Mar 15, 2021 | Advocacy, News
The ICJ and a group of Sri Lankan judges have agreed on the importance of taking effective measures to address discrimination and equal protection in accessing justice in the country.
On 6 and 13 March 2021, the ICJ, in collaboration with the Sri Lanka Judges’ Institute (SLJI), organized the National Judicial Dialogue on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women and Enhancing Women’s Access to Justice. This event was organized under the ‘Enhancing Access to Justice for Women in Asia and the Pacific’ project funded by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (SIDA).
Twenty magistrates and District Court judges from around Sri Lanka, with judicial and legal experts from other countries, participated in this judicial dialogue which was conducted virtually due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The dialogue highlighted how Sri Lankan women continue to face a myriad of challenges including legal, institutional and cultural barriers when accessing justice. Gender biases and discriminatory behaviour prevalent in every aspect of justice delivery needs to be dealt with in order to effectively enhance women’s access to justice.
Boram Jang, ICJ International Legal Advisor remarked that “judiciaries have an important role to play in eliminating gender discrimination in justice delivery as it is a critical component in promoting women’s access to justice. In order to do so, the judges should be equipped with a full understanding of Sri Lanka’s obligations under the CEDAW and other human rights instruments.”
Honorable L. T. B. Dehideniya, Justice of the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka and Executive Director of the SLJI expressed hope that judicial dialogues such as this would “enhance the capacity of participant judges to use the international legal instruments, which Sri Lanka has ratified, in domestic judicial work especially with regard to the elimination of gender inequalities and biases.”
Ms. Bandana Rana, Vice Chair of the CEDAW Committee led a discussion with the judges on the application of the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), pointing out that “judges play a pivotal role in identifying the incongruences between existing laws and international human rights standards and ensuring that the full gamut of women’s human rights is retained in line with the CEDAW framework.”
Justice Ayesha. M. Malik, High Court Judge, Lahore, Pakistan affirmed the importance applying the right to access to justice under international human rights law and suggested strategies for reflecting these international standards in judicial decisions.
Attorney Evalyn Ursua addressed on gender stereotypes and biases in justice delivery and engaged the participants on how these could be effectively eliminated. She stated that “the judiciary as a part of the State has the obligation to eliminate gender discrimination.” She encouraged the judges to use the cultural power of law to change language and attitudes surrounding gender discriminatory behaviour and stigma.
The second day featured a discussion on the specific barriers that women in Sri Lanka face when they access justice. Hon. Shiranee Tilakawardane, former Justice of the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka led a discussion on the role and measures available to the judiciary as an institution to enhance access to justice for Sri Lankan women.
Justice Tilakawardane stated that “While theoretically, the Sri Lankan constitution enshrines equality before the law, in reality women continue to feel disadvantaged when they try to access justice” and added “the Sri Lankan judiciary can empower its women only when it understands, acknowledges and addresses the disadvantages they face owing to their gender.” She impressed upon the participant-judges that “ensuring equality is no longer a choice, nor is it merely aspirational, but a pivotal part of judicial ethics.”
The panelists on the second day surveyed the legal, institutional and cultural challenges faced by women at every step of the judicial process. The panel comprised of Prof. Savitri Goonesekere, Emeritus Professor of Law and Former member of the CEDAW Committee, Mrs. Farzana Jameel, P.C, Additional Solicitor General of the Attorney General’s Department and Mrs. Savithri Wijesekara, Executive Director of Women in Need.
