Jun 23, 2017 | News, Op-eds
An opinion editorial by Belisário dos Santos Júnior, a Brazilian lawyer who is a member of ICJ’s Executive Committee.
When assessing the Brazilian political situation, it is important to always mention the date, since the situation changes almost every minute, following the rhythm of denunciations and accusations.
Over the past three years, the main preoccupation of most people living in Latin America has been the level of violence in their countries.
In Brazil, however, although political and criminal violence is high, corruption has been the primary concern of the population, before health and with violence coming in only third position of the population’s concerns (source: Latino barômetro).
The yearly global corruption perception index of Transparency International put Brazil in the 79th position, of 176 countries rated (where 1st position is given to the country with the lowest perception of corruption and 176th given to the country with the highest perception of corruption) with a grade of 40 (0 is for the most corrupted countries and 100 for the cleanest ones).
Brazil was sharing its position with countries such as China, India and Belarus. Its grade was 3 points below the world average.
The report mentioned a clear relationship between corruption and inequalities, creating a vicious circle between corruption, unequal distribution of power and unequal distribution of wealth. How can we correct this?
Brazil is currently reacting to the problem with new laws, new police investigations and legal proceedings, which are important.
But these measures alone will not be enough to change a culture of bypassing laws into a culture of integrity and respect of honesty.
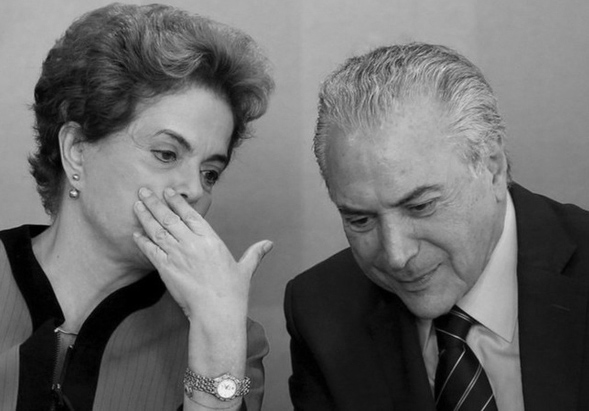
The last elected government, elected in 2014, with Dilma Rousseff as President and Michel Temer as Vice-President (photo), should have lasted until 2018 but fell in 2016 with the impeachment of Dilma Rousseff led by the President of the Federal Supreme Court and decided by the National Congress after two ballots.
Rousseff was accused of having manipulated the federal budget to hide the country’s real economic situation. Michel Temer assumed office as President following Rousseff’s impeachment.
Lula da Silva, the former President (2003-2010), ended his term in the middle of a legal storm when the Federal Supreme Court issued its judgment on the Criminal Lawsuit 470 (corruption of parliamentarians to maintain the influence of the Government in the Congress) and sentenced to prison ministers, businessmen, leaders of Lula’s Workers’ Party and other party leaders.
With the progressive use of the system of delação premiada (which is where a defendant is granted a reduced sentence or other beneficial measure for providing evidence against other persons), a measure included in the new Brazilian law to combat criminal organizations, and a series of police operations (the most famous of which is the operation Lava Jato, or ‘Car Wash’ in English), even more politicians and businessmen have been arrested and/or tried for corruption or money laundering.
More than one third of the National Congress’s members have been targeted by police operations for being implicated in controversial acts, either as agents or beneficiaries.
The current President, Michel Temer, and some of his ministers are under investigation by the Federal Police and on the verge of being denounced by the Federal Prosecutor’s Office for passive corruption.
The last two delação premiada, those of the CEOs of two Brazilian transnational corporations (Odebrecht and JBS), have overturned the political order, and so did the information that more than 2000 politicians received money from slush funds to finance their election campaigns.
Two governors and various parliamentarians are already in jail, including the former President of the Chamber of Deputies, Eduardo Cunha.
Lula da Silva himself is already facing various legal proceedings for corruption.
