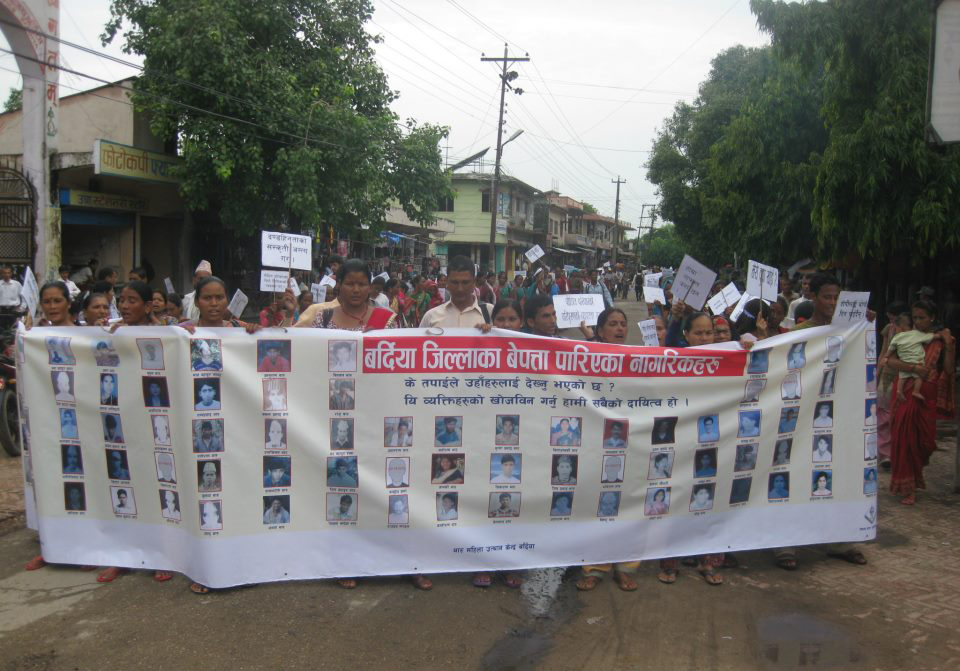

Jun 28, 2012 | News, Reports, Thematic reports
Nepal has avoided its obligation to provide justice for serious human rights violations over the past 20 years by relying on ineffective commissions of inquiry instead of using the criminal justice system, a new ICJ report says.
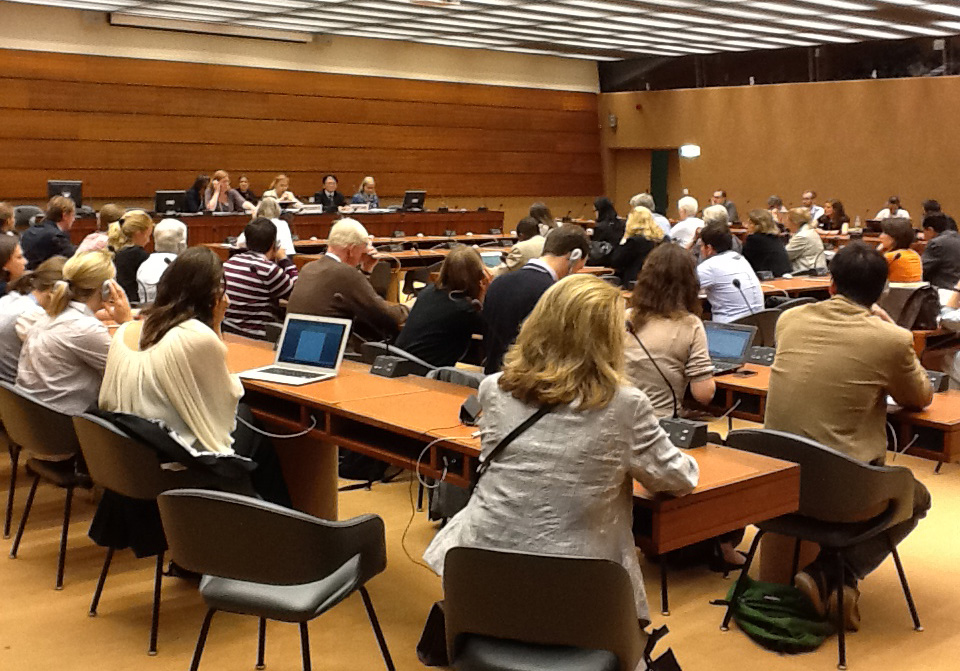

Mar 30, 2012 | Advocacy
During the 19th session of the Human Rights Council, the ICJ made an oral statement during the General Debate concerning situations that require the Council’s attention.
Welcoming the initiative of the United States of America to introduce a draft resolution on promoting reconciliation and accountability in Sri Lanka, the ICJ emphasised that this initiative should receive wide support by Council members as an important first step to ensure that action towards reconciliation is taken, not just words.
Sri Lanka-oral intervention-advocacy-2012 (full text, PDF)

Oct 11, 2011 | Advocacy, Analysis briefs
Since 2009, the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights has called for the strengthening and increased funding for the UN treaty bodies.
The UN treaty bodies are the monitoring mechanisms established under the universal treaties on international human rights.
To date, however, this strengthening process has inadequately addressed the need to strengthen, streamline and coordinate the Individual Communications procedures of the treaty bodies.
A coalition of NGOs has therefore issued a joint statement on the strengthening of these procedures, which represent a key aspect of the right of access by all to international justice in the context of human rights. The joint statement includes recommendations to States, the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, and the treaty bodies themselves.
statement strengthening treaty body-analysis brief-2011 (full text in English, PDF)
Jun 20, 2005 | News
On the eve of the adoption by the Colombian Congress of the so called Justice and Peace bill, the Colombian Commission of Jurists analyzes the articles contained in it.

Nov 22, 1994 | News
This report published today is the outcome of an ICJ mission to the Philippines, the Republic of Korea, the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea and to Japan in April 1993 to study the issue.
The report documents the circumstances in which “sexual services” were forcibly obtained from Korean and Filipino women by the Japanese army before and during World War II. It contains the poignant testimonies of former “comfort women” who have had the courage to reveal their ordeal to the world. It also examines the legal responsibility of the present Japanese government towards these women whose numbers range between 100,000 and 200,000 and what steps must be taken to rehabilitate them.
The report is written by Ms. Ustinia Dolgopol, Lecturer at the School of Law, The Flinders University of South Australia and Ms. Snehal Paranjape, an Advocate of the Bombay High Court, India. They interviewed over 40 victims, three former soldiers, government representatives, NGOs, lawyers, academics and journalists.
The ICJ report finds that the Japanese Imperial Army was responsible for the setting up of a vast network of “comfort stations” for the “enjoyment” of the Japanese Army, before and during World War II. Chinese, Dutch, Filipino, Indonesian, Korean, Malaysian, Taiwanese and other women and girls, often as young as 13, were thrown into these “comfort stations” and “sexual services” were extracted from them through unimaginable violence and cruelty. The Japanese military was fully responsible for the setting up, use, operation and control of the “comfort stations.” Detailed regulations – which are reproduced in the Report – were framed by it in this regard.
This report urges the Government of Japan to take immediate steps to provide full rehabilitation and restitution to the victims as it is clear that it bears a moral and legal obligation towards them. It also contains a list of recommendations as to how this should be done.
The report is available at the ICJ Secretariat in Geneva.









