
Jan 20, 2016 | News
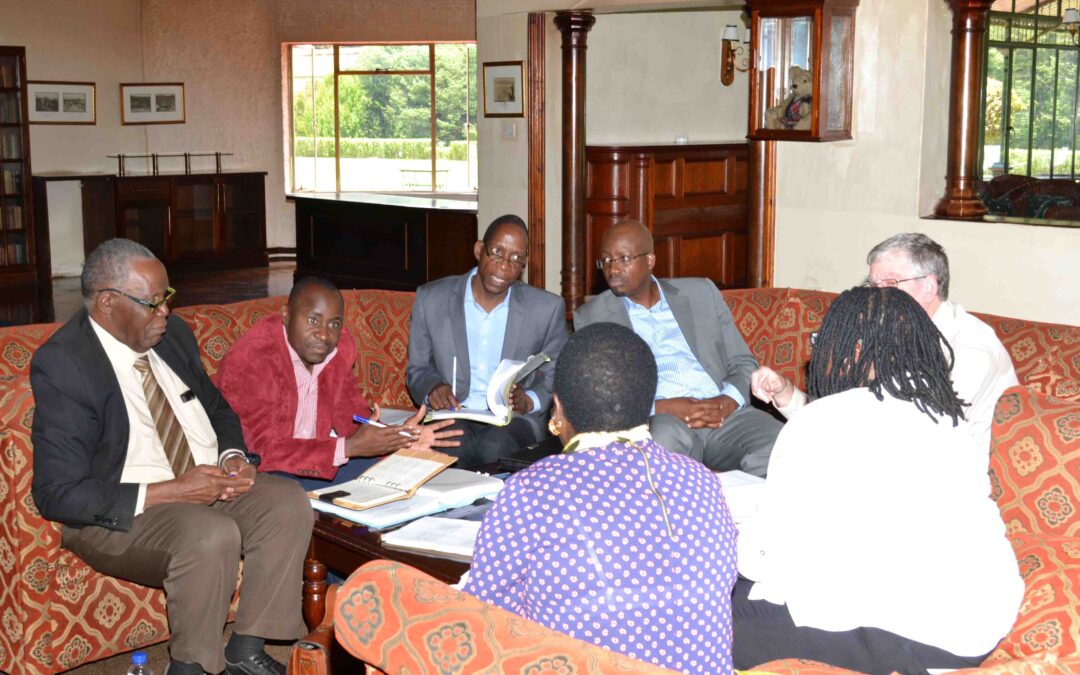
The ICJ supported the convening of a three-day meeting of the Faculty of Law of the University of Zimbabwe. The meeting reviewed the content of the courses offered at the University with the view of aligning the subject matter to the new constitution.
The Dean of Law Mr Magade noted in his introduction that “this Curriculum Review gives us a fabulous opportunity to take a long and hard look at ourselves and self introspect and come up with suggestions on how to improve our curriculum. At the end of the day we need to produce a product or graduate that is fit for purpose.”
The meeting took place at the Troutbeck Inn in Nyanga from 18 to 20 January 2016 and congregated 30 academic staff members from the University including a curriculum expert, Dr Nziramasanga, from the Faculty of Education. Dr Mosito and Dr Dingake from the Lesotho and Botswana respectively also contributed to the review process.
Jan 14, 2016 | News
As today marks the fifth anniversary of the toppling of Ben Ali’s regime, the ICJ calls on Tunisian authorities to adopt key legal and policy reforms to combat impunity and to deliver justice to victims of past human rights violations.
Under Ben Ali’s regime, thousands of human rights violations, including torture and other ill-treatment, unlawful killings, enforced disappearances, and arbitrary arrests and detentions, were committed by law enforcement and other security officers.
Numerous similar violations were also committed during the December 2010 to January 2011 uprising and some of them continue today.
“The political and institutional reforms introduced in Tunisia over the past 5 years should not be the sole yardstick to measure the success of the transition,” said Said Benarbia, Director of the ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme.
