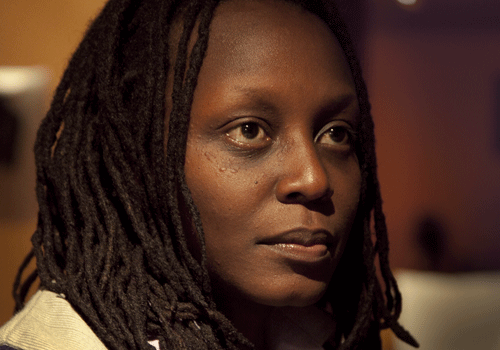Dec 6, 2012 | News
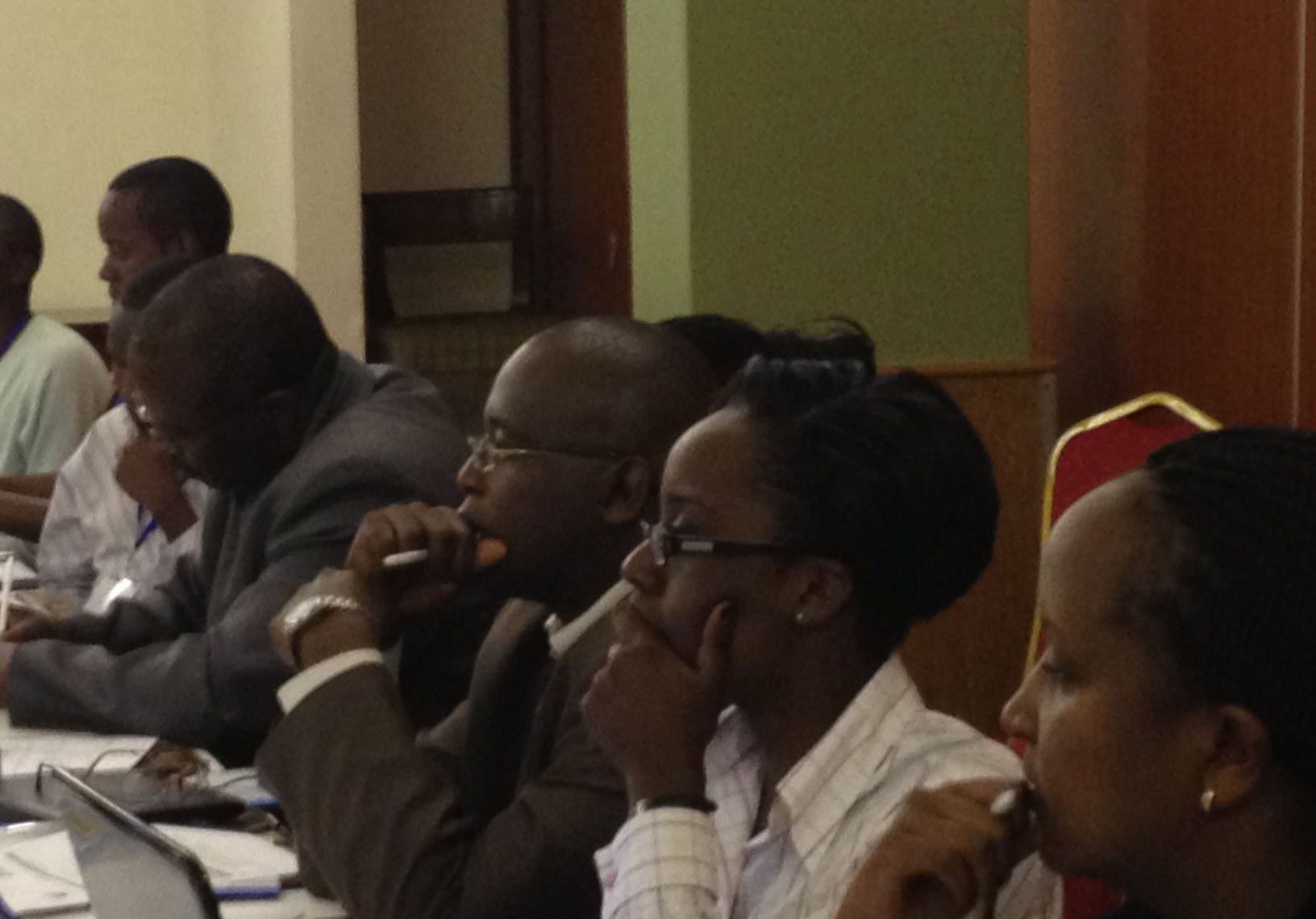 On 6 December 2012, the ICJ and ICJ-Kenya convened a roundtable entitled “LGBT Human Rights” in Nairobi.
