
Apr 29, 2019 | News
On 27 and 28 April 2019, the ICJ held a workshop on “Ensuring accountability through the Specialized Criminal Chambers” in coordination with the Association des Magistrats Tunisiens (AMT).
Participants in the workshop included 28 Tunisian judges attached to the Specialized Criminal Chambers (SCC).
The workshop aimed to reinforce the capacity of SCC judges to effectively exercise their role in adjudicating crimes under international law, in line with international law and standards.
ICJ legal advisers and Tunisian experts gave presentations on State the obligations of State actors to respect and apply international law, the legal framework governing the application of international law in Tunisia, and the principle of legality and statutory limitations to crimes under international law. They also spoke on the international and domestic definitions of crimes under international law and modes of liability.
Through working group and plenary sessions, the participants discussed options for applying international law and standards at the national level.
Expert speakers included Judge Brahim Weslati, Judge Radhouane Werthy and Imen Soussi.

Apr 25, 2019 | News
The statement alerts the public of the danger of a bill which dismantles the specialized criminal chambers in Tunisia and replaces them with an institution which would guarantee impunity for those who committed gross violations of human rights in Tunisia between 1955 and 2013.
The statement has been signed by the ICJ as well as other members of the Coalition for Transitional Justice
The statement can be downloaded here:
Link to French Version
Link to Arabic Version

Apr 24, 2019 | News
Egypt is hosting an Africa human rights summit meeting beginning April 24, 2019, while its government is presiding over the worst human rights crisis in the country in recent decades.
The 64th Ordinary Session of the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights (ACHPR), the African Union’s top rights body, will take place from April 24 to May 14 in Sharm al-Sheikh.
In addition to its systematic failure to respect and protect human rights at home, Egypt has also led efforts to undermine the Commission’s independence. The Commission should strongly raise Egypt’s human rights abuses at the meeting.
“Egypt is trying to appear like a country open for human rights delegates and summits while, at the same time, crushing all dissenting voices and its once-vibrant human rights community,” said Michael page, Middle East and North Africa director at Human Rights Watch.
“We know that many Egyptian and international organizations are not allowed to work freely in Egypt and cannot voice concerns without severe retaliation from the government,” he added.
The commission should ensure that all government and non-government delegations are able to participate freely in the summit. It should also make clear that it will strongly address any measures of reprisals by the Egyptian authorities against criticism of its practices.
A senior staff member of a leading Egyptian rights organization told Human Rights Watch that only three Egyptian human rights groups were considering participating in the summit because most of the groups were concerned about retaliation by the government.
In recent years, the Egyptian authorities have relentlessly cracked down on non-governmental organizations, issued the 2017 draconian law that effectively bans all independent work by nongovernmental groups, and prosecuted scores of staff workers of Egyptian organizations.
It has also frozen the assets of the most prominent human rights defenders in the country and their organizations and issued travel bans against scores of them.
In April 2018, the government said it would repeal the abusive 2017 NGO law but the government has not made a new draft law public.
The Egyptian authorities have also taken reprisals against human rights defenders and activists for cooperating with regional and international human rights monitors, including United Nations agencies and experts.
In late 2018, Egyptian authorities detained several citizens who met with the UN special rapporteur on adequate housing during her official mission to Egypt, as well as demolishing their houses and banning their travel. The government denied any wrongdoing and accused the UN High commissioner on human rights and other UN officials of breaching UN standards and adopting the “lies” of “terrorist” organizations.
In September 2017, officials stopped Ibrahim Metwally, a lawyer and co-founder of the Associations of the Families of the Disappeared, from traveling for meetings with UN officials in Geneva. Security agencies arrested him at the airport and held him incommunicado for a few days. He is still held in “pretrial detention” for farcical charges.
The Egyptian government has tried to undermine the independence of the Commission through spearheading the adoption of African Union’s Executive Council’s Decision 1015, paragraph 5. The provision, which was passed in June 2018, undermines the Commission’s independence by subjecting its work to control by the African Union member countries.