“Victims of human rights violations, in particular under Ben Ali’s rule, and during the uprising still await justice,” he added.
Despite several cases being brought before Tunisian courts, in particular military courts, these proceedings have yet to establish the truth about violations, ensure that all those who are responsible are held to account, and fulfill the rights of victims to effective remedies and reparation.
“Until their rights to effective remedies and reparation are realized, including by holding the perpetrators to account, the transition will remain incomplete,” Benarbia said.
Indeed, despite numerous legal and policy reforms, including the adoption of the “Transitional Justice Law”, and the establishment of the Truth and Dignity Commission (Instance Vérité et Dignité), the ICJ is concerned that justice for victims remains mostly elusive.
Obstacles that impede victims’ access to justice and effective remedies include current weaknesses in the Tunisian criminal procedures, such as the broad discretion of the public prosecutor to dismiss cases without providing specific reasons (and the lack of ability of victims effectively to challenge such decisions), the lack of effective measures for the protection of victims and witness, inadequate laws on the definition of crimes and superior responsibility, and the use of military courts to address human rights violations.
“Key reforms both in law and practice are needed for Tunisia to properly address past abuses in Tunisia, end pervasive impunity and provide victims with justice,” Benarbia said.
Contact:
Theo Boutruche, Legal Adviser of the ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, tel: +96 170 888 961, e-mail: theo.boutruche(a)icj.org
Tunisia-Anniversary-News Press Release-2016-ARA (Arabic version, in PDF)

Dec 22, 2015 | News
The ICJ today called on Egypt’s newly elected House of Representatives to amend or annul the web of repressive presidential decrees promulgated since the ouster of President Morsi.
“Egypt’s House of Representatives must dismantle the catalogue of repressive presidential decrees that have been used by the authorities to stifle dissent, curtail fundamental rights and freedoms and shield state officials from accountability in cases of human rights violations,” said Said Benarbia, Director of the ICJ’s Middle East and North Africa (MENA) Programme.
Article 156 of the Egyptian Constitution provides that decrees issued by the President while the House of Representatives is not in session must be discussed and approved by the new House of Representatives within 15 days of it convening.
Failure to do so results in the laws being automatically nullified with retroactive effect.
The ICJ and others have detailed how many of these presidential decrees, including the Demonstration Law (No.107 of 2013), the Counter-Terrorism Law (No.94 of 2015), the Terrorist Entity Law (No.8 of 2015), the Law on Military Courts (No.136 of 2014) and laws amending the Criminal Code (No.128 of 2014) and the Prison Law (No.106 of 2015), violate Egypt’s obligations under international law.
Key concerns relate to the right to life, the right to liberty and the right not to be subjected to arbitrary detention, fair trial rights, and the rights to freedom of expression, association and assembly.
These fundamental rights are protected by for instance the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, which Egypt ratified in 1982 and which today counts 168 states as parties.
Over the last two years, thousands of individuals have been prosecuted and convicted pursuant to such decrees, including the Demonstration Law, through proceedings that fell short of international fair trial standards.
Further, many of these decrees, in particular the Counter-Terrorism Law and the Demonstration Law, institutionalise the immunity of state officials from legal proceedings against any use of force committed in the course of their duties, including the use of lethal force when it is not strictly necessary to protect lives.
The decrees also fail to provide for any reparations mechanism for victims.
“Egypt’s parliament should, as a matter of urgency, ensure that those who have suffered human rights violations on the basis of these laws obtain effective remedy and reparations, remove all obstacles to justice and accountability, and address the impunity of state officials underpinned by these decrees”, Benarbia added.
