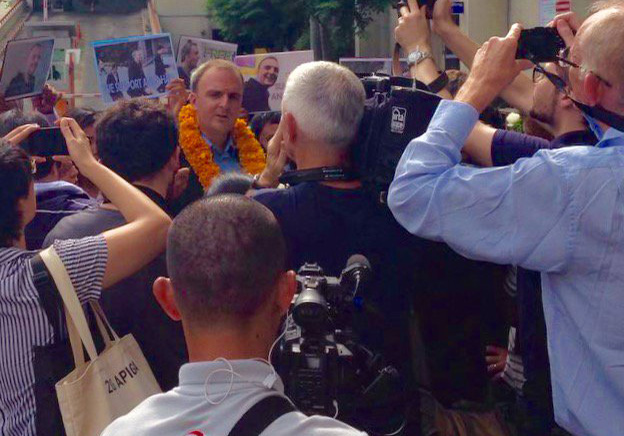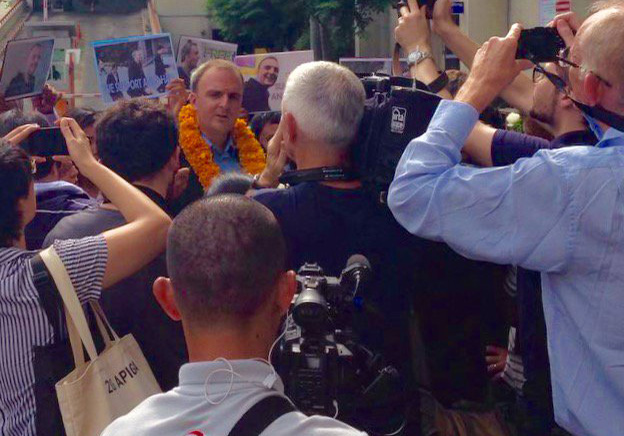
Sep 20, 2016 | News
The ICJ expresses its disappointment with today’s verdict criminalizing the work of human rights defender, Andy Hall, and calls upon Thailand to decriminalize defamation and amend the Computer Crime Act in line with international standards protecting freedom of expression.
This morning, Thailand’s Southern Bangkok Criminal Court found Andy Hall guilty of defaming a Thai fruit processing company under Article 328 of the Thai Criminal Code and violation of Article 14(1) of the Computer Crime Act, and sentenced him to a fine of THB 200,000 (USD$ 5,700) reduced to THB 150,000 (USD $4,300); and four years imprisonment, reduced to three years and suspended for two years.
Andy Hall has said he will appeal the verdict.
“Human rights defenders such as Andy Hall have the right to exercise freedom of expression in advocating for the protection and realization of human rights – a right that Thailand has a duty to protect,” said Kingsley Abbott, Senior International Legal Adviser at the ICJ.
“Unfortunately, there are numerous examples of criminal defamation and the Computer Crime Act being used against human rights defenders in Thailand, a practice that must end, including through a substantial reform of these laws,” he added.
The ICJ and Lawyers Rights Watch Canada submitted a joint amicus curiae brief in the proceedings, arguing that the imposition of harsh penalties such as imprisonment or large fines on a human rights defender risk having a ‘chilling effect’ on the exercise of freedom of expression, which Thailand is bound to protect pursuant to its international legal obligations.
The ICJ anticipates the arguments contained in the joint amicus will be considered on appeal.
“It is also disappointing that the Court did not appear to take into account the recent decision of the Phuket Provincial Court in the Phuketwan case, which found that the Computer Crime Act was not intended to be used in cases of alleged defamation,” said Abbott.
On 1 September 2015, the Phuket Provincial Court acquitted two journalists of criminal defamation and violations of the Computer Crime Act after the Royal Thai Navy complained the journalists defamed it when, on 17 July 2013, the journalists reproduced a paragraph from a Pulitzer prize-winning Reuters article that alleged “Thai naval forces” were complicit in human trafficking.
The criminal defamation proceedings brought against Andy Hall are among several that have been brought against human rights defenders in Thailand in recent years.
