Sep 8, 2020 | Advocacy, News
On 29 August and 5 September, the ICJ collaborated with the Integrated Bar of the Philippines (IBP) to hold a webinar series for legal aid providers in the Philippines on eliminating gender discriminatory attitudes and behaviors towards women.
Members of IBP’s legal aid committees from the Eastern and Western Mindanao Regions participated in these webinars, focused on gender stereotypes and discriminatory practices that exist in the legal profession and in the work of legal aid providers who directly engage with women when they seek justice.
Dato Ambiga Sreenevasan, ICJ’s Commissioner from Malaysia, addressed the promotion and protection of women’s human rights in the context of the legal profession: “While conditions for women have improved, there is still work to be done to achieve equality between men and women in the legal profession. At the entry level, things appear to be going well, but we must look also at women’s opportunities throughout their legal career and question why it is the case that some areas are still male-dominated.”
Mikiko Otani, ICJ’s Commissioner from Japan and a member of the UN Committee on the Rights of the Child, spoke about how gender stereotypes and gender discrimination hinder women from accessing justice. “The Bar should be at the forefront of advocating for improvement in legal structures that would help eliminate gender discrimination,” she said.
The Philippines had previously featured as one of the top ten performers in addressing gender disparities, as measured by the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Index. However, it has recently fallen to rank 16th out of 153 countries. Emerlynne Gil, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, acknowledged various measures adopted by the Philippines to implement the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), such as the adoption of the Anti-Violence Against Women and Children Act and the Magna Carta for Women. She noted, however, that the Philippines still must do a great deal more.
“The existing culture of impunity and lack of effective remedies for women to access the justice system are just some of the difficult challenges the country faces that prevent it from achieving this goal,” Emerlynne Gil said.
The webinar series also featured a discussion on specific challenges faced by women when accessing justice during the COVID 19 pandemic and in the context of the “drug war” in the Philippines. The lawyers discussed their role and also that of the Bar as an institution to immediately identify and eliminate these gender stereotypes to ensure their clients’ right to access to justice.
Judge Amy Alabado Avellano, a Regional Trial Court judge in the Philippines led this discussion. Attorney Burt Estrada, IBP Executive Vice President, and Attorney Marienne Ibadlit, former IBP Governor for Western Visayas, also held a dialogue with the lawyers on how the IBP as a professional association for lawyers in the Philippines could contribute towards enhancing access to justice for women in the country.
Contact
For questions and clarifications, please contact Ms. Emerlynne Gil, Senior International Legal Adviser, t: +662 619 8477 (ext. 206); e: emerlynne.gil(a)icj.org.

Sep 2, 2020 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ has made submissions to the Human Rights Committee, today, on Ukraine’s implementation of, and compliance with, the provisions of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights.
The ICJ broughtto the Committee’s attention some issues of concern pertaining to Ukraine’s compliance with and implementation of the ICCPR.
This submission highlights a number of concerns relating to the security and independence of lawyers in Ukraine, and their consequences for the protection of certain Covenant rights. In particular, this submission addresses:
- the institutional independence of the legal profession;
- security of lawyers and their right to life;
- restrictions on access to clients and the rights of the defence; and
- security of lawyers and access to justice in uncontrolled territories in Ukraine.
These concerns highlight Ukraine’s lack of compliance with its obligations under the Covenant, including in respect of the right to life under article 6 and the right to a fair trial under article 14, in particular, as well as under other Covenant rights, such as Ukraine’s obligations under articles 2, 7, 9, 10, and 17 of the ICCPR.
Ukraine-ICJ-Submission-CCPR-Advocacy-Non-Legal-Submissions-2020-ENG

Sep 1, 2020 | Advocacy, News
Today the ICJ called on the Organization of American States (OAS) to respect the autonomy and independence of the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights (IACHR) as the body in charge of promoting the observance of human rights in the Americas, including in respect of its core administration functions.
