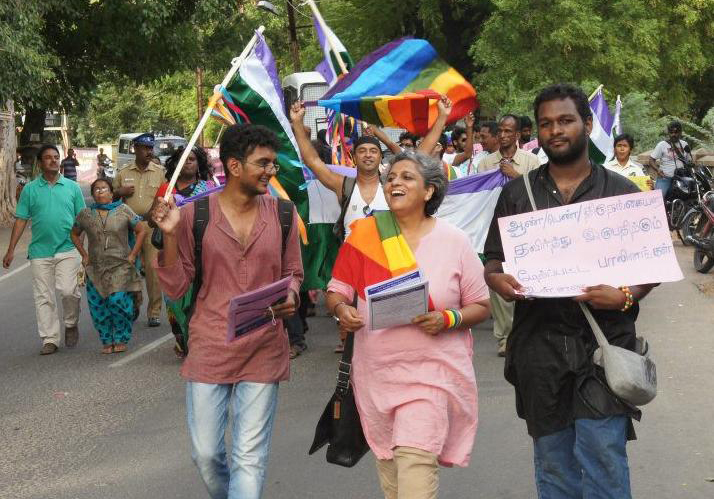
Nov 20, 2018 | News
On the Transgender Day of Remembrance, the ICJ calls on all South Asian States to fulfill their international obligations to respect, protect and ensure the right to life of all transgender persons, including by investigating alleged violations of their right to life promptly, thoroughly and effectively.
While there has been some progress in protecting the human rights of transgender individuals through legislation and judicial decisions, in South Asia rampant violence from both state and non-state actors continues to place their lives at risk.
Most governments do not collect data on violence against transgender persons.
Trans Murder Monitoring, which records cases of murder of transgender persons based on accounts from individuals and civil society organizations, reports 2609 unnatural deaths of trans and gender-diverse persons across 71 countries between January 2008 and September 2018.
In South Asia, between 2008 and 2016, 58 transgender persons were reported murdered in India, 37 in Pakistan, 2 in Nepal, and 2 in Bangladesh.
“It is laudable that Pakistan, India and Nepal have taken measures to end discrimination against transgender persons, and have recognized their right to self-identify,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia-Pacific Director.
“However, violence, harassment, extortion, rape and murder of transgender persons continue to be committed. Police frequently refuse to file complaints, and are often themselves complicit in violence against transgender persons,” he added.
The judiciary has played an important role in protecting transgender rights in India, Nepal and Pakistan.
The Supreme Courts in all three countries have issued decisions recognizing transgender persons’ rights, including the right to self-identity one’s gender.
These decisions have acknowledged that transgender persons are particularly targeted with violence by state and non-state actors, and that police have largely failed to protect them from violence.
In some cases, the courts have ordered that new remedies be created under the law, and sought the enforcement of existing laws protecting transgender rights.
However, many of these decisions remain unimplemented, and violence against transgender people remains rampant in South Asia.
“The ICJ calls on all governments in the region to ensure that laws, policies and practices affecting transgender persons comply with international human rights law and standards,” Rawski said.
“All human rights abuses against transgender persons must be investigated, and the perpetrators brought to justice, including law enforcement officials who harass or abuse persons based on their gender identity,” he added.
Contact
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia Pacific Director, t: +66 644781121 ; e: Frederick.rawski(a)icj.org
Background
In India, in 2014, the Supreme Court in NALSA v. UOI recognized the right of transgender persons to self-identify their gender.
The Court has further acknowledged the existence of human rights violations against transgender persons at the hands of the police and private individuals and recommended that state and central government take steps to create public awareness about transgender persons’ rights.
Per a 2015 survey by the Kerala Government, “52% of the TGs [transgender people] are facing harassment from the police and “96% do not raise complaints against violence because of their gender identity”.
In Nepal, in 2007, the Supreme Court in Sunil Babu Pant v. Government of Nepal recognized the right of individuals to identify as male, female or “third gender”.