Others examples include the charges laid against activists Pornpen Khongkachonkiet, Somchai Homloar and Anchana Heemina in July 2016 for raising allegations of torture in the deep South; and those brought against activists protesting various development projects in Thailand which are allegedly having an adverse impact on communities.
Background
Today’s case is one of four criminal and civil proceedings (two criminal and two civil) a Thai fruit processing company, Natural Fruit Company Ltd., has brought against Andy Hall in relation to the report of a Finnish NGO, Finnwatch, published in January 2013, called Cheap Has a High Price.
Andy Hall’s research was included in the report which alleged that labour rights violations were taking place at Natural Fruit Company Ltd., whose employees included migrant workers from Myanmar.
In September 2015, a Thai Appeal Court upheld the dismissal of the other criminal defamation proceeding Natural Fruit Company Ltd. brought against Andy Hall. That proceeding is currently before the Supreme Court. Two civil proceedings are also before the Thai courts but have been suspended pending resolution of the two criminal proceedings.
The use of criminal defamation laws, carrying penalties of imprisonment, against human rights defenders reporting on alleged human violations, constitutes a violation of Thailand’s obligations under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), to which it is a state party.
thailand-verdict-andy-hall-case-news-press-release-2016-eng (full text in PDF)
thailand-verdict-andy-hall-case-news-press-release-2016-tha (full text in Thai, PDF)
Contact
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Director (Bangkok), t: +66 807819002; e: sam.zarifi(a)icj.org
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, t: +66 9 4470 1345, e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org

Sep 12, 2016 | News
The Thai junta’s Order today phasing out the prosecution of civilians in military courts is a welcome step but the military government must do much more to comply with its international human rights obligations, said the ICJ today.
Head of the National Council for Peace and Order (NCPO) Order 55/2016, dated 12 September 2016 and issued under Article 44 of the Interim Constitution, phases out the heavily criticized practice of prosecuting civilians before military courts for four categories of offences, including offences against internal security; violation of NCPO orders; possession and use of war weapons; and the highly punitive offence of lese majeste.
The Order only applies to offences committed from the date the Order comes into force – today – and not to past or pending cases.
Since the May 2014 coup, at least 1,811 civilians have been tried in Military Courts, based on information the Judge Advocate General’s Department (JAG) provided to Thai Lawyers For Human Rights (TLHR) in July 2016 and covering the period 22 May 2014 to 31 May 2016.
“Almost 2,000 civilians have faced an unjust process and unfair trials before military tribunals, many of whom were prosecuted simply for exercising their rights to freedom of expression and assembly,” said Sam Zarifi, Asia Director at the ICJ. “All pending cases should be transferred to civilian courts and the convictions of all civilians prosecuted in military courts since the 2014 coup should be set aside.”
Head of the NCPO Order 55/2016 also explicitly affirms that the deeply problematic Head of the NCPO Orders 3/2015 (which replaced nationwide Martial Law on 1 April 2015) and 13/2016 shall remain in force.
These Orders prohibit the gathering of more than five people for political purposes; allow for the detention of civilians in military facilities for up to seven days without charge; and provide appointed “Prevention and Suppression Officers” and their assistants, drawn from the commissioned ranks of the Armed Forces, including the paramilitary Ranger Volunteers, with wide-ranging powers to prevent and suppress 27 categories of crimes including against public peace, liberty and reputation, immigration, human trafficking, narcotics, and weapons. The ICJ considers that these orders are not in accordance with Thailand’s international human rights obligations
“Its now crucial for the military to return responsibility for law enforcement to civilian authorities, and ensure they are properly trained and competent,” Zarifi said. “We hope today’s Order is a step toward returning Thailand to the rule of law and respect for human rights.”
Background
Clause 3 of Head of the NCPO Order 55/2016 notes “As appropriate, the Prime Minister may propose to the National Council for Peace and Order to amend this Order.”
Previously, NCPO Announcements 37/2014, 38/2014 and 50/2014 extended the jurisdiction of Thailand’s military courts to four categories of offences, including offences against internal security, violation of NCPO orders, possession and use of war weapons, and lese majeste.