The Egyptian government has ignored decisions and resolutions the Commission and its experts have made addressing several violations and abuses including the crackdown on civil society, restrictions on freedom of religion, unfair trials and mass death sentences, arbitrary arrests, and sexual violence.
The ACHPR session comes at a time when the Egyptian authorities have been severely oppressing dissent and obliterating any space for peaceful expression or gathering before the public vote held between April 19-22 on highly draconian constitutional amendments that will strengthen the military control of public and political life and further undermine the already weak judicial independence.
Egyptian human rights organization have documented the arrests of over 160 people, often in mass arrests, since February in relation to the ongoing crackdown on dissidents and perceived critics.
These amendments, and several other laws that President Abdel Fattah al-Sisi has approved in recent years, such as new media laws and laws to expand the use of military courts to try civilians, violate international law standards including the African Charter on Human and Peoples’ Rights.
Since al-Sisi secured a second term in elections that were largely neither free nor fair in March 2018, his security forces have escalated a campaign of intimidation, violence, and arbitrary arrests against political opponents, activists, and many others who have voiced even mild criticism of the government.
The Egyptian government and state media have framed this repression under the guise of combating terrorism, and al-Sisi has increasingly invoked terrorism and the country’s state of emergency law to silence peaceful activists.
In July 2013, the African Union Peace and Security Council suspended Egypt’s membership in all African Union activities following the forcible removal of former President Mohamed Morsy by the army, which was led by al-Sisi, then the defense minister. The suspension ended after al-Sisi was elected President in June 2014.
But Egypt has failed to effectively investigate or to hold any official or member of the security forces accountable for the mass killings of protesters in the summer of 2013 despite several national and international calls, including by the ACHPR, and despite incriminating evidence.
In August 2013, Egyptian security forces most likely killed at least 817 people in a few hours during its violent dispersal of the largely peaceful pro-Morsy sit-in in Cairo’s Raba’ Square. The killings likely amounted to crimes against humanity.
“Through such summits, Egypt is trying to whitewash its dire record of abuses,” George Kegoro, executive director of Kenya Human Rights Commission said. “The African human rights commission should take the opportunity of this meeting to vigorously engage the Egypt government on its own actions that threaten the rights, and the very lives, of many Egyptians.”
The co-signing organizations are:
Andalus Institute for Tolerance and Anti-Violence Studies
Belady Center for Rights and Freedoms
Cairo Institute for Human Rights Studies
Committee for Justice|
EuroMed Rights
Egyptian Front for Human Rights
Human Rights Watch
Kenya Human Rights Commission
The Egyptian Commission for Rights and Freedoms
The Freedom Initiative
The International Commission of Jurists
Egypt-African Rights Summit-News-2019-ARA (Press release, PDF, Arabic)
Contact:
Said Benarbia, Director of ICJ’s MENA Programme, t: +41-79-878-35-46 ; e: said.benarbia(a)icj.org

Apr 10, 2019 | News
Today, the ICJ called on the parties to the conflict in Libya to comply with their obligations under international humanitarian law (IHL) and international human rights law to protect affected people, particularly the civilian population.
The ICJ also called on the UN Security Council to urge the parties to respect international law.
The gravity of hostilities led UNSMIL to postpone the UN-sponsored Libyan National Conference aimed at finding a solution to the ongoing political deadlock late yesterday. The Conference was planned to commence on 14 April in Ghadames.
“The postponement of the political dialogue is a major setback for peace and the rule of law in Libya, and for the Libyan population,” said Kate Vigneswaran, the ICJ’s Senior Legal Advisor for the Middle East and North Africa Programme.
“Civilians taking no part in the fighting have already suffered the brunt of hostilities between the warring parties in Libya. Those who remain, including the thousands of migrants held in arbitrary detention, are at grave risk,” she added.
IHL requires parties to the conflict to respect the principles of distinction and proportionality and take precautionary measures to avoid, or in any event minimize, incidental loss of civilian life, injury to civilians and damage to civilian objects.
