Jul 11, 2018 | News
Today, the ICJ expressed concern at the adoption of a new law on lawyers in Kazakhstan.
The Law ‘On the Professional Activities of Advocates and Legal Assistance’, signed into law on 10 July 2018, contradicts international law and standards on the independence of the legal profession, by enabling the executive to influence or to have control over who is allowed to practice law and substantial influence on disciplinary proceedings against lawyers.
The law will have negative repercussions for protection of human rights and the rule of law in the Republic of Kazakhstan.
“Some of the key provisions of the adopted law undermine the independence of the legal profession, a cornerstone of the rule of law,” Temur Shakirov, ICJ Europe Program Senior Legal Adviser said today.
“Not only does the law weaken the legal profession, it sends an unfortunate message to the public that, as a result, their human rights, including their right to a fair trial, may be harder to uphold within the legal system,” he added.
More specifically, the ICJ is concerned that, under the new law, the role of the independent Bar Association in the composition of the disciplinary commissions is reduced.
Besides lawyers, the Disciplinary Commission will now include ‘representatives of the public’ designated by the Ministry of Justice. While the law does not specify how these members of the Disciplinary Commission would be selected, the selection is to be made by the Ministry of Justice.
The same procedure is not excluded to select members who are retired judges, which the Law requires also be part of disciplinary commissions.
While many of the specific procedures are unclear, it is apparent that these provisions would give the Ministry extensive influence over the Disciplinary Commission, especially as the law does not explicitly require these members perform their duties independently from the instructions of the Ministry of Justice.
The influence of the executive over the disciplinary proceedings of the Bar Association is contrary to the principles of independence of lawyers.
The UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers provide that disciplinary proceedings against lawyers are to be brought before an impartial disciplinary committee established by the legal profession, before an independent statutory authority, or before a court, and shall be subject to an independent judicial review.
Furthermore, the law continues to give the Ministry of Justice control over admission to the practice of law.
It stipulates that prospective lawyers who have completed their professional training are to be assessed by the Commission for admission to practice established by territorial bodies of the Ministry of Justice.
The commissions consist of seven members, of which only three are members of the Bar Association. The composition of the commissions and the principles of their work are to be approved by the orders of the Minister of Justice of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The Law therefore preserves the previous procedure on admission to the profession criticized by the ICJ earlier, according to which the attestation of applicants for obtaining the membership to the Bar Association and issuing a license were within the exclusive competence of the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
At the same time, many defense rights listed in the Law are curtailed or compromised by the wording that would allow for enactment of restrictions by secondary legislation, including that the adopted Law would not allow lawyers to freely and without interference collect evidence in defense of their clients or that lawyer’s inquiries can be subject to limitation where they seek to obtain “restricted information”.
The ICJ notes that according to the UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers, States must ensure lawyers have access to appropriate information, files and documents in their possession or control in sufficient time to enable lawyers to provide effective legal assistance to their clients. Such access should be provided at the earliest appropriate time (Principle 21).
Read the full text in English here
Read the full text in Russian here

Jul 11, 2018 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ today joined other civil society organizations in calling for respect for human rights, and protection of and participation by civil society, to have a greater role in the UN Global Counter-terrorism Strategy.
The joint statement by the organizations followed adoption by the UN General Assembly on June 26th, 2018 of Resolution 72/284, reviewing the United Nations Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy. The UN’s Global Counterterrorism Strategy, first adopted in 2006, sets out a plan of action for the UN and member states at the global, regional, and national level to counter-terrorism.
The organizations emphasise the value of a global counter-terrorism strategy where human rights are an essential component. It notes that the General Assembly resolution importantly reaffirms states’ obligations to comply with international law, including international human rights law, while countering terrorism and that human rights are the “fundamental basis of the fight against terrorism.”
The joint statement expresses concern at States’ failure to adequately address human rights abuses in relation to counter-terrorism measures. It also sets out concerns about member states’ failure to provide an enabling environment for civil society entities, including those relating to women, to be meaningfully engaged in the Strategy review.
The full statement and list of organizations joining it can be downloaded in PDF format here: UN-Advocacy-JointStatement-CounterTerrorismStrategy-2018

Jul 10, 2018 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ has joined almost 180 other organizations in calling for the final draft of the UN Global Compact on Migration (GCM) to reflect strong legal protections for human rights.
Recognizing the potential of the GCM to protect migrants in irregular and/or vulnerable situations, civil society organizations are calling on all States to ensure that the final document truly lives up to the spirit of the New York Declaration for Refugees and Migrants.
