Mar 4, 2013 | News
The ICJ expressed its concern over the criminal trial of 94 individuals, including judges, lawyers, academics, human rights defenders and civil society activists, in the State Security Chamber of the UAE Federal Supreme Court.
Following a wave of arbitrary arrests and detention, which began in March 2012, the case was referred to the Supreme Court on 27 January 2013.
“The ICJ is gravely concerned over the fairness of the upcoming proceedings, including the lack of any right of appeal, the lack of restrictions on the use of evidence obtained through torture or ill-treatment and severe restrictions imposed on the rights of the defence, in contravention of international human rights law, including the Arab Charter on Human Rights, to which the UAE is a party,” said Said Benarbia, ICJ Senior Legal Adviser of the Middle East and North Africa Programme. “Furthermore, allegations of torture and ill-treatment by detainees, including incommunicado detention, prolonged solitary confinement, sleep deprivation and verbal and physical abuse, must be promptly, impartially and thoroughly investigated.”
The ICJ further notes that there have been violations of international fair standards.
These include the failure of State authorities to formally charge defendants, severe restrictions on access to legal counsel, including during questioning and the failure to disclose case files to the defence until a few days before trial.
Until two weeks before the trial, there was a single lawyer acting for all detainees and other lawyers who tried to assist have faced harassment, including detention and deportation, the ICJ says.
The trial is part of a broader crackdown by the UAE authorities in response to a petition signed by 100 academics, legal professionals, and civil society activists, in March 2011, for political reforms and increased public participation in government.
“The ICJ condemns the use of criminal proceedings to suppress peaceful calls for increased democracy as an unlawful restriction on the right to freedom of expression,” Benarbia added. “Extending the clampdown on critics to include numerous members of the legal profession severely compromises the Rule of Law in the UAE.”
Contact:
Said Benarbia, ICJ Senior Legal Adviser of the Middle East and North Africa Programme, tel: 41 22 979 38 17, e-mail: said.benarbia(at)icj.org

Nov 23, 2012 | News
 The ICJ expressed its grave concerns regarding the new Constitutional Declaration issued by President Mohamed Morsi on 22 November.
The ICJ expressed its grave concerns regarding the new Constitutional Declaration issued by President Mohamed Morsi on 22 November.
The President’s unilateral imposition of a constitutional framework on the Egyptian people, under which Constitutional Declarations, decisions, laws and acts taken by the President are shielded from any judicial review, undermines basic rule of law principles.
“Rather than establishing the rule of law and meeting the democratic aspirations of the Egyptian people, President Morsi perpetuates the practices of the old regime by denying the rights of Egyptians to fully participate in the conduct of public affairs and to challenge executive decisions and actions”, said Said Benarbia, ICJ Senior Legal Advisor for the MENA Programme. “The Egyptian authorities must change course to ensure that the new Constitution is in line with international rule of law and human rights principles, and that the drafting and adoption process is transparent and inclusive.”
Under the Declaration, the President has arrogated to himself sweeping powers “to protect the goals of the revolution, including by tearing down the structure of the former regime, excluding its symbols in the state, society and the judiciary, and purging the Sate institutions”. All decisions taken by the President, since he took office and until a new Constitution is adopted and a People’s Assembly is elected, are characterized as “final and binding and cannot be appealed by any way or to any entity. Nor shall they be suspended or cancelled and all lawsuits related to them and brought before any judicial body against these decisions are annulled”.
The ICJ also expresses its concern about the impact of the new Constitutional Declaration and the decision of President Morsi to dismiss the Prosecutor General on the independence of the judiciary.
Under international standards, all disciplinary, suspension or removal proceedings against members of the judiciary must be determined in accordance with well-established procedures that guarantee the right to a fair and transparent hearing and to an independent review.
Only an independent body can ensure the fairness of these proceedings, the ICJ stresses.
In a report published last week, the ICJ described how the Egyptian authorities have failed to ensure the drafting of a new Constitution in compliance with international principles of inclusive participation and transparency. The report concludes that the draft Constitution conflicts with Egypt’s obligations under international human rights law.
Contact:
Saïd Benarbia, Middle East & North Africa Senior Legal Adviser, ICJ, t +41 22 979 3817; e-mail: said.benarbia(at)icj.org
Alice Goodenough, Middle East & North Africa Legal Adviser, ICJ, t +41 22 979 3811; e-mail: alice.goodenough(at)icj.org

Nov 20, 2012 | News
The ICJ today called on the Israeli authorities to immediately end their military attacks in the Gaza Strip.

