Nov 19, 2020 | News
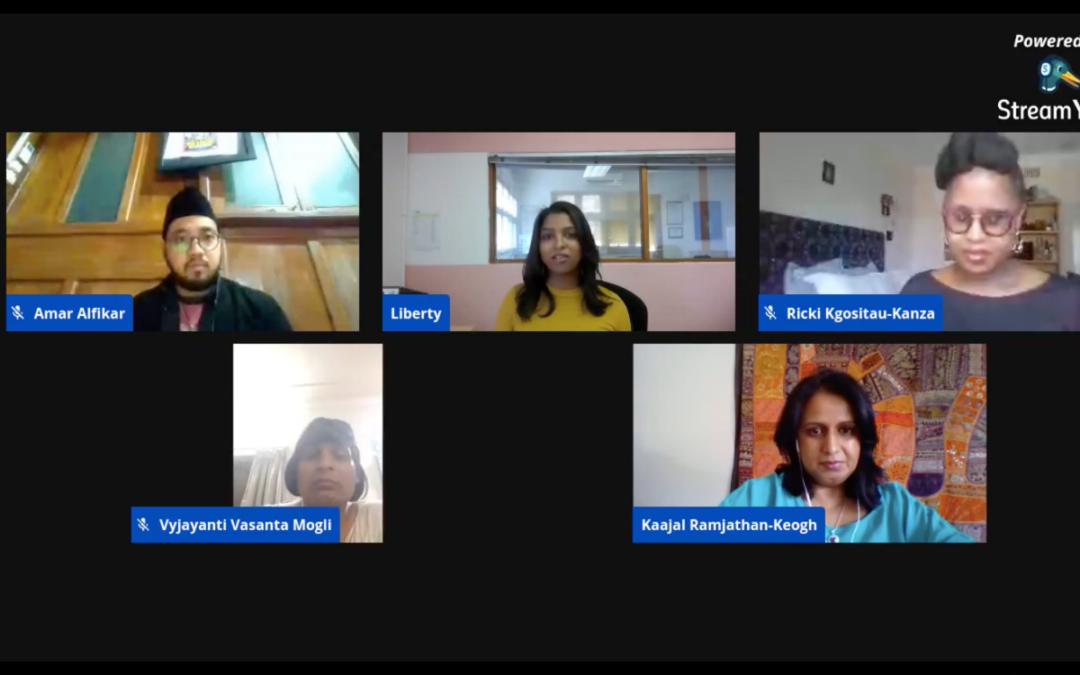
On 18 November 2020, the ICJ hosted a Facebook Live with four transgender human rights activists from Asia and Africa. It highlighted the stark reality between progressive laws and violent lived realities of transgender people.
The 20th November 2020 marks the Transgender Day of Remembrance (TDOR), the day when transgender and gender diverse people who have lost their lives to hate crime, transphobia and targeted violence are remembered, commemorated and memorialized.
The discussions focused on their individual experiences of Transgender Day of Remembrance in their local contexts, the impact of COVID-19 on transgender communities and whether laws are enough to protect and enforce the human rights of transgender and gender diverse people.
The renowned panelists were from four different countries, Amar Alfikar from Indonesia, Liberty Matthyse from South Africa, Tshepo Ricki Kgositau-Kanza from Botswana and Vyjayanti Vasanta Mogli from India. The panel was moderated by the ICJ Africa Regional Director, Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh.
The panel aimed to provide quick glimpses into different regional contexts and a platform for transgender human rights activists’ voices on the meaning of Transgender Day of Remembrance and the varied and devastating impacts of COVID-19 on transgender people.
The speakers discussed the meaning that they individually ascribe to Transgender Day of Remembrance. A common theme running across the conversations was that it is not enough to highlight issues and concerns of the transgender community only on this day. Instead, these discussions should be part of daily conversations about the human rights of transgender people at the local and international level.
Liberty Matthyse discussed the importance of remembering the transgender persons who have lost their lives over the past years, and added:
“South Africa generally is known as a country which has become quite friendly to LGBTI people more broadly and this, of course, stands in stark contradiction to the lived realities of people on the ground as we navigate a society that is excessively violent towards transgender persons and gay people more broadly.”
Amar Alfikar describes his work as “Queering Faiths in Indonesia”. This informs his understanding of what Transgender Day of Remembrance means in his country and he believes that:
“Religion should be a source of humanity and justice. It should be a space where people are safe, not the opposite. When the community and society do not accept queer people, religion should start giving the message, shifting the way of thinking and the way of narrating, to be more accepting, to be more embracing.”