“The parties must ensure that not only civilians but civilian objects are protected, and that measures are taken to ensure they don’t become collateral casualties,” said Kate Vigneswaran.
“International actors should continue to push for a political solution to the situation in Libya based on the rule of law and incorporating human rights protections to avoid further suffering,” she added.
On April 7, the UN Security Council reportedly discussed the situation in Libya but could not find the necessary consensus to issue an official statement.
According to the AFP, the Russian Federation blocked a statement that would have called on Field Marshall Khalifa Haftar, head of the House of Representatives backed Libyan National Army, to stop military operations, on all the parties to de-escalate and for “those who undermine Libya’s peace and security to be held to account.”
“The Security Council should adopt a resolution calling for the protection of civilians and accountability for serious violations of international human rights and humanitarian law. Member States should desist from exercising their veto powers to block resolutions intended to ensure compliance with international law,” said Vigneswaran.
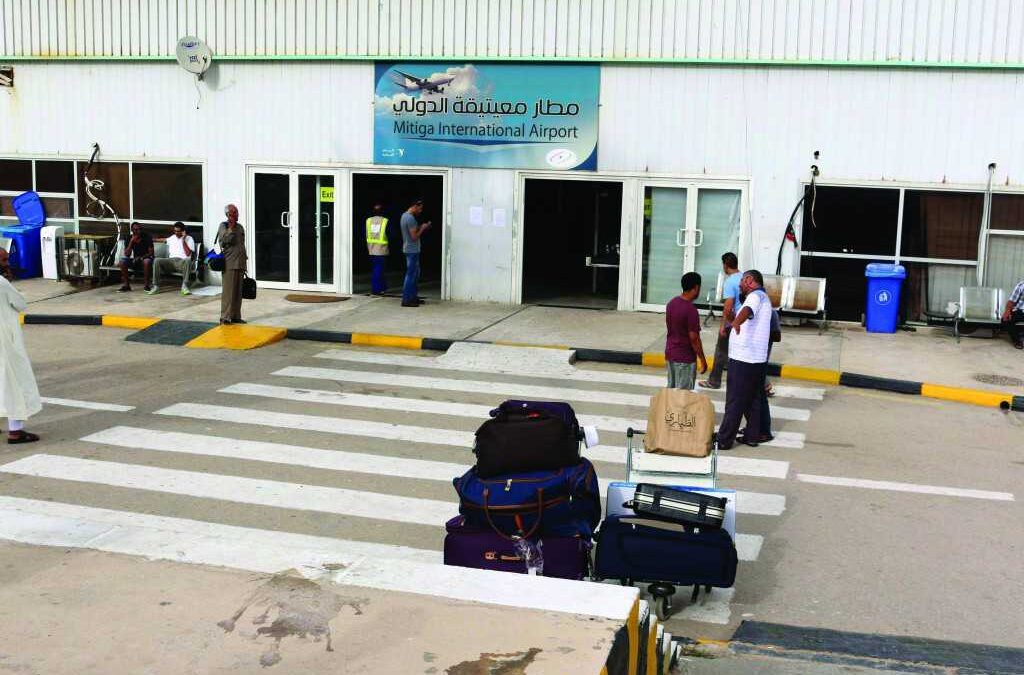
Reportedly, at least 27 people have been killed, including two doctors and two other civilians, 80 have been injured, and more than 2,800 persons have been displaced as a result of the fighting. The only functioning airport in Tripoli (above photo), the hub of the fighting, was closed Monday after being hit by an airstrike by the Libyan National Army (LNA).
Read this article in Arabic
Contact:
Kate Vigneswaran, ICJ Senior Legal Adviser, t: +31624894664, e: kate.vigneswaran(a)icj.org
Mar 29, 2019 | News
As leaders gather for the League of Arab States (LAS) Summit beginning on 31 March 2019 in Tunis, the ICJ called on them to place human rights and accountability for violations at the forefront of their agenda.
In particular, the ICJ urged the Summit to take immediate steps to revise the Statute of the Arab Court of Human Rights in line with international standards to allow access by victims of human rights violations in the region to such a Court.
