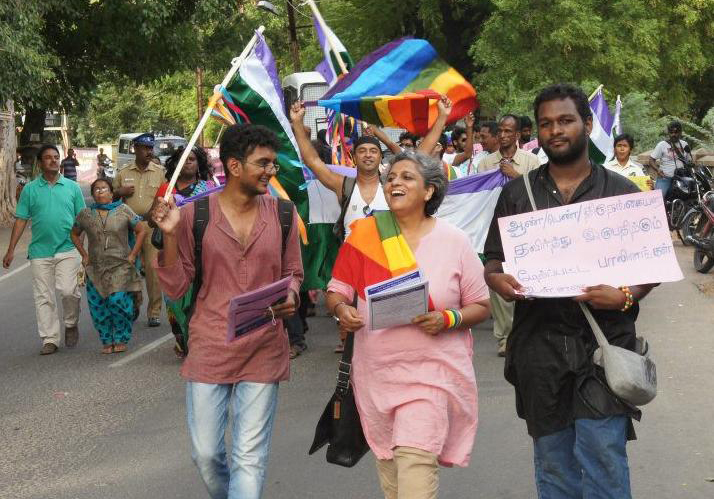May 24, 2018 | News, Publications, Reports, Thematic reports
The widespread occurrence of sexual and gender-based violence (SGBV) in Swaziland requires prompt action to enact the Sexual Offences and Domestic Violence Bill, says the ICJ in a report released today.
The ICJ’s report found that discriminatory practices based on customary laws and traditional beliefs undermine equality between men and women and contribute to an environment in which SGBV is at crisis point in the country.
“As the Senate of Swaziland deliberates over the Sexual Offences and Domestic Violence Bill, it must recall that enactment of the Bill is an essential step in complying with recommendations of the UN Human Rights Committee and CEDAW Committee and as a means of discharging the commitments made by His Majesty’s Government during the 2016 Universal Periodic Review,” said Arnold Tsunga, Director of the ICJ Africa Regional Programme.
In earlier submissions to the Senate of Swaziland, the ICJ noted that enactment of the Bill is a matter required of the Kingdom of Swaziland pursuant to its international human rights law obligations, including those arising from the Africa region, to criminalize and sanction the perpetrators of SGBV.
His Majesty’s Vision 2022, the aims and targets of the Deputy Prime Minister’s Office and Swaziland’s consensus in the adoption of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development reinforce compliance with those obligations.
The Sexual Offences and Domestic Violence Bill 2015, first drafted over ten years ago, has still not been passed into law, including because there is a perception that some of its provisions will infringe Swazi law and custom.
“Legislative and policy reform is needed as is the enhanced technical capacity and commitment of justice actors and policy makers to combat domestic and sexual violence,” Tsunga added.
Contact
Arnold Tsunga, Director, ICJ Africa Regional Programme, t: +27.73.131.8411; e: arnold.tsunga(a)icj.org
Alex Conte, ICJ Global Redress and Accountability Initiative, t: +41.79.957.2733; e: alex.conte(a)icj.org
Download
Swaziland-GRABaselineStudy-Publications-Reports-Thematic reports-2018-ENG (full report in PDF)

May 17, 2018 | Events, News
Today, the ICJ is co-sponsoring a conference in Copenhagen to mark the conclusion of the Danish Presidency of the Council of Europe, and take stock of its contribution to protection of human rights in the Council of Europe region.
The conference, Copenhagen, Elsinore and the Future of Europe: Assessing the Danish Chairmanship of the Council of Europe is organized by iCourts and the University of Copenhagen in collaboration with the Danish Chairmanship of the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe, the Danish Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the ICJ and the Danish Institute for Human Rights.
This conference will assess what has been achieved during the Danish Chairmanship – and what can still be achieved at the final high-level conference in Elsinore where the Ministers of Foreign Affairs of the 47 member states will meet and are scheduled to adopt a decision on the future of the Council of Europe. The conference will focus on the priorities of the Danish Chairmanship, including:
- Reform of the European Court of Human Rights and the Copenhagen Declaration
- Equal opportunities
- Involvement of children and young people in democracy
- Changing attitudes and prejudices about persons with disabilities
- Combating torture.
At the conference, the ICJ will present its analysis of the recent Copenhagen Declaration on the future of the European Convention on Human Rights system, and its recommendations for how its conclusions and recommendations should be taken forward.