The winning ticket of the 2014 presidential election was recently judged in a case concerning potential abuse of economic power during their campaign.
Following a very close vote (4 against 3), the Superior Electoral Court rejected claims that illegal money was used in the Rousseff-Temer campaign.
If convicted, Michel Temer would have been forced out of the presidency.
The claim of economic power abuse was rejected only on a procedural matter: the evidence gathered – recordings, pictures, content of delação premiada – was considered inadmissible.
Aécio Neves, the opposition leader who competed against the Rousseff-Temer ticket in 2014, is in no better situation: a few weeks ago, a judicial decision deprived him of his mandate in the Federal Senate.
His sister and his cousin are already in jail and he himself is at risk of being sent to prison if the Federal Supreme Court requests this from the National Congress.
The Brazilian institutions are under investigation, but they are still functioning. Even members of the judiciary and the prosecutor’s office are being investigated.
There is still a decent level of trust in the work the current economic team is doing.
The National Congress gave its approval for the Constitutional Amendment on the Expenditure Ceiling, which will impose a series of conditions to public spending over the next few years. This somehow increases the credibility of the country’s economy.
On the agenda of the Congress, but affected by the series of denunciations for corruption that have hit parliamentarians, are the social security and labour reform bills considered essential for the future of the country by all the economic experts.
But it must also be noted that in the name of the fight against corruption, the Police and Federal Prosecutor’s Office have committed some abuses, to the point that a judge of the Supreme Court said Brazil was on the way to turning into a police state.
Corruption has reached such a level of intensity in the Brazilian political world that people are left in a severe and dangerous state of disappointment and despair. Already the current President is reaching a mere 1% approval rating…
Only elections would improve such a situation. The next presidential election is scheduled in 2018. But who will be eligible to run for it? The law prevents anyone who has a police record from applying.
However, society is reacting, taking various initiatives that value integrity measures, compliance actions, measures linked to education, in addition to the holding of intense debates demanding respect for democracy and human rights and calling for political reform.
Some people want direct elections now but this is contrary to the Constitution. However, 2018 is a long way to go and in the meantime there will be many public demonstrations.
But one thing is sure: Brazil is greater than the crisis it is facing now. This country has survived worse situations, including two long periods of dictatorship. Brazil will battle against this new agony. Respect for democracy, the Constitution and rule of law will prevail at the end.
A versão portuguesa pode ser descarregada abaixo:
Brazil-Corruption crisis-News-Op-ed-2017-POR (em PDF)
Apr 7, 2015 | News
Venezuela is intimidating and harassing human rights defenders, and making unsubstantiated allegations that they are seeking to undermine Venezuelan democracy, 28 international and Latin American human rights organizations, including the ICJ, said today.
The authorities’ allegations concern the groups’ legitimate functions of documenting abuses and representing victims before international human rights bodies.
Venezuelan authorities should cease this tactic immediately, the groups said.
Governments participating in the Summit of the Americas in Panama on April 10-11, 2015, should press the administration of Nicolás Maduro to ensure that human rights defenders can do their job without fear of reprisals, the organizations said.
The government harassment is clearly intended to discredit and intimidate groups that document human rights violations, the groups said.
On February 12, Diosdado Cabello, president of the National Assembly and member of the governing party, stated on the website of his weekly TV show, Con el Mazo Dando, aired on the state-run Venezolana de Televisión, that “NGO representatives from the Venezuelan extreme right” would participate in hearings before the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights (IACHR) in March.
Cabello had previously criticized Venezuelan human rights defenders who participated in the country’s review by the UN Committee Against Torture in Geneva, or traveled abroad to conduct advocacy meetings.
On March 18, during his show, Cabello read a list of names of individuals and organizations who had traveled to Washington, DC, to participate in the IACHR hearings.