“We’ve been witnessing a spike in gross human rights violations across the Arab region, including in extrajudicial executions, enforced disappearances, arbitrary detentions, and torture and other ill-treatment,” said Said Benarbia, the ICJ’s MENA Programme Director.
“The region is in dire need of a credible and independent judicial mechanism to provide justice for human rights violations, the overwhelming majority of which presently go unaddressed,” he added.
The ICJ called on external participants to prioritize human rights in their discussions with League member States at the Summit.
Expected attendees include United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres, the European Union High Representative for Foreign Affairs and Security Federica Mogherini, the Head of the African Union Commission Moussa Faki Mahamat, and the Secretary General of the Organization of Islamic Cooperation Yousef bin Abdul Al-Othaimeen.
Many States in the region are plagued by widespread and systematic violations.
These range from torture, enforced disappearance and arbitrary detentions in Egypt, attacks against human rights defenders and journalists in Saudi Arabia, including the high profile enforced disappearance and killing of Saudi journalist Jamal Khasshogi, as well as the judicial harassment of human rights defenders and political activists throughout the region.
Civilian populations have borne the brunt of violations and crimes through military operations by governments and armed groups in Yemen, Syria and Libya, and in the context of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
“International leaders mustn’t sit back and follow the agendas of rights-violating States at this Summit, which will no doubt be directed towards further entrenchment of their authoritarian regimes at the expense of victims,” said Benarbia.
“Instead, they should urge LAS members States to ensure accountability for human rights violations in the region, including by revising and then making operational the Statute of the Arab Court,” he added.
The ICJ said that the process of revision should only be done with the participation of a wide range of stakeholders, civil society, judges, academics, bar associations, and victims of violations.
Contact:
Said Benarbia, Director of the ICJ Middle East and North Africa Programme, t: +41-22-979-3817; e: said.benarbia(a)icj.org
Background
The Statute of the Arab Court of Human Rights, which aims to establish a regional human rights court for Arab States, was approved by the LAS Ministerial Council on 7 September 2014, but is yet to come into force.
The ICJ and others have identified significant flaws in the Statute, highlighted in the 2014 ICJ report. The report notes that the Statute does not allow victims themselves to submit complaints directly to the Court, making access to justice an illusion. In addition, the Statute does not provide for sufficient guarantees to ensure judicial independence and impartiality; does not provide adequate protective measures for petitioners, their representatives or witnesses; and fails to require the Court to interpret the Arab Charter in line with international human rights obligations.
MENA-Arab Court HR-News-2019-ARA (full story in Arabic, PDF)

Mar 22, 2019 | News
The ICJ today strongly welcomed the renewal of the key UN expert on counter-terrorism and human rights, on terms that maintain the mandate’s independence, integrity and its essential focus on human rights.
The renewal of the mandate of the Special Rapporteur on the promotion and protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms while countering terrorism, was enacted by a resolution adopted by consensus at the UN Human Rights Council in Geneva.
To acheive this successful outcome, Mexico (which leads the resolution) and other States had to defend the text of the resolution against attempts by Egypt and other States to insert language aimed at diluting, distorting or distracting the mandate from its current focus on preventing and responding to violations of human rights and on securing respect, protection and fulfilment of the human rights of victims of terrorism.
The Special Rapporteur delivers thematic reports to the Human Rights Council, carries out visits to countries, and acts on individual complaints. In the overall counter-terrorism architecture of the UN, the Special Rapporteur is also the only person with an exclusive independent mandate to remind States of their human rights obligations while countering terrorism, to advise them how to do so, and to draw public attention when they do not. So any dilution of the mandate would have also put the integrity and efficacy of the overall UN counter-terrorism strategy and architecture at risk.
Following the adoption of the mandate renewal resolution by the Council, the ICJ and other organisations expressed its deep appreciation for Mexico’s efforts, together with the strong support of numerous other States, to secure the future of the mandate.
The resolution text is available here: https://undocs.org/A/HRC/RES/40/16
Additional background is here.