The prosecution of civilians in military courts is inconsistent with Article 14 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) – to which Thailand is a State Party – which affirms that everyone has the right to a “fair and public hearing by a competent, independent and impartial tribunal established by law.”
The Principles Governing the Administration of Justice through Military Tribunals sets out principles that apply to state use of military tribunals. Principle 5 states “Military courts should, in principle, have no jurisdiction to try civilians. In all circumstances, the State shall ensure that civilians accused of a criminal offence of any nature are tried by civilian courts.”
Contact:
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Director (Bangkok), t: +66 807819002; e: sam.zarifi(a)icj.org
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, t: +66 9 4470 1345, e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org
Download:
thailand-unofficial-translation-head-of-ncpo-order-55_2559-advocacy-2016-eng (full text of Order in English, PDF)
thailand-ncpo-order-55_2559-news-2016-tha (full text of news in Thai, PDF)
Read also:
Thailand: transfer all civilians to civilian courts
Thailand: end prosecution of civilians in military tribunals
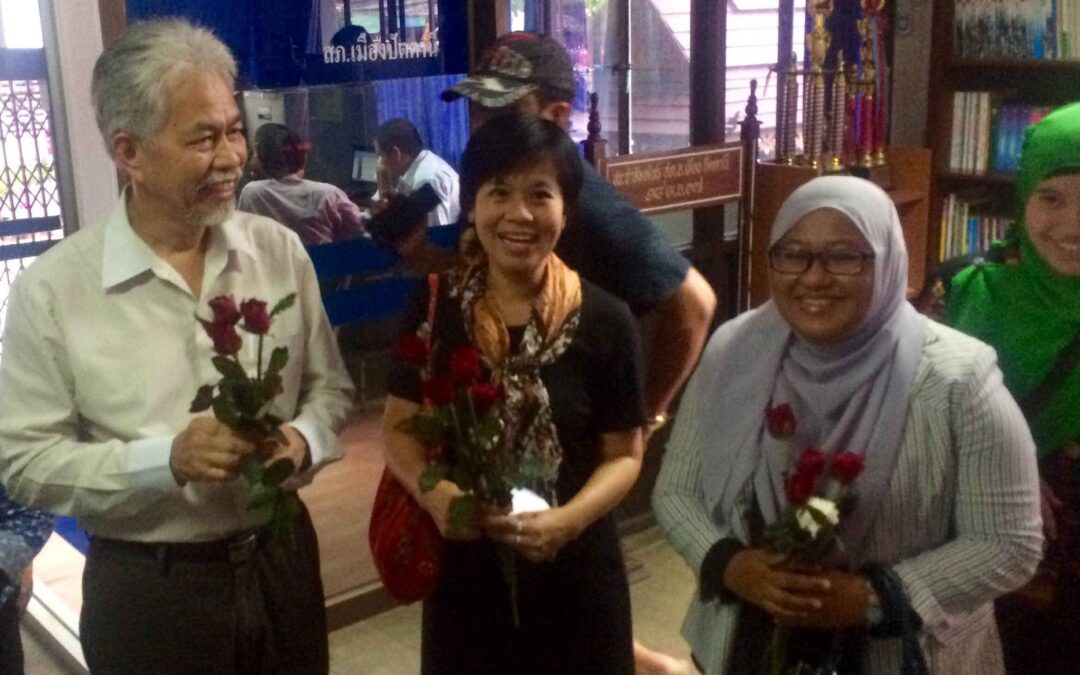

Jul 27, 2016 | News
Thailand’s government should immediately stop allowing criminal defamation laws to be used to harass victims and human rights defenders who seek justice for alleged incidents of torture, the ICJ said today.
Yesterday, the government charged three human rights defenders (Pornpen Khongkachonkiet, Somchai Homloar and Anchana Heemina, photo) under the criminal defamation provisions of the Penal Code and the Computer Crime Act, for publication of a report that documented 54 cases of alleged torture and other ill-treatment by the Thai authorities in the country’s restive deep South since 2004.
