
Apr 17, 2018 | Events, Multimedia items, News, Video clips
International commitment to the rule of law is under assault around the world, said a global panel of eminent academics, diplomats, and jurists.
The panelists, speaking at a public event by the ICJ and the Geneva Graduate Institute, commented that this assault is threatening to reverse the progress made over the last 70 years since the Universal Declaration of Human Rights(UDHR) came into force.
The panelists addressed progress in asserting the rule of law since the UDHR, for instance through the development of the International Criminal Court and greater awareness and commitment to rights, but also highlighted current challenges at the national level, such as in Venezuela, and at the global level, with ongoing discrimination and violence against women.
“The rule of law is a principle that helps the world and also helps individuals,” said ICJ Secretary General Saman Zia-Zarifi, in his introductory remarks.
“It is a principle that elevates democracy from mob rule and is necessary to harness the energy of democracy and give it a direction and progression towards the protection and promotion of human rights and sustainable development for the betterment of the lives of people around the world,” he added.
Professor Carlos Ayala, ICJ Vice-President and former President of the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights, spoke about the importance of having regional rights frameworks that were accessible to individuals when the rule of law has been eradicated at a national level.
Speaking in relation to Venezuela, Professor Ayala explained that the rule of law cannot be simply overturned by a political party, even with a majority, as the erosion of the rule of law puts all human rights at risk and these rights must be safeguarded regionally and internationally.
Next Patricia Schulz, member of the UN Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women, pointed out that in many countries, the rule of law has been weak or never even properly existed.
She addressed failings where access to justice is undermined by systems that are gender discriminatory and explained that in almost all countries, even where the rule of law seems strong, there is a lack of will and/or means to fight gender-based violence.
Professor Andrew Clapham, Professor of Public International Law at the Graduate Institute and member of the UN Commission on Human Rights in South Sudan, evaluated issues of accountability and the rule of law in the context of international criminal law.
He noted the important role international criminal law and its operational mechanisms have in holding individuals to account, but warned that focusing on prosecution and focusing on issues such as genocide and the use of chemical weapons ran the risk of undermining the universality of ideas enshrined in the UDHR.
His Excellency Luis Gallegos, the Permanent Representative of Ecuador to the United Nations, raised concerns about the politicization of human rights and the capacity of UN mechanisms to address transnational rights issues such as migration.
He said that addressing the rule of law was not a simple question but that states had to come together to consistently and systematically address the rights violations that arose from a break-down in the rule of law.
Final panelist, Sanji Monageng, ICJ Commissioner and Justice of the International Criminal Court, spoke about the need for international organizations to rethink their approach to the rule of law and the way they apply this to cases, to avoid focusing narrowly on singular issues when rights violations need to be addressed homogenously.
Justice Monageng explained that for victims, sexual violence, for instance, is rarely a singular incident but part of broader array of rights violations that have far-reaching impacts.
In his concluding remarks, Professor Robert Goldman, who moderated the event, said that “the rule of law deals with a central tenet of any just society, not only equal protection and equal access but it is something that protects the vulnerable.”
He explained that the treat to the rule of law today is endemic and it is global, but the ICJ is uniquely placed to robustly address these difficult questions and to continue to use the rule of law to defend and advance rights protections.
The event, which took place at the Graduate Institute at the Maison de la Paix, promoted by the Permanent Mission of Germany, was attended by 150 persons including academics, diplomats, lawyers and representatives of civil society and international rights mechanisms. The event was also streamed online by RIDH Global.
You can watch the full event here.
https://www.facebook.com/ridhglobal/videos/10158134493084616/UzpfSTQ3MTQ2NzA4NjIyMTM3MzoxOTk5MjM0NDc2Nzc3OTUy/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ije_iAegxFs&feature=youtu.be

Mar 28, 2018 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ today submitted a report to the UN Committee against Torture, calling for recommendations to be made on prevention of and accountability for continued recourse to torture and ill-treatment in Tajikistan.
The ICJ’s submission is made ahead of consideration by the Committee against Torture in April to May 2018 of Tajikistan’s third periodic report on the implementation of its obligations under the Convention against Torture and Other Forms of Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment.
The ICJ’s report draws from an earlier study on Achieving Justice for Gross Human Rights Violations in Tajikistan and calls on the Committee against Torture to make recommendations concerning:
- The obligation to adequately sanction torture;
- The obligation to prevent torture and other forms of ill-treatment, including in places of detention;
- The obligation to investigate allegations of torture and ill-treatment;
- The use of amnesties and pardons for torture;
- The prohibition against the use of evidence obtained by torture;
- The right to complain about torture and ill-treatment; and
- The right of victims to effective remedies and reparation.
Tajikistan-CAT-Advocacy-AlternativeReport-2018ENG (download the ICJ’s submission, in PDF)
Mar 22, 2018 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
Today, the ICJ together with Forum for Human Rights submitted written information to the Committee against Torture ahead of its examination of the periodic report of the Czech Republic.
The two organisations argue that the Czech Republic violates Articles 2, 14 and 16 of the Convention Against Torture, by not ensuring access to a lawyer for children below the age of 15 (the age of criminal responsibility) in the pre-trial stage of juvenile justice proceedings.