Nov 13, 2012 | News, Publications, Reports
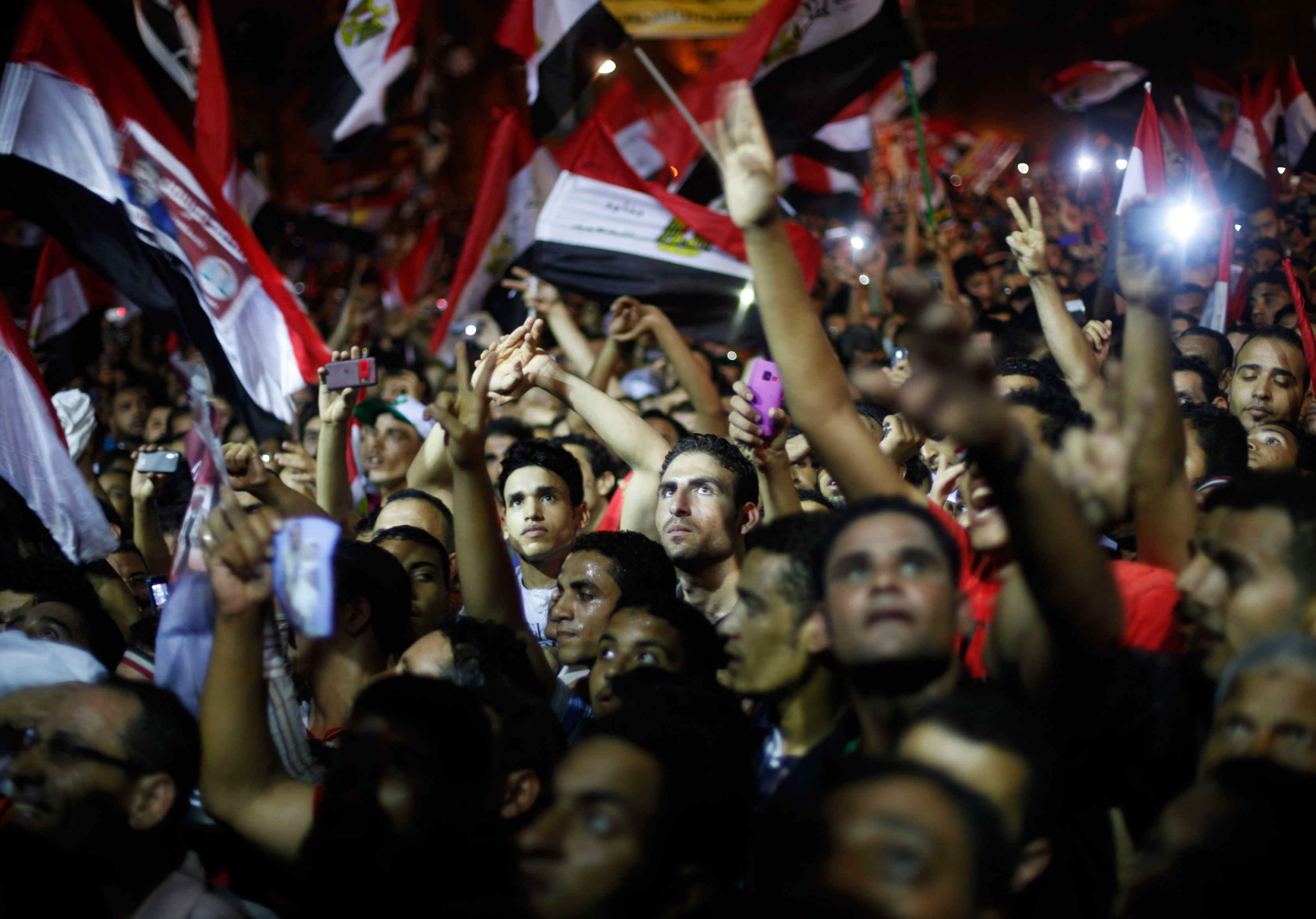 A new ICJ report shows that the constitutional reform process in Egypt has failed to meet international principles of inclusive participation and transparency, thereby undermining the transition to democracy.
A new ICJ report shows that the constitutional reform process in Egypt has failed to meet international principles of inclusive participation and transparency, thereby undermining the transition to democracy.