“Thailand must repeal or revise its vague and broad criminal defamation laws to prevent them from being used to silence human rights defenders and journalists working on important public interest issues,” said Wilder Tayler, the ICJ’s Secretary General.
“The imposition of harsh penalties such as imprisonment or large fines under these laws has a chilling effect on the exercise of freedom of expression – a right which is enshrined in treaties to which Thailand is a party and bound to uphold,” he added.
Also yesterday, the government used the same provisions to charge Naritsarawan Kaewnopparat, the niece of an army conscript who was killed after being severely punished by soldiers on a military base.
Although the Thai government has formally acknowledged that the death was caused by torture and compensated the family, none of the perpetrators have been held accountable for the death of Private Wichian Puaksom and have only faced military disciplinary sanctions of 30 days of detention or less, the ICJ reminds.
The case against Ms Kaewnopparat was brought by a military officer who alleges she accused him of being involved in her uncle’s death in the context of the family’s efforts to seek justice.
Last month, Thailand informed the Human Rights Council during its Universal Periodic Review that the Cabinet was considering a draft Act on Prevention and Suppression of Torture and Enforced Disappearance.
It was reported that the Cabinet approved the draft law on 24 May 2016 and would forward it for approval to the National Legislative Assembly.
At the conclusion of the review, Thailand also adopted several recommendations to protect human rights defenders and investigate reported cases of intimidation, harassment and attacks against them.
“Prosecuting people who seek justice for alleged torture goes against the spirit of the proposed legislation,” Tayler said.
“Thai authorities have an obligation to investigate and ensure justice for incidents of torture, but instead they are harassing and intimidating those responsible for exposing these horrendous acts.”
On 17 December 2015, Thailand joined 127 other states at the UN General Assembly in adopting a UN Resolution on human rights defenders.
The Resolution calls upon states to refrain from intimidation or reprisals against human rights defenders.
Contact:
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Director (Bangkok), t: +66 807819002; e: sam.zarifi(a)icj.org
Thailand-HRDs defamation charges-News-Press releases-2016-ENG (full text of press release in English, PDF)
Thailand-HRDs defamation charges-News-Press releases-2016-THA (full text of press release in Thai, PDF)
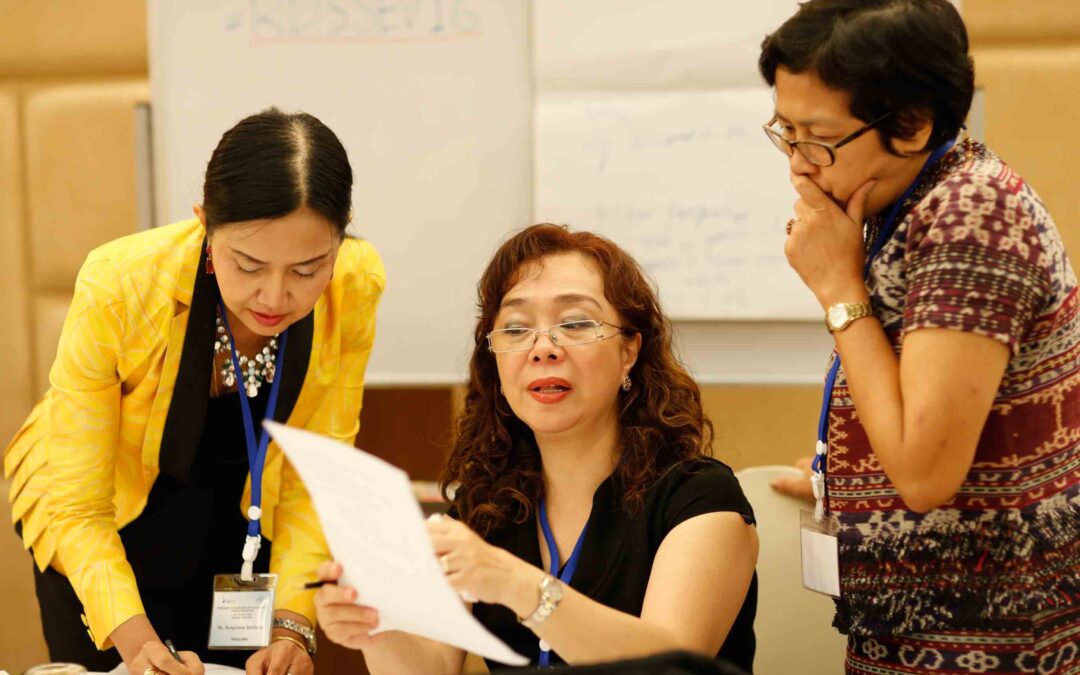

Jun 25, 2016 | Advocacy
The ICJ today published a General Guidance aimed at assisting judges and others in the justice sector to effectively incorporate a gender perspective in their work.