Contact
Osama Motiwala, Communications Officer – osama.motiwala@icj.org

Mar 15, 2021 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
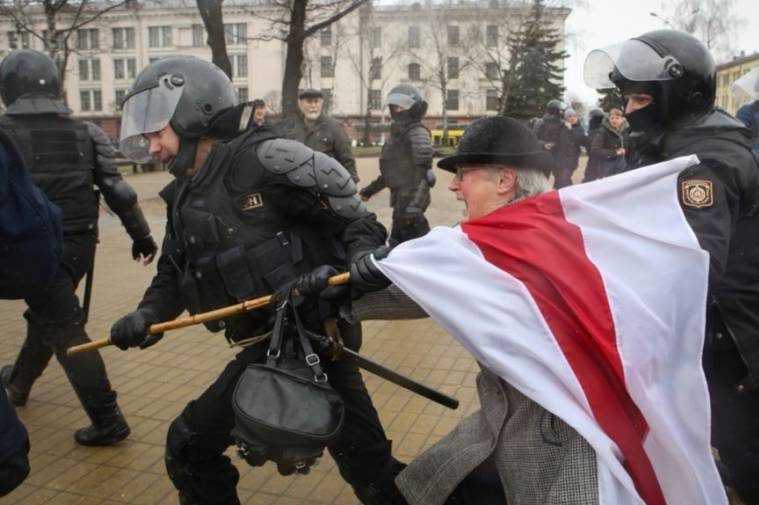
Today, the ICJ joined IBAHRI, Human Rights House Foundation and the OMCT in a statement before the UN Human Rights Council condemning human rights violations against lawyers in the country.
The joint statement delivered during the debate on the outcome of the UPR of Belarus reads as follows:
“The IBAHRI, the International Commission of Jurists, the Human Rights House Foundation and the OMCT would like to echo concerns that have been raised during the UPR review and are reflected in the UPR outcome document.
We strongly condemn the numerous, widespread human rights violations committed in the aftermath of the 2020 Belarus Presidential election, in particular:
- First – The disproportionate use of force by security forces against peaceful protestors, the arbitrary arrest and detention of thousands of people, systematic torture and ill-treatment following arrest or during detention, reports of enforced disappearances and denied access to a lawyer.
- Second – The systematic control of the executive over the judiciary and the court system. The judiciary continues to selectively use legislation to intimidate dissenting voices and tightly controls the licensing and activities of lawyers working under threat of being targeted.
- Third – The Illegal and arbitrary restrictions to fundamental rights and freedoms, including the right to peaceful assembly, free expression and access to information. From violent targeting of journalists and the media, to state sanctioned internet shutdowns resulting in censorship.
Therefore, we urge Belarus to:
- Immediately and unconditionally release all individuals arbitrarily detained and stop any practices of torture and ill-treatment of detainees;
- Undertake impartial, independent, effective and prompt investigations into allegations of human rights abuses;
- Bring perpetrators to justice, ensuring effective remedy and reparation for victims;
- Allow professionals – including legal and media professionals – to conduct their work without fear of targeting;
- Ensure respect and practice for all human rights, including free expression, online and offline, providing unconstrained access to information for all; lastly
- Adopt all necessary measures to prevent further human rights violations, without delay.”
Contact:
Massimo Frigo, ICJ UN Representative, e: massimo.frigo(a)icj.org, t: +41797499949

Mar 15, 2021 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
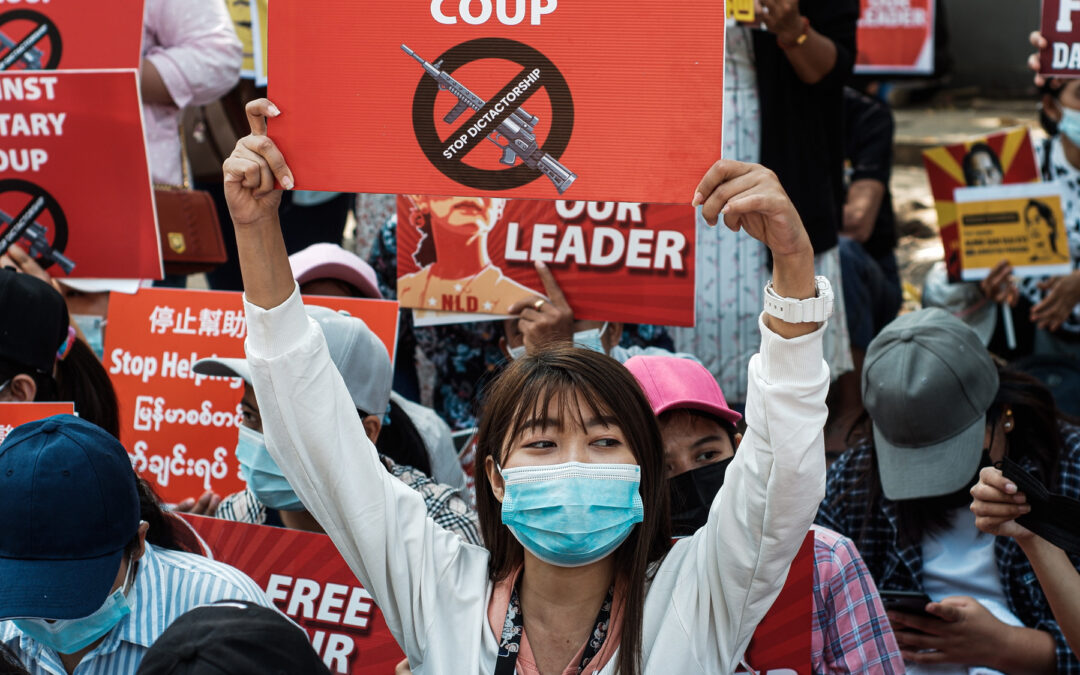
Today, during a General Debate, the ICJ called on the UN Human Rights Council to condemns a set of laws amendend by the military governmentn in Myanmar and restricting human rights, and to demand the return to of Myanmar civilian rule respecting the rule of law.
The statement reads as follows:
“Madame President,
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) condemns the illegitimate attempts to “amend” several laws by the Military appointed Myanmar’s State Administration Council (SAC) following its unlawful seizure of power on 1 February 2021.
