
Jul 4, 2018 | News
Today the ICJ called on Thai prosecutorial authorities to immediately end the prosecution of five persons associated with academic activities in Chiang Mai. The five have been made subject to prosecution solely for exercising their rights to free expression and assembly.
Those subject to prosecution include Pakawadee Veerapatpong, an independent writer and translator; Chaipong Samnieng, a PhD candidate at Chiang Mai University; Nontawat Machai, an undergraduate student at Chiang Mai University; Teeramon Bua-ngam, a Masters student at Chiang Mai University and news editor; and Dr. Chayan Vaddhanaphuti, a Professor at Chiang Mai University.
The ICJ also called for the revocation or amendment of all laws, orders and announcements inconsistent with Thailand’s international human rights obligations.
Today, the Region V Public Prosecutor in Chiang Mai province formally notified the five individuals that they would be prosecuted for violating HNCPO Order No. 3/2558 (2015) (‘HNCPO Order 3’) for merely expressing their opinions at an academic forum at Chiang Mai University in July 2017.
HNCPO Order 3 prohibits the gathering of five or more persons for political purposes, carrying a penalty of imprisonment not exceeding six months and/or a fine not exceeding 10,000 Baht.
“The ongoing and abusive use of HNCPO Order 3 to stifle free expression in Thailand remains indefensible and an obstacle to the full restoration of the rule of law in Thailand,” said Kingsley Abbott, Senior Legal Adviser at the ICJ.
“The decision to indict these five individuals is clearly in breach of Thailand’s international human rights obligations and should be reversed immediately together with the termination of the proceedings and the revocation of HNCPO Order 3,” he added.
The Public Prosecutor’s decision to indict the five was made against a backdrop of recently increasing repression of fundamental freedoms in the country.
This year alone, at least 132 persons were reportedly charged under HNCPO Order 3 in 10 cases and six incidents in connection with a movement calling for elections to be held this year.
Twenty-seven of these individuals were also charged with a sedition-like offence, which carries a maximum penalty of seven years’ imprisonment.
Since the military coup of 22 May 2014, at least 378 persons have been reportedly charged in relation to 50 cases of violating the ban on political gatherings of five or more persons according to a report launched on 22 June 2018 by leading Thai NGO, Thai Lawyers for Human Rights (TLHR).
In March and June 2018, at the Human Rights Council, the ICJ called on Thailand to revoke or amend all laws, orders and announcements that are contrary to the rule of law and human rights protections.
“Four years have passed since the military coup resulting in numerous unjustifiable restrictions on fundamental freedoms – it is long past time for Thailand to undertake reform necessary to prevent the legal system from being misused to harass individuals who merely exercise their human rights,” said Abbott.
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, email: kingsley.abbott@icj.org
Background
The Region V Public Prosecutor’s decision in Chiang Mai province follows charges filed against the individuals by a military officer in 2017.
Pakawadee Veerapatpong, Chaipong Samnieng and Nontawat Machai had allegedly held up three A4-sized messages which read “an academic forum is not a military barracks” at the academic conference.
Teeramon Bua-ngam had reportedly taken a picture of himself standing next to the messages and posted the same on social media.
Dr. Chayan Vaddhanaphuti had reportedly watched the display of the messages without asking for them to be removed, despite being an organizer of the conference.
Thailand is a State party to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR). Articles 19, 21 and 22 of the ICCPR guarantee the rights to freedom of opinion and expression, freedom of peaceful assembly and freedom of association.
Since the military coup, the ICJ has expressed its concern about the use of a new legal framework and pre-existing laws to clamp down on the rights to freedom of expression, association and assembly, including criminal defamation (Articles 326-328 of the Thai Criminal Code), the Computer-Related Crime Act B.E.2550 (2007), a sedition-like offence (Article 116 of the Thai Criminal Code), and HNCPO Order 3.
Read also
ICJ and TLHR Joint Submission to the UN Human Rights Committee, 13 February 2017
ICJ and TLHR Joint Follow-up Submission to the Human Rights Committee, 27 March 2018
Thailand-Academics indicted-News-Web Story-2018-THA (story in Thai, PDF)
Jun 28, 2018 | News
On 24-25 June, ICJ Commissioners from the Latin America region came together in Bogotá, Colombia, to consider and enhance ICJ strategies to combat past and resurging trends in extrajudicial executions and enforced disappearances in the region.
