
Aug 7, 2021 | Advocacy
Discriminatory practices, lack of access to adequate housing, food and safe drinking water and poor health conditions in detentions centers are just some of the many human rights deprivations faced by migrants and refugees in Thailand amidst the continuing COVID-19 pandemic.

Jul 7, 2021 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ today addressed the UN Human Rights Council in the Interactive Dialogue with the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights for her update on the human rights situation in Myanmar.

Jun 29, 2021 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ joined civil society organisations in a statement to the UN Human Rights Council during the interactive dialogue with the UN Special Rapporteur on the independence of judges and lawyers.

Jun 1, 2021 | Advocacy, News
Thailand’s laws and practices governing the rights of land users may result in unnecessary and disproportionate restrictions on various economic, social, and cultural rights, particularly for forest dwellers and indigenous communities, the ICJ said during discussions last week with members of Thai civil society as well as government authorities.
On 28 May 2021, the ICJ co-hosted a discussion on international human rights law and standards on land rights in Thailand, with 70 members of civil society organizations, human rights lawyers, and academics in attendance. On 4 June 2021, the ICJ spoke at a discussion on the same topic, organized by Thailand’s Ministry of Justice, bringing together 80 governmental officials from several Ministries.
“Thailand’s land regulatory laws do not adequately protect the rights of indigenous people to access their ancestral lands and natural resources and to conduct cultural practices,” said Sanhawan Srisod, ICJ Legal Advisor. “We hope the Thai government will improve its general policies for land use and tenure, especially for indigenous peoples and forest dwellers, in line with its obligations under international law.”
Dr. Seree Nonthasoot, member of the UN Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (CESCR) from Thailand, spoke at both discussions to introduce participants to the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) to which Thailand is a party and the role of the CESCR. The CESCR is a body of independent experts from across the world established by ICESCR and tasked with providing authoritative interpretations of ICESCR in its body of jurisprudence.
“The CESCR recommended [that] Thailand […] effectively remove all obstacles to enjoyment of traditional individual and communal rights by ethnic minorities in their ancestral lands […] and ensure that forced evictions are only used as a measure of last resort. These should be addressed without any further delay,” said Dr. Seree Nonthasoot.
Specific issues highlighted by participants in the discussions included:
- Prosecution and Eviction: The use of laws ostensibly designed to counter climate change and forest conservation policies and legislatures, such as the Forest Act, the National Reserved Forests Act and the National Park Act, to prosecute forest dwellers and indigenous communities for trespassing and forcibly evict them from the land belonging to national reserved forests and national parks;
- Participation and Consultation: The inadequate participatory mechanisms and consultations with people affected by land-related policies and practices, in particular the increasing use of online mechanisms as the main platforms for consultation in Thailand, despite the low rate of access to the internet among affected communities;
- Judicial Recognition: The lack of explicit judicial recognition of historical and other indigenous forms of evidence and knowledge in order to establish validity of territorial claims;
- Impact of Tourism: The impact of tourism development projects on communities’ economic, social and cultural rights in land-related contexts, including on their traditional landownership and livelihood practices;
- Compensation and Assessment: The impact of large-scale land acquisitions in areas that had already been occupied or used, without carrying out adequate impact assessments and with inadequate compensation.
Sanhawan Srisod introduced participants to the CESCR’s draft General Comment No. 26, which is open for public comment until 27 July 2021. If a revised General Comment is adopted by the CESCR, it will provide an authoritative interpretation of States’ ICESCR obligations relating to land.
At the meeting’s conclusion, participants discussed advocacy strategies to strengthen Thailand’s legal frameworks once the draft General Comment is adopted by the CESCR.