The OAS Secretary-General has declined to endorse the unanimous decision taken in January by the seven-person IACHR to renew the mandate of its Executive Secretary, Paulo Abrão, whose term expired on 15 August.
The Secretary General indicated that his action was motivated by concern at internal complaints that are still to be resolved.
The refusal to renew this mandate, however, must not be made on the basis of pending complaints, which must nonetheless be resolved in a reasonably short period of time, based on the principles of due process for all parties concerned
The ICJ recognizes the importance of processing the staffs’ complaints in a timely manner which respects the due process rights of the parties concerned through an independent and transparent process.
The ICJ recalls that it is essential to ensure the independence and autonomy of the Inter-American Commission, which necessarily includes the functions related to the appointment process of the Executive Secretary.
“The IACHR has played a critical role in the Americas to advance human rights and to protect victims of human rights violations,” said ICJ Secretary General Sam Zarifi.
He also mentioned that “the situation requires an urgent resolution that guarantees respect for the principles of independence and autonomy of the IACHR.”

Aug 31, 2020 | Advocacy, News
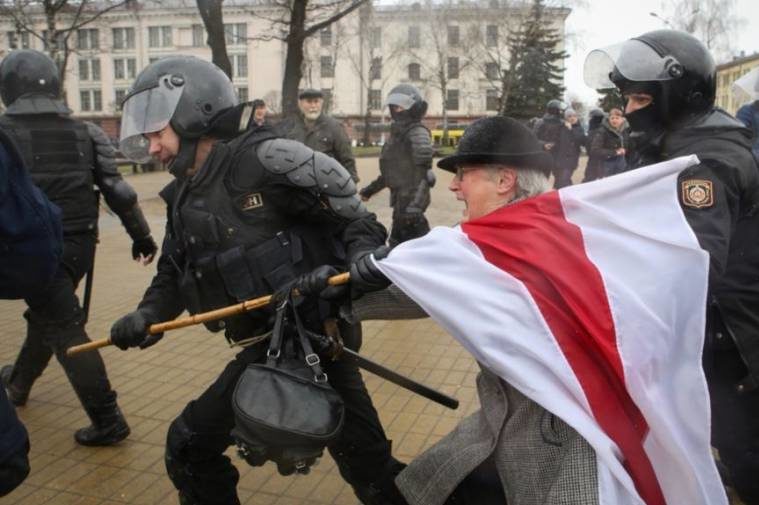
Today, the ICJ called on Belarus to comply with its international human rights law obligations in its response to the protests taking place in the aftermath of the presidential elections and in the treatment of those detained.
This includes immediately releasing persons arbitrarily detained, providing prompt access to lawyers for those still detained, accounting for the fate and whereabouts of missing protestors and promptly and effectively investigating torture and other ill-treatment.
The widespread arbitrary arrests of peaceful protesters, and credible allegations of torture and ill-treatment and enforced disappearances of detainees, are particularly alarming in light of obstacles faced by detainees in accessing lawyers, the ICJ said.
The ICJ recalls that under international human rights law, all persons have the right to peaceful assembly, and any restriction of this right must be provided in law be strictly necessary and proportionate to a specified legitimate purpose. The mass arrest of protesters does not appear to meet these requirements.
Belarus has obligations, including under treaties to which it is party, to respect the right to liberty and refrain from arbitrary arrests or other unwarranted interferences with the freedom of assembly, or freedom of expression, of protesters, protected under international law.
Law enforcement authorities must respect the right to life and the prohibition on torture or other ill-treatment at all times. Allegations of arbitrary killing, enforced disappearances and torture and other ill-treatment must be promptly, thoroughly and independently investigated, and those responsible brought to justice.
Effective remedies must be provided to victims of such serious human rights violations.
The ICJ is concerned about reports of the widespread denial of access to a lawyer and further obstacles that lawyers face while carrying out their professional duties in the current context in Belarus.
Reportedly, lawyers are not provided with access to the case file or further information necessary for the provision of effective legal assistance to their clients. This is of particular concern in light of multiple reports of torture or other ill-treatment of those detained following the election.