It was clear from the discussions that a lot of the issues that have become prominent during the COVID-19 pandemic, have not arisen due to the pandemic. In fact, the COVID-19 pandemic has had the effect of a magnifying glass, amplifying existing challenges in the way that transgender communities are treated and driven to margins of society. Speaking about the intersectionality of transgender human rights, Vyjayanti Vasanta Mogli said:
“I don’t think LGBT rights or transgender rights exist in isolation, they are part of a larger gamut of climate change, racial equality, gender equality, the elimination of plastics, and all of that.”
The panelists had different opinions on whether it is enough to rely on the law for the recognition and protection of the human rights of transgender individuals.
The common denominator, however, was that the laws as they stand have a long way to go before fully giving effect to the right of equality before the law and equal protection of the law without discrimination of transgender people.
Tshepo Ricki Kgositau-Kanza, who was a litigant in a landmark case in Botswana in which the judiciary upheld the right of transgender persons to have their gender marker changed on national identity documents, explained the challenges with policies which, on their face, seem uniform:
“Uniform policies… are very violent experiences for transgender persons in a Botswana context where the uniform application of laws and policies is binary and arbitrarily assigned based on one’s sex marker on one’s identity document which reflects them either as male or female. Anybody in between or outside of that kind of dichotomy is often rendered invisible and vulnerable to a system that can easily abuse them.”
This conversation can be viewed here.
Contact
Tanveer Jeewa, Communications Officer, African Regional Programme, e: tanveer.jeewa(a)icj.org

Oct 30, 2020 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The Gauteng Township Economic Development Bill aims to promote local economic development in designated townships by creating and facilitating the creation of viable township businesses. The Bill establishes a Development Fund whose economic benefits and incentives are strictly reserved for citizens and permanent residents only.
The Bill would prohibit most non-citizens from large swathes of economic activity.
“This would include documented non-citizens like asylum seekers and refugees most of whom are not eligible for social assistance. It might prevent many non-citizens from making a living and could leave many destitute and homeless,” the ICJ Africa Director Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh said.
“The Bill might also fuel existing xenophobic sentiment and could result in recurrences of xenophobic violence. Courts in South Africa have repeatedly warned government officials and departments against conduct that risks perpetuating xenophobia.”
If this Bill were to be enacted, South Africa would fall short of its requirements under both national and international law.
The ICJ has thus submitted their comments to the Gauteng Provincial Government, which you can find below.
Watch the animation on this issue
Oct 23, 2020 | News
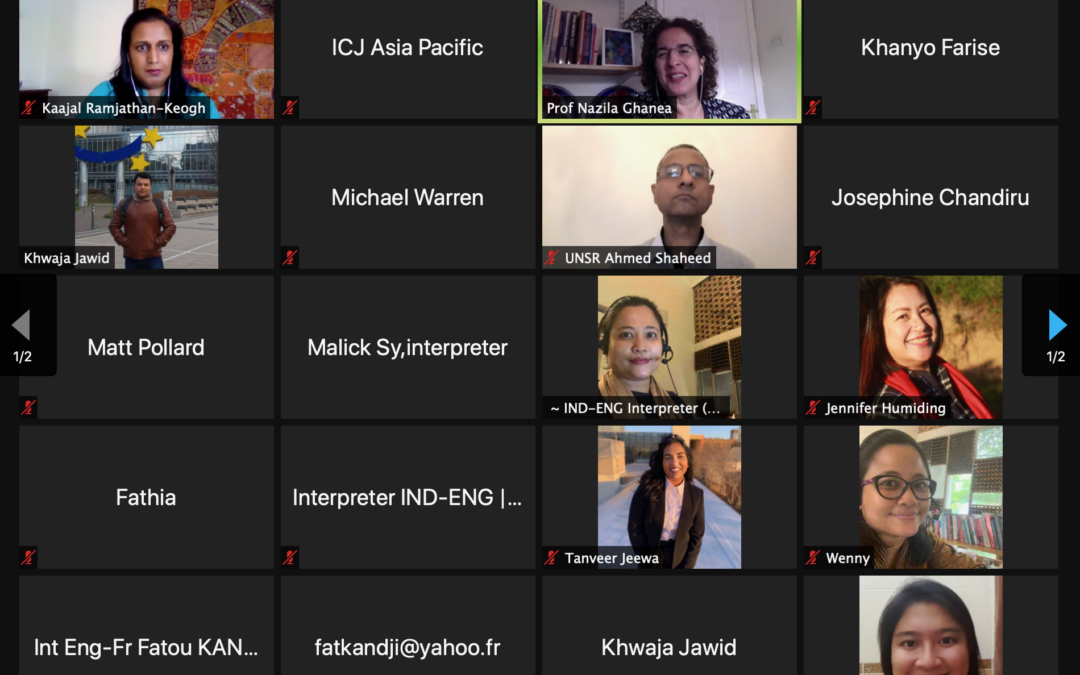
On 21 and 22 October, the ICJ and Cordaid held a webinar series aimed at tackling the challenges of protecting and promoting women’s human rights and access to justice for women in the context of religious and customary laws in operation around the world.
