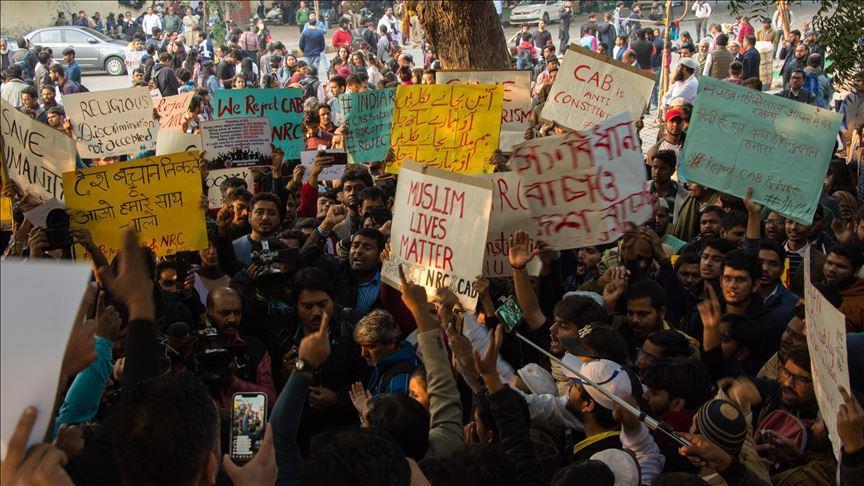Jan 15, 2020 | News
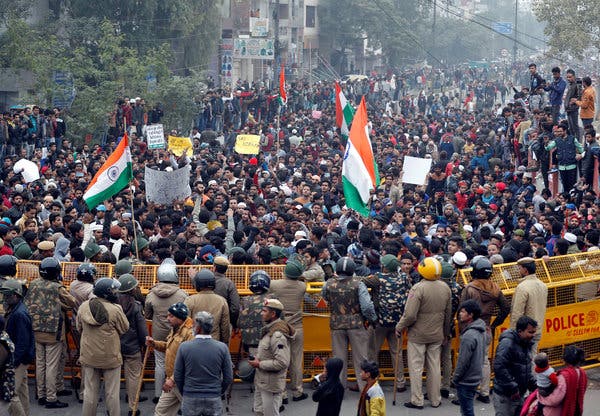
The Indian government must investigate the use of excessive and unlawful force by Uttar Pradesh police against demonstrators protesting the imposition of a discriminatory new law, the International Commission of Jurists said today in a briefing paper.
The briefing paper, based in part on firsthand interviews with witnesses and victims, documents the unnecessary, excessive and indiscriminate use of force in the state of Uttar Pradesh that have led to more than 19 deaths and several more critical injuries since 11 December 2019 as a result of use of firearms as well as teargas, water cannons, and baton charging by the police in response the ongoing protests against the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2020.
Section 144 of the Code of Criminal Procedure, which restricts right to assembly of more than 4 persons, has been imposed in Uttar Pradesh since December 19, 2019, thereby effectively preventing people from protesting. However, protests broke out in several cities in Uttar Pradesh despite the ban. While police authorities claim that the protestors initiated the violence, firsthand interviews with victims and witnesses and numerous other credible reports indicate that the police used force on peaceful protestors including lathis, teargas, bullets.
“The high death toll of peaceful protestors in Uttar Pradesh highlights the use of excessive force by the police, in contravention of international standards of policing and human rights. The state and federal governments must investigate any death or injury that occurs during protests by law enforcement officials and to ensure access to justice to victims and their families,” Sam Zarifi, ICJ Secretary General said.
Individuals reported that they had not been able to get their medico-legal certificates and victims’ families reported inability to access postmortem reports.
The right to life and freedom from ill treatment is protected under international law including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights to which India is a party and requires that when arbitrary deprivation of life occurs, there is accountability and reparation for victims.
The Allahabad High Court is hearing Shree Ajay Kumar v. State of Uttar Pradesh starting 16 January 2020, wherein it has taken suo moto cognizance of a letter sent by Ajay Kumar a lawyer in Bombay and has treated it as a basis for the commencement of a public interest litigation. The letter alleges that “the situation in the State of Uttar Pradesh is antithetical to core constitutional values and warrants interference of this Court.”