On 6 December 2012, the ICJ and ICJ-Kenya convened a roundtable entitled “LGBT Human Rights” in Nairobi.
The event brought together members of the Kenyan bar with LGBT human rights activists for a full discussion of criminal and constitutional law and international human rights standards, as well as possibilities for reform through either judicial or parliamentary processes.
The event was opened by Lawrence Mute, a former national human rights commissioner, signatory of the Yogyakarta Principles, and winner of ICJ-Kenya’s Jurist of the Year award.
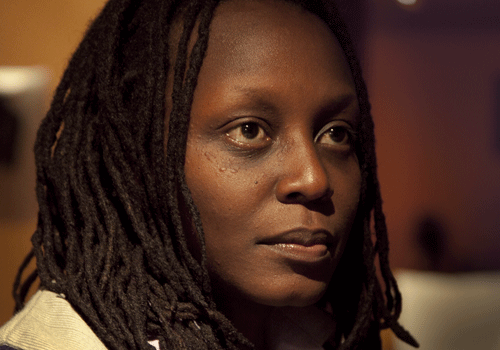
Nov 30, 2012 | News
The ICJ condemns the reintroduction of Anti-Homosexuality Bill in the Ugandan Parliament. The bill has passed out of committee and is expected to come to a floor vote in early December.
According to reports from civil society organizations in Uganda, the bill still contains the death penalty for acts of “aggravated homosexuality.”
In addition, the Anti-Homosexuality Bill criminalizes the promotion of homosexuality, which is defined to include all advocacy activities.
“Adopting the Anti-Homosexuality Bill would be a serious threat to the human rights and human dignity of LGBT individuals and organizations,” said Alli Jernow, Senior Legal Adviser at the ICJ. “Under the Bill, not only might someone face life in prison or the death penalty for being gay, but human rights defenders would also be prevented from speaking out to challenge the law.”
Under the Bill, anyone in authority, such as a teacher or medical professional, who fails to report an offence to law enforcement within twenty-four hours, is liable to three years’ imprisonment.
The ICJ says the bill is dangerous and deadly and urges Parliament to reject it.
Parliament must also reaffirm the rights to non-discrimination, privacy, freedom of expression and freedom of association for all Ugandans, the ICJ adds.
The Anti-Homosexuality Bill has already been used to justify a general clampdown on civil society in Uganda.
Meetings and workshops have been disrupted and advocacy groups working on human rights have been threatened.
In February 2012, the Minister of State for Ethics and Integrity, Simon Lokodo, shut down a capacity-building session for LGBT activists organized by Freedom and Roam Uganda (FARUG) at a hotel in Entebbe and threatened to arrest FARUG’s executive director Kasha Jacqueline Nabagesera (picture above).
In June 2012, police raided a workshop for East African LGBT human rights defenders that had been organized by the East and Horn of Africa Human Rights Defenders Project and they detained participants for several hours.
Minister Lokodo also told the press that he was going to ban 38 organizations that were “sympathetic to LGBT people.”
“If adopted, the bill would clearly violate the human rights of all Ugandans,” Jernow added.
International human rights law, including treaties to which Uganda is a party, prohibit the criminalization of same-sex sexual conduct and forbid the imposition of the death penalty for non-violent conduct, including sexual relations between consenting adults.
International human rights law also guarantees the right of everyone, regardless of sexual orientation or gender identity, to freedom of expression, association and peaceful assembly.
Contact:
Alli Jernow, ICJ Senior Legal Advisor, t + 41 22 979 3823 ; e-mail: alison.jernow(at)icj.org

Nov 27, 2012 | News
 The ICJ and ILGA-Europe welcome the historic decision by the UN Human Rights Committee in Irina Fedotova v. Russian Federation, which was released on 19 November.
The ICJ and ILGA-Europe welcome the historic decision by the UN Human Rights Committee in Irina Fedotova v. Russian Federation, which was released on 19 November.
“We are very pleased with the Committee’s Views in this case and in particular with the recognition that expressing opinions and information about same-sex sexual orientation cannot be limited in the name of public morality,” said Alli Jernow, ICJ Senior Legal Advisor.
In March 2009, Fedotova had displayed posters declaring “Homosexuality is normal” and “I am proud of my homosexuality” near a secondary school building in Ryazan.
The Ryazan Law on Administrative Offences prohibited “public actions aimed at propaganda of homosexuality among minors.” She was arrested, convicted, and ordered to pay a fine of 1,500 roubles.
Fedotova lost her appeal to the district court and the Constitutional Court ruled that the prohibition of information that was “capable of harming health, morals and spiritual development, as well as forming perverted conceptions about equal social value of traditional and non-traditional family relations” could not be considered a violation of the right to freedom of expression.