However, transgender persons continue to face arbitrary harassment and detention by security forces under laws like Public Offences Act, 1970, which allow for arrests without due process for up to 25 days.
This resulted in the Supreme Court of Nepal ordering law enforcement officials to desist from arresting persons based on their “personal interest or appearance,” though the decision remains largely unimplemented.
In Pakistan, in 2009, the Supreme Court directed the Government to recognize the human rights of transgender persons and subsequently, in 2018, the Parliament passed a law prohibiting discrimination against transgender persons.
The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2018 of Pakistan prohibits harassment of transgender persons, including sexual, physical, mental and psychological harassment, and creates new remedies for complainants in addition to those available under the criminal justice system.
The effectiveness of the law remains to be seen, as police are often complicit in violence against transgender persons, particularly in extorting money from transgender women sex workers.
Read also
ICJ Practitioners’ Guide No. 4: Sexual Orientation, Gender Identity and International Human Rights Law, which provides legal practitioners, activists and policy-makers with detailed and practical references on international standards on sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, and sexual characteristics.
ICJ Comparative Law Casebook: Sexual Orientation, Gender Identity, and Justice, which provides legal practitioners, activists and policy-makers with a compilation of legal cases on sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics.
ICJ India 2017 Report: “Unnatural Offences” Obstacles to Justice in India Based on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity, which provides a legal analysis of the discrimination and abuse faced by the LGBTI community in India based on over 100 interviews with LGBTI persons.

Sep 6, 2018 | News
The ICJ welcomed the Supreme Court’s judgment in Navtej Singh Johar et al v. Union of India and others, which effectively ends the threat to a large segment of the Indian population that they will be held criminally liable for exercising their human rights.
The Court has issued a long-overdue ruling that the criminalization of consensual same-sex relationships under Section 377 violates the Indian Constitution, and is in breach of India’s obligations under international law. This long-awaited judgment testifies to the work of activists and lawyers in India, who have shown the potential of the law to affirm human rights and equality.
“This judgment will not only have an impact in India. Its influence should extend across the world. The ICJ hopes that it will provide an impetus for other countries, especially those of the Commonwealth of Nations, to revoke similar provisions that criminalize consensual sexual relations,” ICJ Asia Pacific Director Frederick Rawski stated.
The Court underscored that provisions of Section 377 contravened international law and standards on equality, privacy, non-discrimination and dignity guaranteed in international human rights treaties to which India is a party. These include the International Covenant Civil and Political Rights and International Covenant on Economic Social and Cultural Rights.
The Court also noted that the Yogyakarta Principles, which address sexual orientation and gender identity in international law, reinforce these protections. This is a vital jurisprudential recognition that LGBTI persons are entitled to full equality, and protection of their rights under India’s Constitutional and international human rights law.
In the judgement, which reverses the December 2013 Koushal decision, the Court held that discrimination based on sexual orientation is a violation of fundamental rights to autonomy, privacy, equality, dignity, and non-discrimination. It underscored that decriminalization of homosexuality is only the first step and that LGBTI persons are entitled to equal citizenship in all its manifestations. The Court also recommended that wide publicity be given to judgment to ensure de-stigmatization of identity through sensitization training on barriers to access to justice faced by LGBTI persons.
“Even a landmark decision by the Indian Supreme Court cannot alone end the discrimination against people based on their sexual orientation or gender identity. It is time for the Indian Parliament to conduct wide-ranging review of existing legal framework, repeal discriminatory laws, and address other gaps in the law that prevent LGBT persons from fully exercising their rights,” Rawski added.
Background
For background, see the ICJ’s July 2018 Briefing Paper on Navtej Singh Johar et al. v. Union of India and Others, and its February 2017 report, “Unnatural Offences”: Obstacles to Justice in India Based on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity.
Contact
Maitreyi Gupta (Delhi), ICJ International Legal Advisor for India
e: maitreyi.gupta(a)icj.org, t: +91 7756028369