“A ruling that the Uttar Pradesh police violated protestors right to life by use of firearms and indiscriminate use of batons, teargas will serve as an important reminder to the police and the Indian State to respect the rights to life, freedom from ill-treatment and freedom of assembly and expression of protestors and that the use of such force against peaceful protestors will not be condoned by the State” said Sam Zarifi.
To download the full statement with additional background information, click here.
Contact
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Secretary General , e: sam.zarifi(a)icj.org
Maitreyi Gupta, International Legal Adviser for India, t: +91 7756028369 ; e: maitreyi.gupta(a)icj.org
Read also
ICJ Press Release: India: Discriminatory citizenship law passed by Parliament violates international and constitutional law, December 11, 2019
ICJ Press Release: India: Authorities must cease the excessive use of force and ill-treatment of Citizenship (Amendment) Act 2019 protestors, December 16, 2019

Jan 9, 2020 | Agendas, Events, News
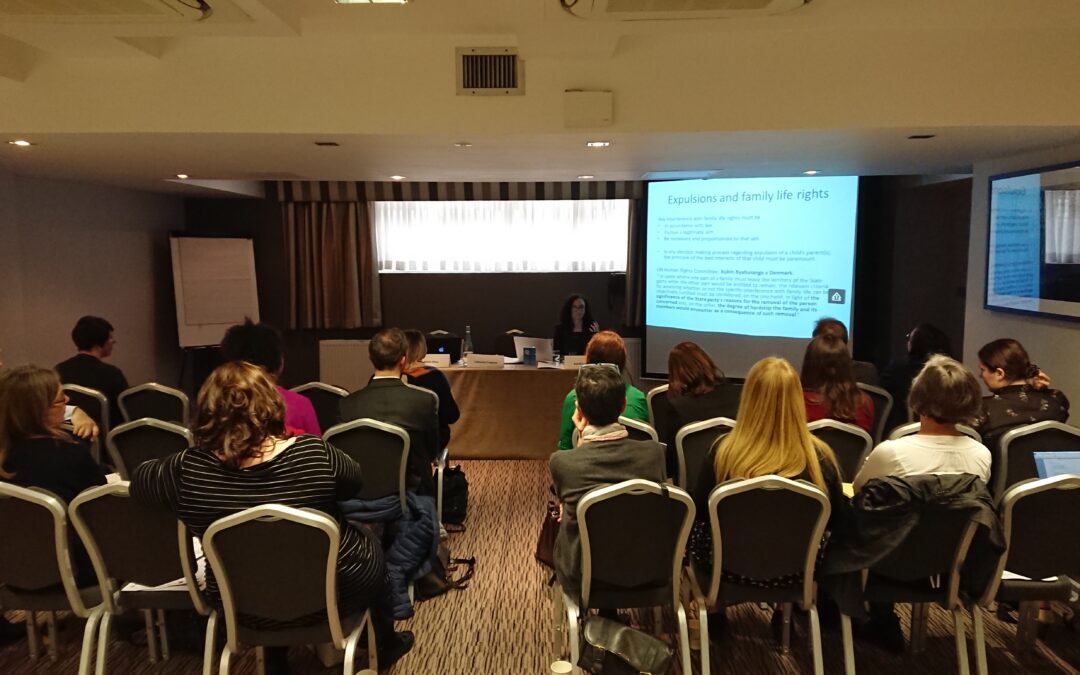
Today, the ICJ and Immigrant Council of Ireland (ICI) are holding a 2-day training seminar for judges and lawyers in Dublin, Ireland, on the rights of migrants, in particular the right to family life and due process in asylum proceedings.
The participants consist of about 30 judges and judicial assistants from the International Protection Appeals Tribunal (IPAT) administrative decision makers (IPO/INIS), and legal professionals.
During the two days of training, experts from the European Court of Human Rights, the UK Immigration Tribunal, Trinity College Dublin, the Immigrant Council of Ireland and the ICJ will deliver the training, bringing international human rights and EU law perspectives to the discussion on the Irish context.