But the Human Rights Committee held that Russia had violated Fedotova’s rights to freedom of expression and to be free from discrimination.
These rights are guaranteed by articles 19 and 26 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights.
“The decision is especially important because it effectively reverses the position taken by the Committee in the 1982 case of Hertzberg v. Finland, which upheld a ban similar to the one in the Fedotova case,” Jernow added.
The Human Rights Committee ordered the Russian Federation to reimburse the fine paid by Fedotova as well as her legal costs and to ensure that the relevant provisions of domestic law are made compatible with articles 19 and 26 of the Covenant.
Since the Ryazan law was adopted, a number of other regions in Russia have adopted legislation banning “homosexual propaganda.” Activists across the country, including in St. Petersburg, have been arrested and convicted under such laws.
In its decision, the Human Rights Committee emphasized that limitations for the purpose of public morals, which are derived “from many social, philosophical and religious traditions,” could not be based exclusively on a single tradition.
Furthermore, any such limitations “must be understood in light of universality of human rights and the principle of non-discrimination.” The Committee recalled that the “prohibition against discrimination under article 26 comprises also discrimination based on sexual orientation.”
The Committee stated that Russia “has not shown that a restriction on the right to freedom of expression in relation to ‘propaganda of homosexuality’ – as opposed to propaganda of heterosexuality or sexuality generally – among minors is based on reasonable and objective criteria.”
Fedotova’s actions were not aimed at involving minors in any particular sexual activity. Rather, “she was giving expression to her sexual identity and seeking understanding for it.”
“We hope this landmark decision will send a strong signal to Russia to reconsider such discriminatory steps and to abandon any legislative proposals criminalising ‘homosexual propaganda’,” said Evelyne Paradis, Executive Director of ILGA-Europe.
The ICJ had submitted a legal opinion, which the Committee excerpted in detail, arguing that the law was discriminatory and that limitations on rights could not discriminate. Earlier this year, the ICJ and ILGA-Europe published a briefing paper titled “Homosexual Propaganda Bans: Analysis and Recommendations.”
Contact:
Alli Jernow, ICJ Senior Legal Advisor, t + 41 22 979 3823
Juris Lavrikovs, ILGA-Europe, t + 32 2 609 54 16 and + 32 496 708 375
Oct 3, 2012 | News
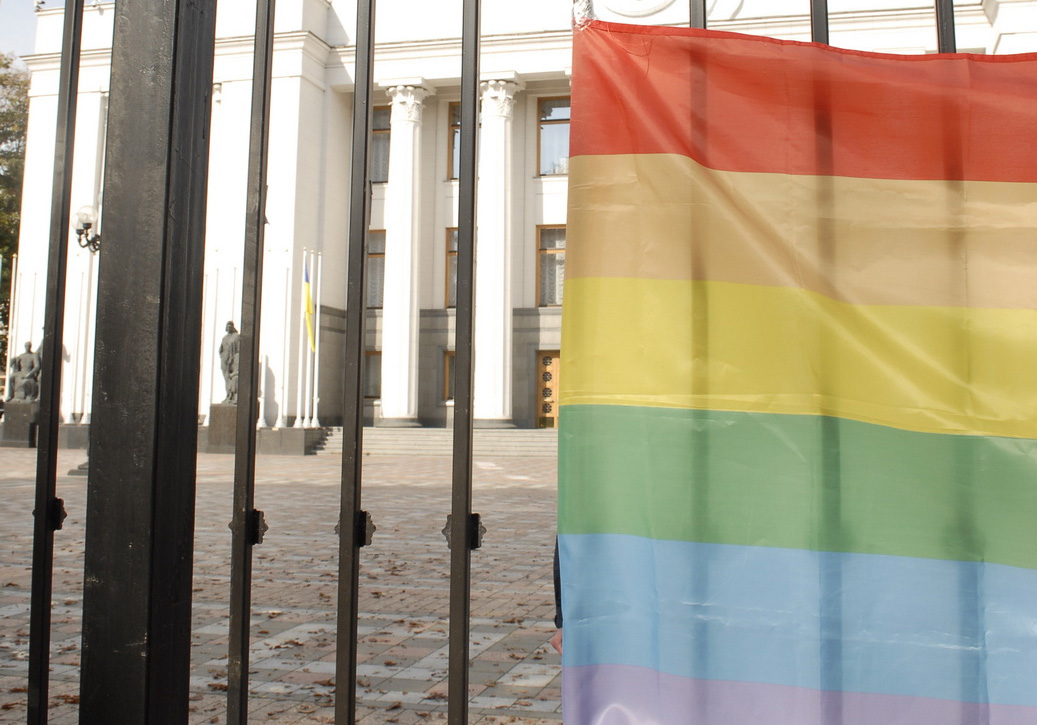 The Verkhovna Rada, the Ukrainian parliament, voted on 2 October 2012 in favor of a bill that would ban “homosexual propaganda”. The ICJ and ILGA-Europe have condemned the draft law and called on Ukrainian authorities not to adopt it. Two hundred and eighty-nine out of 450 members of parliament supported the bill, which is now expected to move for a second round of reading in parliament later this month.