1273 children younger than 15 were part of these pre-trial stage proceedings in the Czech Republic in 2017 without access to procedural guarantees, including legal counsel, unlike children aged 15-18 have under national legislation.
Children below the age of criminal responsibility do not benefit from such procedural rights and therefore, during the police questioning, they are typically left without any legal assistance and presence of a lawyer who neither can deter the police from resorting to ill-treatment or other abuses, nor work as a protection for police officers in case they face unfounded allegations of ill-treatment.
This situation constitutes a violation of the obligation to prevent torture or acts of cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment which do not amount to torture under Articles 2 and 16 of the CAT. Additionally, the Czech Republic fails to ensure access legal counsel for the purposes of an effective remedy under Article 14 of the CAT.
The joint submission aims to inform the 63rd session of the Committee Against Torture in April-May 2018 during which the Sixth periodic report of the Czech Republic will be examined.
Read the full joint submission here:
Czech-Republic-Joint-writteninformation- against-torture-2018-ENG (Full text in ENG, PDF)
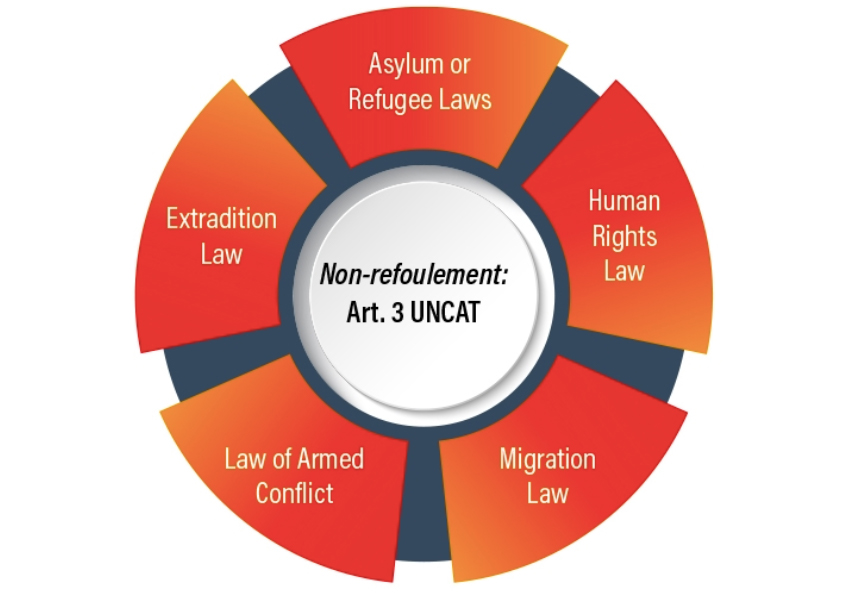
Mar 14, 2018 | News
The new CTI tool on non-refoulement covers:
- constitutional and legislative provisions;
- national procedures;
- procedural rights to be guaranteed to those facing deportation or expulsion;
- training; and
- visa and stay arrangements for when return is prohibited.
There is also a section on non- refoulement in the extradition context.
The purpose of this and other CTI Implementation Tools is to inspire other States to take action through exchanges of good practices.
The tool also provides timely and practical information and advice for States in light of the recently released UN Committee against Torture’s General comment on the implementation of Article 3 of the Convention in the context of Article 22.
Some of the laws mentioned in this tool detail the powers that can be exercised by State authorities to remove a person and the constraints on those powers, as well as the relevant administrative and judicial procedures to be followed. National legislation has also detailed the rights of persons within those procedures (photo).
The tool was developed for the CTI by the ICJ with the support of the University of Bristol’s Human Rights Implementation Centre.
CTI’s series of UNCAT Implementation Tools are available here.

Mar 14, 2018 | Events, Multimedia items, News, Video clips
Today, the ICJ highlighted threats to and defenders of the rule of law around the world, at a side event to the UN Human Rights Council, at the Palais des Nations in Geneva.
The rule of law is under attack and human rights and human rights defenders everywhere are at risk, whether as targets or “collateral damage”.
The human rights movement has overcome similar challenges in the past. This side event to the 37th session of the Human Rights Council discussed the situation today and lessons from the ICJ’s history since its founding in 1952.
ICJ’s regional directors, gathering in Geneva from around the world, provided a unique snapshot of the “state of the world” for rule of law and human rights, from ICJ’s position on the global frontlines of the struggle to defend essential legal safeguards:
• Saïd Benarbia, Director for Middle East North Africa
• Ramón Cadena Rámila, Director for Central America
• Róisín Pillay, Director for Europe and Central Asia
• Frederick Rawski, Director for Asia and Pacific
• Arnold Tsunga, Director for Africa
Moderator: Saman Zia-Zarifi, Secretary General
In addition to highlighting the global and regional trends, specific examples for discussion included Azerbaijan, Cambodia, China, Egypt, Guatemala, Honduras, Hungary, Kenya, Lesotho, Libya, Myanmar, the Philippines, Poland, the Russian Federation, South Sudan, Swaziland, Syria, Thailand, Turkey, the United States of America, Venezuela and Zimbabwe.
For more information, contact un@icj.org
Watch the video:
https://www.facebook.com/ridhglobal/videos/10157996747579616/
Universal – Rule of law frontlines – News – Event – 2018 – ENG (Event flyer in PDF)