The meeting was the first of its kind to bring together ICJ Commissioners on a regional basis: Carlos Ayala (Venezuela); Miguel Carbonell (Mexico); Gustavo Gallón (Colombia); Roberto Garretón (Chile); Juan Mendez (Argentina); Victor Rodriguez Rescia (Costa Rica); Alejandro Salinas Rivera (Chile); Mónica Pinto (Argentina); Belisário dos Santos Júnior (Brazil); and Wilder Tayler (Uruguay).
The meeting was followed by a preparatory mission (involving two Commissioners and the ICJ’s legal representative in Colombia) on the transitional justice mechanisms envisaged under the Havana Agreement, with a particular emphasis on the jurisdiction and operation of the ‘Special Jurisdiction for Peace’. A full high-level mission will follow in September, at which time the ICJ intends to identify minimum benchmarks for the effective operation and sustainable impact of those mechanisms.
In all regions of the world, recourse to enforced disappearances and extrajudicial killings continues; victims and their families (the overwhelming majority of whom are women, children and indigenous peoples from rural areas dominated by poverty and social and political exclusion, as well as trade unionists and human rights defenders) struggle to obtain prompt and effective remedies and reparation; and perpetrators enjoy impunity through inadequate or improper laws, ineffective institutional frameworks, selective recourse to accountability mechanisms and/or political interference in the functioning of those mechanisms.
The meeting confirmed that these challenges are particularly evident in Latin America, where there has been a resurgence in recourse to enforced disappearances and extrajudicial killings in countries throughout the region and where violations of the past have in very many cases been inadequately addressed. By way of example:
- In Brazil, official statistics from 2016 attest to the occurrence of 62,000 violent deaths and potentially up to 22,000 enforced disappearances each year.
- 45 years after the coup d’état in Chile, about 800 people have been convicted and sentenced to imprisonment, but those figures belie the extensive occurrence and levels of responsibility for gross violations of human rights that occurred.
- In Colombia, more than 70,000 cases of enforced disappearance were documented by the Attorney General for the period 1970-2015 and there is general consensus that the number of missing persons likely exceeds 100,000. The wide and persistent extent of extrajudicial killings has been noted by UN and Inter-American experts and bodies as well as the Office of the Prosecutor of the International Criminal Court.
- In Guatemala, only 34 convictions for conduct involving conflict-era violations have been secured, despite the fact that the internal armed conflict of 1960-1996 involved massive and systematic human rights violations. Impunity has undermined redress and accountability and severely weakened the prevention of violations, with the National Civil Police having recorded more than 25,000 people ‘disappeared’ in 2003-2014, more than half of which were women.
- Peru’s internal armed conflict of 1980-2000 resulted in more than 69,000 people killed and ‘disappeared’, but less than 100 convictions have been secured under the judicial subsystem established in 2004 that specializes in accountability for gross human rights violations.
- In Venezuela, civil society reports at least 12,000 real or perceived political opponents having been arbitrarily detained between January 2014 and April 2018; and almost 6,000 alleged extrajudicial killings between 2012 and 2016.
In all the countries from which the Commissioners originate, several common factors were identified:
- The intrinsic risks to continuation of and lack of redress and accountability for gross human rights violations posed by executive action that undermines the rule of law;
- Also inherent to the rule of law, the critical need for independent and impartial judicial mechanisms and individual judges and lawyers to allow for transitional justice, in particular for victims and their families to access effective remedies and reparation and for the holding to account of perpetrators;
- A high level of correspondence between impunity for gross human rights violations and the corruption of public officials;
- The increased, and in some cases extensive, recourse to arbitrary and detention, which in many cases precede and allow for the occurrence of extrajudicial executions and enforced disappearances;
- A similar inter-relationship between enforced disappearances and the occurrence of torture and other forms of ill-treatment;
- The detrimental impact to ensuring accountability for violations of the past when omitting non-State and paramilitary actors from transitional justice processes; and
- The increase in highly conservative (political and popular) sentiments and movements within the region and the corresponding need to tailor responses depending on the democratic versus autocratic nature of government and its institutions.
Noting that the ICJ has long sought to combat extrajudicial executions and enforced disappearances, including through the development of UN and regional instruments and standards and through its action in Latin America and the globe, the ICJ’s Commissioners urged the ICJ to continue and expand its engagement. Noting also the increasing call by local civil society actors for support and intervention by the ICJ, the meeting considered the organization’s role in seeking redress and accountability for, and prevention of, gross violations of human rights.