The programme is available here: http://jura.ku.dk/icourts/calendar/copenhagen-elsinore-future-of-europe/
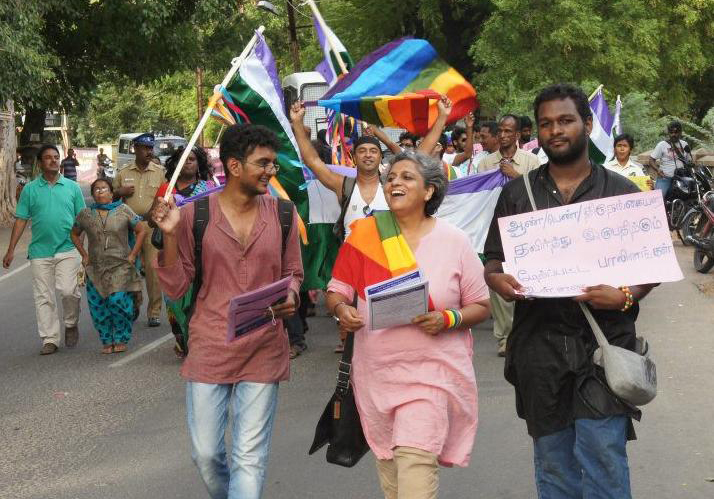
May 17, 2018 | Feature articles, News
South Asian States must repeal laws that discriminate against LGBTI persons, and must respect, protect and fulfill the full range of their human rights, the ICJ said today on International Day Against Homophobia and Transphobia (IDAHO-T).
These rights include the right to equality before the law and equal protection of the law for all without discrimination, to which LGBTI persons are entitled due to their inherent dignity as human beings.
Across South Asia, discriminatory laws have enabled socially constructed gender and sexual norms to foster and perpetuate intimidation, harassment, threats of violence and violence against lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) persons, due to animosity, hostility and hatred motivated in whole or in part by their actual or perceived sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and/or intersex status.
Under international law, including the International Bill of Rights, that is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the two Covenants – the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights – discrimination on the grounds of sexual orientation and/or gender identity is prohibited.
In this context, the Office of the UN High Commissioner of the Human Rights has underscored five core international human rights law obligations for States: (1) protecting individuals from homophobic and trans-phobic violence; (2) preventing torture and cruel, inhuman, and degrading treatment of LGBTI persons; (3) decriminalizing homosexuality; (4) prohibiting discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity; and (5) respecting the freedom of expression, association and peaceful assembly of LGBTI persons.
Under international human rights law, the principle of non-discrimination includes the right to determine one’s sexuality, sexual orientation, and gender identity and gender expression.
Contrary to their international human rights law obligations in this respect, States’ policing of gender and sexuality has created a pattern of stigma, harassment and violence.
For example, consensual same-sex sexual relations remain criminalized in seven out of eight countries in South Asia – Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka – based on colonial era laws, such as S. 377 of the Penal Codes of Pakistan, India, Maldives and Bangladesh, and similar legal provisions in Sri Lanka and Bhutan, that criminalize “carnal intercourse against the order of nature”.
While the enforcement of these laws rarely lead to actual criminal convictions and sentences of imprisonment, their mere continued existence creates an ominous and ongoing threat against and criminalizes entire sectors of the populations in these countries.
This, in turn, gives rise to a climate that encourages and is ripe for extortion, harassment and blackmail of LGBTI persons, by the police, as well as non-State actors, including the general public and even their own families.
While there have been some progressive developments, discrimination, violence and other human rights abuses against LGBTI people – both at the hands of State and non-State actors – remain rampant in South Asia.
Hence, on IDAHO-T, the ICJ renews its call on all South Asian Governments to repeal discriminatory laws against LGBTI persons, including laws that criminalize consensual same-sex sexual relations.
In addition, the organization urges all South Asian Governments to enable transgender persons’ right to self-identification of their gender, and to enact legislation that establishes prior, free, full, informed, genuine and consistent consent for any medically unnecessary interventions on intersex persons.
Contact
Maitreyi Gupta, ICJ International Legal Adviser in India, t: +91 7756028369; e: maitreyi.gupta@icj.org
Full text in ENG (PDF): India-IDAHO-T call-News-Feature article-2018-ENG

May 15, 2018 | News
The Africa Judges and Jurists Forum (AJJF) and the ICJ today called on the authorities in Lesotho to guarantee the independence of the judiciary and to immediately take all legal and administrative measures necessary to make the Court of Appeal function independently and impartially.
The call came as the AJJF and ICJ concluded a 5-day Fact Finding Mission to Lesotho (7-12 May 2018).
The mission emphasized the importance of the Lesotho authorities ensuring that the constitutional and legal framework on the selection, appointment and tenure of judges and the actual practices conform to the international obligations of Lesotho pursuant the international human rights treaties to which it is party, as well as other applicable international standards.