Further reading
The Human Rights Consequences of the Eastern Economic Corridor and Special Economic Zones in Thailand
Thai Companies in Southeast Asia: Access to Justice for Extraterritorial Human Rights Harms
Joint submissions by ICJ and its partners to the Universal Periodic Review (UPR)
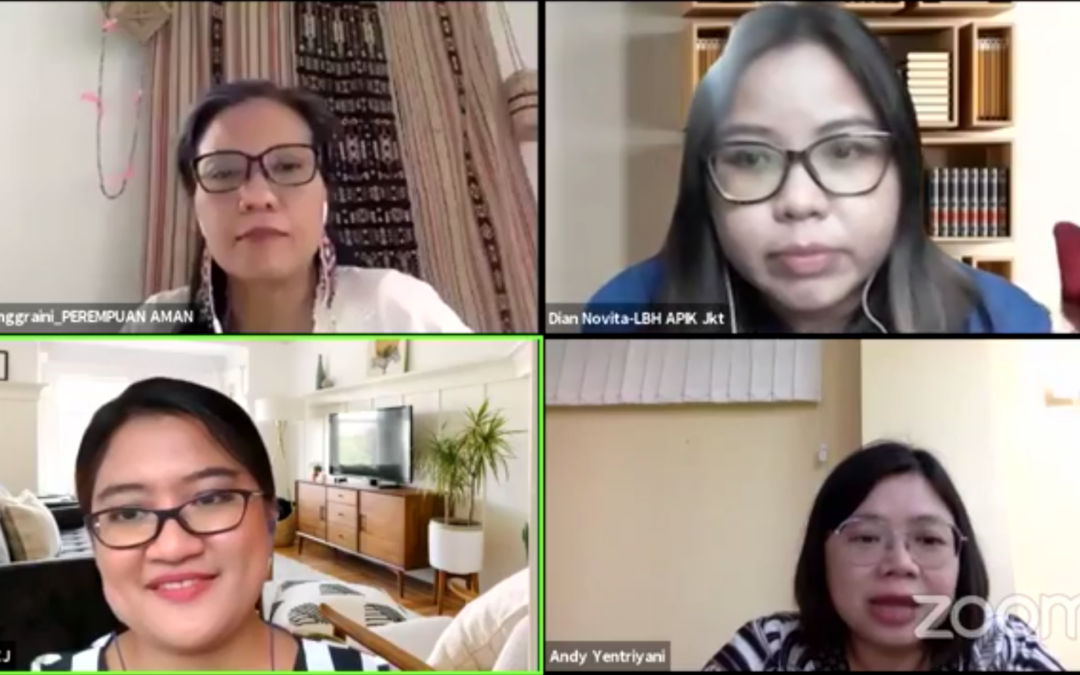
Apr 9, 2021 | Advocacy, News
The ICJ, together with the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) and the National Commission on Violence Against Women (Komnas Perempuan) in Indonesia, held a webinar on 6 April to consider ways to combat discrimination and violence faced by Indonesian women.
In particular, participants identified advocacy strategies towards strengthening Indonesia’s compliance with its international legal obligations under the UN Convention on the Elimination of all forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW).
The webinar was broadcast live on Facebook and showcased the Bahasa Indonesia version of CEDAW video and attended by more than 50 women human rights defenders. The participants discussed the adequacy of measures taken by the Indonesian government to implement recommendations issued by the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW Committee) after it had reviewed Indonesia’s report in 2012. These recommendations included a call to repeal discriminatory by-laws adopted at the provincial level that restrict women’s rights in Aceh province and elsewhere; the adoption of measures taken to ensure that the draft or proposed amendments to the Criminal Code Bill and other bills do not contain provisions that discriminate against women; the need to address gender based violence and sexual violence against women including indigenous women; and the protection of women human rights defenders.
Devi Anggraini, Chairperson of Association of Indigenous Women of the Archipelago (Perempuan Aman) said although Indonesia had ratified CEDAW through Law No. 7 year 1984 to protect the individual rights of Indonesian women, policies had yet to effectively protect the collective rights of indigenous women. She shared her concerns regarding discrimination against Indigenous women in the context of large-scale development projects, exploitation of natural resources, deforestation, and expansion of agriculture, as well as their access to land and resources.
“The Indonesian government does not seek ‘free, prior, and informed consent’ by the affected indigenous people, especially indigenous women and this has caused 87.8% of indigenous women to lose control of their traditional lands,” said Devi.
Dian Novita, Coordinator of Policy Advocacy Division from Legal aid for Women and Children (LBH APIK Jakarta) raised concern about discriminatory draft laws and provincial laws.