At its global 2019 Congress in Tunis, the ICJ identified the problem, concluding that: “Worldwide, increasing attacks on the rule of law have intensified longstanding inequalities and compounded intersecting forms of discrimination against women and girls and persons from marginalized groups. This has limited their enjoyment of human rights and their effective access to justice. Moreover, in many countries, culture, tradition, or religion are being used to justify laws, policies and practices that discriminate against women and girls.”
In light of the obstacles for women, the ICJ together with Cordaid created this webinar platform for an exchange of views and strategies among human rights defenders, justice sector actors and those from the religious community. Participants came from Asia, the Middle East and Africa. Webinar 1 addressed the ways in which custom and religion shape the ability of women to access justice. The meeting also grappled with the perceived clashes between women’s human rights and pathways to justice based on custom and religion.
“Custom and religious preferences are not superior to women’s rights, they operate simultaneously,” said Nazila Ghanea, Associate Professor in International Human Rights Law at the University of Oxford.
Speakers included Professor Nazila Ghanea, Clara Rita Padilla, a lawyer from the Philippines with experience on women’s sexual and reproductive rights, Josephine Chandiru, Executive Director of Stewardwomen from South Sudan, and Claudine Tsongo, Director of Dynamique des Femmes Juristes. They focused on practical subjects, including the persistence of certain religious and cultural practices which have the potential to negatively affect women’s ability to defend their human rights. The session was moderated by ICJ Africa’s director, Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh.
Webinar 2, moderated by ICJ Commissioner and CEDAW Committee Member, Nahla Haidar, discussed obligations under international human rights law and best practice to ensure access to justice in cultural and religious contexts.
UN Special Rapporteur on Freedom of Religion or belief, Professor Ahmed Shaheed explained that “custom and religious law are, in some countries, used as cover to discriminate against women or to stop them from getting justice. These are not issues which are only present in the global south, they are rampant globally.”
Participants discussed practical measures which could be adopted by States, international organizations and civil society, to eliminate practices which exacerbate women’s inequality. In this regard, Shareena Sheriff from Sisters in Islam based in Malaysia, shared her experience on how they successfully embarked on advocacy to eliminate the harmful practice of Female Genital Mutilation in her country. She explained how Sisters in Islam worked closely with various stakeholders including community members, religious and justice actors to raise awareness on this issue.
Many speakers endorsed the importance of creating platforms such as the webinar to allow different voices from around the world to contribute their experience so as to learn from one another.
Contact
Nokukhanya (Khanyo) Farisè, Legal Adviser (Africa Regional Programme), e: nokukhanya.farise(a)icj.org
Tanveer Jeewa, Communications Officer (Africa Regional Programme), e: tanveer.jeewa(a)icj.org
Watch
The first webinar is available here.
The second webinar is available here.
Read
The report on the Tunis Declaration is available here.
Cordaid, Diverse Pathways to Justice for all: Supporting everyday justice providers to achieve SDG16.3, September 2019, available here.
Download
Universal-ICJ The Tunis Declaration-Advocacy-2019-ENG (the Tunis Declaration, in PDF)
Universal-ICJ Congresses-Publications-Reports-2019-ENG (the ICJ Congresses booklet, in PDF)

Jul 31, 2020 | Advocacy, Open letters
The ICJ and the South African Human Rights Defenders Network (SAHRDN) have written to the United Nations Special Rapporteur on the Situation of Human Rights Defenders, the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights Special Rapporteur on Human Rights Defenders, and the Chairperson of African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights.