The statement was presented to Member States and the GCM Co-Facilitators (the governments of Switzerland and Mexico) in an informal dialogue on Tuesday, 10 July.
The statement calls on States to address the following issues:
- Regular vs. irregular: The GCM must not include a distinction between migrants with regular status and those whose status is irregular which falls below human rights law, international labor standards and other international obligations.
- Non-Refoulement: The GCM must explicitly mention the principle of non-refoulement, which prohibits returning a person to a place where her/his life would be in danger. Including it is fundamental to ensure that migrants are provided with full live-saving protection.
- Vulnerable situations: The GCM must address the situation of vulnerable migrants, and it must not weaken protection for victims of natural disasters and climate change, who are not adequately addressed in the Global Compact for Refugees.
- Right to privacy: The final document must protect migrants’ right to privacy of personal information. Otherwise, the GCM risks preventing them from accessing certain social services and discouraging them from participating in data collection efforts, which are vital for migration management.
- Criminalization of migrants and those who assist them: The GCM must avoid all provisions and language that criminalizes migrants crossing an international border in search of safety or of people and organizations that support to them.
- Detention of migrant children: The GCM must include provisions towards ending the practice of detaining migrant children by explicitly mentioning the availability and accessibility of non-custodial and community-based alternatives.
- Implementation, review, and follow-up mechanisms: The Compact needs robust implementation, review, and follow-up mechanisms to ensure accountability and transparency in achieving its goals. Civil society organizations ask for a fully mandated partnership role in implementation and monitoring the GCM.
To be effective, the statement concludes, migration management must be credible not only to States, but also to migrants.
The statement is available in PDF format here: UN-Advocacy-JointStatement-Migrants-2018
Jul 10, 2018 | News
The SC is set to reconsider the criminalization of consensual same-sex relationships between adults, in response to a writ petition with significant ramifications for addressing the full range of human rights violations based on sexual orientation or gender identity in India said the ICJ.
The Indian Supreme Court commenced hearing the case, Navtej Singh Johar v. Union of India, which is joined with five connected cases, today, concerning the constitutional validity of the criminalization of consensual same-sex relations between adults under Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code in response to writ petitions filed by several LGBTI individuals.
Section 377 criminalizes “carnal intercourse against the order of nature”. Section 377 is a relic of the British colonial penal code and is replicated in several former British colonies even though it was it was finally repealed in Northern Ireland in 1982, following repeals in Scotland in 1980 and England and Wales in 1967.
“Hopefully, the Indian Supreme Court will follow and build upon the strong precedent set by the Delhi High Court in the Naz Foundation v. Govt. of NCT of Delhi that declared Section 377 and the criminalization of consensual same-sex relationships to be in violation of the Indian Constitution as well as international law in 2009,” said Sam Zarifi, ICJ’s Secretary General.
“There are real grounds for optimism as the Indian Supreme court as recently as August 2017 handed a landmark judgment in Justice K.S. Puttaswamy and Another v. Union of India and Others that declared the right to determine one’s sexual orientation and gender identity as core to the right of privacy,” he added
The ICJ has documented how section 377 has created a climate in which arbitrary arrest, extortion, harassment and blackmail of LGBTI persons in India thrives.
“The Indian judiciary’s decision to read down section 377 in Naz Foundation v. Govt. of NCT of Delhi, which was then overruled by the Supreme Court, has been used by several other jurisdictions, such as Trinidad and Tobago as support for putting an end to criminalization of same-sex relationships. So the outcome of this petition before the Indian Supreme Court is of significance not just to people in India, but to the fight against discrimination around the world,” Zarifi said.
“But even a good decision by the Indian Supreme Court will not end the discrimination against people on the basis of their sexual orientation or gender identity in India. It’s time for the Indian Parliament to repeal section 377 in its entirety and engage in a wide-ranging review to consider which gaps, if any, need to be filled, for example with respect to acts constituting rape or other sexual offences,” he added.