“LBH APIK assists many cases of women who are victims of gender-based violence in which their videos containing private sexual conducts were distributed online. However, they were criminalized under the pornography law and Electronic Information’s and Transactions (EIT) Law. We are currently trying to pursue judicial review of the ETI Law from women’s perspective”, said Dian.
Andy Yentriyani, Head of Komnas Perempuan said that despite existing challenges and new obstacles, there had been some progress in responding to the Recommendations of the CEDAW Committee from the previous cycle, such as the enactment of Supreme Court Regulation no.3 year 2017 on guidance for judges in adjudicating cases involving women and similar gender sensitive regulation released by the Attorney General’s Office and the Police. “It is now our duty to monitor that these policies and training are effectively implemented. For example, we gained extraordinary support from the civil society during the campaign urging the Government to adopt the Sexual Violence Bill and this expanded participatory space for constructive dialogue for public to understand more about State responsibilities to protect and promote the fundamental rights of women.”
Watch
Contact
Ruth Panjaitan, Legal Adviser for Indonesia, e: ruthstephani.panjaitan(a)icj.org

Mar 29, 2021 | Advocacy, News
On 25 March 2021, the ICJ filed two submissions to the UN Human Rights Council Working Group on the Universal Periodic Review (UPR) ahead of the review of Thailand’s human rights record in November 2021.
For this particular review cycle, the ICJ made two joint UPR submissions to the Human Rights Council.
In the joint submission by ICJ and Thai Lawyers for Human Rights (TLHR), the organizations provided information and analysis to assist the Working Group on the UPR to make recommendations addressing various human rights concerns that arise as a result of Thailand’s failure to guarantee, properly or at all, a number of civil and political rights, including with respect to:
- Constitution and Legal Framework: concerning the 2017 Constitution that continues to give effect to some repressive orders issued by the military junta after the 2014 coup d’état, the Emergency Decree, the Martial Law, and the Internal Security Act;
- Freedom of Expression and Assembly: concerning the use of laws that are not human rights compliant and, as such, arbitrarily restrict the rights to freedom of expression, association and peaceful assembly, in the context of the Thai government’s response to the pro-democracy protests and, purportedly, to COVID-19; and
- Right to Life, Freedom from Torture and Enforced Disappearance: concerning the resumption of death penalty, the failure to undertake prompt, thorough and impartial investigations, and to ensure accountability of those responsible for the commission of torture, other ill-treatment and enforced disappearance, and the failure, to date, to enact domestic legislation criminalizing torture, other ill-treatment and enforced disappearance.
In the second, joint submission by ICJ, ENLAWTHAI Foundation and Land Watch Thai, the organizations provided information and analysis to assist the Working Group to make recommendations addressing various human rights concerns that arise as a result of Thailand’s failure to guarantee, properly or at all, a number of economic, social and cultural rights, including with respect to:
- Human Rights Defenders: concerning threats and other human rights violations against human rights defenders, and the restrictions on civil society space and on the ability to raise issues that the government deems as criticism of its conduct or that it otherwise disfavours;
- Constitution and Legal Framework: concerning the continuing detrimental impact of the legal framework imposed since the 2014 coup d’état on economic, social and cultural rights;
- Community Consultation: concerning the lack of participatory mechanisms and consultations, as well as limited access to information, for affected individuals and communities in the execution of economic activities that adversely impact local communities’ economic, social and cultural rights;
- Land and Housing: concerning issues relating to access to land and adequate housing, reports of large-scale evictions without appropriate procedural protections as required by international law, and the denial of the traditional rights of indigenous peoples to their ancestral lands and natural resources; and
- Environment: concerning the widespread and well-documented detrimental impacts of hazardous and industrial wastes on the environment, the lack of adequate legal protections for the right to health and the environment, and the effectiveness of the environmental impact assessment process set out under Thai laws.
The ICJ further called upon the Human Rights Council and the Working Group on the Universal Periodic Review to recommend that Thailand should take various measures to immediately cease all aforementioned human rights violations; ensure adequate legal protection against such violations; ensure the rights to access to justice and effective remedies for victims of such violations; and ensure that steps be taken to prevent any future violations.
Download
UPR Submission 1 (PDF)
UPR Submission 2 (PDF)