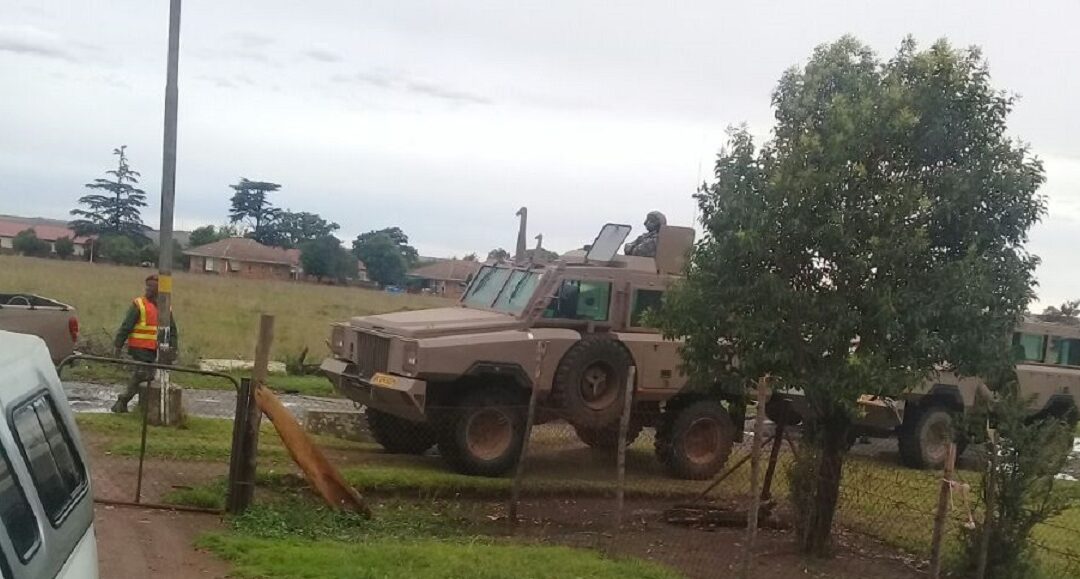
They have detailed the continued intimidation and harassment of the residents of Happiness village by the South African National Defence Force (SANDF).
“We have written to the Special Rapporteurs because the SANDF is unrelenting in its abuse of the resident’s despite the best efforts of their legal representatives and repeated court orders,” said ICJ Legal Adviser in South Africa Tim Fish Hodgson.
“A community leader was placed under house arrest guarded by four soldiers for seven days. Another resident was subjected to a punishment by which was told to lie flat on the ground and ‘pray to his God’ for simply leaving his home. Others have been assaulted. The SANDF deliberately conducts military exercises near the residents’ homes late at night to scare and intimidate them. All this with utter disregard for the law and in direct violation of a number of court judgments and orders”, he added.
The residents, who were forcibly and violently evicted from Marievale military base beginning in 2017, have repeatedly been granted court orders by the High Court declaring such evictions unlawful and directing the SANDF to refrain from harassing, threatening and intimidating the residents and not to restrict their movement.
Despite this, and in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic, further evictions and constant harassment and intimidation continues unabated and has intensified to a point that the residents describe the SANDF as having “laid siege” to their homes in Happiness Village which is adjacent to Marievale military base.
Soldiers now police checkpoints, preventing visitors from entering the area and even journalists have been prevented from entering Happiness Village. The residents’ legal representatives were only allowed to visit a single community representative under armed military guard.
As the letter reveals, the SANDF’s actions amount to violations of the residents’ right to adequate housing protection in terms of the South African Constitution, the African Charter on Human and People’s Rights and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights.
The intimidation, harassment, humiliation and assault of the residents’ amount to violations of the residents’ rights to liberty and security of person and may also amount to cruel, inhumane and degrading treatment or punishment in violation of the South African Constitution and international human rights law.
They seem to be geared at making the resident’s lives intolerable in order to secure evictions “through the backdoor”, which is explicitly prohibited in South African law.
The residents, represented by Lawyers for Human Rights, will once again be in urgent court on July 31 seeking an interdict to prevent further harassment, intimidation and restrictions on their movement by the SANDF. The legal representatives of the SANDF have indicated that they intend to oppose their application.