Among the issues discussed will be – on day 1 – the right to private and family life in migration, including, and recent developments at the ECtHR, and right to private and family life in the national context as well as best interests of the child determination and family life rights in return decisions. On day 2 discussion will focus on procedural rights and remedies in the context of international protection,. Issues discussed will include due process rights in asylum procedures, safe third country concept, and credibitity assesments and vulnerability in international protection applications.
In parallel, a training for 20 social care professionals working with migrant children is being delivered.
This is the second national training under the FAIR PLUS project, following the first training held last December in Pisa.
See the full agenda here.
This training is a part of FAIR PLUS project. It was carried out with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents are the sole responsibility of ICJ and do not necessarily reflect the views of the European Union.
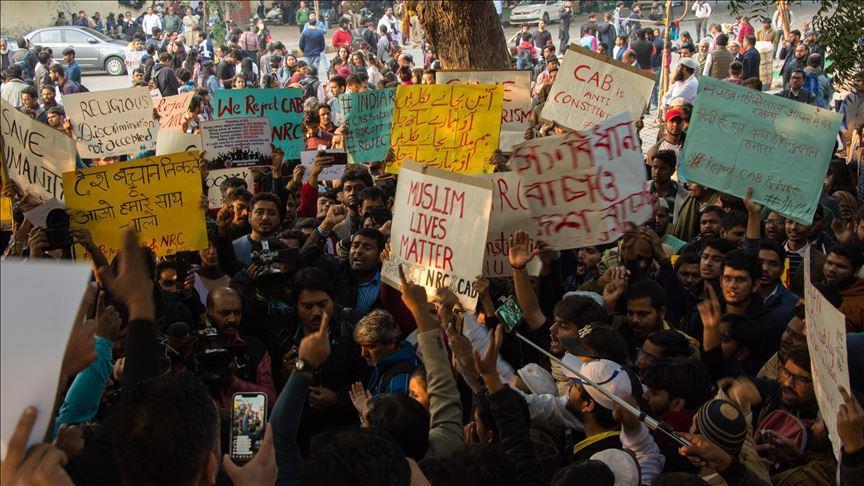
Dec 16, 2019 | News
The Indian Police Service and the paramilitary Central Reserve Police Force must desist from the use of unlawful force and ill-treatment against demonstrators protesting the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, the ICJ said today.
The Indian authorities must also hold police and other public officials accountable for the human rights violations arising from these police actions, the ICJ added.
“The violent tactics that police have used over the past several days in Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, and other Indian states must cease and the government must address the legitimate concerns raised by the public about the discriminatory impacts of both the Citizenship Amendment Act and National Register of Indian Citizenship,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia Pacific Director.
“Any officials who use excessive force, including the unlawful or disproportionate use of pellet guns or tear gas cannons against unarmed student protestors, must be fully and impartially investigated and held accountable for their actions,” he added.
In its operations policing the demonstrations, the ICJ called on the authorities to abide by Indian Constitutional guarantees and international legal obligations on human rights.
These protect persons from torture and ill-treatment and the rights to freedom of expression, association and assembly.
They also require that police refrain from using unnecessary and disproportionate force and never use potentially lethal force unless to protect against an imminent threat to life.
The ICJ also called on the authorities to ensure that any person detained not be subjected to torture or other ill-treatment; have prompt and confidential access to counsel; and that those injured or otherwise provided with access to medical services.
“The police need to respond to prevent acts of violence, but they must use force only when strictly necessary. Potentially lethal force is only justifiably employed in self-defence or in defence of others against an imminent threat of death or serious injury,” said Rawski.
“If arrests need to be made, they must be done without exception in accordance with the law, respecting the rights of detainees to have access to legal counsel, to be free of torture and other ill-treatment of any kind, and to receive needed medical treatment,” he added.
The ICJ said that the authorities must undertake prompt, independent, impartial and thorough investigation of all allegations of unlawful use of force, with a view to holding accountable any responsible authorities and providing an effective remedy and reparation to victims.
Background
In response to the passage of the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019, protests erupted all over the country, including in Assam, Tripura, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, Delhi, West Bengal, Kerala, and Hyderabad.