The implementation of the Amended Law Protecting the Privacy and Security of Citizens (2017) would undermine the democratic process, criminalize peaceful protests and remove various human rights protections. It would provide for broad and unchecked power to the military to arrest anyone without a warrant and aim to remove basic protections, including the rights to be free from arbitrary detention and from warrantless surveillance and search and seizure.
The amendments to the Penal Code and the Criminal Procedural Code have made non-bailable certain offenses, specifically targeting persons criticizing the coup or the military junta, as well as those encouraging others to support the “Civil Disobedience Movement.”
In addition, Amendments made to other existing laws, such as the Ward and Tract Administration Law and Electronic Transactions Law, allow for search and seizure at night without arrest warrant and allow for the silencing of critical voices against the coup and human rights violations of the military, in violation of international standards.
The ICJ calls on the Council to adopt a resolution, which, among other things, univocally condemns and demands the repeal of these laws and the return to of Myanmar civilian rule respecting the rule of law.
Thank you.”

Mar 12, 2021 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
Today, the ICJ delivered a statement to the UN Human Rights Council calling for accountability for crimes against humanity committed in Myanmar during the Interactive Dialogue on the report by the UN Special Rapporteur on the situation of human rights in Myanmar.
The statement reads as follows:
“Madame President,
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) welcomes the recent report of the Special Rapporteur on the situation of human rights in Myanmar.
The widespread gross violations of human rights documented in the report – including extrajudicial killings, arbitrary arrests and detention- underscore the need for urgent measures of accountability to redress these and to deter further violations.
ICJ has documented further evidence that the unlawful crackdown against peaceful protestors have continued to worsen leading to more extrajudicial killings. More than 50 people have already been unlawfully killed and several hundreds have been severely injured.
Hundreds of others have been arbitrarily arrested and detained, with some subjected to torture and ill-treatment. As the scale of violations continues to increase in many parts of the country, these attacks have become systematic and widespread, and must be investigated as crimes against humanity.
The ICJ therefore supports the recommendations made by the Special Rapporteur, including for referral of the situation to the ICC.
The ICJ urges the Council to adopt a resolution that would strengthen and support the IIMM’s work to collect and preserve evidence for accountability; and to extend the mandate of the Special Rapporteur, including to ensure the immediate, full and unrestricted monitoring of the situations and prompt and effective implementation of their recommendations.
Thank you.”
Contact:
Massimo Frigo, ICJ UN Representative, e: massimo.frigo(a)icj.org, t: +41797499949

Mar 12, 2021 | Advocacy, News
Several Iranian and international human rights organisations urge member states of the United Nations Human Rights Council to support the renewal of the mandate of the United Nations Special Rapporteur on the situation of human rights in Iran.