“The Egyptian authorities, including the Constituent Assembly, have failed so far to meet the aspirations of the Egyptian people to adopt a Constitution that establishes the rule of law, recognizes and protects universally accepted human rights without restriction, guarantees the independence of the judiciary in all circumstances, and ensures the effectiveness of democratic institutions,” said Wilder Tayler, ICJ Secretary General.
The ICJ is calling upon the Egyptian authorities to address the challenges currently facing the constitutional reform process, as a matter of urgency; ensure that this process is in full compliance with international standards of inclusive participation and transparency; and guarantee that the new Constitution fully conforms with the rule of law and international law, including human rights standards.
The ICJ report Egypt’s new Constitution: a flawed process; uncertain outcomes details how, in overseeing the process leading to the adoption of a new Constitution, the Supreme Council of Armed Forces (SCAF) failed to ensure the rights of Egyptians to take part in public affairs and to meaningfully participate in the drafting and adoption of a new Constitution.
“Instead of paving the way for a clear and participatory reform process, the SCAF consistently opted for opaque, rushed and non-consensual policies that aimed to shield the armed forces from any form of accountability and that have severely undermined both the legitimacy of the process itself and its outcomes,” Tayler added.
Even though the administration of President Morsi replaced the SCAF on 30 June 2012, the constitution-making process continues to be carried out under the legal framework enacted by the SCAF.
The report also describes how several judicial decisions, in particular the dissolution of the first Constituent Assembly, by a decision from the High Administrative Court, and the dissolution of the People’s Assembly, following a decision by the Supreme Constitutional Court, have contributed to the confusion and uncertainty regarding the drafting of a new constitution.
As a result of this confused process, the draft of the new Constitution, published by the Constituent Assembly on 14 October 2012, has failed to provide for effective guarantees to reinforce the protection of human rights and the supremacy of the rule of law, including by ensuring that the powers of the State are not exercised arbitrarily.
“The draft Constitution does not sufficiently incorporate the rule of law and international law, including human rights standards. This is particularly evident as regards the accountability of the armed forces and their subordination to a legally constituted civilian authority, the content and scope of constitutional human rights, and the compliance of the whole judicial system, including the Office of the Public Prosecutor and the Constitutional Court, with international standards of independence, impartiality and accountability,” said Said Benarbia, ICJ Senior Legal Adviser for the MENA programme.