In Delhi and Uttar Pradesh, yesterday, members of the police and Central Reserve Police Force forced their way onto the campuses of Jamia Milia University and the Aligarh Muslim University in response to protests against the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019.
At Jamia Milia University, the police and Central Reserve Police Force used tear gas cannons upon students who had been reportedly protesting peacefully. Police entered the university library and beat students who were there studying for their exams. The police detained (and subsequently released) some 50 students. Some reported being beaten while in detention, held for over six hours in a locked police station, and denied access to lawyers and family. Medical attention was also reportedly denied to some injured students.
At Aligarh Muslim University, the police and Central Reserve Police Force reportedly demolished the gates, and used tear gas, pellet guns, and lathi (wooden sticks) charge. They were said to have entered student hostels, wherein they reportedly caused damage to one room which had students inside it. According to a lawyer at the University, at least one’s student whereabouts is unknown and some 50 students and others have reported been injured, some severely. Some were reportedly taken to the hospital by the police.
The Citizenship (amendment) Act, 2019 amends the Citizenship Act, 1955, which governs questions of citizenship and aspects of lawfulness of migration status in India. The Act gives protected status to Hindu, Sikh, Jain, Parsi, Buddhist and Christian migrants from Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh, all Muslim-majority countries, who entered India on or before 31 December 2014. Similarly situated Muslims are categorized as “illegal migrants”.
The Bill provides to the above-mentioned religious communities and countries an expedited route of citizenship giving them the opportunity to be eligible for citizenship by naturalization if they have lived or worked in India for six years, as opposed to twelve years, as otherwise required. The Bill controversially excludes from its ambit certain ethnic and religious groups, such as Muslims, in violation of international law and standards protecting against discrimination.
To download the full statement with additional background information, click here.
Contact
Maitreyi Gupta, ICJ India Legal Adviser, t: +91 77 560 28369 e: maitreyi.gupta(a)icj.org
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia-Pacific Director, t: +66 64 478 1121; e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org

Dec 10, 2019 | News
Today’s decision from the European Court of Human Rights in the case of Turkish human rights defender Osman Kavala must be immediately complied with by releasing him from detention, the International Bar Association Human Rights Institute (IBAHRI) and the ICJ said today.
In the case of Kavala v Turkey, the European Court of Human Rights held that the detention of Mr Kavala, in connection with his role in the Gezi Park protests of 2013, violated the right to liberty (Article 5.1) and the right to a speedy judicial review of detention (Article 5.4) under the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR). The Court also found that his detention involves a restriction on rights for an improper purpose (Article 18). As a consequence of these findings, the Court specifically held that ‘the government must take every measure to put an end to the applicant’s detention and to secure his immediate release’.
The Turkish government has a legal obligation to comply with the judgment of the European Court of Human Rights. The IBAHRI and ICJ urge the authorities to abide by their obligations under the ECHR by immediately releasing Mr Kavala.
Mr Kavala has been in detention since 18 October 2017 pending trial on charges connected to the Gezi Park protests. The Gezi Park protests began in May 2013 as an effort by a group of environmentalists to save a park in central Istanbul from being rezoned, but soon grew into nationwide demonstrations. Police quelled the protest in Taksim Square with the use of tear gas and water cannons.
Mr Kavala’s trial, along with 15 other defendants, is ongoing before Istanbul 30th Assize Court. The defendants are charged under Article 312 of the Turkish Criminal Code (an attempt to overthrow the Turkish government or an attempt to prevent it from fulfilling its duties), Article 151 (damage to property), Article 152 (qualified damage to property), Article 174 (possession or exchange of hazardous substances without permission), Article 153 (damaging places of worship and cemeteries), Article 149 (qualified robbery), Article 86 (intentional injury), crimes under the Law on Firearms, Knives and Other Tools no. 6136, and crimes under the Law on Protection of Cultural and Natural Assets no. 2863.
The IBAHRI and the ICJ have jointly sent international observers to attend all hearings of the trial. The organisations will jointly release a trial observation report upon conclusion of the trial.
Contact:
Róisín Pillay, Director, Europe and Central Asia Programme, t: +32 2 734 84 46 ; e: roisin.pillay(a)icj.org