Contact:
Alice Goodenough, Legal Adviser of the ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, t: +44 7815 570 834; e: alice.goodenough(a)icj.org
Nader Diab, Associate Legal Adviser of the ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, t: +41 229 793 804; e: nader.diab(a)icj.org
Egypt-New House of Representatives-News-Press releases-2015-ARA (full text in Arabic, PDF)

Dec 22, 2015 | News
The upcoming Supreme Court verdict in the case of Somchai Neelapaijit is an important test of Thailand’s treatment of cases of enforced disappearance, the ICJ said today.
The Supreme Court is expected to rule on whether the Court of Appeal was correct in overturning the conviction of one police officer for coercion and upholding the acquittals of four other police officers, and whether Somchai Neelapaijit’s family should be permitted to participate in the proceedings as plaintiffs.
The case concerns the 2005 trial of five police officers for coercion and gang-robbery after Somchai Neelapaijit, a leading Thai lawyer and human rights defender, was last seen on 12 March 2004 being pushed into a car by several men in Bangkok.
In March 2014, the ICJ published a report in Thai and English, which summarises the history of the case and provides a background to the upcoming decision, which will be delivered in Bangkok on 29 December 2015.
“This decision is an important milestone in the long and torturous history of this case,” said Sam Zarifi, the ICJ’s Regional Director for Asia and the Pacific.
“But whatever the result, Thailand must not waver from its repeated commitments to promptly and effectively investigate this enforced disappearance, to seek to identify those responsible and bring them to justice, and to provide the family with full remedies and reparation,” he added.
The police never charged the five police officers with more serious crimes – despite the statements of numerous officials, including past Prime Minister Thaksin Shinawatra, expressing certainty about his death – as Somchai Neelapaijit’s body or remains were never found.
The Department of Special Investigations (DSI), often described as the FBI of Thailand, is still conducting an investigation into his fate or whereabouts.
Angkhana Neelapaijit, Somchai Neelapaijit’s wife and now Commissioner of the Thai Human Rights Commission, told the ICJ: “Ensuring that all victims of enforced disappearance have their rights fully recognised by the Thai courts is equally important to me as seeking justice in my own case. My long battle through Thailand’s justice system has shown me Thailand’s laws are currently inadequate to deal with cases of enforced disappearance and that significant reforms are needed before the rights of victims are fully recognized.”
Contacts
Sam Zarifi, Regional Director, Asia-Paicific Programme, sam.zarifi(a)icj.org, +66 (0) 80 781 900
Kingsley Abbott, International Legal Adviser for Southeast Asia, Asia-Pacific Programme, kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org, +66 (0) 94 470 1345
Additional information:
On 11 December 2015, the ICJ published an English version of its Practitioners Guide “Enforced Disappearance and Extrajudicial Execution: Investigation and Sanction”, originally published in Spanish in March 2015.
Thailand-Somchai Verdict-News-Press releases-2015-ENG (full text, in PDF)

Dec 18, 2015 | Events, News
Today the ICJ held a round table “Organisation and operation of the Legal Profession: International Comparative Perspective” in Dushanbe, Tajikistan.
The ICJ invited experts to speak about comparative experiences from their countries to inform the national debate about the reform of the legal profession currently underway in Tajikistan.
Experts contributing to the discussion included: Tamara Morschakova, an ICJ Commissioner and former Justice of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation; Olga Swartz, a legal scholar from the Russian Federation; Daniyar Kanafin, a lawyer from Kazakhstan; Gulniza Kozhomova, President of the Bar Association of the Kyrgyz Republic; Almaz Osmanova, Member of the Board of the Bishkek Bar Association (Kyrgyz Republic); Jeroen Brower, Chair of the Ethics Commission of the Dutch Bar Association; and lawyers and other stakeholders from Tajikistan.
Participants discussed the principles and practice of the independence and self-governance of bar associations, as well as other issues of significance for the independence of lawyers, including the qualification process and disciplinary action.
Programme of the event in English and in Russian:
Tajikistan_roundtable_ agenda_Eng (PDF, English)
Tajikistan_roundtable_ agenda_Rus (PDF, Russian)