Commissioners reinforced, and commented on the effective parameters of, the ICJ’s strategic and victim-centred approach to address and prevent gross human rights violations, including extrajudicial executions and enforced disappearances. Having regard to the ICJ’s mandate and worldwide network of judges and lawyers, Commissioners emphasized the unique role that the organization has by grounding its work on the transformative role of the law, justice institutions and justice actors.
The particular means by which this role can be achieved by the ICJ were discussed against the background of recent and planned activities in the region and beyond. Commissioners overwhelmingly supported these plans and the Secretariat is now poised to continue implementation of its strategies in its current programmes of work and in the development of future projects.

Jun 21, 2018 | Events, News
The ICJ will participate today in the side event “State of emergency and attacks on the legal profession in Turkey” organized by IBAHRI, the Law Society, and the Bar Human Rights Committee of England and Wales.
This side event at the Human Rights Council takes place on Thursday, 21 June, 15:00-16:00, room XXV of the Palais des Nations.
It is co-sponsored by Lawyers for Lawyers, Union Internationale des Avocats, Lawyers’ Rights Watch Canada.
In this side event, panelists will share their analysis on the impact of the state of emergency on the rule of law and the ongoing obstacles faced by the legal profession in Turkey since the failed coup in 2016.
They will also discuss Turkey’s derogations from its international and regional human rights obligations, as well as the response of regional and international human rights mechanisms to this situation.
Panelists:
- Özlem Zingil, Turkish lawyer;
- Massimo Frigo, International Commission of Jurists;
- Tony Fisher, Chair of the Human Rights Committee of the Law Society of England and Wales;
- Stephen Cragg QC, Secretary of the Bar Human Rights Committee of England and Wales;
- Natacha Bracq, Programme Lawyer, International Bar Association’s Human Rights Institute.
Geneva-SideEvent-StateofEmergencyLawyersTurkey-IBAHRI&others-June2018-ENG (download the flyer)

May 17, 2018 | Events, News
Today, the ICJ is co-sponsoring a conference in Copenhagen to mark the conclusion of the Danish Presidency of the Council of Europe, and take stock of its contribution to protection of human rights in the Council of Europe region.
The conference, Copenhagen, Elsinore and the Future of Europe: Assessing the Danish Chairmanship of the Council of Europe is organized by iCourts and the University of Copenhagen in collaboration with the Danish Chairmanship of the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe, the Danish Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the ICJ and the Danish Institute for Human Rights.
This conference will assess what has been achieved during the Danish Chairmanship – and what can still be achieved at the final high-level conference in Elsinore where the Ministers of Foreign Affairs of the 47 member states will meet and are scheduled to adopt a decision on the future of the Council of Europe. The conference will focus on the priorities of the Danish Chairmanship, including:
- Reform of the European Court of Human Rights and the Copenhagen Declaration
- Equal opportunities
- Involvement of children and young people in democracy
- Changing attitudes and prejudices about persons with disabilities
- Combating torture.
At the conference, the ICJ will present its analysis of the recent Copenhagen Declaration on the future of the European Convention on Human Rights system, and its recommendations for how its conclusions and recommendations should be taken forward.
The programme is available here: http://jura.ku.dk/icourts/calendar/copenhagen-elsinore-future-of-europe/

May 7, 2018 | News
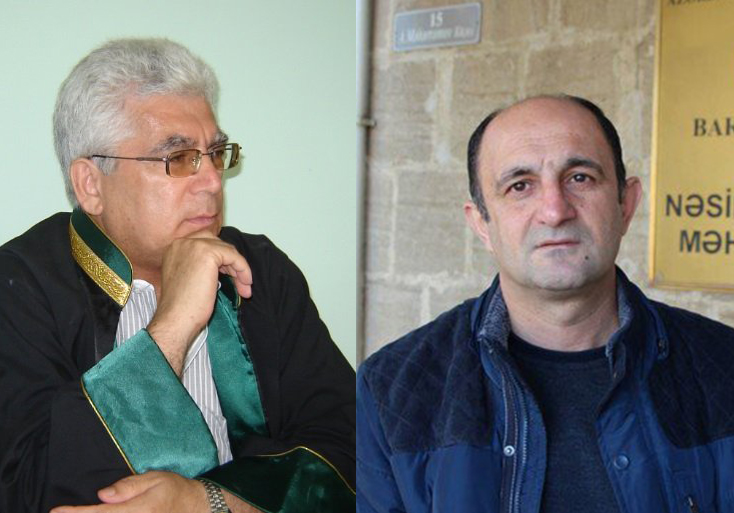
The ICJ today denounced the decision of the Presidium of the Azerbaijan Bar Association, of 23 April 2018, to suspend the licences of two Azerbaijan human rights lawyers Asabali Mustafayev (photo, on the left) and Nemat Karimli (photo, on the right).