The letter reads:
We, the undersigned Iranian and international human rights organisations, call on your government to support the renewal of the mandate of the United Nations Special Rapporteur on the situation of human rights in Iran at the 46th session of the Human Rights Council. We also urge your government to use this opportunity to voice concern at the grave and systematic violations of human rights reported by the Special Rapporteur, and to call on Iranian authorities to put an end to the endemic impunity that surrounds these violations.
The renewal of this mandate is essential in light of the persistence of widespread and systematic violations of human rights committed by Iranian authorities with total impunity.
Iran remains second only to China in the number of executions carried out each year. In 2020, the authorities executed more than 240 people, including for drug offences and other acts that do not amount to the ‘most serious crimes’ under international law. Several people were executed in secret without prior notice to their families and lawyers. Among those executed was dissident and journalist Ruhollah Zam who was sentenced to death in connection with his anti-establishment social media news channel. Several protesters were sentenced to death and dozens of others faced capital crimes in relation to the nationwide November 2019 protests. The Iranian authorities executed at least three juvenile offenders in 2020, in violation of international law and despite repeated calls from UN bodies and member states for Iran to cease this unlawful practice and high-level bilateral engagement with the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights on this issue.
Fair trial rights continue to be systematically violated, making the hundreds of death sentences, corporal punishment sentences and long prison terms issued all the more egregious. The UN Working Group on Arbitrary Detention has raised alarm at ‘a familiar pattern of arrest and detention that does not comply with international norms’, including ‘lengthy detention pending trial with no access to judicial review; denial of access to legal counsel; incommunicado detention and solitary confinement; prosecution under vaguely worded criminal offences for the peaceful exercise of human rights; a closed trial and appeal by courts lacking in independence; disproportionately harsh sentencing; torture and ill-treatment; and denial of medical care’. In addition to these concerns, courts consistency rely on forced ‘confessions’ extracted under torture and other ill-treatment to issue convictions, as in the recent case of Navid Afkari, executed on 12 September 2020.
The Iranian authorities continue to routinely arbitrarily arrest, detain and sentence individuals to prison terms and flogging for the exercise of their rights to freedom of expression, association and peaceful assembly. Among those who are targeted are protesters, media workers, journalists, political dissidents, artists, writers, and human rights defenders, including lawyers, women’s rights defenders, labour rights activists, minority rights activists, conservationists, anti-death penalty campaigners and
those demanding truth, justice and reparation for the mass extrajudicial executions of the 1980s.
Authorities in Iran have further quashed civic space through state policies and the recent introduction of new provisions in the Islamic Penal Code, which further criminalise the exercise of the rights to freedom of expression, religion or belief. Violent crackdowns on protests have become intertwined with the imposition of internet shutdowns or disruptions in recent years. These measures stifle internet freedom and have been used by the authorities to prevent protesters from mobilising and to conceal the scale of grave human rights violations and international crimes carried out by the state and its security forces.
Conditions in many prisons and detention facilities are cruel and inhuman, with prisoners suffering from overcrowding, bad ventilation, lack of adequate food, poor hygiene and sanitation and inadequate access to toilet and washing facilities. Despite such conditions providing a breeding ground for infectious diseases, authorities have failed to adequately resource prisons to control the spread of COVID-19 and treat infected prisoners. They have excluded prisoners of conscience and others held for politically motivated reasons from temporary releases or pardons announced to mitigate the spread of COVID-19 and have deliberately denied them access to adequate health care.
As highlighted in the report of the Special Rapporteur before the Human Rights Council, discrimination in law and practice remains pervasive and a daily reality for women and girls, for persons belonging to ethnic, religious or linguistic minorities, as well as for lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) individuals. Women and girls continue to face widespread and systematic discrimination in law and practice in all aspects of their lives, amid the authorities’ continued failure to protect them from gender-based violence.