Contact:
Maitreyi Gupta (Delhi), International Legal Adviser for India, t: +91 7756028369 ; e: maitreyi.gupta(a)icj.org
India-Supreme Court and Section377-News-press release-2018-ENG (full story with additional information, in PDF)

Jul 9, 2018 | News
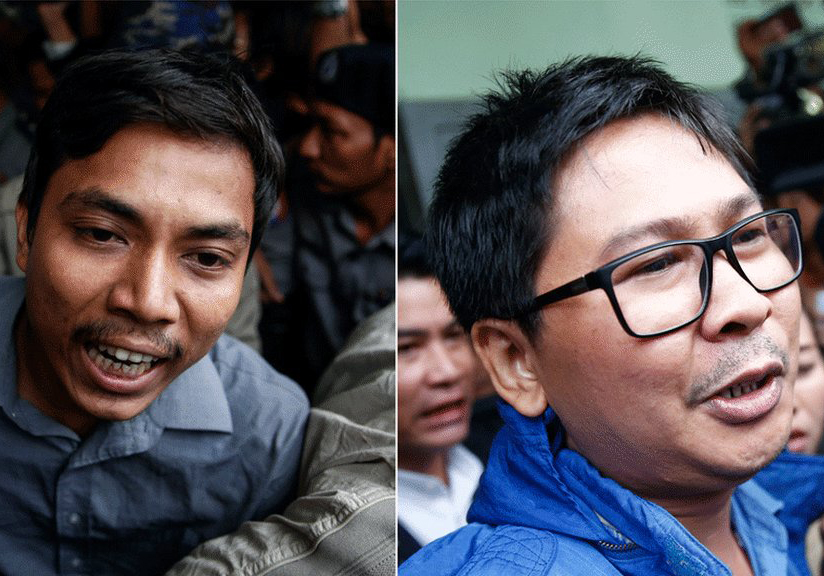
Today the ICJ called on Myanmar’s prosecutorial authorities to immediately end the prosecution of Reuters journalists Wa Lone and Kyaw Soe Oo.
The two have been subject to prosecution solely for doing their job as journalists and for exposing human rights violations in Rakhine State, including unlawful killings in Inn Dinn Village admitted to by the military.
In Yangon this morning a Northern District Court Judge accepted charges filed under the 1923 Official Secrets Act.
This decision permits ongoing prosecution of the journalists and extends their detention.
“The prosecution has failed to provide credible evidence of any wrongdoing throughout six months of hearings. It is therefore hard to imagine a valid legal rationale for allowing ongoing prosecution of the journalists,” said Mr Sean Bain, legal adviser for the ICJ in Yangon.
Section 253(1) of Myanmar’s Code of Criminal Procedure requires a judge to dismiss charges against accused persons if the evidence presented fails to warrant a conviction.
A motion for charges to be dismissed on this basis, submitted by defense lawyers, was effectively rejected by the decision today.
“Today’s decision raises real concerns about the independence and impartiality of the judiciary and prosecution when confronted with politically sensitive cases,” Bain said.
“The case significantly undermines the government’s stated commitments to reforming and building public confidence in judicial process,” he added.
ICJ legal advisers have monitored the case and were present in Court today. The journalists were first detained on 12 December 2017 and had no access to legal representation for almost two weeks.
“The case is also emblematic of the lack of adherence to fair trial rights in Myanmar,” Bain said.
“Their confinement remains unlawful given an initial period of incommunicado detention without access to lawyers, and other flagrant violations of the fair trial rights guaranteed in the Constitution, statues and international law.”
“Authorities should immediately end criminal proceedings against these men who appear to have been lawfully doing their job as investigative journalists,” he added.
The detention and prosecution of anyone, including journalists, based solely on the collection and publication of evidence relevant to serious human rights violations, is inconsistent with international law and standards on freedom of expression and on human rights defenders.
Article 14 of the 1990 UN Guidelines on the Role of Prosecutors states that prosecutors are obliged to discontinue prosecution when the investigation shows the charges to be unfounded.
Myanmar’s new Code of Ethics for Law Officers, launched in 2017, requires prosecutors to protect rights enshrined in the Constitution and to “provide a proper and fair administration of justice.”
The right to legal counsel is a bedrock rule of law principle that is set out in a range of international human rights laws and standards, including in article 11 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Sections 19 and 375 of the Myanmar Constitution guarantee the right of legal defense, as does Myanmar’s Code of Criminal Procedure (section 340), Courts Manual (section 455(1)), the Police Manual (section 1198c) and the Prisons Act (section 40).
Fair trial rights, freedom of expression, and the right to liberty are also recognised by the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Also relevant are the UN Declaration on Human Rights Defenders, and the Global Principles on National Security and the Right to Information (The Tshwane Principles).
Contact:
Sean Bain, ICJ legal adviser, e: sean.bain(a)icj.org
Read also:
ICJ (May 2016), Handbook on Habeas Corpus in Myanmar – English and Burmese
ICJ (December 2017), Reuters Journalists in Myanmar: respect their rights, end their incommunicado detention – English and Burmese
Full text in Burmese (PDF): Myanmar-drop-charges-against-Reuters-journalists-News-Press-releases-2018-BUR