The ICJ called on the Presidium to reverse their decision and allow the lawyers to resume their practice.
It stressed that disciplinary proceedings pending against the lawyers should be immediately terminated.
The ICJ said that the decision of the Presidium was contrary to international standards on the role of lawyers including the right to freedom of expression as guaranteed under international law.
The ICJ understands that the proceedings against the two lawyers, initiated following a submission of the Deputy Prosecutor General, were related to the critical statements made by the lawyers in the media, regarding high profile criminal cases.
Nemat Karimli, had stated in media interviews that his client Afgan Mukhtarli, an opposition activist convicted on charges of smuggling, had been illegally and forcibly transferred from Georgia to Azerbaijan and that his life could be at risk if he was returned to Azerbaijan.
The lawyer also complained of excessive searches and being prevented from communicating in private while visiting his client in detention.
The disciplinary proceedings against Asabali Mustafayev relate to allegations he made on social media that the prosecution of politician Gozal Bayramli, on a charge of smuggling, was politically motivated.
Both lawyers were charged with spreading false statements and slanderous information about investigative authorities.
The submission of the Prosecutor to the Bar Association, on 25 October 2017, alleged that lawyers Nemat Karimli and Asabali Mustafayev in their interviews to the media had “politicized” the criminal cases of Bayramli and Mukhtarli, tried to mislead the public and slandered investigative authorities. According to the information provided by the lawyers, no evidence had been attached to this submission.
Instead, the Disciplinary Commission collected evidence to submit to the Presidium of the Bar Association, which subsequently suspended the licence of the lawyers.
Furthermore, the lawyers state that, contrary to what is required by the Law on Lawyers and Advocates Activities, they have not received a copy of the opinion of the Disciplinary Commission submitted to the Presidium of the Bar Association.
The ICJ is concerned that the suspension of the lawyers’ licences, for comments which drew attention to possible violations of human rights, may violate the lawyers’ right to freedom of expression.
These comments appear to be within the bounds of lawyers professional responsibility to protect their clients in every appropriate way (UN Basic Principles, principle 13(b)).
The right to freedom of expression is protected under international treaties to which Azerbaijan is a party, including by Article 19 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and article 10 of the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR).
The UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers specify that lawyers “…have the right to take part in public discussion of matters concerning the law, the administration of justice and the promotion and protection of human rights …”.
The European Court of Human Rights has emphasized that lawyers are entitled to comment in public on the administration of justice, provided that their criticism does not overstep certain bounds, based on principles of dignity, honor, integrity, and respect for the fair administration of justice.
The ICJ emphasizes that protection of lawyers’ freedom of expression, in particular as regards issues of the rule of law and the administration of justice, is not only important to the individuals in question, it also serves as an important safeguard for the protection of human rights.
Where lawyers are subject to disciplinary sanctions for such statements, the role of lawyers in upholding the rule of law in the administration of justice is undermined.
The ICJ therefore calls on the Azerbaijan Bar Association to lift the disciplinary sanctions that would unjustifiably interfere with lawyers’ freedom of expression.
The ICJ also calls on the Azerbaijan Bar Association to ensure that the lawyers subject to disciplinary proceedings obtain a copy of the opinion to be able to prepare their arguments and defence.
Background
Asabali Mustafayev represented Gozal Bayramli who was found guilty and sentenced to three years in prison for smuggling €12,000 ($13,400) in cash. Mustafayev had expressed his opinion about the arrest of Gozal Bayramli in his social media profile, alleging that it was politically motivated. He stated that when he shared this opinion he was not yet engaged as Gozal Bayramli’s lawyer.
Nemat Karimli represented Afgan Mukhtarli, an opposition activist based in Tbilisi, who was convicted of smuggling € 10,000, illegally crossing the border and resisting police arrest and was sentenced to six years in prison. Karimli in an interview stated that Mukhtarli was taken to Azerbaijan illegally and called on the Georgian authorities not to hand him to Azerbaijan authorities since it might endanger Mukhtarli’s life.