Ethnic minorities, including Ahwazi Arabs, Azerbaijani Turks, Baluchis, Kurds and Turkmen continue to face entrenched discrimination, which curtails their economic, social, cultural and other rights. The High Commissioner has recently noted that ‘an apparently coordinated campaign has been targeting minority groups since December, including in Sistan and Balochistan; Khuzestan; and in the Kurdish provinces. Mass arrests and enforced disappearances have been reported, as well as increasing
numbers of executions, following deeply flawed processes’. Some ethnic minorities have also been disproportionately affected by the imposition of the death penalty in 2020.
Freedom of religion or belief continues to be systematically violated, including for Baha’is who face widespread and systematic persecution, hate speech and obstacles to access education and work. Christian converts, the Yarsan (Ahl-e Haq), Sunni Muslims and non-believers also face discrimination and persecution for expressing or practising their faith or beliefs.
These long-standing patters of human rights violations have been facilitated by systematic impunity and lack of transparency. An illustration of this crisis of impunity is the continued failure of the authorities to investigate and prosecute crimes and human rights violations committed in the context of the violent repression of the nationwide protests of November 2019. The state repression resulted in the unlawful killing of hundreds of men, women and children, the arrest of at least 7,000 others, and widespread patterns of enforced disappearances and torture and other ill-treatment of detainees to obtain ‘confessions’ that have been used to issue convictions in unfair trials. In his report before the Human Rights Council, the UN Special Rapporteur has expressed dismay that ‘more than one year on, the Government has failed to conduct an impartial, independent and transparent investigation into the use of excessive and lethal force during nationwide demonstrations in November 2019’. On the contrary, the authorities have engaged in harassment and violence against victims and their families for seeking truth, justice and reparation, as documented in the recent reports of the Special Rapporteur.
In this context, the mandate of the Special Rapporteur on the situation of human rights in Iran continues to be critical to monitor, document and report to this Council on steps taken by Iran to uphold its human rights obligations or of its failure to take such measures. It is essential to engage with Iranian authorities on issues of concern, and to make potentially life-saving urgent appeals and other communications. The mandate draws the attention of this Council to the voices of victims, and its expert findings and recommendations steer and inform the efforts of UN bodies and member states to encourage Iran’s authorities to undertake long overdue human rights reforms and hold them to account for human rights violations.
For these reasons, we urge your government to support the renewal of the mandate of the UN Special Rapporteur on the situation of human rights in Iran at this session and to press Iran to give unfettered access to the Special Rapporteur. We also call on your government to voice concern at the dire situation of human rights in Iran, and to send a strong message to the Iranian authorities that the cycle of impunity must be broken, and that members of the Council expect without delay the adoption of long-overdue
human rights reforms and tangible improvements to the human rights situation in the country.
Download
Joint letter with a list of organizations in English.

Mar 11, 2021 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
Today, the ICJ called on the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights to guarantee transparency and participation in its activities in Venezuela in an oral statement delivered during the interactive dialogue on the oral update by the UN’s High Commissioner of Human Rights on Venezuela.
The statement reads as follows:
“Madame President,
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) welcomes the High Commissioner’s oral update on the situation of human rights in Venezuela, particularly regarding the cooperation between her office and the Venezuelan authorities.
The ICJ underscores the importance of transparency on the activities conducted under the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed by both parties. Publication of the MoU to inform the public and ensure the optimal engagement of stakeholders is critical to its success.
The ICJ stresses that in addition to civil and political rights, economic, social, cultural rights continue to be violated in Venezuela, a situation aggravated by the COVID-19 pandemic. As of January 2021, at least 37 health workers have died due to the lack of protective equipment and basic supplies in healthcare centers.
In light of recent announcements by Venezuelan authorities, political considerations appear to be a driving factor in the COVID-19 vaccine prioritization plan, instead of objective and public health criteria, which could lead to discrimination and a denial of equal protection of law.
The ICJ recommends that the High Commissioner monitor and report on the status of the Venezuelan authorities’ compliance with her previous recommendations, and on her broader engagement with local civil society with a view to protecting human rights.
Thank you.”
Contact:
Massimo Frigo, ICJ UN Representative, e: massimo.frigo(a)icj.org, t: +41797499949