The General Guidance is especially significant as it reaffirms that customs and traditions should not be invoked to justify discrimination against women.
The Bangkok General Guidance for Judges in Applying a Gender Perspective was discussed and adopted by judges from Philippines, Thailand, Timor Leste, and Indonesia, at a gathering in Bangkok from 24 to 25 June 2016, hosted by the ICJ and UN Women.
During the workshop, judges from the four Southeast Asian countries deliberated extensively how best to assist judges in employing a gender perspective in deciding cases before them.
“The Bangkok General Guidance can make a powerful contribution towards achieving gender equality under the law in Southeast Asia,” said Sam Zarifi, Regional Director for Asia and the Pacific at the ICJ. “It is crucial that judges now work to implement this General Guidance in their home countries.”
The idea to initiate the development of th Bangkok General Guidance emerged from the ASEAN Regional Dialogue on Judging with a Gender Perspective, which was held in Jakarta, Indonesia in 2015.
The Supreme Court of the Philippines offered to take the lead on the project during that regional judicial dialogue.
“Women have a right to equal treatment and equal protection and non-discrimination under the law. It is our responsibility as judges to ensure that women receive equal treatment in law and in practice,” said Justice Teresita de Castro of the Supreme Court of the Philippines.
Judges attended several sessions over the course of the two-day workshop, participating in exercises focused on identifying and addressing gender stereotypes.
“Women in the region face many obstacles in accessing justice,” said Roberta Clarke, Regional Director for Asia and the Pacific at UN Women.
“But judges may be either unaware of these issues or unsure how to address these issues through the legal process,” she added.
The Bangkok General Guidance will make judges aware of means to consider evidence without resorting to gender stereotypes and decide cases based on the principle of equality recognized under international human rights standards, including the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW).
Recommendations for institutional policies that should be adopted by courts to help them become more gender sensitive and gender responsive are also set out in the General Guidance.
Contact:
Emerlynne Gil, Senior International Legal Adviser for Southeast Asia, t: +66840923575 ; e: emerlynne.gil@icj.org
Southeast Asia-Bangkok-Guidance-Advocacy-2016-ENG (full PDF, in English)
Southeast Asia-Bangkok-Guidance-Advocacy-2016-BUR (full PDF, in Burmese)
Southeast Asia-Bangkok-Guidance-Advocacy-2016-MON (full PDF, in Mon language)
Southeast Asia-Bangkok-Guidance-Advocacy-2016-SHAN (full PDF, in Shan language)

Jun 24, 2016 | Advocacy
The ICJ, International IDEA (Australia) and the Office of the United Nations Resident Coordinator in Thailand have collaborated to produce an unofficial translation of the draft Constitution of Thailand which is scheduled to be the subject of a national referendum on 7 August 2016.
The original Thai text as formally published by the Royal Thai Government shall in all events remain the sole authority having legal force.
Thailand-Draft-Constitution-EnglishTr-Advocacy-2016-ENG (full text in PDF)
Contact
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Regional Director for Asia and the Pacific, t: +66807819002; e: sam.zarifi(a)icj.org
Kingsley Abbott, Senior International Legal Adviser, t: +66 94 470 1345; e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org