The report sets out urgent institutional and legal reforms that, together with sufficient political will, may help ensure a clean break with the practices and policies of Mubarak’s regime and the transition to a genuine democracy in Egypt.
Contact:
Saïd Benarbia, Middle East & North Africa Senior Legal Adviser, ICJ, t +41 22 979 3817; e-mail: said.benarbia(at)icj.org
Alice Goodenough, Middle East & North Africa Legal Adviser, ICJ, t +41 22 979 3811; e-mail: alice.goodenough(at)icj.org
Egypt-Flawed constitutional reform process-report-2012
Photo by Reuters
Sep 29, 2012 | News
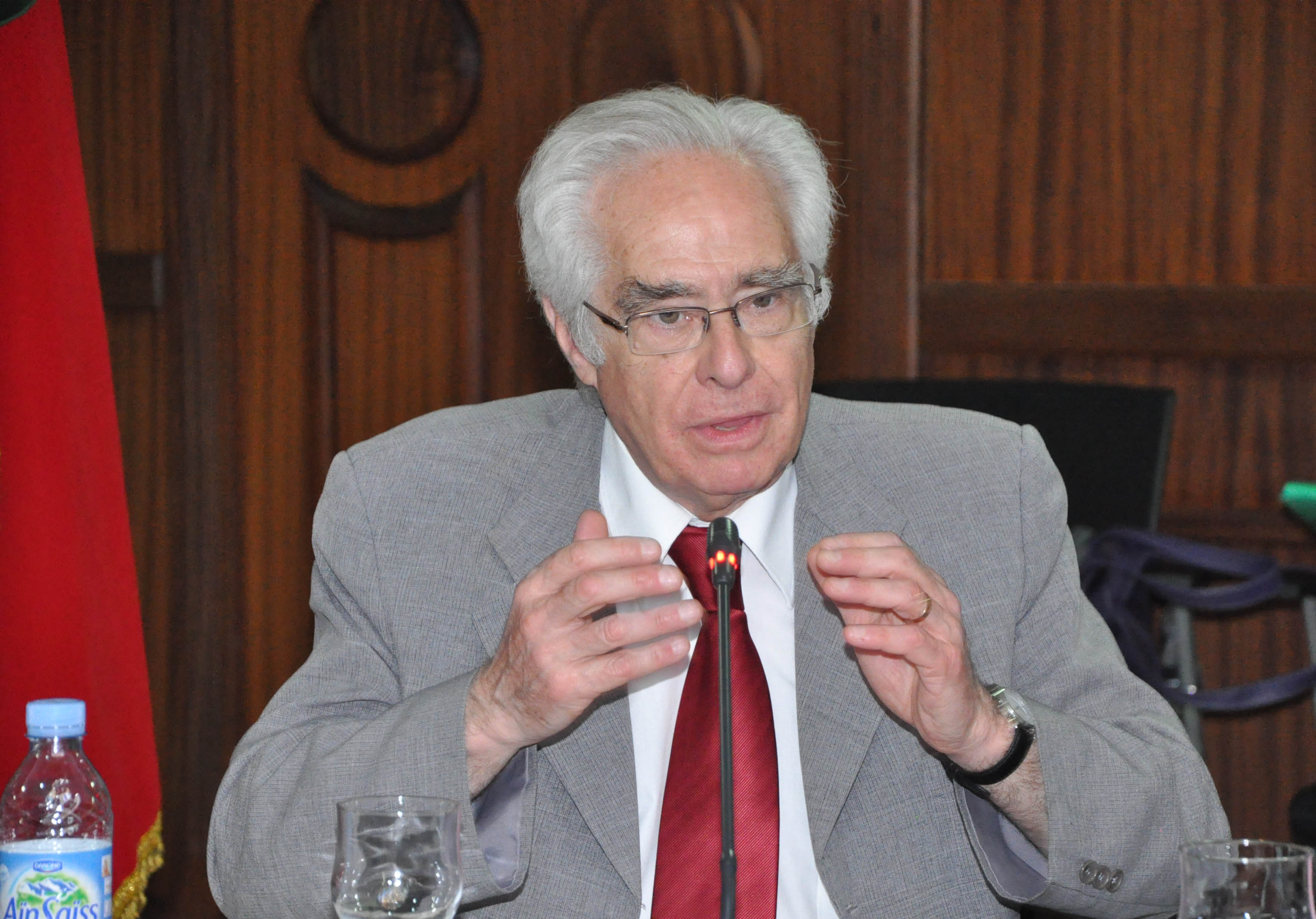 During three days, from September 26 to 28, 2012 in Rabat, the ICJ ESCR Programme and the MENA Regional Programme organized two events in collaboration with the OMDH (Organisation Marocaine des Droits Humains).
During three days, from September 26 to 28, 2012 in Rabat, the ICJ ESCR Programme and the MENA Regional Programme organized two events in collaboration with the OMDH (Organisation Marocaine des Droits Humains).
ICJ Commissioner Mr. Roberto Garreton supported the three-day programme. The first two days were dedicated to a workshop gathering 30 representatives of human rights NGOs, service providers, consumer protection groups, lawyers and academic experts.
The participants were trained and had discussions on the opportunities, the challenges and the remedies that the Moroccan legal and institutional framework offers to individuals and groups seeking justice for violations.
Discussions also concerned the legal reforms undertaken in the country and how they will impact the ability for victims of human rights violations to access justice.
The participants particularly welcomed the workshop setting and focus that brought together a variety of groups working in relevant areas.
On the third day, 28 September 2012, a symposium attended by civil society actors, lawyers and academia as well as by members of the judiciary and of the Conseil National des Droits de l’Homme was the opportunity to discuss the role of judges in the realization of economic, social and cultural rights.
The two events are part of a project that will involve further research and consultation on access to justice for ESCR in close collaboration with national civil society.
Background of the Workshop
With national projects such as the one in El Salvador, the ICJ programme on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights aims at contributing to improve accountability for human rights violations and access to justice for all, including for victims of threats against and violations of economic, social and cultural rights.
The ICJ has embarked on research processes at national level to identify obstacles and opportunities for access to justice, as well as on consultation and collaboration processes with national allies to define strategies to address gaps.
Depending on the needs identified, the ICJ will support the implementation of recommendations and steps that includes trainings and legal interventions.