The ICJ stresses that the right of access to qualified legal representation is crucial for the protection of the human rights of those arrested in connection with the current political upheaval in Belarus.
The right of access to a lawyer is recognized as an essential element of the right to a fair trial and the right to liberty, protected under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, to which Belarus is a party.
The UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers provide that governments should ensure that lawyers are able to perform all of their professional functions without intimidation, hindrance, harassment or improper interference and should be able to consult with their clients freely and have access to appropriate information, files and documents in their possession or control in sufficient time to provide effective legal assistance to their clients.
It is essential that lawyers and other human rights defenders can carry out protection of human rights of their clients especially in times of emergency.
The ICJ also calls on the Belarus Republic Bar Association to bolster its efforts in protecting its members who provide legal representation in cases related to the ongoing protests.
Background:
The Republic of Belarus ratified the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights in 1973
Following the presidential elections of 9 August 2020 in Belarus, widespread protests across Belarus took place following the discredited result, which were recognized as neither free nor by the European Union and other observers. Following the initial dispersal of these protests by the authorities, more than 6000 people were arrested and detained, many arbitrarily. There is credible evidence that many of those arrested or detained have been subjected to torture or other ill-treatment and that decisions regarding their arrest and detention have been made by courts temporarily established in detention centres.
While estimates of numbers differ, the whereabouts of at least tens of those who took part in the protest have not been established to date. One of the missing persons, Nikita Krivtsov, was recently found dead in a forest near Minsk.
The reports that defence lawyers were denied access to those arrested include high-profile cases, such as the case of the former presidential candidate Victor Babaryka whose lawyer was not allowed to see his client in the detention centre for more than a week.
According to the Belarusian Republican Bar Association, lawyers face problems with meeting their clients held in the detention centres and access to the case files and further information necessary to carry out their professional duties.

Aug 30, 2020 | Advocacy, News
While commemorating the International Day of the Disappeared 2020, the ICJ and 47 other national and international organizations and groups of victims, in Nepal, call on the responsible authorities to undertake immediate steps towards reinvigoration of the transitional justice (TJ) process, adopting a transparent and consultative process.
On this occasion, the victims’ groups and human rights organizations in Nepal commend the patience and resilience shown by the family members of those subjected to enforced disappearance during the 10-year-long internal armed conflict from 1996-2006. They have worked tirelessly advanced the TJ process (Truth, Justice, Reparation and Institutional Reform) in Nepal for more than a decade through their peaceful struggle, despite many difficult hurdles.
In 2015 the Supreme Court found several sections of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC) Act, including the one empowering the commissions to offer amnesty and facilitate mediation/reconciliation between victims and perpetrators, including those involved in gross human rights violations, to be unconstitutional and non compliant with Nepal’s international obligations. More recently, on 26 April 2020 the Court rejected the petitions of the Government to review and revise the 2015 decision.
To date, the Government has not initiated any effort to amend the law as per these decisions. Rather, it has been misusing these Commissions in a manner that has prevented victims from accessing remedies through the regular criminal justice system and has made no efforts to strengthen these Commissions to delivery their mandates effectively. Two years back, Nepal recognized enforced disappearance as a distinct crime for the first time when enacting a new Penal Code. While this step is commendable, these legal provisions have not ensured justice for victims, the police typically refuse to investigate cases from the conflict period,arguing that they come under the jurisdiction of the TJ mechanisms.
Despite civil society’s repeated calls to appoint the Commissioners after amending the TRC Act following wider consultations with victims and civil society, the Government recently appointed Commissioners under the same Act that the SC had deemed flawed five years ago. Moreover, the Government has not addressed the repeated calls and concerns regarding the political interference and lack of transparency in the appointment of the Commissioners and the overall TJ process.
Human rights organizations and many victims groups have lost confidence in and stopped supporting to these Commissions.