The list included leading human rights groups such as Provea, Espacio Público (Public Space), Observatorio Venezolano de Prisiones (Venezuelan Observatory of Prisons), Transparencia Venezuela (Transparency Venezuela), Cofavic, Codevida, and Observatorio Venezolano de Conflictividad Social (Venezuelan Observatory of Social Conflicts).
Cabello accused them of receiving instructions from the US Embassy in Caracas before traveling to the hearings.
Cabello contends that the information presented on the show had been provided by anonymous “patriotic informants” (patriotas cooperantes).
Twelve human rights defenders who arrived in Caracas on various flights between March 20 and 22 have said that they were followed by unidentified men from when they landed until they left the airport, were filmed or photographed, and/or that officials irregularly searched their bags.
On March 23, María Alejandra Díaz, a lawyer who represented the government at the IACHR hearings, said on Venezolana de Televisión that “The issue of human rights is just a façade” and that nongovernmental groups that participated in the hearings “say they are Venezuelan” but “play the imperialist game” and “lie in front of the IACHR to make Venezuela look like the devil.”
An article published on April 3 in the official newspaper Correo del Orinoco accused two well-respected human rights defenders of being part of the US Central Intelligence Agency’s “Venezuelan delegation” at the Summit of the Americas.
Their objective is to “legitimize destabilization actions” in Venezuela, the article says.
Under international law, governments must ensure that human rights defenders are allowed to pursue their legitimiate activities without reprisals, threats, intimidation, harassment, discrimination, or unnecessary legal obstacles.
The Inter-American Court of Human Rights held in 2003 that “[r]espect for human rights in a democratic state depends largely on human rights defenders enjoying effective and adequate guarantees so as to freely go about their activities.”
The rights to freedom of expression and association may be subject to limitations, but the limitations must adhere to strict standards so that they do not improperly impede the exercise of those rights. Any restrictions should be prescribed by law, be necessary in a democratic society, and proportionate to the aim pursued.
In 2012, the UN special rapporteur on the rights to freedom of peaceful assembly and of association called on countries to ensure that these rights “are enjoyed by everyone and any registered or unregistered entities” and that no one is subject to “harassment, persecution, intimidation or reprisals” for exercising them.
Signatories
Amnesty International
Asociación Pro Derechos Humanos (APRODEH) (Peru)
Asociación por los Derechos Civiles (ADC) (Argentina)
Centro de Derechos Humanos de la Montaña Tlachinollan (Mexico)
Centro de Derechos Humanos Miguel Agustín Pro Juárez, A.C. (Centro Prodh) (Mexico)
Centro de Estudios de Derecho, Justicia y Sociedad (Dejusticia) (Colombia)
Center for Justice and International Law (CEJIL)
CIVICUS
Ciudadanos en Apoyo a los Derechos Humanos, A.C. (CADHAC) (Mexico)
Comisión Colombiana de Juristas (Colombia)
Comisión Ecuménica de Derechos Humanos (CEDHU) (Ecuador)
Corporación Humanas (Chile)
Coordinadora Nacional de Derechos Humanos (Peru)
Due Process of Law Foundation (DPLF)
Instituto de Estudios Legales y Sociales del Uruguay (IELSUR) (Uruguay)
Instituto de Defensa Legal (IDL) (Peru)
Instituto de Desenvolvimento e Direitos Humanos (Brazil)
International Commission of Jurists
International Federation for Human Rights (FIDH)
International Service for Human Rights (ISHR)
Frontline Defenders
Fundación Myrna Mack (Guatemala)
Fundación Regional de Asesoría en Derechos Humanos (INREDH) (Ecuador)
Human Rights Watch
Observatorio Ciudadano (Chile)
Robert F. Kennedy Center for Justice & Human Rights
Transparency International
World Organization Against Torture
Venezuela-Harassment of HRDs-News-web stories-2015-SPA (full text in PDF, Spanish version)
Venezuela-Harassment of HRDs-News-web stories-2015-POR (full text in PDF, Portuguese version)