“During our mission we were troubled to discovered that the Court of Appeal has not sat in the past two of its scheduled sessions and with the current impasse we are concerned that it may not convene anytime soon,” said Retired Chief Justice Othman Chande of Tanzania who led the AJJF/ICJ mission.
“We also found that the Prime Minister had initiated a process that may result in the impeachment of the Chief Justice under controversial circumstances,” he added.
The AJJF and the ICJ have been concerned for a number of years about threats to judicial independence in Lesotho.
The ICJ carried out a fact finding mission in 2013 exposing and evaluating some of these concerns. The report of the mission contained specific recommendations.
The AJJF and the ICJ are concerned that most of the recommendations that were made to address structural issues to do with guaranteeing the independence of the judiciary at law and in practice have not been implemented or otherwise addressed.
The appointment of the Chief Justice and the President of Court of Appeal is made by the King on the singular advice of the Prime Minister.
Any impeachment of the Chief Justice and the President of the Court of Appeal is also initiated by the Prime Minister.
These arrangements do not comport with international standards and give rise to the perception that the appointment of judicial officials and any impeachment action against them will be politically motivated.
This has also lead to friction or strong perception of friction between the Executive and the Judiciary in a deeply polarized society.
The appointment process of the President of the Court of Appeal has been subject to prolonged political dispute and litigation that has resulted in a leadership vacuum at the appex court that has made it dysfunctional.
The result is that all litigants who expect justice from the Court of Appeal have years of waiting before they can get their matters resolved.
While the case challenging the appointment of an acting President of the Court of Appeal is presently set down for hearing at the High Court in the coming weeks, it is not clear that this adjucation will conclude the legal process and pave way for the appointment of the acting President of the Court of Appeal.
The appointment of ordinary judges of the High Court is done by the King on the advice of the Judicial Services Commission (JSC), which is chaired by the Chief Justice chairing a panel of only four people comprising the Chief Justice herself, Chairperson of the Public Service Commission, the Attorney General and one Judge.
All these officials are effectively appointed by the Prime Minister or closely work with the Chief Justice, resulting in an appointment process of judges of the High Court that lacks transparency and is perceived as open to cronyism.
“It is important that the legal profession and the judiciary speak strongly in defence of independence of the judiciary, but currently the legal profession is deeply divided, distrustful and polarized,” said Retired Chief Justice Sakala (Zambia).
“It is therefore important that a practice of regular bar-bench dialogue be initiated to reduce toxic relations that are being exploited to undermine judicial independence,” he added.
The broader reforms that were recommended by the SADC Commission of Inquiry to strengthen governance in Lesotho have not been wholly implemented.
The country needs broad reforms including in the judicial sector, but these reforms have been threatened or at least slowed down significantly by the instability in the successive coalition governments that make it impossible for the reforms to be carried out when the country is in a constant electoral mode.
The AJJF/ICJ mission hopes that the ongoing efforts to impeach the Chief Justice will fully respect her right to a fair hearing as stipulated in international obligations binding on Lesotho and that such efforts will strengthen rather than weaken the rule of law in an already fragile environment.
A report of the mission will be published and made publicly available.
Lesotho-End of Mission statement-News-2018-ENG (full story, in PDF)

May 12, 2018 | Agendas, Events
Today begins in Istanbul (Turkey) a two-day seminar for lawyers and CSO practitioners representing and working with migrants, refugees and asylum-seekers.
This event is organized by ICJ, in cooperation with its partners Refugee Rights Turkey, the European Council on Refugees and Exiles (ECRE), Mülteci-Der (MD) and ICJ-EI, as part of the EU co-financed project Fostering Access to Rights for Migrants, Refugees and Asylum-Seekers in Turkey.
40 lawyers and civil society practitioners – representing different bar associations and relevant organisations from the all over Turkey – are taking part in the seminar on 12 and 13 May.
The seminar aims to update lawyers and CSOs on the international law mechanisms in the United Nations and the Council of Europe, deputed to the protection of the rights of refugees, migrants and asylum-seekers . It aims at an effective implementation of the Turkish legal framework on asylum and migration.
The training will use as a basis the draft training materials prepared by the ICJ and its partners (to be published an the end of 2019) and, among other sources, the ICJ Practitioners Guide no. 6: Migration and International Human Rights Law.
The project “Fostering Access to Rights for Migrants, Refugees and Asylum-Seekers in Turkey” is funded by the European Instrument for Democracy and Human Rights (EIDHR) of the European Union.
Turkey-Seminar-Istanbul-MigrationAsylum-Agenda-2018-eng (download the agenda)