The undersigned organizations call upon the Government of Nepal:
- To ensure the Commissions provide for, rather than delay and deny, truth and justice to
victims;
- Start fresh consultations to amend its law in compliance international human rights law
and Supreme Court directives, including by removing of amnesty for the perpetrators
provisions;
- Appoint a new set of commissioners under the revised Act that respects victims basic right
to truth and justice;
- Immediately ensure the social, cultural, economic, psychological and legal support
suffered by the victims and families of enforced disappearance as part of victims’ rights
to reparation;
- Revise the Penal Code to bring it in line with international standards. As a minimum, this
should include:
- amending the definition of enforced disappearances to bring it in line with Nepal’s international obligations and the Convention on the Protection of All Persons from Enforced Disappearance
- revising the penalty for enforced disappearance in the Penal Code to make it proportionate to the gravity of the crime
- removal of the statute of limitations for enforced disappearance cases
- Ratify International Convention for the Protection of All Persons from Enforced Disappearances Punishment.
Download
Full joint-statement with detailed information in English and Nepali. (PDF)
Contact
Ian Seiderman: ICJ Legal and Policy Director, e: ian.seiderman(a)icj.org
Mandira Sharma: ICJ Senior Legal Adviser, e: mandira.sharma(a)icj.org

Aug 27, 2020 | Advocacy, News
The ICJ, in collaboration with the Zimbabwe Anti-Corruption Commission (ZACC), convened a virtual Asset Recovery Training Workshop from 18-26 August. The training was part of the ICJ efforts to advance the rule of law in Zimbabwe.
The training was held with investigators from ZACC. It was led by Dr Prosper Maguchu, a legal expert on human rights and financial crimes.
The objective of the training was to enhance the capacity of ZACC investigators to conduct financial investigations and apply asset tracing techniques in relation to corruption and money laundering cases.
Over the past 50 years, it is estimated that Africa has lost in excess of one trillion US dollars in illicit financial flows (IFFs) with claims that this is roughly equivalent to all of the official development assistance received by the continent during the same timeframe.
Zimbabwe is not immune to this challenge of IFFs.
ZACC chairperson Justice Loice Matanda-Moyo remarked that financial crimes and illicit financial flows had become a serious threat the Zimbabwe economy and beyond our borders. She pointed to the prevalence of tax evasion, smuggling, corruption, fraud, drug trafficking and money laundering and noted that ill-gotten proceeds involving money were moving across borders. In such instances it is a daunting task for investigators and asset recovery officers to follow the money trails and recover proceeds of crime. She noted that the virtual asset recovery workshop was an opportune moment time to enhance the capacity of investigators and asset recovery officers.
“This training was very timely and critical. It enhanced the capacity of ZACC in its pursuit to recover assets accumulated though corruption. The investigators were equipped with the requisite skills and techniques involved in asset recovery that include collecting evidence, issuing restraint and freezing orders and making mutual legal assistance requests. Recovering stolen assets is an important process in the fight against corruption as it deters corruption by turning it into a high-risk, low-reward activity. Additionally, asset recovery is a means to obtain resources for the development of the country, which resources can also be channelled towards strengthening the fight against corruption in Zimbabwe, thus contributing to the greater respect for the rule of law,” said ICJ Senior Legal Adviser Blessing Gorejena.
The training workshop provided a comprehensive overview on what asset recovery means, exploring approaches and tools in asset recovery and enhance the technical capacity of the investigators to trace, seize and confiscate and repatriate illicitly acquired assets.
Participants in this workshop included 18 investigative officers and two Commissioners. Overall there were 11 female and 9 male participants in attendance.
This workshop was supported by the European Union Delegation in Zimbabwe.
Contact:
Shaazia Ebrahim (ICJ media officer), c: +277 167 067 19 e: shaazia.ebrahim(a)icj.org
Vimbai Mutandwa (ICJ legal advisor), c: +263 77 351 7733 e: vimbai.mutandwa(a)icj.org