The ICJ has therefore implored the Special Rapporteurs to:
1. Call on the SANDF, the Minister of Defence and Military Veterans and on the Ekurhuleni Municipality to desist from any further evictions, relocation, intimidation, harassment, humiliation, and assault of the Marievale community residents;
2. Call on the SANDF, the Minister of Defence and Military Veterans and the Ekurhuleni Municipality to immediately lift and ensure the non-recurrence of restrictions on the movement on Happiness Village residents;
3. Call on the President of South Africa, as the Commander in Chief of the SANDF, to take appropriate action to ensure that the human rights violations that the residents of Marievale have suffered at the hands of the SANDF on a continuous basis since 2017 be investigated, and that appropriate action be taken to ensure access to justice and effective remedies for the residents; and
4. Call on the Parliamentary Portfolio Committee on Defence and Military Veterans to ensure the accountability of the Minister of Defence and Military Veterans for the human rights violations to which the SANDF has subjected the residents on a continuous basis since 2017.
Read the full letter here.
SouthAfrica-SAHRDN-ICJ Letter to SRs on HRDs-Advocacy-open letters-2020-ENG
Contact:
Tim Fish Hodgson (ICJ Legal Adviser) t: +27828719905; e: timothy.hodgson(a)icj.org

Jul 31, 2020 | Agendas, Events, News
The ICJ, together with the Global Initiative on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (GI-ESCR) and the Right to Education Initiative (RTE), held webinars on 24 and 31 July.
The discussions explored The Guiding Principles on the Human Rights Obligations of States to provide public education and to regulate private involvement in education (Abidjan Principles) and their application in the context of COVID-19.
The webinars focused respectively on public education and private education.
Participants included judges and representatives of civil society organizations from Kenya, Uganda, South Africa and Sierra Leone.
“The aim of the conversation in these webinars is to better understand the problems facing civil society and judiciaries in the four countries in ensuring the protection of the right to education in the context of Covid-19 and the increased privatization of education,” said ICJ Commissioner Justice Jamesina King of Sierra Leone.
The Abidjan Principles, based in large measures on existing international law and standards, were developed by leading international experts and adopted in 2019.
They clarify and set out elements of State obligations to uphold the right to education and related standards in both public and private educational settings.
Participants were able to deepen their understanding of the Abidjan Principles as well as the increased pressure placed on education systems across Africa as a result of COVID-19.
“COVID-19 has dramatically exacerbated already well-known issues in the realization of the right to education” and the “divide in quality of access to education between public and private sectors,” added Justice King.
“Private actors in particular… have been reported to have capitalized on the pandemic to extend their business in the education sectors.”
Participants raised concerns about the use of public funds to support private actors in education, an issue which is addressed by the Abidjan Principles.
Ashina Mtsumi from the GI-ESCR, summarized the Abidjan Principles and emphasized that “States’ first priority should be public education, as there is no obligation for states to fund private actors in education.”
A theme emerging from the discussions was the important role of the State in regulating private actors in education in the context of the global pandemic. Judges discussed the role of the judiciaries in their respective countries in ensuring the protection of the right to education.
“Can courts force private institutions to continue [operating] or even reduce school fees as an incidence of the right to education?,” Justice Joel Ngugi of Kenya asked.
Justice Ngugi also highlighted the need for governments to ensure that schools are safe for all learners in the context of COVID-19.
Judge Lydia Mugambe said that while in Uganda the pandemic had seen some private schools continuing with online learning, learners in public schools had had to depend on State provision of learning through newspapers and news stations which had not been sufficient. In the COVID-19 context, States must ensure that they continue to “require private instructional educational institutions to meet the minimum standards set by the State”, as indicated by the Abidjan Principles.
“The real problem is that our infrastructure is bad, the education system is bad and we have had a constitutional right to education since 1994 and I am embarrassed to say that the Covid-19 crisis has not exacerbated the problems, but has exposed the problems and have left no place to hide for years and years of government negligence,” said former Justice of the Constitutional Court in South Africa Zak Yacoob.
Representative from civil society organizations from all four countries emphasized the increasing risks introduced to the right to education as a result of privatization of education in Africa.
Watch the first webinar here.
Contact:
Khanyo Farisè (ICJ Legal Adviser) e: Nokukhanya.Farise(a)icj.org
Tim Fish Hodgson (ICJ Legal Adviser) t: +27828719905; e: timothy.hodgson(a)icj.org