The Verkhovna Rada, the Ukrainian parliament, voted on 2 October 2012 in favor of a bill that would ban “homosexual propaganda”. The ICJ and ILGA-Europe have condemned the draft law and called on Ukrainian authorities not to adopt it. Two hundred and eighty-nine out of 450 members of parliament supported the bill, which is now expected to move for a second round of reading in parliament later this month.
The organisations are deeply concerned about the impact of Draft Law no. 8711 on the rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in Ukraine as well as the rights of everyone to the freedoms of expression, peaceful assembly and association. ICJ and ILGA-Europe urge the Ukrainian parliament to withdraw the bill from its agenda and call on the Chair of the Parliament and the President, who would both need to sign the bill in order for it to become law, to speak out against it.
The bill would modify several existing laws in Ukraine, including criminal law, and introduce sanctions for the import, production and distribution of products that would “promote” homosexuality. “Promotion of homosexuality” is itself undefined. “If voted into law, it would lead to the further marginalisation of the lesbian, gay, bisexual and trans community in the country and would limit the work of human rights defenders,” Evelyne Paradis, Executive Director of ILGA-Europe said.
ILGA-Europe and the ICJ believe that Draft Law no. 8711 is incompatible with international human rights law. First it is so vague that it fails to conform to the requirement that restrictions must be provided for by law. Under the draft law, it is impossible for an individual to determine what kind of expression is banned. Second, the asserted reasons for the “homosexual propaganda” ban fail the tests of proportionality and necessity. In other words, the restriction serves no permissible purpose. Third and finally, the homosexual propaganda ban discriminates against LGBT people by prohibiting public discourse on issues that matter to LGBT lives. “Restrictions on rights may not be discriminatory, and discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation is clearly prohibited under international law,” said Alli Jernow, Senior Legal Adviser of the International Commission of Jurists.
The EU should raise these developments in the context of the monitoring of the implementation of the Visa Liberalisation Action Plan. Parliamentary discussion of this law clearly demonstrates that progress is stalled. If the bill passes a second reading, further negotiations with Ukraine should be delayed or ultimately suspended. We also call on the Council of Europe to unequivocally denounce Draft Law no. 8711 in representations to the Ukrainian government.
The law is expected to be discussed at a second hearing in the coming weeks. After that the Chair of the Parliament and the President would need to sign the bill before it would become official law.
ICJ and ILGA-Europe earlier this year issued a joint briefing paper on “homosexual propaganda bans” that have been enacted or proposed in Europe and other Eastern European countries.
Photo credit: Insight NGO

Oct 1, 2012
 Nikolai Alekseyev was convicted under the new homosexual propaganda ban and he is currently challenging the constitutionality of the law. The ICJ filed an amicus brief.
Nikolai Alekseyev was convicted under the new homosexual propaganda ban and he is currently challenging the constitutionality of the law. The ICJ filed an amicus brief.
The activist was arrested and fined for holding up a sign quoting a famous Soviet era actress, who said: “Homosexuality is not a perversion. Field hockey and ice ballet are.”
The ICJ brief argues that the St. Petersburg law violates the right to freedom of expression, guaranteed by both the ICCPR and the European Convention on Human Rights. The homosexual propaganda bans are not only vague, they also fail the tests of proportionality and necessity and discriminate on the basis of sexual orientation, all contrary to human rights law.
The case is currently pending. A hearing scheduled for 27 September 2012 was postponed due to the recusal of one of the judges.
For more information on the homosexual propaganda bans, see the ILGA-Europe ICJ briefing paper.
Russia-homosexual propaganda ban challenged-ICJ Amicus Brief-2012 (full text in PDF)
Russia-homosexual propaganda ban challenged-ICJ Amicus Brief-2012-ru (full text in PDF)

 On 6 December 2012, the ICJ and ICJ-Kenya convened a roundtable entitled “LGBT Human Rights” in Nairobi.
On 6 December 2012, the ICJ and ICJ-Kenya convened a roundtable entitled “LGBT Human Rights” in Nairobi.